相对布局 (RelativeContainer) 基本概念
HarmonyOS 的 RelativeContainer 是一种基于相对位置的布局容器,允许组件通过锚点关系(如对齐、居中等)动态调整位置,适合复杂界面设计。与线性布局(DirectionalLayout)不同,它不依赖固定排列方向,而是通过组件间的相对约束实现灵活布局。
基本概念
-
参考边界:设置当前组件的哪个边界对齐到锚点。
-
锚点:通过锚点设置当前元素基于哪个元素确定位置。
-
对齐方式:通过对齐方式,设置当前元素是基于锚点的上中下对齐,还是基于锚点的左中右对齐。
1.设置参考边界
设置当前组件的哪个边界对齐到锚点。容器内子组件的参考边界区分水平方向和垂直方向。
-
在水平方向上,可以按照起始(left)、居中(middle)或尾端(right)的组件边界与锚点对齐
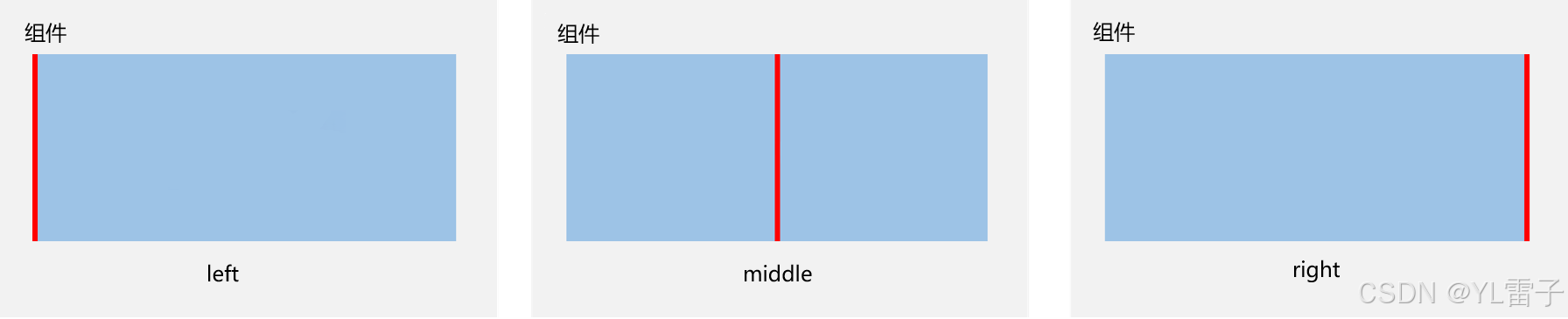
-
在垂直方向上,可以设置组件边界与锚点对齐,具体包括顶部(top)、居中(center)和底部(bottom)。
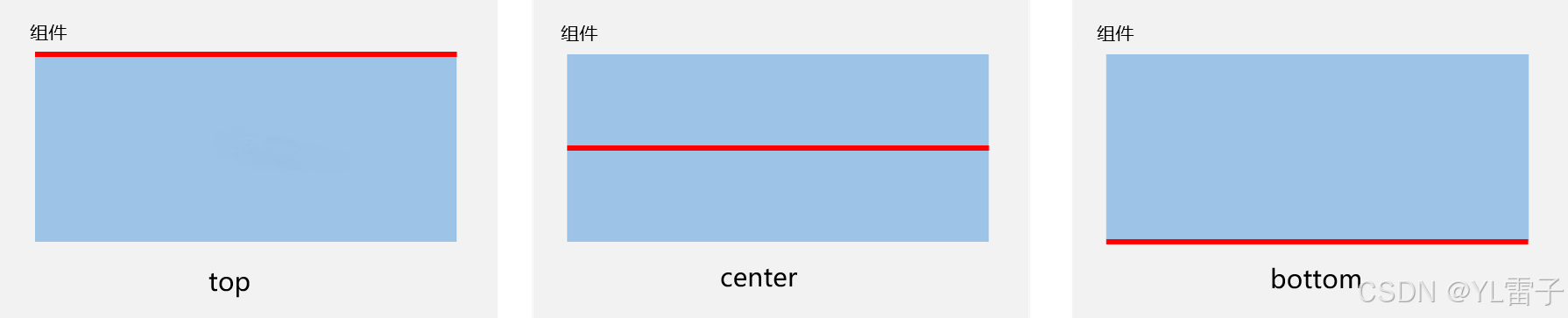
2.设置锚点
锚点设置涉及子元素相对于其父元素或兄弟元素的位置依赖关系。
为了准确定义锚点,RelativeContainer的子元素必须拥有唯一的组件标识(id),用于指定锚点信息。父元素RelativeContainer的标识默认为"container",其他子元素的组件标识(id)则通过id属性设置。
java
let AlignRus: Record<string, Record<string, string | VerticalAlign | HorizontalAlign>> = {
'top': { 'anchor': '__container__', 'align': VerticalAlign.Top },
'left': { 'anchor': '__container__', 'align': HorizontalAlign.Start }
}
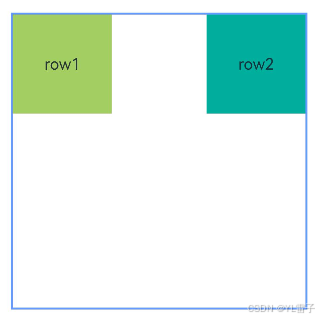
// 图一,RelativeContainer以父组件为锚点
let AlignRue: Record<string, Record<string, string | VerticalAlign | HorizontalAlign>> = {
