文章目录
1、前言
本文仅记录本人学习过程,不具备教学指导意义。
2、目标
使用野火提供的示例程序,体验 RKNN-ToolKit2 在PC端,从加载模型到模型转换到模型推理的示例流程。
3、RKNN-ToolKit2流程图
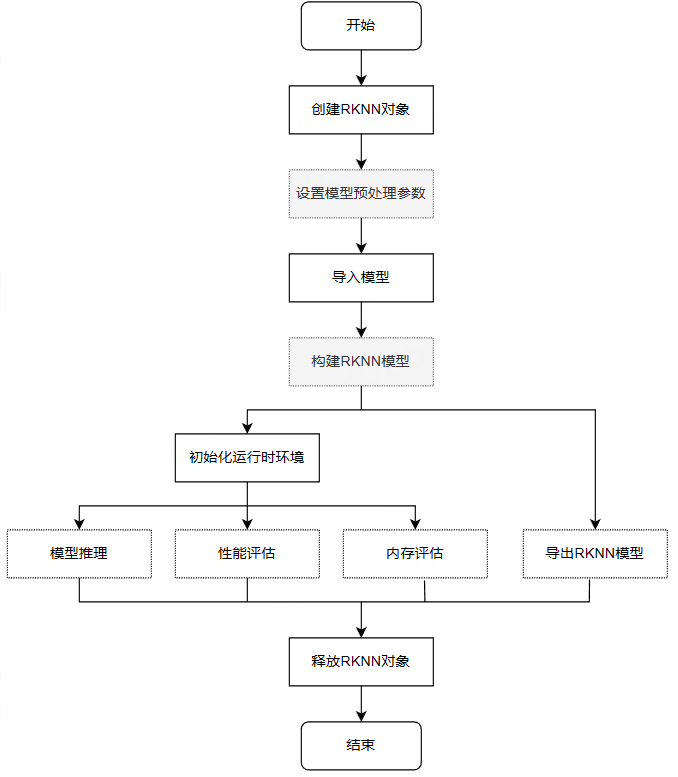
4、完整的测试程序
python
import os
import urllib
import traceback
import time
import sys
import numpy as np
import cv2
from rknn.api import RKNN
ONNX_MODEL = 'yolov5s.onnx'
RKNN_MODEL = 'yolov5s.rknn'
IMG_PATH = './bus.jpg'
DATASET = './dataset.txt'
QUANTIZE_ON = True
OBJ_THRESH = 0.25
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
IMG_SIZE = 640
CLASSES = ("person", "bicycle", "car", "motorbike ", "aeroplane ", "bus ", "train", "truck ", "boat", "traffic light",
"fire hydrant", "stop sign ", "parking meter", "bench", "bird", "cat", "dog ", "horse ", "sheep", "cow", "elephant",
"bear", "zebra ", "giraffe", "backpack", "umbrella", "handbag", "tie", "suitcase", "frisbee", "skis", "snowboard", "sports ball", "kite",
"baseball bat", "baseball glove", "skateboard", "surfboard", "tennis racket", "bottle", "wine glass", "cup", "fork", "knife ",
"spoon", "bowl", "banana", "apple", "sandwich", "orange", "broccoli", "carrot", "hot dog", "pizza ", "donut", "cake", "chair", "sofa",
"pottedplant", "bed", "diningtable", "toilet ", "tvmonitor", "laptop ", "mouse ", "remote ", "keyboard ", "cell phone", "microwave ",
"oven ", "toaster", "sink", "refrigerator ", "book", "clock", "vase", "scissors ", "teddy bear ", "hair drier", "toothbrush ")
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# Convert [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
y = np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2 # top left x
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2 # top left y
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2 # bottom right x
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2 # bottom right y
return y
def process(input, mask, anchors):
anchors = [anchors[i] for i in mask]
grid_h, grid_w = map(int, input.shape[0:2])
box_confidence = sigmoid(input[..., 4])
box_confidence = np.expand_dims(box_confidence, axis=-1)
box_class_probs = sigmoid(input[..., 5:])
box_xy = sigmoid(input[..., :2])*2 - 0.5
col = np.tile(np.arange(0, grid_w), grid_w).reshape(-1, grid_w)
row = np.tile(np.arange(0, grid_h).reshape(-1, 1), grid_h)
col = col.reshape(grid_h, grid_w, 1, 1).repeat(3, axis=-2)
row = row.reshape(grid_h, grid_w, 1, 1).repeat(3, axis=-2)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=-1)
box_xy += grid
box_xy *= int(IMG_SIZE/grid_h)
box_wh = pow(sigmoid(input[..., 2:4])*2, 2)
box_wh = box_wh * anchors
box = np.concatenate((box_xy, box_wh), axis=-1)
return box, box_confidence, box_class_probs
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Filter boxes with box threshold. It's a bit different with origin yolov5 post process!
