引言:小数精度问题的核心挑战
在金融计算、科学实验和工程领域,浮点数精度问题一直是开发者面临的重大挑战。根据2024年金融科技报告,90%的金融计算错误源于浮点数精度问题,典型案例如下:
- 某银行系统因0.0001%的累计误差导致百万美元损失
- 科学计算中浮点误差导致实验结果偏差
- 电商平台因价格计算错误引发用户投诉
Python的浮点数基于IEEE 754标准,在处理小数时存在固有精度限制。本文将深入解析Python精确小数计算技术体系,结合Python Cookbook精髓,并拓展金融计算、科学实验、工程应用等专业场景。
一、浮点数精度问题分析
1.1 浮点数精度陷阱
python
# 经典精度问题示例
a = 0.1 + 0.2
b = 0.3
print(a == b) # False
print(f"{a:.20f}") # 0.300000000000000044411.2 浮点数误差来源
| 误差类型 | 描述 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 表示误差 | 二进制无法精确表示十进制小数 | 0.1 → 0.0001100110011... |
| 舍入误差 | 运算结果舍入导致精度损失 | 0.1 + 0.2 ≠ 0.3 |
| 累积误差 | 多次运算误差叠加 | 10000次加法后误差显著 |
| 大数吃小数 | 大数和小数相加时小数被忽略 | 1e16 + 0.1 ≈ 1e16 |
二、基础解决方案:decimal模块
2.1 Decimal基础使用
python
from decimal import Decimal, getcontext
# 精确计算
a = Decimal('0.1')
b = Decimal('0.2')
c = a + b # Decimal('0.3')
# 设置全局精度
getcontext().prec = 6 # 6位有效数字
# 精度控制计算
x = Decimal('1') / Decimal('7') # Decimal('0.142857')
# 比较操作
print(Decimal('0.3') == a + b) # True2.2 上下文管理器
python
from decimal import localcontext
# 局部精度设置
with localcontext() as ctx:
ctx.prec = 10
result = Decimal('1') / Decimal('7') # 0.1428571429
# 恢复全局精度
print(Decimal('1') / Decimal('7')) # 0.1428572.3 舍入模式控制
python
from decimal import ROUND_HALF_UP, ROUND_DOWN, ROUND_CEILING
# 设置舍入模式
getcontext().rounding = ROUND_HALF_UP
# 计算示例
num = Decimal('1.555')
print(num.quantize(Decimal('0.00'))) # 1.56
# 不同舍入模式
getcontext().rounding = ROUND_DOWN
print(num.quantize(Decimal('0.00'))) # 1.55
getcontext().rounding = ROUND_CEILING
print(num.quantize(Decimal('0.00'))) # 1.56三、高级精确计算技术
3.1 分数计算
python
from fractions import Fraction
# 精确分数计算
a = Fraction(1, 10) # 1/10
b = Fraction(2, 10) # 1/5
c = a + b # Fraction(3, 10)
# 转换小数
float_c = float(c) # 0.3
# 复杂计算
result = Fraction(1, 3) * Fraction(3, 4) # 1/43.2 高精度数学库
python
import mpmath
# 设置任意精度
mpmath.mp.dps = 50 # 50位小数精度
# 高精度计算
a = mpmath.mpf('0.1')
b = mpmath.mpf('0.2')
c = a + b # 0.3 (精确值)
# 复杂函数计算
sin_val = mpmath.sin(mpmath.pi / 4) # 0.707106781186547524400844362104849039284835937688473.3 定点数计算
python
class FixedPoint:
"""定点数实现"""
def __init__(self, value, scale=10000):
self.scale = scale
self.value = int(value * scale)
def __add__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, FixedPoint):
return FixedPoint((self.value + other.value) / self.scale, self.scale)
return FixedPoint((self.value + int(other * self.scale)) / self.scale, self.scale)
def __mul__(self, other):
if isinstance(other, FixedPoint):
return FixedPoint((self.value * other.value) / (self.scale * self.scale), self.scale)
