
(以下所有内容全部来自上述课程)

分布式锁
1. Redisson功能介绍
基于setnx实现的分布式锁存在下面的问题:
- 不可重入:同一个线程无法多次获取同一把锁
- 不可重试:获取锁只尝试一次就返回false,没有重试机制
- 超时释放:锁超时释放虽然可以避免死锁,但如果是业务执行耗时较长,也会导致锁释放,存在安全隐患
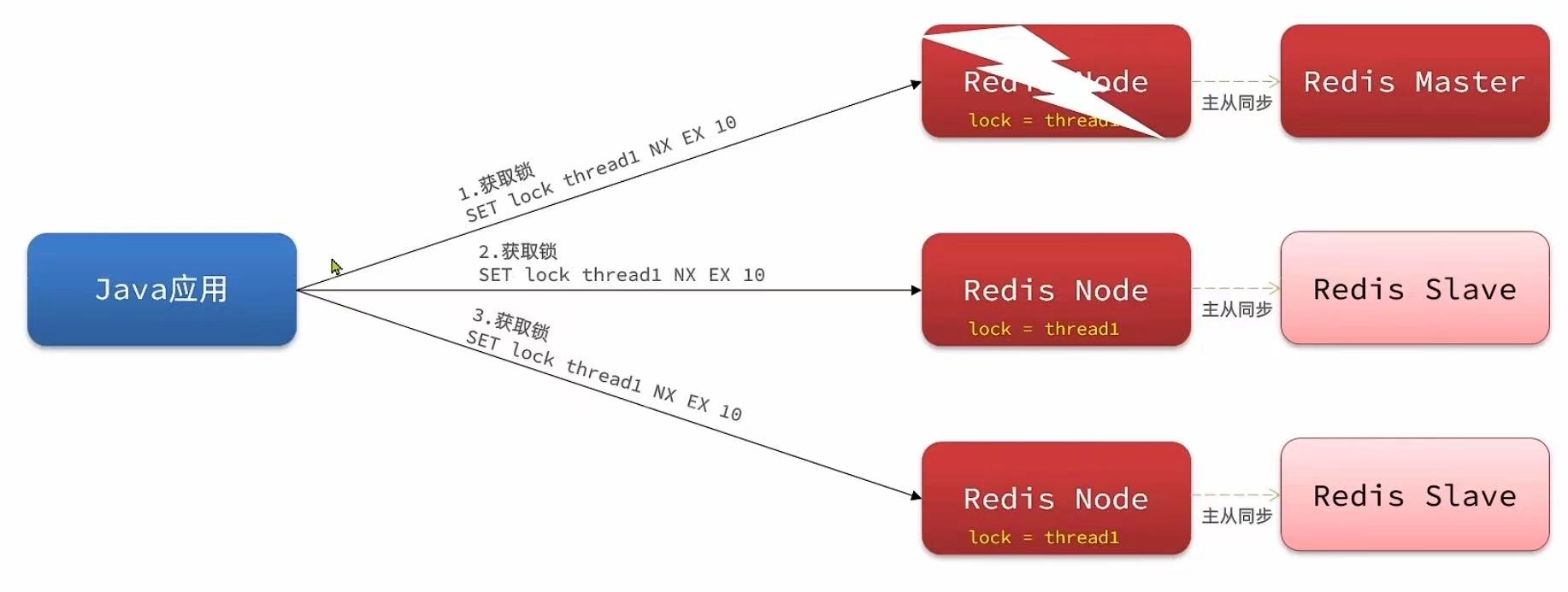
- 主从一致性:如果Redis提供了主从集群,主从同步存在延迟,当主宕机时,如果从并同步主中的锁数据,则会出现锁实现
Redisson是一个在Redis的基础上实现的lava驻内存数据网格(In-Memory Data Grid)。它不仅提供了一系列的分布式的Java常用对象,还提供了许多分布式服务,其中就包含了各种分布式锁的实现。

官网地址:https://redisson.org
GitHub地址:https://github.com/redisson/redisson
jar包下载:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.redisson/redisson/3.50.0
2. Redis入门
- 引入依赖:
java
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId><artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.13.6</version>
</dependency>- 配置Redisson客户端:
java
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
// 配置类
Config config =new Config();
//添加redis地址,这里添加了单点的地址,也可以使用config.useClusterServers()添加集群地址
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.150.101:6379").setPassword("123321");
// 创建客户端
return Redisson.create(config);
}
} - 使用Redisson的分布式锁
java
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Test
void testRedisson()throws InterruptedException {
// 获取锁(可重入),指定锁的名称
RLock lock=redissonClient.getLock("anyLock");
//尝试获取锁,参数分别是:获取锁的最大等待时间(期间会重试),锁自动释放时间,时间单位
boolean isLock =lock.tryLock(1,10,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 判断释放获取成功
if(isLock){
try {