'top': { 'anchor': '__container__', 'align': VerticalAlign.Top },
'right': { 'anchor': '__container__', 'align': HorizontalAlign.End }
}
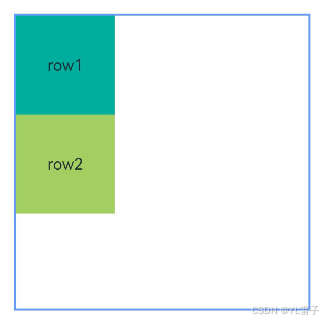
// 图二,以兄弟元素为锚点。
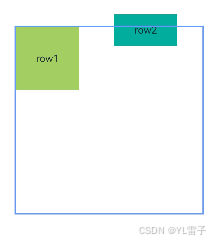
let RelConB: Record<string, Record<string, string | VerticalAlign | HorizontalAlign>> = {
'top': { 'anchor': 'row1', 'align': VerticalAlign.Bottom },
'left': { 'anchor': 'row1', 'align': HorizontalAlign.Start }
}
let Mleft: Record<string, number> = { 'left': 20 }
let BWC: Record<string, number | string> = { 'width': 2, 'color': '#6699FF' }
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
build() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules(AlignRus)
.id("row1")
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules(AlignRue) // 图一
.alignRules(RelConB) // 图二
.id("row2")
}.width(300).height(300)
.margin(Mleft)
.border(BWC)
}
}
3.设置相对于锚点的对齐位置
设置了锚点之后,可以通过alignRules属性的align设置相对于锚点的对齐位置。
在水平方向上,对齐位置可以设置为HorizontalAlign.Start、HorizontalAlign.Center、HorizontalAlign.End。
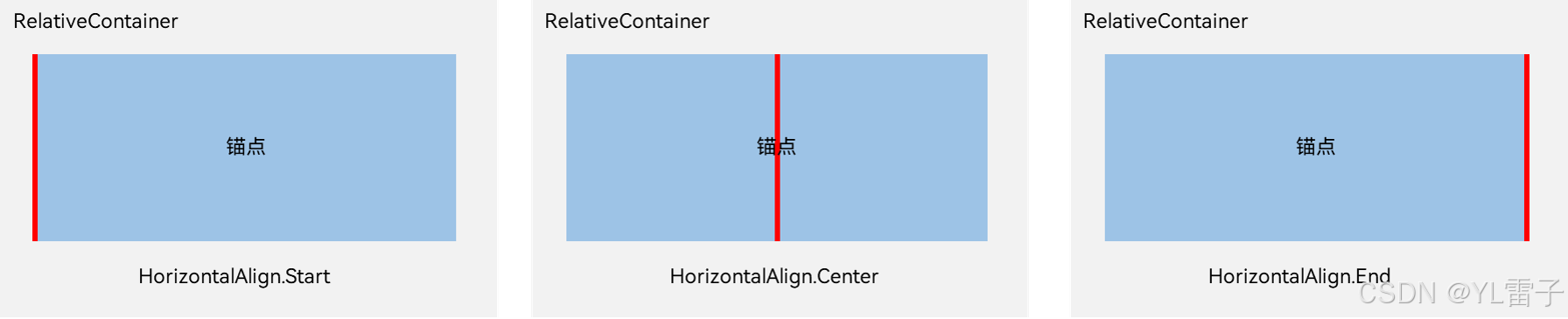
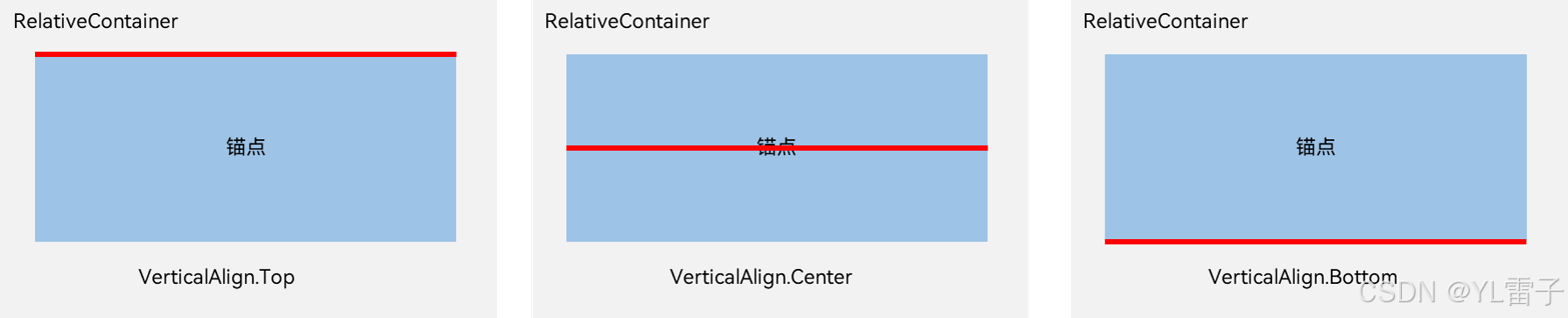