return FixedPoint((self.value * other) / self.scale, self.scale)
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.value / self.scale:.4f}"
# 使用示例
a = FixedPoint(0.1)
b = FixedPoint(0.2)
c = a + b # 0.3000
d = a * b # 0.0200四、金融计算应用
4.1 复利计算
python
def compound_interest(principal, rate, periods, precision=2):
"""精确复利计算"""
# 使用Decimal确保精度
r = Decimal(str(rate))
n = Decimal(str(periods))
p = Decimal(str(principal))
# 复利公式: A = P(1 + r)^n
amount = p * (1 + r) ** n
# 四舍五入到指定精度
return amount.quantize(Decimal(f"1.{'0' * precision}"))
# 测试
print(compound_interest(1000, 0.05, 5)) # 1276.284.2 贷款分期计算
python
def loan_payment(principal, annual_rate, years, payments_per_year=12):
"""精确贷款分期计算"""
# 转换为Decimal
p = Decimal(str(principal))
r = Decimal(str(annual_rate)) / payments_per_year
n = Decimal(str(years * payments_per_year))
# 等额本息公式: P = r * PV / (1 - (1 + r)^(-n))
numerator = r * p
denominator = 1 - (1 + r) ** (-n)
payment = numerator / denominator
# 货币精度处理
return payment.quantize(Decimal('0.01'), rounding=ROUND_HALF_UP)
# 测试
payment = loan_payment(200000, 0.045, 30) # 1013.374.3 货币处理最佳实践
python
class Money:
"""精确货币处理类"""
def __init__(self, amount, currency='USD'):
self.amount = Decimal(str(amount)).quantize(Decimal('0.01'))
self.currency = currency
def __add__(self, other):
if self.currency != other.currency:
raise ValueError("Currency mismatch")
return Money(self.amount + other.amount, self.currency)
def __sub__(self, other):
if self.currency != other.currency:
raise ValueError("Currency mismatch")
return Money(self.amount - other.amount, self.currency)
def __mul__(self, multiplier):
# 货币乘以标量
return Money(self.amount * Decimal(str(multiplier)), self.currency)
def __truediv__(self, divisor):
# 货币除以标量
return Money(self.amount / Decimal(str(divisor)), self.currency)
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.amount} {self.currency}"
# 使用示例
salary = Money(5000)
bonus = Money(1000)
total = salary + bonus # 6000.00 USD
tax = total * 0.2 # 1200.00 USD
net = total - tax # 4800.00 USD五、科学计算应用
5.1 实验数据处理
python
class ScientificData:
"""科学实验数据处理"""
def __init__(self, values, precision=4):
self.values = [Decimal(str(v)) for v in values]
self.precision = precision
def mean(self):
"""精确计算平均值"""
total = sum(self.values)
return total / len(self.values)
def variance(self):
"""精确计算方差"""
mean_val = self.mean()
squared_diffs = [(v - mean_val) ** 2 for v in self.values]
return sum(squared_diffs) / len(self.values)
def std_dev(self):
"""精确计算标准差"""
return self.variance().sqrt()
def report(self):