System.out.println("执行业务");
}finally {
// 释放锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
}3. Redisson的可重入锁原理
java
// 创建锁对象
RLock lock=redissonClient.getLock("lock");
@Test
void method1(){
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock();
if(!isLock){
log.error("获取锁失败,1");
return;
}try{
log.info("获取锁成功,1");
method2();
} finally {
log.info("释放锁,1");
lock.unlock();
}
}
void method2(){
boolean isLock =lock.tryLock();
if(!isLock){
log.error("获取锁失败,2");
return;
}try {
log.info("获取锁成功,2");
} finally {
log.info("释放锁,2");
lock.unlock();
}
}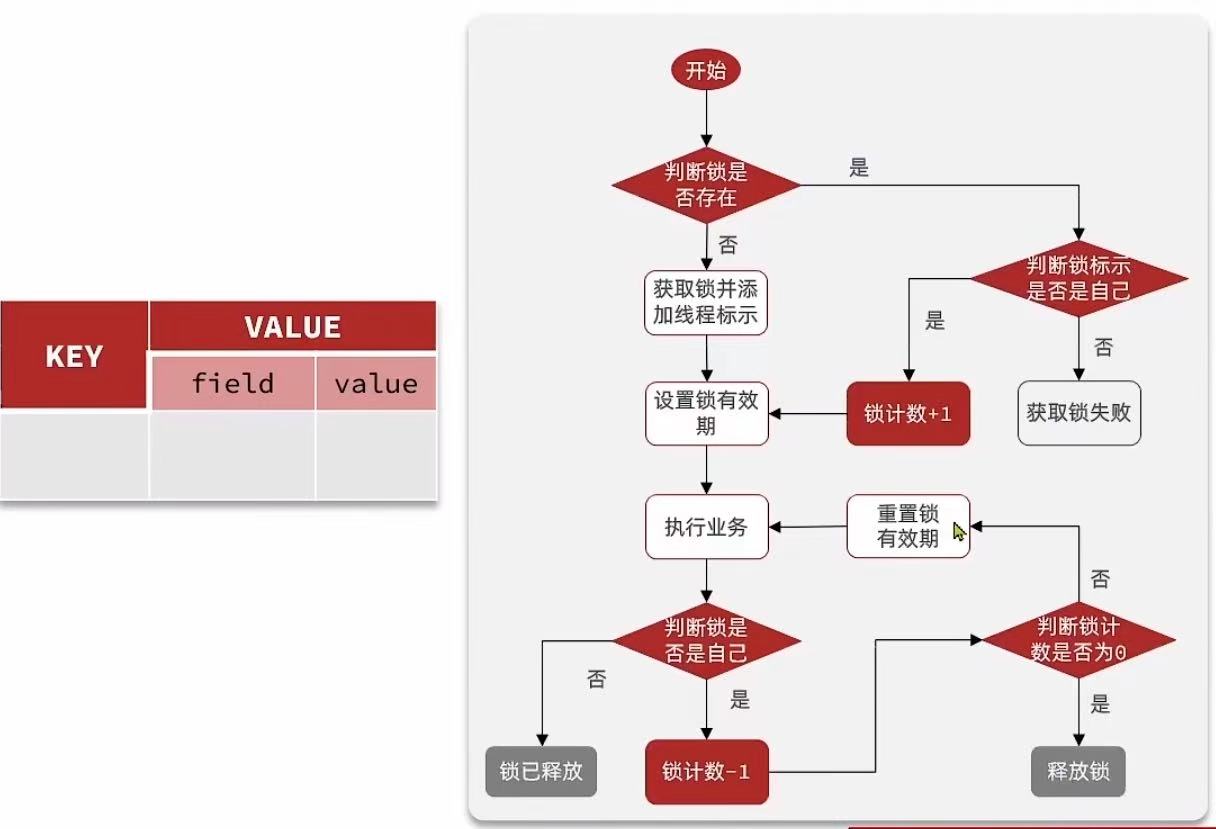
获取锁的lua脚本:
lua
local key = KEYS[1]; -- 锁的key
local threadId= ARGV[1];-- 线程唯一标识
local releaseTime =ARGV[2];-- 锁的自动释放时间
--判断是否存在
if(redis.call('exists',key)== 0)then
-- 不存在,获取锁
redis.call('hset',key, threadId,"1');
-- 设置有效期
redis.call('expire',key, releaseTime);
return 1;--返回结果
end ;
--锁已经存在,判断threadId是否是自己
if(redis.call("hexists",key,threadId)== 1) then
--不存在,获取锁,重入次数+1
redis.call("hincrby", key, threadId, '1');
--设置有效期
redis.call('expire',key, releaseTime);
return 1;--返回结果
end ;
return 0; --代码走到这里,说明获取锁的不是自己,获取锁失败释放锁的lua脚本:
lua
local key =KEYS[1];-- 锁的key
local threadId= ARGV[1];-- 线程唯一标识
local releseTime=ARGV[2];--锁的自动释放时间
--判断当前锁是否还是被自己持有
if(redis.call("HEXISTs",key,threadId)==0)then
return nil;--如果已经不是自己,则直接返回
end ;
--是自己的锁,则重入次数-1
