基础知识
雪花算法 (Snowflake)是一种生成分布式全局唯一ID的算法,这种算法由Twitter创建,使用64位来进行存储,Java中使用Long类型表示,id跟随时间增长。
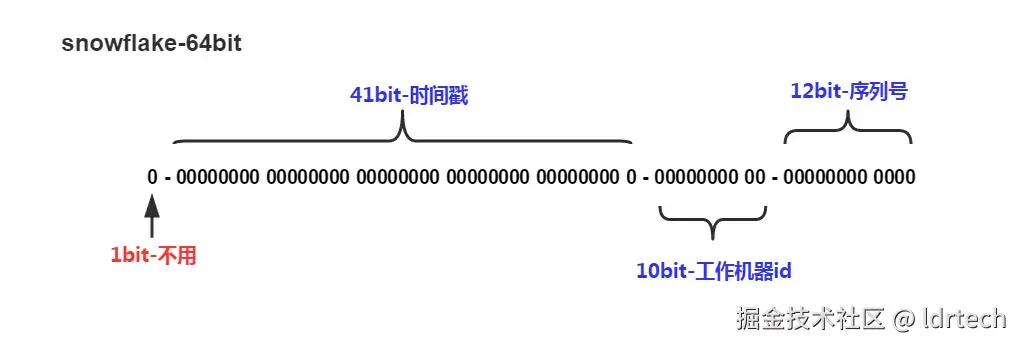
1位,符号位不用,二进制中最高位为1的都是负数,id使用整数,最高位固定是041位,用来记录时间戳(毫秒),最大值为2^41-1,约等于69.7年10位,用来记录工作机器id,最多为2^10= 1024个节点,10位中包括5位的datacenterId和5位的workerId,实际使用中不用区分datacenterId和workerId,只需保证工作机器id分配唯一即可12位,序列号,用来记录同毫秒内产生的不同id,可表示4096个数,即1毫秒内同一机器最大处理4096请求
开源实现
很多开源的代码中比如MyBatis-Plus的icom.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.toolkit.Sequence,和Hutool的cn.hutool.core.lang.Snowflake都有体现。
java
package cn.hutool.core.lang;
import cn.hutool.core.date.SystemClock;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Twitter的Snowflake 算法<br>
* 分布式系统中,有一些需要使用全局唯一ID的场景,有些时候我们希望能使用一种简单一些的ID,并且希望ID能够按照时间有序生成。
*
* <p>
* snowflake的结构如下(每部分用-分开):<br>
*
* <pre>
* 0 - 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0000000000 0 - 00000 - 00000 - 000000000000
* </pre>
* <p>
* 第一位为未使用(符号位表示正数),接下来的41位为毫秒级时间(41位的长度可以使用69年)<br>
* 然后是5位datacenterId和5位workerId(10位的长度最多支持部署1024个节点)<br>
* 最后12位是毫秒内的计数(12位的计数顺序号支持每个节点每毫秒产生4096个ID序号)
* <p>
* 并且可以通过生成的id反推出生成时间,datacenterId和workerId
* <p>
* 参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/relucent/p/4955340.html
*
* @author Looly
* @since 3.0.1
*/
public class Snowflake implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private final long twepoch;
private final long workerIdBits = 5L;
// 最大支持机器节点数0~31,一共32个
@SuppressWarnings({"PointlessBitwiseExpression", "FieldCanBeLocal"})
private final long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
private final long dataCenterIdBits = 5L;
// 最大支持数据中心节点数0~31,一共32个
@SuppressWarnings({"PointlessBitwiseExpression", "FieldCanBeLocal"})
private final long maxDataCenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << dataCenterIdBits);
// 序列号12位
private final long sequenceBits = 12L;
// 机器节点左移12位
private final long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
// 数据中心节点左移17位
private final long dataCenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
// 时间毫秒数左移22位
private final long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + dataCenterIdBits;
// 序列掩码,用于限定序列最大值不能超过4095
@SuppressWarnings("FieldCanBeLocal")
private final long sequenceMask = ~(-1L << sequenceBits);// 4095
private final long workerId;
private final long dataCenterId;
private final boolean useSystemClock;
private long sequence = 0L;
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
/**
* 构造
*
* @param workerId 终端ID
* @param dataCenterId 数据中心ID
*/
public Snowflake(long workerId, long dataCenterId) {
this(workerId, dataCenterId, false);
}
/**
* 构造
*
* @param workerId 终端ID
* @param dataCenterId 数据中心ID
* @param isUseSystemClock 是否使用{@link SystemClock} 获取当前时间戳
*/
public Snowflake(long workerId, long dataCenterId, boolean isUseSystemClock) {
this(null, workerId, dataCenterId, isUseSystemClock);
