一、核心概念
1. 定义与作用
ModelAndView是 Spring MVC 框架的核心类,用于封装模型数据和视图信息。它允许控制器一次性返回:
-
模型数据:需要在视图中展示的数据
-
视图信息:指定如何渲染响应(视图名称或视图对象)
2. 设计目的
-
统一返回类型:标准化控制器方法的返回值
-
解耦视图技术:支持 JSP、Thymeleaf、FreeMarker 等多种视图技术
-
简化开发:一站式处理模型和视图
二、核心结构
public class ModelAndView {
private Object view; // 视图名称或视图对象
private ModelMap model; // 模型数据存储
private HttpStatus status; // HTTP状态码(可选)
private boolean cleared; // 是否已清除
}三、核心方法
1. 构造方法
// 空构造
ModelAndView()
// 指定视图名称
ModelAndView(String viewName)
// 指定视图对象
ModelAndView(View view)
// 指定视图名称和模型
ModelAndView(String viewName, Map<String, ?> model)
// 指定视图对象和模型
ModelAndView(View view, Map<String, ?> model)2. 关键操作方法
// 设置视图名称
void setViewName(String viewName)
// 获取视图名称
String getViewName()
// 设置视图对象
void setView(View view)
// 添加模型属性
ModelAndView addObject(String attributeName, Object attributeValue)
// 添加多个模型属性
ModelAndView addAllObjects(Map<String, ?> modelMap)
// 获取模型
ModelMap getModelMap()
// 设置HTTP状态码
void setStatus(HttpStatus status)四、使用场景与示例
1. 基本使用
@Controller
public class ProductController {
@GetMapping("/products")
public ModelAndView listProducts() {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("product/list"); // 视图名称
// 添加模型数据
mav.addObject("products", productService.getAllProducts());
mav.addObject("categories", categoryService.getCategories());
return mav;
}
}2. 链式调用(推荐)
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
public ModelAndView getProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
return new ModelAndView("product/detail")
.addObject("product", productService.getProductById(id))
.addObject("related", productService.getRelatedProducts(id));
}3. 重定向
@PostMapping("/product/create")
public ModelAndView createProduct(Product product) {
productService.saveProduct(product);
// 重定向到列表页
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/products")
.addObject("success", "产品创建成功");
}4. 转发请求
@GetMapping("/product/preview/{id}")
public ModelAndView previewProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
Product product = productService.getProductById(id);
// 转发到详情页
return new ModelAndView("forward:/product/" + id)