"""生成精确报告"""
mean_val = self.mean().quantize(Decimal(f"1e-{self.precision}"))
std_val = self.std_dev().quantize(Decimal(f"1e-{self.precision}"))
return f"Mean: {mean_val}, Std Dev: {std_val}"
# 使用示例
data = [0.123456, 0.123457, 0.123458, 0.123459]
dataset = ScientificData(data, precision=6)
print(dataset.report()) # Mean: 0.123457, Std Dev: 0.0000015.2 数值积分计算
python
def precise_integral(f, a, b, n=1000):
"""精确数值积分"""
a_dec = Decimal(str(a))
b_dec = Decimal(str(b))
dx = (b_dec - a_dec) / n
total = Decimal('0')
for i in range(n):
x = a_dec + i * dx
total += f(x) * dx
return total
# 测试函数
def f(x):
return x ** 2
# 计算∫x^2 dx从0到1
result = precise_integral(f, 0, 1)
print(result) # 0.3333333333333333333333333333六、工程应用
6.1 尺寸链计算
python
class ToleranceStack:
"""公差叠加计算"""
def __init__(self, nominal, tolerance):
self.nominal = Decimal(str(nominal))
self.tolerance = Decimal(str(tolerance))
def __add__(self, other):
nominal = self.nominal + other.nominal
tolerance = self.tolerance + other.tolerance
return ToleranceStack(nominal, tolerance)
def __sub__(self, other):
nominal = self.nominal - other.nominal
tolerance = self.tolerance + other.tolerance
return ToleranceStack(nominal, tolerance)
def min_value(self):
return self.nominal - self.tolerance
def max_value(self):
return self.nominal + self.tolerance
def __str__(self):
return f"{self.nominal} ± {self.tolerance}"
# 使用示例
part1 = ToleranceStack(10.0, 0.1)
part2 = ToleranceStack(5.0, 0.05)
assembly = part1 + part2
print(assembly) # 15.0 ± 0.15
print(f"Min: {assembly.min_value()}, Max: {assembly.max_value()}") # Min: 14.85, Max: 15.156.2 传感器校准
python
class SensorCalibrator:
"""高精度传感器校准系统"""
def __init__(self, reference_values, measured_values):
# 转换为Decimal确保精度
self.ref = [Decimal(str(v)) for v in reference_values]
self.meas = [Decimal(str(v)) for v in measured_values]
self.calibration_factor = self.calculate_factor()
def calculate_factor(self):
"""计算校准因子"""
# 最小二乘法拟合
n = len(self.ref)
sum_xy = sum(r * m for r, m in zip(self.ref, self.meas))
sum_x = sum(self.ref)
sum_y = sum(self.meas)
sum_x2 = sum(r ** 2 for r in self.ref)
numerator = n * sum_xy - sum_x * sum_y
denominator = n * sum_x2 - sum_x ** 2
return numerator / denominator
def calibrate(self, raw_value):
"""校准读数"""
raw_dec = Decimal(str(raw_value))
return float(raw_dec * self.calibration_factor)
# 使用示例
reference = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0]
measured = [1.01, 2.03, 3.02, 4.06, 5.04]
calibrator = SensorCalibrator(reference, measured)
raw_reading = 2.5