}
/**
* @param epochDate 初始化时间起点(null表示默认起始日期),后期修改会导致id重复,如果要修改连workerId dataCenterId,慎用
* @param workerId 工作机器节点id
* @param dataCenterId 数据中心id
* @param isUseSystemClock 是否使用{@link SystemClock} 获取当前时间戳
* @since 5.1.3
*/
public Snowflake(Date epochDate, long workerId, long dataCenterId, boolean isUseSystemClock) {
if (null != epochDate) {
this.twepoch = epochDate.getTime();
} else{
// Thu, 04 Nov 2010 01:42:54 GMT
this.twepoch = 1288834974657L;
}
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(StrUtil.format("worker Id can't be greater than {} or less than 0", maxWorkerId));
}
if (dataCenterId > maxDataCenterId || dataCenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(StrUtil.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than {} or less than 0", maxDataCenterId));
}
this.workerId = workerId;
this.dataCenterId = dataCenterId;
this.useSystemClock = isUseSystemClock;
}
/**
* 根据Snowflake的ID,获取机器id
*
* @param id snowflake算法生成的id
* @return 所属机器的id
*/
public long getWorkerId(long id) {
return id >> workerIdShift & ~(-1L << workerIdBits);
}
/**
* 根据Snowflake的ID,获取数据中心id
*
* @param id snowflake算法生成的id
* @return 所属数据中心
*/
public long getDataCenterId(long id) {
return id >> dataCenterIdShift & ~(-1L << dataCenterIdBits);
}
/**
* 根据Snowflake的ID,获取生成时间
*
* @param id snowflake算法生成的id
* @return 生成的时间
*/
public long getGenerateDateTime(long id) {
return (id >> timestampLeftShift & ~(-1L << 41L)) + twepoch;
}
/**
* 下一个ID
*
* @return ID
*/
public synchronized long nextId() {
long timestamp = genTime();
if (timestamp < this.lastTimestamp) {
if(this.lastTimestamp - timestamp < 2000){
// 容忍2秒内的回拨,避免NTP校时造成的异常
timestamp = lastTimestamp;
} else{
// 如果服务器时间有问题(时钟后退) 报错。
throw new IllegalStateException(StrUtil.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for {}ms", lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
}
if (timestamp == this.lastTimestamp) {
final long sequence = (this.sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
this.sequence = sequence;
} else {
sequence = 0L;
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) | (dataCenterId << dataCenterIdShift) | (workerId << workerIdShift) | sequence;
}
/**
* 下一个ID(字符串形式)
*
* @return ID 字符串形式
*/
public String nextIdStr() {
return Long.toString(nextId());
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Private method start
/**
* 循环等待下一个时间
*
* @param lastTimestamp 上次记录的时间
* @return 下一个时间
*/
private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = genTime();
// 循环直到操作系统时间戳变化
while (timestamp == lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = genTime();
}
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
// 如果发现新的时间戳比上次记录的时间戳数值小,说明操作系统时间发生了倒退,报错
throw new IllegalStateException(
StrUtil.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for {}ms", lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
