1.list的介绍及使用
1.1list的文档介绍:
cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/?kw=list。
同样我们也可以借助文档来学习:list - C++ Reference。
1.2list的使用
注意这里的list为带头双向循环链表。
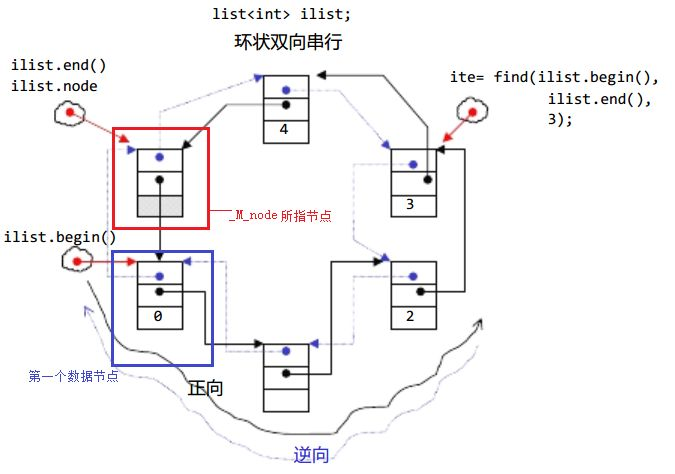
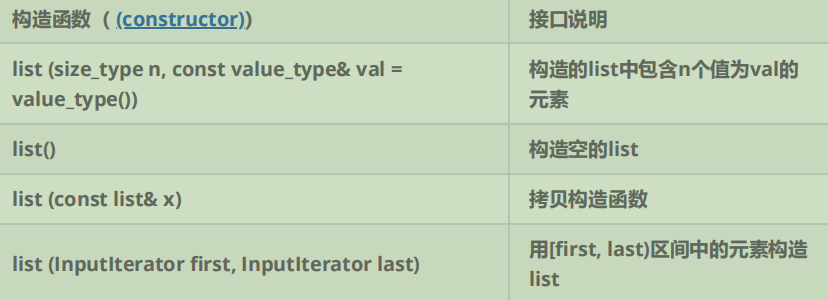
1.2.1 构造函数
cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/list/
常用的:
1.2.2 list iterator的使用

基本和vector、string迭代器的使用类似。
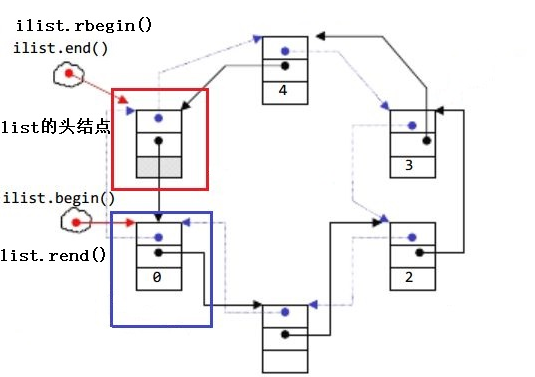
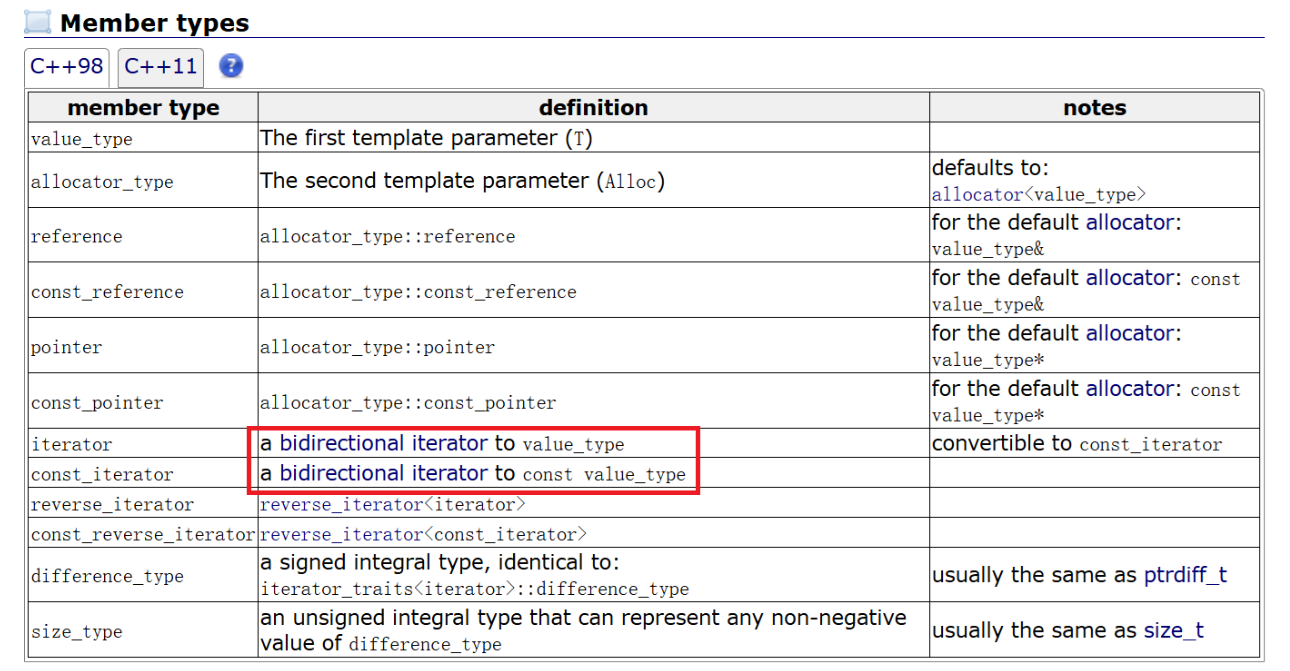
我们观察文档可以发现list的迭代器是一个双向迭代器,这似乎和我们之前学习的vector和string类的迭代器有所不同。
list的Member types
vector的Member types
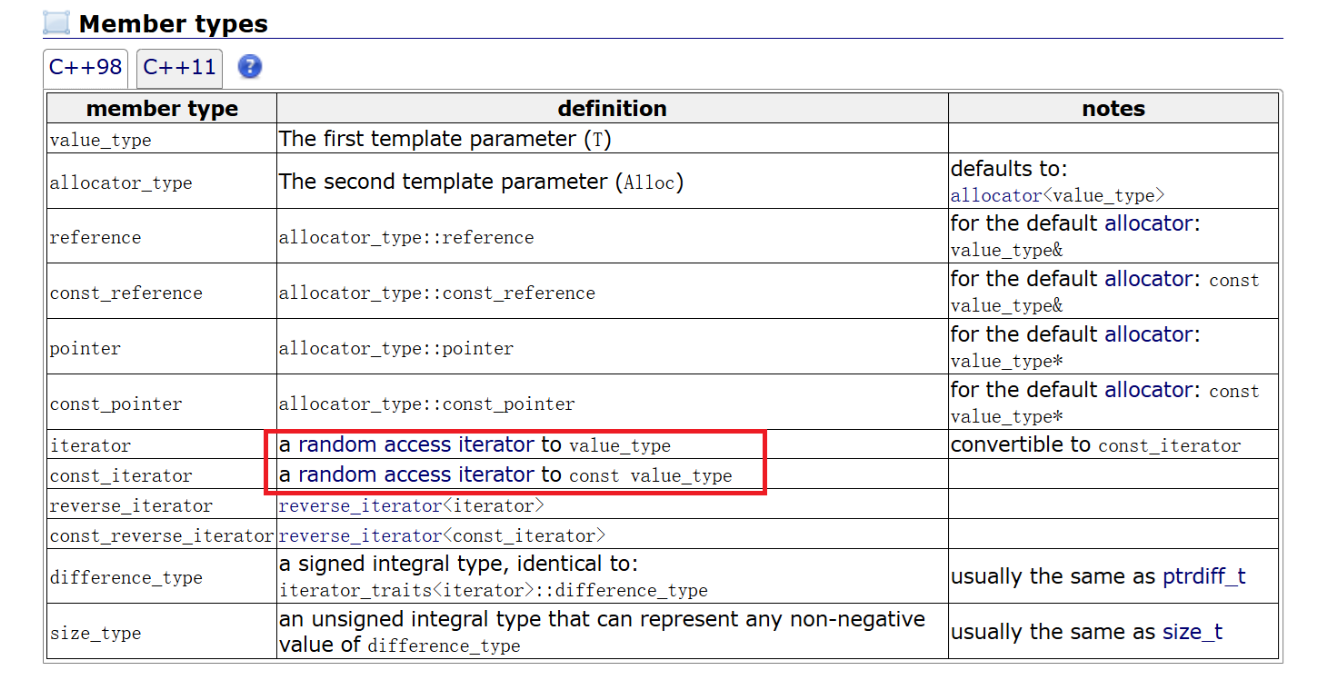
vector为随机迭代器,这里我们就需要做一下比较和区分。

【注意】
- begin与end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动。
- rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动。
1.2.3 list capacity

1.2.4 list element access
1.2.5 list modifiers
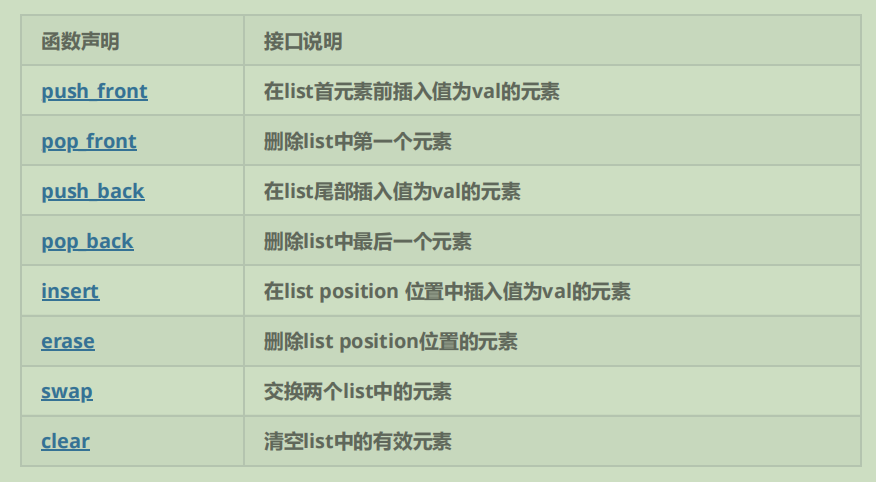
list中还有一些操作,需要用到时大家可参阅list的文档说明。
1.2.6 list的迭代器失效
前面说过可将迭代器暂时理解成类似于 指针 ,迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点的无效,即该节点被删除了 。因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表 ,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代器失效的,只有在 删除时才会失效 ,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void TestListIterator1()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
// erase()函数执行后,it所指向的节点已被删除,因此it无效,在下一次使用it时,必须先给其赋值
l.erase(it);
++it;
}
}
// 改正
void TestListIterator2()
{
int array[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0 };
list<int> l(array, array + sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]));
auto it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
l.erase(it++); // it = l.erase(it);
}
}
int main()
{
TestListIterator2();
return 0;
}1.2.7 test.cpp
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//不支持
/*it = lt.begin();
lt.erase(it + 3);*/
//不支持,要求随机迭代器
//sort(lt.begin(), lt.end());
string s("dadawdfadsa");//string 随机迭代器
cout << s << endl;
sort(s.begin(), s.end());
cout << s << endl;
}
struct A
{
public:
A(int a1 = 1, int a2 = 1)
:_a1(a1)
, _a2(a2)
{
cout << "A(int a1 = 1, int a2 = 1)" << endl;
}
A(const A& aa)
:_a1(aa._a1)
, _a2(aa._a2)
{
cout << "A(const A& aa)" << endl;
}
int _a1;
int _a2;
};
void test_list2()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
//和push_back类似
lt1.emplace_back(2);
lt1.emplace_back(3);
lt1.emplace_back(4);
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<A> lt2;
A aa1(1, 1);
lt2.push_back(aa1);
lt2.push_back(A(2, 2));
//push_back不支持
//lt2.push_back(3, 3);
