前言
❝
叠加分析是地理信息系统(GIS)空间分析的核心功能之一。它通过两个或者两个以上的图层进行叠加,揭示要素间的空间关联与交互规律。提取出目标结果进行分析,在项目选址、土地占用方面特别有用。叠加分析不仅能够提取多源数据的复合信息,还可通过逻辑运算(如交集、并集)生成新的空间特征,为科学决策提供关键的空间关系支撑。
本篇教程在之前一系列文章的基础上讲解如何将使用GeoTools工具结合OpenLayers实现空间数据的空间缓冲区分析功能。
- GeoTools 开发环境搭建[1]
- 将 Shp 导入 PostGIS 空间数据的五种方式(全)[2]
- GeoTools 结合 OpenLayers 实现空间查询[3]
如果你还没有看过,建议从那里开始。
本文实现流程大致如下。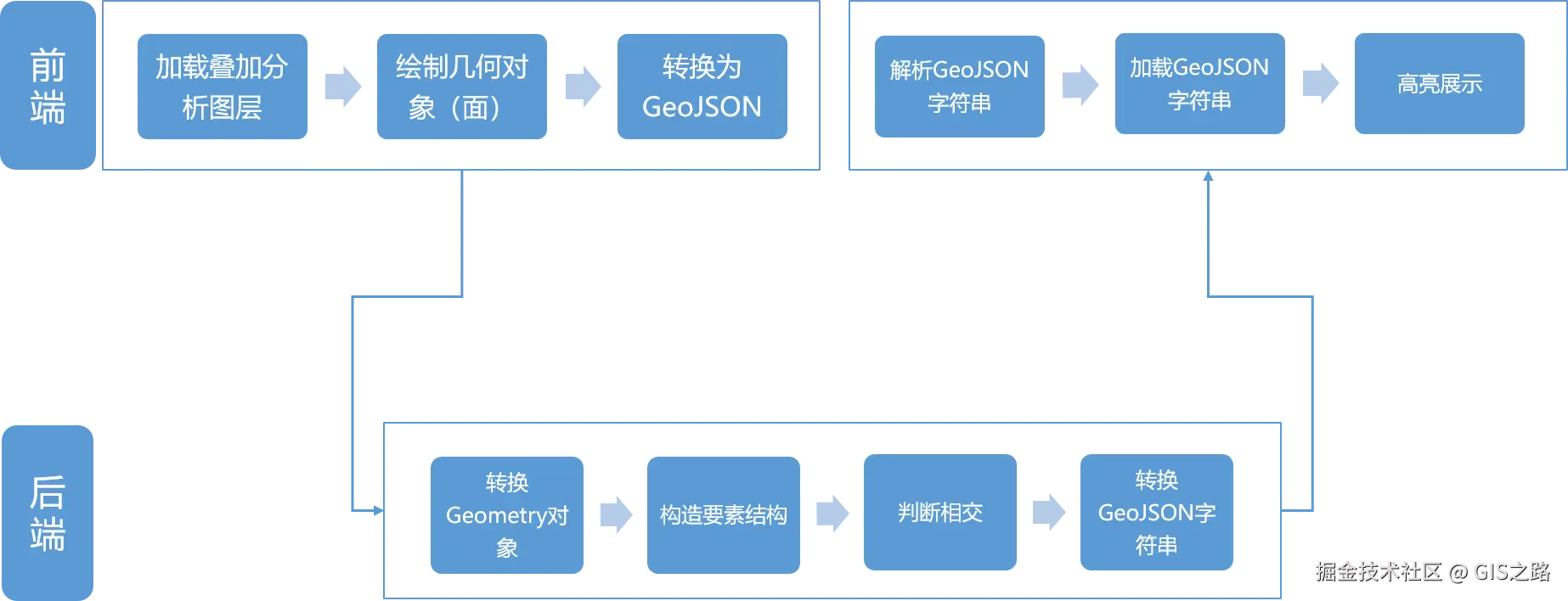
1. 开发环境
本文使用如下开发环境,以供参考。
时间:2025年
GeoTools:v34-SNAPSHOT
IDE:IDEA2025.1.2
JDK:v17
OpenLayers:v9.2.4
Layui:v2.9.14
2. 搭建后端服务
当前在GeoTools 结合 OpenLayers 实现缓冲区分析[4]的基础上进行改造,具体修改如下。
在项目控制层SpatialAnalyseController创建叠加分析方法overlapAnalyse,该方法接收一个GeoJSON字符串参数。
kotlin
package com.example.geotoolsboot.controller;
import com.example.geotoolsboot.service.ISpatialAnalyseService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @name: SpatialAnalyseController
* @description: 空间分析控制器
* @author: gis_road
* @date: 2025-08-05
*/
@CrossOrigin(origins = "*") // 允许跨域
@RestController
public class SpatialAnalyseController {
@Autowired
private ISpatialAnalyseService spatialAnalyseService;
@GetMapping("/overlapAnalyse")
public Map<String,Object> overlapAnalyse(@RequestParam() String geoJSON) throws Exception {
return spatialAnalyseService.overlapAnalyse(geoJSON);
}
}在服务层创建ISpatialAnalyseService接口并定义缓冲分析方法。
typescript
package com.example.geotoolsboot.service;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @name: ISpatialAnalyseService
* @description: 空间分析管理层
* @author: gis_road
* @date: 2025-08-05
*/
public interface ISpatialAnalyseService {
Map<String,Object> overlapAnalyse(String geoJSON) throws Exception;
}在服务层中实现ISpatialAnalyseService接口。首先使用方法geoJsonToGeometry将前端传递过来Geomery类型的GeoJSON字符串对象转换为GeoTools中的Geometry对象,然后使用buildSchema方法构造返回要素数据结构。
需要注意 的是在判断数据相交时至少要得考虑几何对象类型为Polygon和MultiPolygon两种情况。在代码中sourceGeometry instanceof MultiPolygon使用instanceof关键字很容易判断出几何数据类型。
在分析完成之后,使用方法feature2JSON将结果数据转换为GeoJSON字符串返回给前端。
ini
package com.example.geotoolsboot.service.impl;
import com.example.geotoolsboot.service.ISpatialAnalyseService;
import org.geotools.api.data.SimpleFeatureSource;
import org.geotools.api.feature.simple.SimpleFeature;
import org.geotools.api.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureType;
import org.geotools.api.feature.type.AttributeDescriptor;
import org.geotools.api.feature.type.GeometryDescriptor;
import org.geotools.api.referencing.crs.CoordinateReferenceSystem;
import org.geotools.data.shapefile.ShapefileDataStore;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureCollection;
import org.geotools.data.simple.SimpleFeatureIterator;
import org.geotools.feature.DefaultFeatureCollection;
import org.geotools.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureBuilder;
import org.geotools.feature.simple.SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder;
import org.geotools.geojson.feature.FeatureJSON;
import org.geotools.geojson.geom.GeometryJSON;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Geometry;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.MultiPolygon;
import org.locationtech.jts.geom.Polygon;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @name: SpatialAnalyseServiceImpl