return timestamp;
}
/**
* 生成时间戳
*
* @return 时间戳
*/
private long genTime() {
return this.useSystemClock ? SystemClock.now() : System.currentTimeMillis();
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Private method end
}有趣的小知识
计算机使用补码来表示和存储有符号整数,包括正数和负数,这使得计算机能够统一处理加法和减法运算。 -1的补码(32位表示): 1 111111-1111111-111111-111111 每一位都为1,进行左移操作后高位为1,低位为0,与-1经行&运算可以得到高位的表示,与-1进行^运算可到低位,如代码中的
-1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits)Java线程池的的代码也有这种相似的逻辑。
Java
private final AtomicInteger ctl = new AtomicInteger(ctlOf(RUNNING, 0));
private static final int COUNT_BITS = Integer.SIZE - 3;
private static final int CAPACITY = (1 << COUNT_BITS) - 1;
// runState is stored in the high-order bits
private static final int RUNNING = -1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int SHUTDOWN = 0 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int STOP = 1 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TIDYING = 2 << COUNT_BITS;
private static final int TERMINATED = 3 << COUNT_BITS;
// Packing and unpacking ctl
private static int runStateOf(int c) { return c & ~CAPACITY; }
private static int workerCountOf(int c) { return c & CAPACITY; }
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }存在的问题与解决
结构问题
Twitter的雪花id结构未必适合自己的应用场景(没有这么大的并发量,机器id数量也无需这么大),Twitter的雪花id实现也容易根据id推到出生成时间、机器id、序列号信息。
- 其中时间戳开始年份可以自己手动设置一个较前的时间点,Twitter的实现从1970年01月01日00时00分00算起69年时间,工具到2039年就达到最大值,如hutool Snowflake这里开始时间戳为2010-11-04 01:42:54。
- 一般应用没有这么高的并发量不需要表示到毫秒级别,可以把毫秒折算成秒级别,这样41位数下可以表示上69730年的时间,甚至可以缩减表示的位数,仅需32位就可以表示136年的时间,足以使用,还有额外的好处,因为时间戳在高位,同样的位数时间越小,生成的雪花id数值越小。
可以在一些开源的框架看到对于结构的改变。
百度uid-generator默认实现(github.com/baidu/uid-g...)

ini
<bean id="defaultUidGenerator" class="com.baidu.fsg.uid.impl.DefaultUidGenerator" lazy-init="false">
<property name="timeBits" value="29"/>
<property name="workerBits" value="21"/>
<property name="seqBits" value="13"/>
<property name="epochStr" value="2016-09-20"/>
</bean>Butterfly默认实现(github.com/simonalong/...)
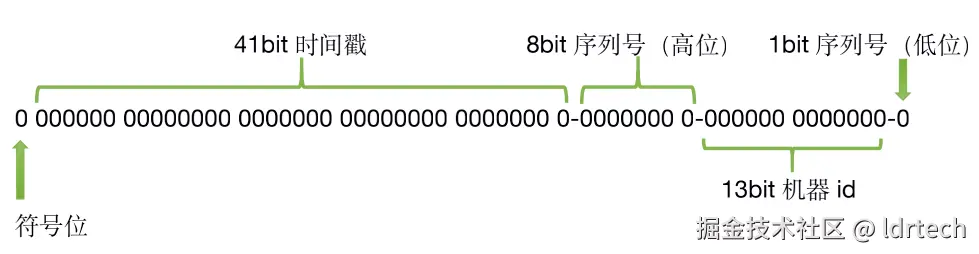
系统时间回拨
如果服务器时间发生回拨,可能会导致相同毫秒内生成两个相同的ID,从而产生重复。
每个开源框架都有不同处理方式。
hutool中Snowflake容忍2秒内的回拨异常。
java
long timestamp = genTime();
if (timestamp < this.lastTimestamp) {
if(this.lastTimestamp - timestamp < 2000){
// 容忍2秒内的回拨,避免NTP校时造成的异常
timestamp = lastTimestamp;
} else{
// 如果服务器时间有问题(时钟后退) 报错。
throw new IllegalStateException(StrUtil.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for {}ms", lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
}百度uid-generator中不允许时间进行回拨,抛出异常提示。
java
protected synchronized long nextId() {
long currentSecond = getCurrentSecond();
// Clock moved backwards, refuse to generate uid
if (currentSecond < lastSecond) {
long refusedSeconds = lastSecond - currentSecond;
throw new UidGenerateException("Clock moved backwards. Refusing for %d seconds", refusedSeconds);
}
...
