
(以下内容全部来自上述课程)

附近商铺
1. GEO数据结构
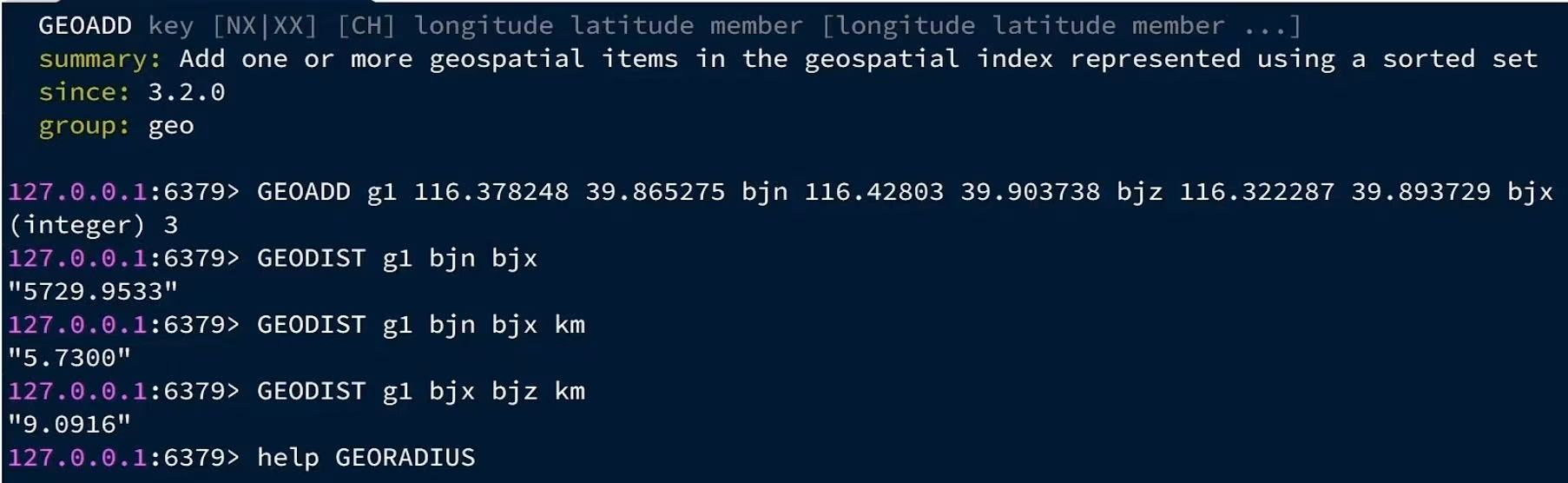
GEO就是Geolocation的简写形式,代表地理坐标。Redis在3.2版本中加入了对GEO的支持,允许存储地理坐标信息,帮助我们根据经纬度来检索数据。常见的命令有:
- GEOADD:添加一个地理空间信息,包含:经度(longitude)、纬度(latitude)、值(member)
- GEODIST:计算指定的两个点之间的距离并返回
- GEOHASH:将指定member的坐标转为hash字符串形式并返回
- GEOPOS:返回指定member的坐标
- GEORADIUS:指定圆心、半径,找到该圆内包含的所有member,并按照与圆心之间的距离排序后返回。6.2以后已废弃
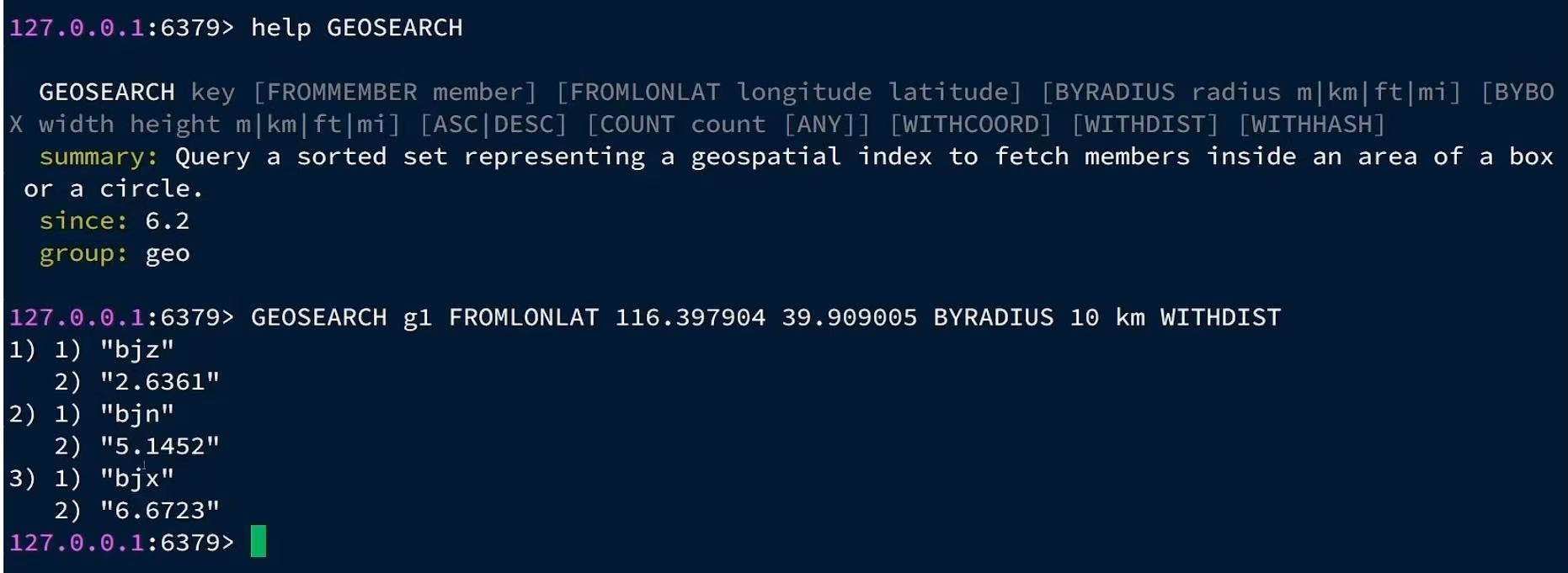
- GEOSEARCH:在指定范围内搜索member,并按照与指定点之间的距离排序后返回。范围可以是圆形或矩形。6.2.新功能
- GEOSEARCHSTORE:与GEOSEARCH功能一致,不过可以把结果存储到一个指定的key。6.2.新功能
需求
1.添加下面几条数据:
- 北京南站(116.378248 39.865275)
- 北京站(116.42803 39.903738)
- 北京西站(116.32228739.893729)
- 计算北京西站到北京站的距离
- 搜索天安门(116.39790439.909005)附近10km内的所有火车站,并按照距离升序排序
2. 导入店铺数据到GEO
在首页中点击某个频道,即可看到频道下的商户:
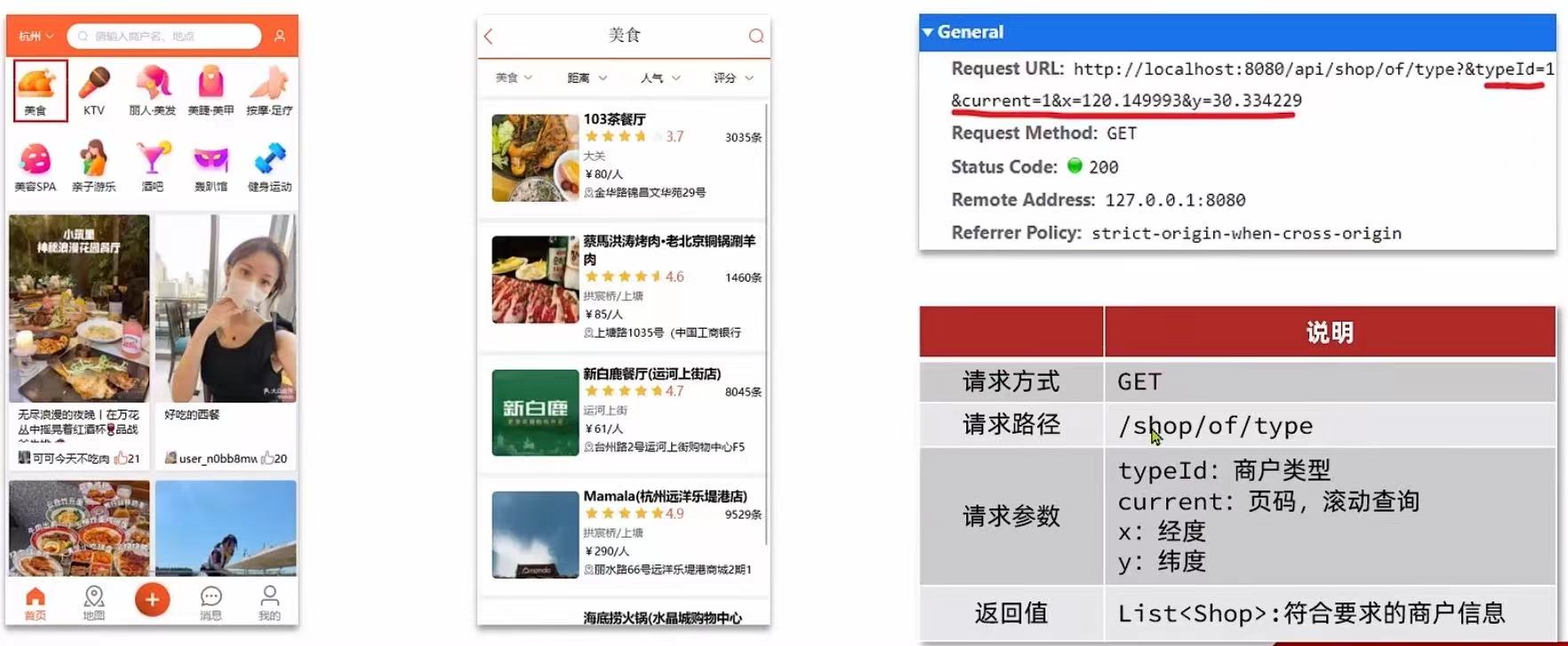
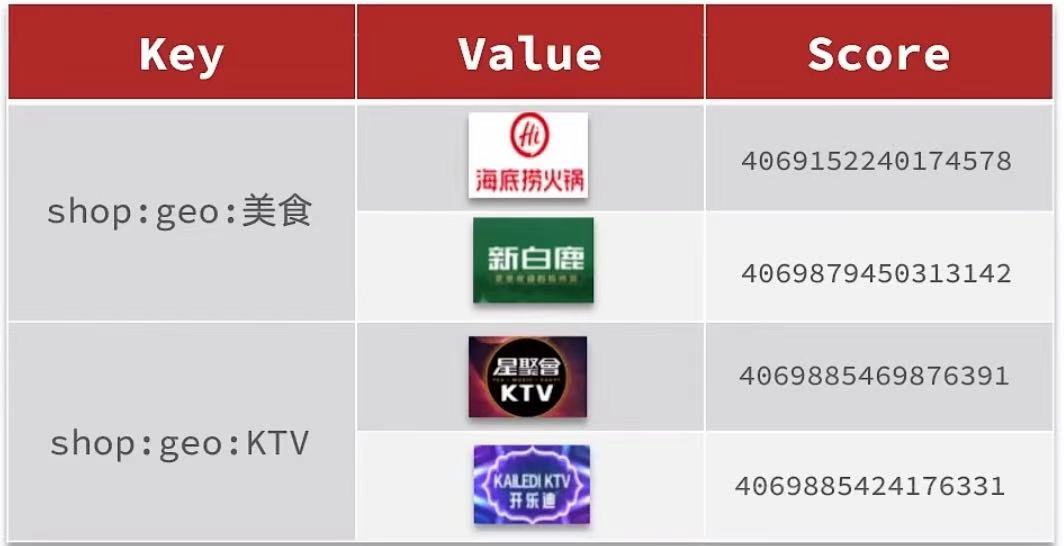
按照商户类型进行分组,类型相同的商户作为一组,以typeId为key存入同一个GEO集合中即可
Test:
java
@Test
void loadshopData() {
// 1.查询店铺信息
List<Shop> list = shopService.list();
//2.把店铺分组,按照typeId分组,typeId一致的放到一个集合