lt2.emplace_back(aa1);
lt2.emplace_back(A(2, 2));
cout << endl;
//emplace_back支持直接传构造A对象的参数 不用拷贝构造 可以提高效率
lt2.emplace_back(3, 3);
}
//运行结果:
//1 2 3 4
//A(int a1 = 1, int a2 = 1)
//A(const A & aa)
//A(int a1 = 1, int a2 = 1)
//A(const A & aa)
//A(const A & aa)
//A(int a1 = 1, int a2 = 1)
//A(const A & aa)
//
//A(int a1 = 1, int a2 = 1)
void test_list3()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
auto it = lt.begin();
int k = 3;
while (k--)
{
++it;
}
lt.insert(it, 30);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int x = 0;
cin >> x;
it = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), x);
if (it != lt.end())
{
lt.erase(it);
}
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list4()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(20);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//升序
lt.sort();
//降序 - 传仿函数
less<int> ls;
greater<int> gt;
lt.sort(gt);
lt.sort(greater<int>());
lt.reverse();
reverse(lt.begin(), lt.end());
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
std::list<double> first, second;
first.push_back(3.1);
first.push_back(2.2);
first.push_back(2.9);
second.push_back(3.7);
second.push_back(7.1);
second.push_back(1.4);
first.sort();
for (auto e : first)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
second.sort();
for (auto e : second)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//把second里面的数据归并到frist second里面的数据清空
first.merge(second);
for (auto e : first)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : second)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list5()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(20);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
lt.sort();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//去重
lt.unique();
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list6()
{
// 一个链表节点转移给另一个链表
list<int> mylist1, mylist2;
list<int>::iterator it;
// set some initial values:
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; ++i)
mylist1.push_back(i); // mylist1: 1 2 3 4
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i)
mylist2.push_back(i * 10); // mylist2: 10 20 30
it = mylist1.begin();
++it; // points to 2
//splice : Transfer elements from list to list
mylist1.splice(it, mylist2); // mylist1: 1 10 20 30 2 3 4
// mylist2 (empty)
// "it" still points to 2 (the 5th element
// 调整当前链表节点的顺序
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
lt.push_back(5);