}Butterfly则是回避了回拨问题
大概思路是:时间戳采用的是"历史时间",每次请求只增序列值,序列值增满,然后"历史时间"增1,序列值归0,其中"历史时间"的初始值是应用启动时候的当前时间。
workId冲突
如果不同机器应用配置了相同的机器ID,它们生成的ID可能会冲突,无法保证全局唯一,如hutool Snowflake中workId依赖人为指定,存在冲突风险。
解决方式很简单,依赖与数据库或者ZooKeeper等分配workId就可。
百度uid-generator,依赖数据库分配,通过host、port来保证唯一。
sql
CREATE TABLE WORKER_NODE
(
ID BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'auto increment id',
HOST_NAME VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL COMMENT 'host name',
PORT VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL COMMENT 'port',
TYPE INT NOT NULL COMMENT 'node type: ACTUAL or CONTAINER',
LAUNCH_DATE DATE NOT NULL COMMENT 'launch date',
MODIFIED TIMESTAMP NOT NULL COMMENT 'modified time',
CREATED TIMESTAMP NOT NULL COMMENT 'created time',
PRIMARY KEY(ID)
)
COMMENT='DB WorkerID Assigner for UID Generator',ENGINE = INNODB;
xml
<insert id="addWorkerNode" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"
parameterType="com.baidu.fsg.uid.worker.entity.WorkerNodeEntity">
INSERT INTO WORKER_NODE
(HOST_NAME,
PORT,
TYPE,
LAUNCH_DATE,
MODIFIED,
CREATED)
VALUES (
#{hostName},
#{port},
#{type},
#{launchDate},
NOW(),
NOW())
</insert>
<select id="getWorkerNodeByHostPort" resultMap="workerNodeRes">
SELECT
ID,
HOST_NAME,
PORT,
TYPE,
LAUNCH_DATE,
MODIFIED,
CREATED
FROM
WORKER_NODE
WHERE
HOST_NAME = #{host} AND PORT = #{port}
</select>Butterfly可数据库和zk进行分配,数据库配置依赖与命名空间与表锁。
sql
CREATE TABLE `butterfly_uuid_generator` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键id',
`namespace` varchar(128) DEFAULT '' COMMENT '命名空间',
`work_id` int(16) COMMENT '工作id',
`last_expire_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '下次失效时间',
`uid` varchar(128) DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '本次启动唯一id',
`ip` bigint(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT 'ip',
`process_id` varchar(128) NOT NULL DEFAULT '0' COMMENT '进程id',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `idx_name_work` (`namespace`,`work_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='发号器表';Butterfly DbWorkerIdHandler.java
java
private void insertWorker() {
try {
// 强制加表锁
neo.execute("lock tables %s write", UUID_TABLE);
Integer maxWorkerId = neo.exeValue(Integer.class, "select max(work_id) from %s where namespace = ?", UUID_TABLE, namespace);
if (null == maxWorkerId) {
uuidGeneratorDO = neo.insert(UUID_TABLE, generateUuidGeneratorDo(null, 0));
} else {
if (maxWorkerId + 1 < MAX_WORKER_SIZE) {
uuidGeneratorDO = neo.insert(UUID_TABLE, generateUuidGeneratorDo(null, maxWorkerId + 1));
} else {
log.error(DB_LOG_PRE + "namespace {} have full worker, init fail", namespace);
throw new WorkerIdFullException("namespace " + namespace + " have full worker, init fail");
}
}
} finally {
// 解锁
neo.execute("unlock tables");
}
}并发量超出设计
如果同一毫秒内并发请求超过了序列号的上限(4096,12位序列号),也会导致ID重复。
处理方式也很容易,这一时刻的序号超出上限了,就等待使用下一时刻的时间再生成id,hutool Snowflake、uid-generator的做法一致。
hutool Snowflake
java
if (timestamp == this.lastTimestamp) {
final long sequence = (this.sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
this.sequence = sequence;
} else {
sequence = 0L;
}uid-generator
java
// At the same second, increase sequence
if (currentSecond == lastSecond) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & bitsAllocator.getMaxSequence();
// Exceed the max sequence, we wait the next second to generate uid
if (sequence == 0) {
currentSecond = getNextSecond(lastSecond);
}
// At the different second, sequence restart from zero
} else {
sequence = 0L;
}前端展示问题
JS对long类型数据存在数字精度丢失问题,与前端交互需要考虑转换成String后传输。
总结
Snowflake包含很多位运算,很适合计算机基础的巩固学习。网络上有很多可以选择的雪花id框架,可以根据自己定制化需求(位数调整)、workId分配策略来选择适合的。