Map<Long, List<Shop>> map = list.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Shop::getTypeId));
//3.分批完成写入Redis
for (Map.Entry<Long, List<Shop>> entry : map.entrySet()) {
//3.1.获取类型id
Long typeId = entry.getKey();
String key = "shop:geo:" + typeId;
//3.2.获取同类型的店铺的集合
List<Shop> value = entry.getValue();
List<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>> locations = new ArrayList<>(value.size());
//3.3.写入redis GE0ADD key 经度纬度 member
for (Shop shop : value) {
// stringRedisTemplate.opsForGeo().add(key, new Point(shop.getX(), shop.getY()), shop.getId().tostring());
locations.add(new RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<>(
shop.getId().toString(), new Point(shop.getX(), shop.getY())
));
}
stringRedisTemplate.opsForGeo().add(key, locations);
}
}3. 实现附近商户功能
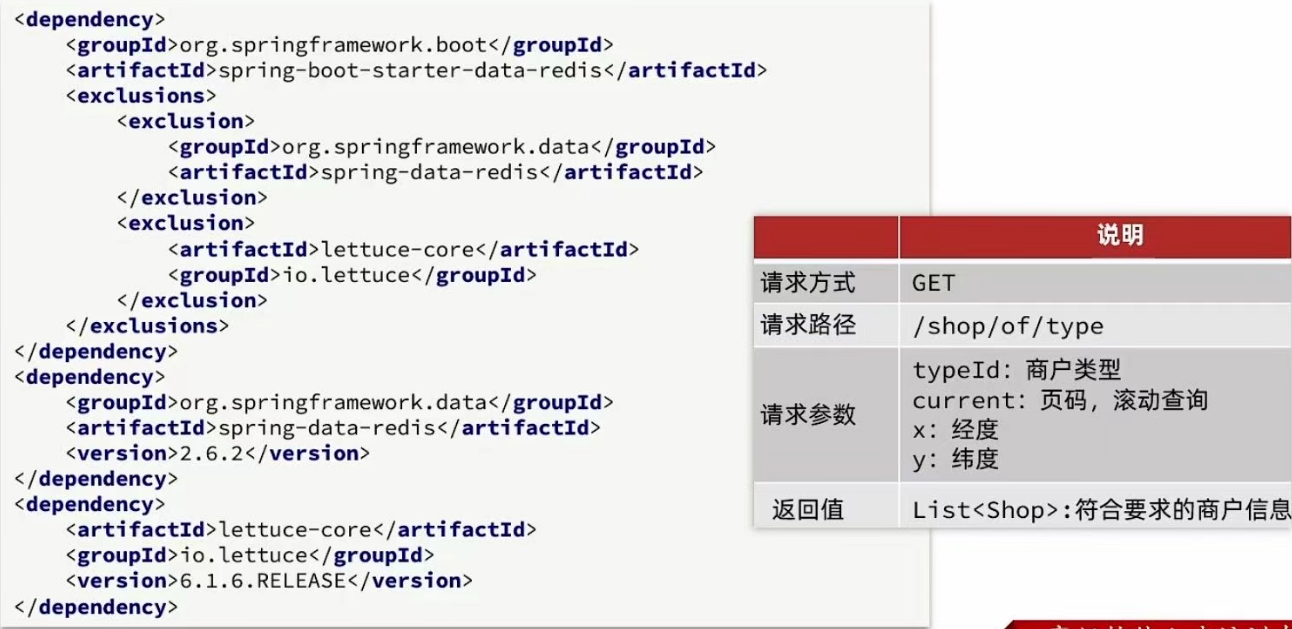
SpringDataRedis的2.3.9版本并不支持Redis 6.2提供的GEOSEARCH命令,因此我们需要提示其版本,修改自己的POM文
件,内容如下:(把上两个删除换成下两个)
ShopController:
java
@GetMapping("/of/type")
public Result queryShopByType(
@RequestParam("typeId") Integer typeId,
@RequestParam(value = "current", defaultValue = "1") Integer current,