lt.push_back(6);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int x = 0;
cin >> x;
it = find(lt.begin(), lt.end(), x);
if (it != lt.end())
{
//lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt, it);
lt.splice(lt.begin(), lt, it, lt.end());
//把it到lt.end() 内的值 转移到lt.begin()
}
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//输入4
//运行结果:
//1 2 3 4 5 6
//4
//4 5 6 1 2 3
//排序效率测试
void test_op1()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 1000000;
list<int> lt1;
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
lt1.push_back(e);
v.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
// 排序
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
lt1.sort();
int end2 = clock();
printf("vector sort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("list sort:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
//运行结果:
//vector sort : 296
//list sort : 506
void test_op2()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 1000000;
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
lt1.push_back(e);
lt2.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
// 拷贝vector
vector<int> v(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
// 排序
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
// 拷贝回lt2
lt2.assign(v.begin(), v.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
lt1.sort();
int end2 = clock();
printf("list copy vector sort copy list sort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("list sort:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
//运行结果:
//list copy vector sort copy list sort : 543
//list sort : 572
int main()
{
test_list6();
//test_op2();
return 0;
}2.list的模拟实现
我们在之前数据结构部分学习过双链表的内容,所以实现起来也不算太难。数据结构之顺序表和链表-CSDN博客
list.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace sy
{
//定义节点
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
T _data;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
//使用T的默认构造 const T& data = T()
list_node(const T& data = T())
: _data(data)
, _next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
{}
};
//list迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
//就是指针
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//类似指针的解引用
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//类似指针的指向
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
//list反向迭代器
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct reverse_list_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef reverse_list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _node;