local count = redis.call('HINCRBY', key, threadId, -1);
--判断是否重入次数是否已经为0
if(count>0)then
--大于0说明不能释放锁,重置有效期然后返回
redis.call('EXPIRE',key, releaseTime);
return nil;
else--等于0说明可以释放锁,直接删除
redis.call('DEL', key);
return nil;
end ;4. Redisson的锁重试和WatchDog机制
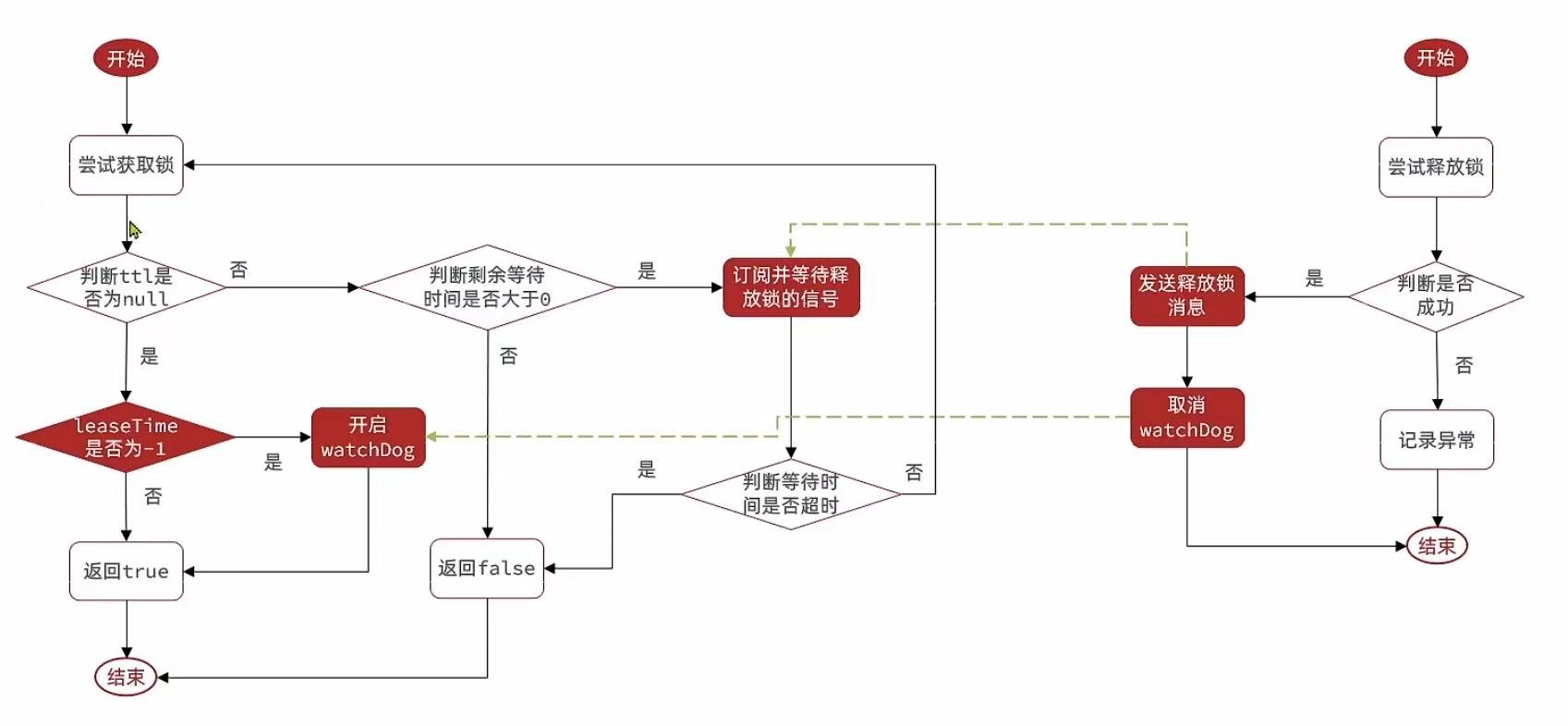
tryLock ctrl+alt+B 打开源码
java
private Long tryAcquire(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) { //第三处查看
//阻塞等待Future结果,就是剩余有效期 把Long接着返回-->第二处查看(往下滑)
return get(tryAcquireAsync0(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId)); //查看tryAcquireAsync0(往下滑)
}
private RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) { //第四处查看
RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture;
if (leaseTime > 0) {
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} else { //命令行已经发出去了,但是结果拿没拿到还不清楚-->Future
ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, internalLockLeaseTime, //查看tryLockInnerAsync(向下滑)
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);
} //返回第三处查看(向上滑)
CompletionStage<Long> s = handleNoSync(threadId, ttlRemainingFuture);
ttlRemainingFuture = new CompletableFutureWrapper<>(s);
CompletionStage<Long> f = ttlRemainingFuture.thenApply(ttlRemaining -> {
// lock acquired
if (ttlRemaining == null) { //剩余有效期=null
if (leaseTime > 0) {
internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);
} else {
scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId); //自动更新有效期续约 --> 查看scheduleExpirationRenewal(下一个板块的代码)
}
}
return ttlRemaining;
});
return new CompletableFutureWrapper<>(f);
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
return get(tryLockAsync());
}
<T> RFuture<T> tryLockInnerAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId, RedisStrictCommand<T> command) { //第五处查看
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, command,
"if ((redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) " +
"or (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1)) then " +
"redis.call('hincrby', KEYS[1], ARGV[2], 1); " +
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
"return nil; " +
"end; " + //上面是获取成功,下面是没成功
"return redis.call('pttl', KEYS[1]);", //pttl(毫秒的单位)=ttl(秒的单位) 获取指定key的剩余有效期
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()), unit.toMillis(leaseTime), getLockName(threadId));
} //返回第四处(向上滑)
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException { //第二处查看
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime); //把等待时间转换为毫秒
long current = System.currentTimeMillis(); //获取当前时间
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId(); //获取当前线程id 也就是线程标识
Long ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId); //尝试获取锁 -->看tryAcquire方法(往上滑)
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true; //获取成功。直接返回
}
//获取失败,继续尝试(重点!)