@RequestParam(value = "x",required = false) Double x,
@RequestParam(value = "y",required = false) Double y
) {
return shopService.queryShopByType(typeId,current,x,y);
}IShopService:
java
public interface IShopService extends IService<Shop>{
Result queryById(Long id) throws InterruptedException;
Result update(Shop shop);
Result queryShopByType(Integer typeId, Integer current, Double x, Double y
);
}ShopServiceImpl:
java
@Override
public Result queryShopByType(Integer typeId, Integer current, Double x, Double y) {
// 1. 判断是否需要根据坐标查询
if (x == null || y == null){
//不需要坐标查询、按照数据库查询
Page<Shop> page = query()
.eq("type_id", typeId)
.page(new Page<>(current, SystemConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE));
// 返回数据
return Result.ok(page.getRecords());
}
//2. 计算分页参数
int from = (current - 1) * SystemConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
int end = current * SystemConstants.DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
//3. 查询redis、按照距离排序、分页。结果:shopId、distance
String key = SHOP_GEO_KEY + typeId;
GeoResults<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>> results = stringRedisTemplate.opsForGeo()
//GEOSEARCH key BYLONLAT x y BYRADIUS 10 WITHDISTANCE
.search(
key,
GeoReference.fromCoordinate(x,y),
new Distance(5000),
RedisGeoCommands.GeoSearchCommandArgs.newGeoSearchArgs().includeDistance().limit(end)
);
//4. 解析出id
if (results == null){
return Result.ok(Collections.emptyList());
}
List<GeoResult<RedisGeoCommands.GeoLocation<String>>> list = results.getContent();
if (list.size() <= from){
//没有下一页了,结束
return Result.ok(Collections.emptyList());
}
//4.1 截取from~end的部分
List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>(list.size());
Map<String,Distance> distanceMap = new HashMap<>(list.size());
list.stream().skip(from).forEach(result ->{
//4.2 获取店铺id
String shopIdStr = result.getContent().getName();
ids.add(Long.valueOf(shopIdStr));
//4.3 获取距离
Distance distance = result.getDistance();
distanceMap.put(shopIdStr,distance);
});
//5. 根据id查询Shop
String idStr = StrUtil.join(",",ids);