# Arguments
boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.
box_confidences: ndarray, confidences of objects.
box_class_probs: ndarray, class_probs of objects.
# Returns
boxes: ndarray, filtered boxes.
classes: ndarray, classes for boxes.
scores: ndarray, scores for boxes.
"""
boxes = boxes.reshape(-1, 4)
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
box_class_probs = box_class_probs.reshape(-1, box_class_probs.shape[-1])
_box_pos = np.where(box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
boxes = boxes[_box_pos]
box_confidences = box_confidences[_box_pos]
box_class_probs = box_class_probs[_box_pos]
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score >= OBJ_THRESH)
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
scores = (class_max_score* box_confidences)[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Arguments
boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.
scores: ndarray, scores of objects.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def yolov5_post_process(input_data):
masks = [[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]]
anchors = [[10, 13], [16, 30], [33, 23], [30, 61], [62, 45],
[59, 119], [116, 90], [156, 198], [373, 326]]
boxes, classes, scores = [], [], []
for input, mask in zip(input_data, masks):
b, c, s = process(input, mask, anchors)
b, c, s = filter_boxes(b, c, s)
boxes.append(b)
classes.append(c)
scores.append(s)
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes)
classes = np.concatenate(classes)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
"""Draw the boxes on the image.
# Argument:
image: original image.
boxes: ndarray, boxes of objects.
classes: ndarray, classes of objects.
scores: ndarray, scores of objects.
all_classes: all classes name.
"""
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(top, left, right, bottom))
top = int(top)
left = int(left)
right = int(right)
bottom = int(bottom)
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left - 6),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
def letterbox(im, new_shape=(640, 640), color=(0, 0, 0)):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create RKNN object
rknn = RKNN(verbose=True)
# 指定平台,添加target_platform='rk3588'配置,默认rk3566
print('--> Config model')
rknn.config(mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]], std_values=[[255, 255, 255]])
print('done')
# Load ONNX model
print('--> Loading model')
ret = rknn.load_onnx(model=ONNX_MODEL)
if ret != 0:
print('Load model failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Build model
print('--> Building model')
ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=QUANTIZE_ON, dataset=DATASET)
if ret != 0:
print('Build model failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Export RKNN model
print('--> Export rknn model')
ret = rknn.export_rknn(RKNN_MODEL)
if ret != 0:
print('Export rknn model failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Init runtime environment
print('--> Init runtime environment')
ret = rknn.init_runtime()