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current; //现在的时间减去之前的当前时间(就是获取锁消耗的时间)
//然后最大等待时间减去消耗的时间,就是剩余等待时间
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false; //没有剩余等待时间,就直接获取失败
}
//获取失败,继续尝试(但没有立即-->subscribe)
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = subscribe(threadId); //订阅了别人释放锁的信号(publish)
try {
subscribeFuture.get(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); //因为时间不确定,所以也是Future
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
if (!subscribeFuture.completeExceptionally(new RedisTimeoutException( //最大剩余时间结束-->返回false,继续往下走
"Unable to acquire subscription lock after " + time + "ms. " +
"Try to increase 'subscriptionsPerConnection' and/or 'subscriptionConnectionPoolSize' parameters."))) {
subscribeFuture.whenComplete((res, ex) -> {
if (ex == null) { //判断有没有时间了
unsubscribe(res, threadId); //超时,取消订阅
}
});
}
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false; //获取锁失败
}
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current; //又计算一次等待消耗时间
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false; //套娃,没时间了还是没获取到锁,直接返回获取失败
}
//小总结:上方一直计算剩余时间,有就直接到这儿,没有就一直重复计算
//计算终于有剩余时间(true)
while (true) {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId); //第一次重试(tryAcquire)
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true; //成功
}
//失败就再计算剩余时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) {
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false; //没有就失败
}
// waiting for message 失败就继续计算时间
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0 && ttl < time) { //ttl和time ,哪个小就先等哪个(time是根本底线,没了也不用等了)
//getLatch() 信号量,类似与publish抛出获取信号
//ttl是施放时间,更灵活一些,锁释放了就重试(重新获取锁)
commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else { //time到期了,还没释放也就不用等了
commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
//再获取时间
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0) { //没时间了,还是直接失败
acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
} //时间充足就while(true),返回上面又开始重试
} finally {
unsubscribe(commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture), threadId);
}
// return get(tryLockAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit));
} //至此,重试问题解决 --> 去看超时问题:第四处(向上滑)
java
protected void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {
ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry();
//EntryName:当前锁的名称
//一个锁一个entry,第一次来创建新的entry,之后来的返回旧的entry
//保证这把锁不管重复了几次,返回的都是同一个entry
ExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {
oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId); //同一个线程多次来获取
} else {
entry.addThreadId(threadId);
try {
renewExpiration(); //第一次来:续约,更新有效期 -->看renewExpiration
} finally {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);
}
}
}
}
//renewExpiration:
private void renewExpiration() { //更新有效期
ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName()); //先得到entry
if (ee == null) {
return;
}
Timeout task = getServiceManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName()); //拿出entry
if (ent == null) {
return;
}
Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId(); //取出线程id
if (threadId == null) {
return;
}
CompletionStage<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);
//刷新有效期-->查看renewExpirationAsync
future.whenComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
log.error("Can't update lock {} expiration", getRawName(), e);
EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());
return;
}
if (res) {
// reschedule itself
renewExpiration();
//自己调用自己:递归--重复每十秒更新一次有效期,解决超时问题(重点!)