在竖直方向上,对齐位置可以设置为VerticalAlign.Top、VerticalAlign.Center、VerticalAlign.Bottom。
子组件位置偏移
开发者可根据需要设置额外偏移(offset)。当使用offset调整位置的组件作为锚点时,对齐位置为设置offset之前的位置。
java
@Entry
@Component
struct RelativeContainerIndex {
build() {
Row() {
RelativeContainer() {
Row() {
Text('row1')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.height(100)
.backgroundColor('#a3cf62')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
left: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.Start }
})
.id("row1")
Row() {
Text('row2')
}
.justifyContent(FlexAlign.Center)
.width(100)
.backgroundColor('#00ae9d')
.alignRules({
top: { anchor: "__container__", align: VerticalAlign.Top },
right: { anchor: "__container__", align: HorizontalAlign.End },
bottom: { anchor: "row1", align: VerticalAlign.Center },
})
.offset({
x: -40,
y: -20
})
.id("row2")
}
.width(300).height(300)
.margin({ left: 50 })
.border({ width: 2, color: "#6699FF" })
}
.height('100%')
}
}
常见场景与技巧
-
动态调整布局
- 通过修改
alignRules可实时更新组件位置,适合响应式设计。
- 通过修改
-
避免过度嵌套
- 优先使用
RelativeContainer替代多层嵌套的线性布局,提升渲染性能。
- 优先使用
-
调试工具
- 使用 DevEco Studio 的布局检查器(Layout Inspector)可视化查看约束关系。