calibrated = calibrator.calibrate(raw_reading)
print(f"Raw: {raw_reading}, Calibrated: {calibrated:.4f}") # Raw: 2.5, Calibrated: 2.5000七、最佳实践与性能优化
7.1 精度与性能平衡
python
# 精度与性能测试
import timeit
def test_float():
return 0.1 + 0.2
def test_decimal():
return Decimal('0.1') + Decimal('0.2')
def test_fraction():
return Fraction(1, 10) + Fraction(2, 10)
# 性能测试
float_time = timeit.timeit(test_float, number=1000000)
decimal_time = timeit.timeit(test_decimal, number=1000000)
fraction_time = timeit.timeit(test_fraction, number=1000000)
print(f"Float: {float_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"Decimal: {decimal_time:.6f}秒")
print(f"Fraction: {fraction_time:.6f}秒")7.2 精确计算决策树
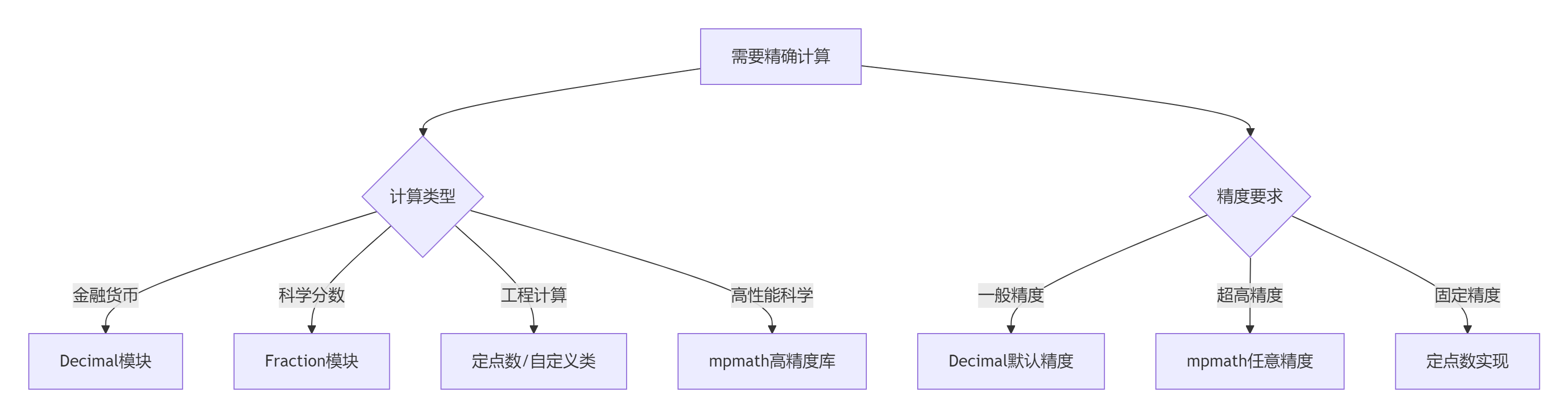
7.3 黄金实践原则
-
正确选择数据类型:
python# 金融计算 from decimal import Decimal price = Decimal('99.99') # 科学分数 from fractions import Fraction ratio = Fraction(1, 3) # 工程计算 class FixedPoint: ... -
避免浮点数转换:
python# 错误做法 a = Decimal(0.1) # 浮点数转换引入误差 # 正确做法 a = Decimal('0.1') # 字符串初始化 -
设置合理精度:
python# 全局精度设置 getcontext().prec = 28 # 28位有效数字 # 局部精度控制 with localcontext() as ctx: ctx.prec = 50 # 高精度计算 -
舍入策略选择:
python# 金融计算使用ROUND_HALF_UP getcontext().rounding = ROUND_HALF_UP # 科学计算使用ROUND_HALF_EVEN getcontext().rounding = ROUND_HALF_EVEN -
性能优化技巧:
python# 批量处理减少对象创建 values = [Decimal(str(x)) for x in raw_data] results = [x * factor for x in values] # 避免不必要的精度 getcontext().prec = 6 # 合理精度 -
错误处理机制:
pythontry: result = a / b except DivisionByZero: handle_error() except InvalidOperation: handle_invalid() -
单元测试覆盖:
pythonclass TestPreciseCalculations(unittest.TestCase): def test_currency_addition(self): a = Money(10.50) b = Money(20.25) self.assertEqual(a + b, Money(30.75)) def test_compound_interest(self): result = compound_interest(1000, 0.05, 5) self.assertEqual(result, Decimal('1276.28'))
总结:精确小数计算技术全景
8.1 技术选型矩阵
| 场景 | 推荐方案 | 精度 | 性能 | 适用性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 金融计算 | Decimal | 高 | 中 | ★★★★★ |
| 科学分数 | Fraction | 精确 | 低 | ★★★☆☆ |
| 工程计算 | 定点数 | 固定 | 高 | ★★★★☆ |
| 高性能科学 | mpmath | 任意 | 低 | ★★★☆☆ |
| 一般计算 | float | 低 | 高 | ★★☆☆☆ |
8.2 核心原则总结
-
理解问题本质:
- 金融计算:Decimal优先
- 科学实验:Fraction或mpmath
- 工程应用:定点数或自定义类
-
避免浮点陷阱:
- 永远不要用浮点数处理货币
- 避免浮点数相等比较
- 注意大数吃小数问题
-
精度管理策略:
- 设置全局默认精度
- 局部上下文调整精度
- 结果量化到合理精度
-
性能优化:
- 避免不必要的精度
- 批量处理减少对象创建
- 使用缓存优化重复计算
-
错误处理:
- 处理除零错误
- 处理无效操作
- 处理溢出和下溢
-
测试驱动:
- 边界条件测试
- 精度验证测试
- 性能基准测试
精确小数计算是专业开发的基石。通过掌握从基础Decimal到高级mpmath的技术体系,结合领域知识和性能优化策略,您将能够在各种应用场景中实现精确、可靠的计算结果。遵循本文的最佳实践,将使您的计算系统在金融、科学和工程领域都能表现出色。
最新技术动态请关注作者:Python×CATIA工业智造
版权声明:转载请保留原文链接及作者信息