# ret = rknn.init_runtime('rk3566')
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# Set inputs
img = cv2.imread(IMG_PATH)
# img, ratio, (dw, dh) = letterbox(img, new_shape=(IMG_SIZE, IMG_SIZE))
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img = cv2.resize(img, (IMG_SIZE, IMG_SIZE))
# Inference
print('--> Running model')
outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[img])
np.save('./onnx_yolov5_0.npy', outputs[0])
np.save('./onnx_yolov5_1.npy', outputs[1])
np.save('./onnx_yolov5_2.npy', outputs[2])
print('done')
# post process
input0_data = outputs[0]
input1_data = outputs[1]
input2_data = outputs[2]
input0_data = input0_data.reshape([3, -1]+list(input0_data.shape[-2:]))
input1_data = input1_data.reshape([3, -1]+list(input1_data.shape[-2:]))
input2_data = input2_data.reshape([3, -1]+list(input2_data.shape[-2:]))
input_data = list()
input_data.append(np.transpose(input0_data, (2, 3, 0, 1)))
input_data.append(np.transpose(input1_data, (2, 3, 0, 1)))
input_data.append(np.transpose(input2_data, (2, 3, 0, 1)))
boxes, classes, scores = yolov5_post_process(input_data)
img_1 = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
if boxes is not None:
draw(img_1, boxes, scores, classes)
cv2.imwrite('result.jpg', img_1)
rknn.release()5、运行测试程序
shell
# git clone https://gitee.com/LubanCat/lubancat_ai_manual_code.git
cd lubancat_ai_manual_code/dev_env/rknn-toolkit2/examples/conversion/yolov5
python3 test.py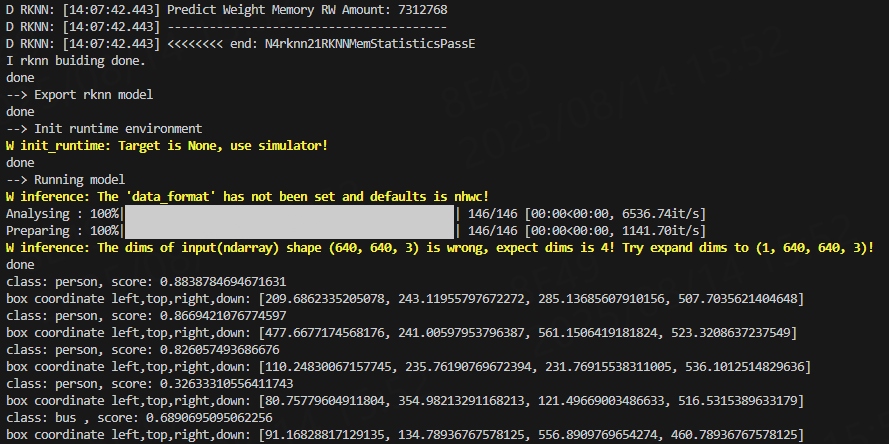
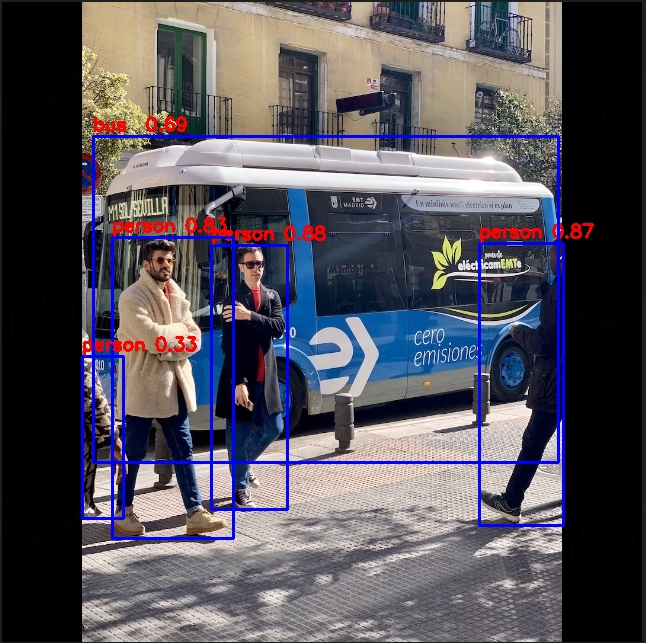
6、程序拆解
- 创建 RKNN 对象
python
rknn = RKNN(verbose=True)- 创建一个 RKNN 模型对象,用于后续配置、加载模型、推理等操作。
verbose=True表示打印详细信息,方便调试。
- 配置模型参数
python
rknn.config(mean_values=[[0, 0, 0]], std_values=[[255, 255, 255]])- 配置输入数据的归一化参数:
mean_values:输入图像每个通道减去的均值。std_values:输入图像每个通道除以的标准差。
- 这些参数要与训练模型时使用的预处理一致。
- 加载 ONNX 模型
python
ret = rknn.load_onnx(model=ONNX_MODEL)- 将已经训练好的 YOLOv5 ONNX 模型加载到 RKNN 对象中。
ONNX_MODEL指向模型文件路径(例:yolov5s.onnx)。
- 构建 RKNN 模型
python
ret = rknn.build(do_quantization=QUANTIZE_ON, dataset=DATASET)- 将 ONNX 模型转换为 RKNN 可用格式:
- 如果
do_quantization=True,会进行量化处理(把浮点权重转成低精度,优化推理速度和内存)。 dataset是量化或优化时使用的样本数据,用于统计输入分布。
- 如果
- 导出 RKNN 模型
python
ret = rknn.export_rknn(RKNN_MODEL)- 把构建好的模型保存为
.rknn文件,方便后续加载或部署到 RK 系列板子上。
- 初始化运行环境
python
ret = rknn.init_runtime()- 初始化 RKNN 推理环境(比如加载到 RK3588 / RK3566 板卡上)。默认为 None,即在 PC 使用工具时,模型在模拟器上运行。target 设为 None 时,需要先调用 build 或 hybrid_quantization 接口才可让模型在模拟器上运行。
- 模型推理(Inference)
python
outputs = rknn.inference(inputs=[img])- 将图像输入到模型中,得到输出。
- YOLOv5 输出 3 个不同尺度的特征层,对应小、中、大目标。
- 后处理(Post-process)
python
input0_data = outputs[0]
input1_data = outputs[1]
input2_data = outputs[2]
# reshape & transpose
input0_data = input0_data.reshape([3, -1]+list(input0_data.shape[-2:]))
...
input_data.append(np.transpose(...))
boxes, classes, scores = yolov5_post_process(input_data)- 把模型输出的原始特征层转成
[boxes, scores, classes]:- boxes:预测的边界框坐标
- classes:对应的类别
- scores:置信度
- 后处理包含:
- 将输出从网络特征图映射到图像坐标
- 置信度筛选
- 非极大值抑制(NMS),去掉重叠过多的框
7、总结
参考文章:
https://doc.embedfire.com/linux/rk356x/Ai/zh/latest/lubancat_ai/env/toolkit2.html#id5