* @description: 空间分析实现层
* @author: gis_road
* @date: 2025-08-05
*/
@Service
public class SpatialAnalyseServiceImpl implements ISpatialAnalyseService {
/**叠加分析**/
@Override
public Map<String,Object> overlapAnalyse(String geoJSON) throws Exception {
// 保存输出结果
List<Object> resultFeatures = new ArrayList<>();
// 叠加分析数据
String shpPath = "E:\data\scland_4326.shp";
File shpFile = new File(shpPath);
ShapefileDataStore shapefileDataStore = new ShapefileDataStore(shpFile.toURI().toURL());
// 设置中文字符集,防止乱码
shapefileDataStore.setCharset(Charset.forName("GBK"));
// 获取分析数据结构
String typeName = shapefileDataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
SimpleFeatureType sourceSchema = shapefileDataStore.getSchema(typeName);
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = shapefileDataStore.getFeatureSource();
// 目标数据
SimpleFeatureCollection sourceFeatureCollection = featureSource.getFeatures();
CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = sourceSchema.getCoordinateReferenceSystem();
// 解析字符串分析参数为JSON对象
Map<String,Object> resultMap = new HashMap<>();
// 将GeoJSON数据转换为Geometry
Geometry analyseGeometry = geoJsonToGeometry(geoJSON);
// 创建结果要素类型
SimpleFeatureType resultSchema = buildSchema(sourceSchema, crs);
// 相交分析,获取两个图层的相交集合
try(SimpleFeatureIterator iterator = sourceFeatureCollection.features()){
while(iterator.hasNext()){
SimpleFeature sourceFeature = iterator.next();
Geometry sourceGeometry = (Geometry)sourceFeature.getDefaultGeometry();
if(sourceGeometry instanceof Polygon){
// 执行相交操作
Geometry intersection = sourceGeometry.intersection(analyseGeometry);
if(!intersection.isEmpty()){
resultFeatures.add(intersection);
}
} else if (sourceGeometry instanceof MultiPolygon) {
MultiPolygon multiPolygon = (MultiPolygon) sourceGeometry;
for (int i = 0; i < multiPolygon.getNumGeometries(); i++) {
Geometry subGeom = multiPolygon.getGeometryN(i);
if (subGeom instanceof Polygon) {
Geometry intersection = subGeom.intersection(analyseGeometry);
if (!intersection.isEmpty()) {
List<Object> attributes = new ArrayList<>();
attributes.add(null); // 预留几何位置
// 添加要素的属性
for(AttributeDescriptor attr:sourceSchema.getAttributeDescriptors()) {
if (!(attr instanceof GeometryDescriptor)) {
attributes.add(sourceFeature.getAttribute(attr.getName()));
}
}
SimpleFeature resultFeature = SimpleFeatureBuilder.build(
resultSchema,
attributes,
null
);
resultFeature.setDefaultGeometry(intersection);
String feature = (String)feature2JSON(resultFeature);
resultFeatures.add(feature);
}
}
}
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
resultMap.put("data",resultFeatures);
return resultMap;
}
/**
* 创建要素结构
* @param schema
* @param crs
* @return
*/
private static SimpleFeatureType buildSchema(SimpleFeatureType schema,CoordinateReferenceSystem crs) {
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder typeBuilder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
typeBuilder.setName(schema.getName().getLocalPart());
typeBuilder.setCRS(crs);
// 添加几何字段(保留主图层的几何类型)
GeometryDescriptor geomDescriptor = schema.getGeometryDescriptor();