reverse_list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//类似指针的解引用
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
//类似指针的指向
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)//后置
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
//写一个const_iterator比较冗余
/*template<class T>
struct list_const_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_const_iterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
list_const_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
const T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
const T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s) const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s) const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};*/
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:
/*typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;
typedef list_const_iterator<T> const_iterator;*/
typedef list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef reverse_list_iterator<T, T&, T*> Reverse_iterator;
typedef reverse_list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_reverse_list_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
Reverse_iterator rbegin()
{
return _head->_prev;
}
Reverse_iterator rend()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _head;
}
void empty_init()
{
//双向循环链表
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
_size = 0;
}
list()
{
empty_init();
}
//初始化列表构造
list(initializer_list<T> il)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& e : il)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
// lt2(lt1)
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
// lt1 = lt3
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void clear()
{
auto it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
/*Node* newnode = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = tail;
newnode->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = newnode;
++_size;*/
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
// prev newnode cur
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* next = pos._node->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete pos._node;
--_size;
return next;
}
size_t size() const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty() const
{
return _size == 0;
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
struct AA
{
int _a1 = 1;
int _a2 = 1;
};
// 按需实例化
// T* const ptr1
// const T* ptr2
//遍历各种容器
template<class Container>
void print_container(const Container& con)
{
// const iterator -> 迭代器本身不能修改
// const_iterator -> 指向内容不能修改
typename Container::const_iterator it = con.begin();//这里如果不加typename告诉编译器这是类型会报错
//auto it = con.begin();
while (it != con.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//or
for (auto e : con)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list1()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
*it += 10;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
print_container(lt);
list<AA> lta;
lta.push_back(AA());
lta.push_back(AA());
lta.push_back(AA());
lta.push_back(AA());
list<AA>::iterator ita = lta.begin();
while (ita != lta.end())
{
//cout << (*ita)._a1 << ":" << (*ita)._a2 << endl;
// 特殊处理,本来应该是两个->才合理,为了可读性,省略了一个->
cout << ita->_a1 << ":" << ita->_a2 << endl;
cout << ita.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << ita.operator->()->_a2 << endl;
++ita;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list2()
{
list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
// insert以后迭代器不失效
list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
lt.insert(it, 10);
*it += 100;
print_container(lt);
// erase以后迭代器失效
// 删除所有的偶数
it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
it = lt.erase(it);
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
print_container(lt);
}
void test_list3()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(4);
list<int> lt2(lt1);
print_container(lt1);
print_container(lt2);
list<int> lt3;
lt3.push_back(10);
lt3.push_back(20);
lt3.push_back(30);
lt3.push_back(40);
lt1 = lt3;
print_container(lt1);
print_container(lt3);
}
void func(const list<int>& lt)
{
print_container(lt);
}
void test_list4()
{
// 直接构造
list<int> lt0({ 1,2,3,4,5,6 });
// 隐式类型转换
list<int> lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
const list<int>& lt3 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
func(lt0);
func({ 1,2,3,4,5,6 });
print_container(lt1);
/*auto il = { 10, 20, 30 };
initializer_list<int> il = { 10, 20, 30 };
cout << typeid(il).name() << endl;
cout << sizeof(il) << endl;*/
}
void test_list5()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(3);
lt1.push_back(4);
print_container(lt1);
auto it = lt1.rbegin();
while (it != lt1.rend())
{
*it += 10;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}test.cpp
cpp
#include"List.h"
int main()
{
sy::test_list4();
return 0;
}