.addObject("preview", true);
}5. 设置HTTP状态码
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
public ModelAndView getProduct(@PathVariable Long id) {
Product product = productService.getProductById(id);
if (product == null) {
return new ModelAndView("error/404")
.setStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
return new ModelAndView("product/detail")
.addObject("product", product)
.setStatus(HttpStatus.OK);
}五、内部工作机制
1. 请求处理流程
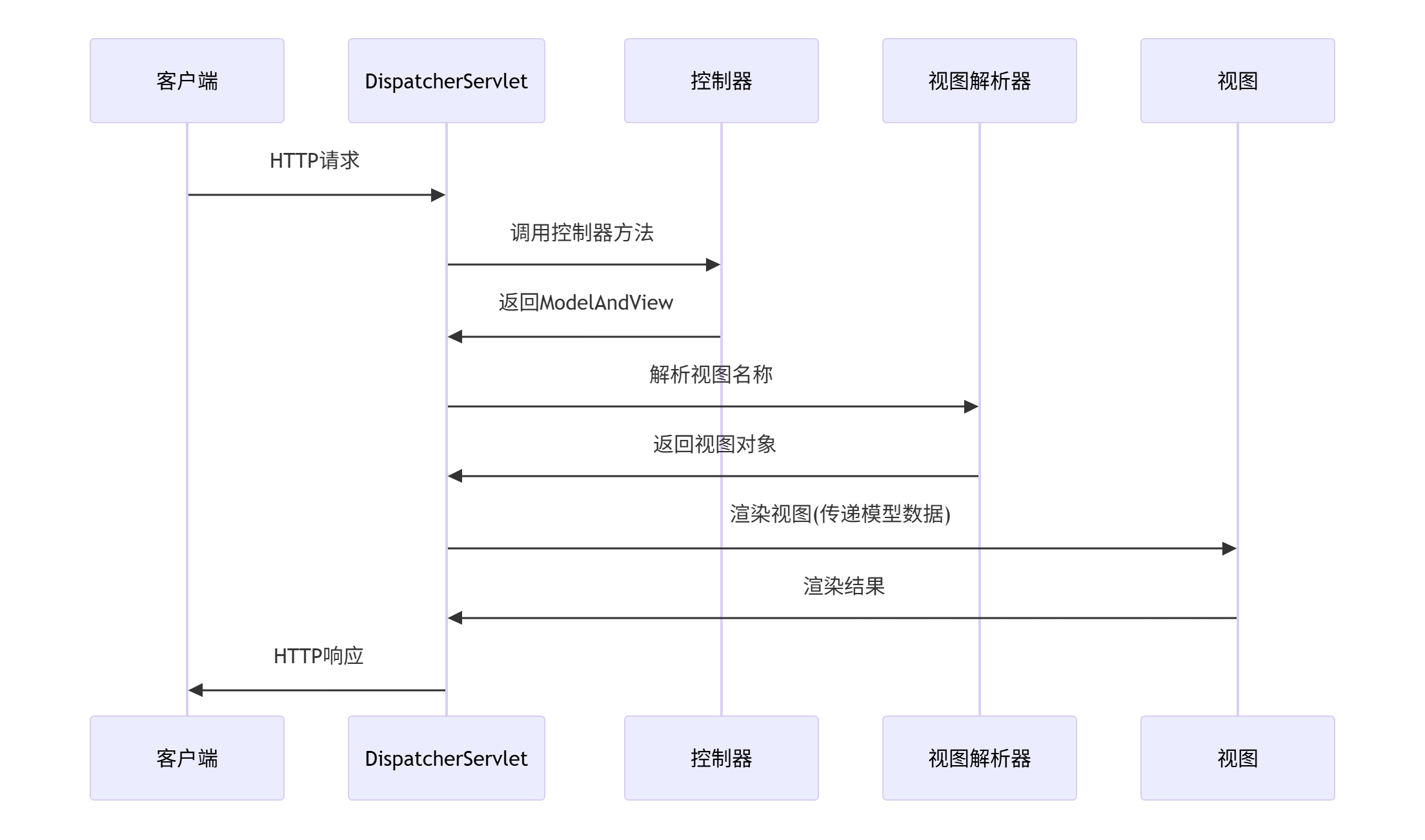
2. 模型数据传递
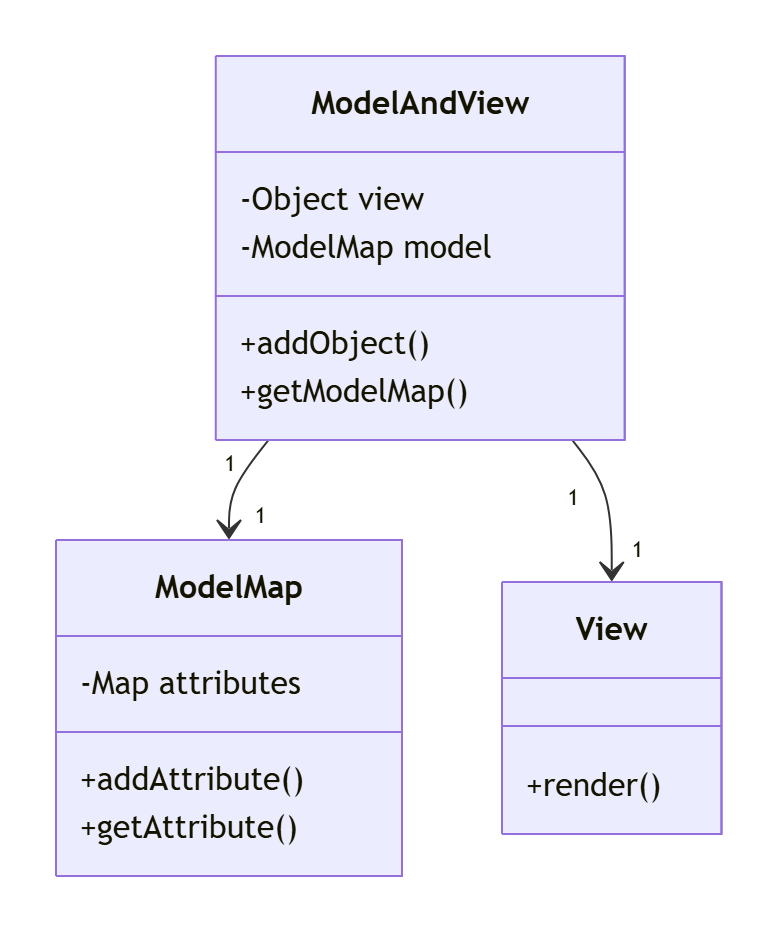
六、与其它返回类型对比
| 返回类型 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ModelAndView | 完整封装模型和视图 支持重定向/转发 可设置状态码 | 代码稍显冗长 | 复杂视图逻辑 需要精确控制响应 |
| String (视图名) | 简洁 易读 | 需单独处理模型 功能有限 | 简单页面渲染 |
| @ResponseBody | 适合REST API 直接返回数据 | 不适用传统页面 | JSON/XML API |
| void | 直接写响应 | 灵活性差 | 特殊响应处理 |
七、最佳实践
1. 视图命名策略
// 使用视图解析器配置
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return resolver;
}
// 控制器中简化视图名
@GetMapping("/users")
public ModelAndView listUsers() {
return new ModelAndView("user/list") // 自动解析为 /WEB-INF/views/user/list.jsp
.addObject("users", userService.getAll());
}2. 模型数据管理
// 使用模型工具类
public class ModelUtils {
public static ModelAndView withSuccess(ModelAndView mav, String message) {
return mav.addObject("success", message);
}
public static ModelAndView withError(ModelAndView mav, String error) {
return mav.addObject("error", error);
}
}
// 控制器中使用
@PostMapping("/order")
public ModelAndView createOrder(OrderForm form) {
try {
orderService.createOrder(form);
return ModelUtils.withSuccess(
new ModelAndView("redirect:/orders"),
"订单创建成功"
);
} catch (Exception e) {
return ModelUtils.withError(
new ModelAndView("order/form"),
"创建订单失败: " + e.getMessage()
);
}
}3. 响应式扩展
// 结合Thymeleaf模板引擎
@GetMapping("/dashboard")
public ModelAndView dashboard() {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("dashboard");
// 添加复杂数据
mav.addObject("stats", Map.of(
"sales", salesService.getMonthlySales(),
"users", userService.getActiveUserCount(),
"products", productService.getTopProducts()
));
return mav;
}八、常见问题解决方案
1. 重定向时保留参数
@PostMapping("/update")