} else {
cancelExpirationRenewal(null);
}
});
}
}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); //内部锁施放时间/3
ee.setTimeout(task);
}
//renewExpirationAsync:
//重置有效期
protected CompletionStage<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {
return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,
"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +
//判断当前线程的锁是不是自己线程拿的--肯定能成功,不是自己线程进不来
"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +
//更新有效期
"return 1; " +
"end; " +
"return 0;",
Collections.singletonList(getRawName()),
internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));
}
//释放锁的逻辑:
@Override
public void unlock() {
try {
get(unlockAsync(Thread.currentThread().getId())); //查看unlockAsync
} catch (RedisException e) {
if (e.getCause() instanceof IllegalMonitorStateException) {
throw (IllegalMonitorStateException) e.getCause();
} else {
throw e;
}
}
//unlockAsync:
@Override
public RFuture<Void> unlockAsync(long threadId) {
return getServiceManager().execute(() -> unlockAsync0(threadId));
}
private RFuture<Void> unlockAsync0(long threadId) {
CompletionStage<Boolean> future = unlockInnerAsync(threadId);
CompletionStage<Void> f = future.handle((opStatus, e) -> {
cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId); //取消更新任务 -->查看:cancelExpirationRenewal
if (e != null) {
if (e instanceof CompletionException) {
throw (CompletionException) e;
}
throw new CompletionException(e);
}
if (opStatus == null) {
IllegalMonitorStateException cause = new IllegalMonitorStateException("attempt to unlock lock, not locked by current thread by node id: "
+ id + " thread-id: " + threadId);
throw new CompletionException(cause);
}
return null;
});
return new CompletableFutureWrapper<>(f);
}
//cancelExpirationRenewal:
//定时任务的删除
protected void cancelExpirationRenewal(Long threadId) {
ExpirationEntry task = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName()); //从map中取
if (task == null) {
return;
}
if (threadId != null) {
task.removeThreadId(threadId); //先把id干掉
}
if (threadId == null || task.hasNoThreads()) {
Timeout timeout = task.getTimeout();
if (timeout != null) {
timeout.cancel(); //然后再把任务取消
}
EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName()); //最后再把entry取消掉
}
}
小总结
Redisson分布式锁原理
- 可重入:利用hash结构记录线程id和重入次数
- 可重试:利用信号量和PubSub功能实现等待、唤醒,获取锁失败的重试机制
- 超时续约:利用watchDog,每隔一段时间(releaseTime/3),重置超时时间
5. Redisson的multiLock原理
RedisConfig.java:
java
package com.hmdp.config;
import org.redisson.Redisson;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.redisson.config.Config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RedissionConfig {
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient(){
// 配置类
Config config =new Config();
//添加redis地址,这里添加了单点的地址,也可以使用config.useClusterServers()添加集群地址
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.150.101:6379").setPassword("123456");
// 创建客户端
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient2(){
// 配置类
Config config =new Config();
//添加redis地址,这里添加了单点的地址,也可以使用config.useClusterServers()添加集群地址
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.150.101:6380");
// 创建客户端
return Redisson.create(config);
}
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient3(){
// 配置类
Config config =new Config();
//添加redis地址,这里添加了单点的地址,也可以使用config.useClusterServers()添加集群地址
config.useSingleServer().setAddress("redis://192.168.150.101:6381");
// 创建客户端
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}RedissonTest.java:
java
package com.hmdp;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.redisson.api.RLock;
import org.redisson.api.RedissonClient;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class RedissonTest {
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient2;
@Resource
private RedissonClient redissonClient3;
private RLock lock;
@BeforeEach
void setUp(){
RLock lock1 = redissonClient.getLock("order");
RLock lock2 = redissonClient2.getLock("order");
RLock lock3 = redissonClient3.getLock("order");
//创建联锁
lock = redissonClient.getMultiLock(lock1,lock2,lock3);
}
@Test
void method1() throws InterruptedException{
//尝试获取锁
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock(1L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (!isLock){
log.error("获取锁失败....1");
return;
}
try {
log.info("获取锁成功....1");
method2();
log.info("开始执行业务....1");
}finally {
log.warn("准备释放锁....1");
lock.unlock();
}
}
void method2(){
//尝试获取锁
boolean isLock = lock.tryLock();
if (!isLock){
log.error("获取锁失败....2");
return;
}
try {
log.info("获取锁成功....2");
log.info("开始执行业务....2");
}finally {
log.warn("准备释放锁....2");
lock.unlock();
}
}
}总结
- 不可重入Redis分布式锁:
原理:利用setnx的互斥性;利用ex避免死锁;释放锁时判断线程标示
缺陷:不可重入、无法重试、锁超时失效 - 可重入的Redis分布式锁:
原理:利用hash结构,记录线程标示和重入次数;利用watchDog延续锁时间;利用信号量控制锁重试等待
缺陷:redis宕机引起锁失效问题 - Redisson的multiLock:
原理:多个独立的Redis节点,必须在所有节点都获取重入锁,才算获取锁成功
缺陷:运维成本高、实现复杂