typeBuilder.add(geomDescriptor.getLocalName(), geomDescriptor.getType().getBinding(), crs);
for (AttributeDescriptor attr : schema.getAttributeDescriptors()) {
// 跳过几何字段(已单独添加)
if (attr instanceof GeometryDescriptor) continue;
String attrName = attr.getLocalName();
// 添加属性(保留原始类型和约束)
typeBuilder.add(attrName, attr.getType().getBinding());
// 复制属性约束(如是否可为空、默认值等)
if (!attr.isNillable()) {
typeBuilder.nillable(false);
}
if (attr.getDefaultValue() != null) {
typeBuilder.defaultValue(attr.getDefaultValue());
}
}
return typeBuilder.buildFeatureType();
}
/**
* 将GeoJSON字符串转换为Geometry对象
* @param geoJson
* @return
*/
private static Geometry geoJsonToGeometry(String geoJson) throws Exception {
GeometryJSON geometryJson = new GeometryJSON(6); // 保留6位小数
try (StringReader reader = new StringReader(geoJson)) {
return geometryJson.read(reader);
}
}
/**
* 将Feature转换为GeoJSON字符串
* @param feature
* @return
*/
private Object feature2JSON(SimpleFeature feature) throws Exception {
FeatureJSON featureJSON = new FeatureJSON();
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
featureJSON.writeFeature(feature,writer);
return writer.toString();
}
}3. OpenLayers 加载叠加服务
前端实现逻辑首先加载叠加分析图层,然后绘制面对象,在绘制完成之后将面Geometry对象转换为GeoJSON数据,之后在点击提交按钮时,将几何数据传递到后端。
后端分析完成将叠加成果返回到前端之后,使用一个列表展示分析结果,点击当前行缩放到目标数据范围,图层高亮显示并打开信息弹窗。
前端CSS结构:
css
.query-wrap {
position: absolute;
padding: 10px;
top: 80px;
left: 90px;
background: #ffffff;
width: 250px;
border-radius: 2.5px;
}
.table-div {
position: absolute;
padding: 10px;
top: 250px;
left: 90px;
max-height: 350px;
overflow-y: scroll;
background: #ffffff;
width: 350px;
border-radius: 2.5px;
display: none;
}前端HTML结构:
xml
<body>
<div id="top-content">
<span>GeoTools 结合 OpenLayers 实现叠加分析</span>
</div>
<div id="map" title=""></div>
<div class="query-wrap">
<form class="layui-form layui-form-pane" action="">
<div class="layui-form-item">
<label class="layui-form-label">绘制对象</label>
<div class="layui-input-block">
<select name="condition" lay-filter="draw-select-filter">
<option value="None">请选择绘制类型</option>
<option value="Point">点</option>
<option value="LineString">线</option>
<option value="Polygon">面</option>
</select>
</div>
</div>
<div class="layui-form-item">
<button lay-submit lay-filter="clearAll" class="layui-btn layui-btn-primary">清除</button>
<button class="layui-btn" lay-submit lay-filter="spatialAnalyse">确认</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
<div class="table-div">
<table id="feature-data"></table>
</div>
</body>前端JS实现,其他逻辑大体不变,这次主要使用了parseFeatureFromService方法统一将后端叠加成功数据转换为Feature数组对象进行展示。
less
layui.use(['form', 'table'], function () {
const form = layui.form;
const layer = layui.layer;
const table = layui.table;
// 绘制事件
form.on('select(draw-select-filter)', function (data) {
removeInteraction()
const value = data.value; // 获得被选中的值
drawShape(value)
});
// 清除事件
form.on("submit(clearAll)", function (data) {
// 清除绘制事件
removeInteraction()
document.querySelector(".table-div").style.display = "none"
// 清除图形
removeAllLayer(map)
return false; // 阻止默认 form 跳转
})
let properties = []
// 提交事件