public ModelAndView updateProduct(Product product) {
productService.update(product);
// 使用RedirectAttributes
RedirectAttributes redirectAttrs = new RedirectAttributesModelMap();
redirectAttrs.addAttribute("id", product.getId()); // URL参数
redirectAttrs.addFlashAttribute("message", "更新成功"); // 闪存属性
return new ModelAndView("redirect:/product/{id}", redirectAttrs);
}2. 处理文件下载
@GetMapping("/download/report")
public ModelAndView downloadReport() {
// 使用AbstractView实现
return new ModelAndView(new AbstractView() {
@Override
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model,
HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response
) throws Exception {
// 设置响应头
response.setContentType("application/pdf");
response.setHeader("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=report.pdf");
// 生成并写入PDF
byte[] pdf = reportService.generatePdfReport();
response.getOutputStream().write(pdf);
}
});
}3. 国际化支持
@GetMapping("/home")
public ModelAndView home(Locale locale) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("home");
// 添加本地化消息
mav.addObject("welcomeMsg", messageSource.getMessage("welcome", null, locale));
mav.addObject("currentDate", new Date());
return mav;
}九、在 REST 中的应用
1. 返回 HTML 片段
@GetMapping("/product/{id}/detail")
public ModelAndView productDetail(@PathVariable Long id) {
return new ModelAndView("fragments/product-detail")
.addObject("product", productService.getProductById(id));
}2. 错误页面处理
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ProductNotFoundException.class)
public ModelAndView handleProductNotFound(ProductNotFoundException ex) {
return new ModelAndView("error/product-not-found")
.addObject("productId", ex.getProductId())
.setStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND);
}
}十、总结
1. 核心价值
-
统一封装:模型和视图的一体化容器
-
灵活控制:支持重定向、转发、状态码设置
-
技术解耦:独立于具体视图技术
2. 适用场景
-
传统服务端渲染应用
-
需要精确控制HTTP响应的场景
-
复杂页面包含多个数据源
-
需要重定向或转发的操作
3. 最佳实践建议
-
使用链式调用简化代码
-
结合视图解析器简化视图路径
-
对复杂模型使用工具类封装
-
重定向时使用RedirectAttributes
-
合理使用HTTP状态码增强API语义
ModelAndView 是 Spring MVC 中处理传统 Web 页面的核心组件,虽然现代开发中 REST API 和前端框架更流行,但在需要服务端渲染的场景下,它仍然是高效可靠的解决方案。