form.on('submit(spatialAnalyse)', function (data) {
if (!geoJSON) {
layer.msg("请绘制缓冲区域")
return false
}
const queryParam = encodeURIComponent(geoJSON)
// 后端服务地址
const spatial = `http://127.0.0.1:8080/overlapAnalyse?geoJSON=${queryParam}`
fetch(spatial).then(response => response.json()
.then(result => {
const { resultFeatures: features, tabelData } = parseFeatureFromService(result.data)
properties = tabelData
const vectorSource = new ol.source.Vector({
features: features,
format: new ol.format.GeoJSON()
})
// 分析结果图层
const resultLayer = new ol.layer.Vector({
source: vectorSource,
style: new ol.style.Style({
fill: new ol.style.Fill({
color: "#e77b7e8f"
}),
stroke: new ol.style.Stroke({
color: "red",
width: 2.5,
}),
})
})
resultLayer.set("layerName", "resultLayer")
resultLayer.setZIndex(999)
map.addLayer(resultLayer)
if (properties.length) {
document.querySelector(".table-div").style.display = "block"
// 已知数据渲染
let inst = table.render({
elem: '#feature-data',
url: spatial,
cols: [[ //标题栏
{ field: 'SICHUAN_ID', title: 'ID', width: 30 },
{ field: 'dlbm', title: '地类编码', width: 100 },
{ field: 'dlmc', title: '地类名称', width: 100 },
{ field: 'AREA', title: '面积(平方米)', width: 80, sort: true }
]],
parseData: (res) => {
const { tabelData } = parseFeatureFromService(res.data)
const newTable = tabelData.map(feature => {
let table = {}
table = feature.properties
table.geometry = feature.geometry
return table
})
return {
"code": 0, // 解析接口状态
"msg": "", // 解析提示文本
"count": "", // 解析数据长度
"data": newTable // 解析数据列表
}
}
})
// 行单击事件
table.on('row(feature-data)', function (obj) {
removeLayerByName("highlightLayer")
const data = obj.data; // 得到当前行数据
const geom = new ol.format.GeoJSON().readGeometry(data.geometry)
const source = new ol.source.Vector({
features: [
new ol.Feature({
geometry: geom,
properties: data
})
],
format: new ol.format.GeoJSON()
})
const overLayer = new ol.layer.Vector({
source: source,
style: new ol.style.Style({
stroke: new ol.style.Stroke({
color: "#00bcd4",
width: 2.5
}),
fill: new ol.style.Fill({
color: "#ffffff00"
})
})
})
overLayer.set("layerName", "highlightLayer")
overLayer.setZIndex(9999)
map.addLayer(overLayer)
const extent = geom.getExtent()
map.getView().fit(extent)
// Popup 模板
const popupColums = [
{
name: "SICHUAN_ID",
comment: "要素编号"
},
{
name: "dlbm",
comment: "地类编码"
},
{
name: "dlmc",
comment: "地类名称"
},
{
name: "AREA",
comment: "面积(平方米)"
}
]
// 获取中心点
const center = ol.extent.getCenter(extent)
openPopupTable(data, popupColums, center)
});
}
})
)
return false; // 阻止默认 form 跳转
});
});
// 解析GeoJSON字符串
const parseFeatureFromService = (result) => {
const tabelData = []
let features = []
let resultFeatures = []
if (!Array.isArray(result)) {
features.push(result)
} else {
features = result
}
if (features.length) {
resultFeatures = features.map(current => {
const resultFeature = JSON.parse(current)
tabelData.push(resultFeature)
return new ol.format.GeoJSON().readFeature(resultFeature)
})
}
return {
resultFeatures,
tabelData
}
}4. 实现效果
参考资料
1\]GeoTools 开发环境搭建 \[2\]将 Shp 导入 PostGIS 空间数据的五种方式(全) \[3\]GeoTools 结合 OpenLayers 实现空间查询 \[4\]GeoTools 结合 OpenLayers 实现缓冲区分析