List<Shop> shops = query().in("id",ids).last("ORDER BY FIELD(id,"+idStr+")").list();
for (Shop shop : shops){
shop.setDistance(distanceMap.get(shop.getId().toString().getValue()));
}
//6. 返回
return Result.ok(shops);
}用户签到
1. BitMap功能演示
假如我们用一张表来存储用户签到信息,其结构应该如下:
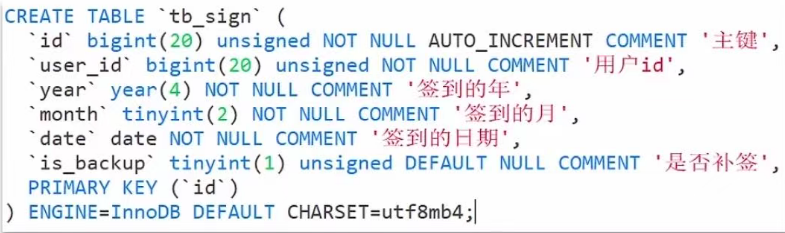
假如有1000万用户,平均每人每年签到次数为10次,则这张表一年的数据量为1亿条
每签到一次需要使用(8+8+1+1+3+1)共22字节的内存,一个月则最多需要600多字节
我们按月来统计用户签到信息,签到记录为1,未签到则记录为0.
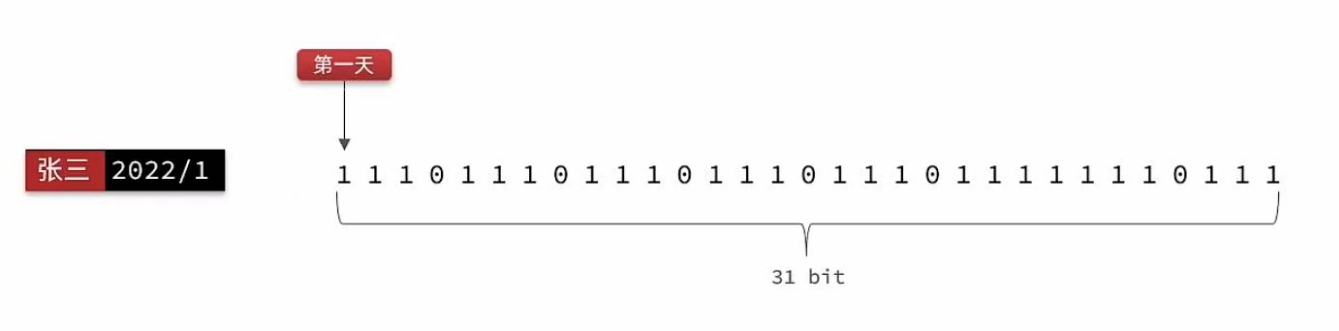
把每一个bit位对应当月的每一天,形成了映射关系。用0和1标示业务状态,这种思路就称为位图(BitMap)
Redis中是利用string类型数据结构实现BitMap,因此最大上限是512M,转换为bit则是2^32个bit位。
BitMap的操作命令有:
- SETBIT:向指定位置(offset)存入一个0或1
- GETBIT:获取指定位置(offset)的bit值
- BITCOUNT:统计BitMap中值为1的bit位的数量
- BITFIELD:操作(查询、修改、自增)BitMap中bit数组中的指定位置(offset)的值
- BITFIELD_RO:获取BitMap中bit数组,并以十进制形式返回
- BITOP:将多个BitMap的结果做位运算(与、或、异或)
- BITPOS:查找bit数组中指定范围内第一个0或1出现的位置
2. 实现签到功能
需求:实现签到接口,将当前用户当天签到信息保存到Redis中
提示:因为BitMap底层是基于String数据结构,因此其操作也都封装在字符串相关操作中了。

UserController:
java
@PutMapping("/sign")
public Result sign(){
return userService.sign();
}IUserService:
java
public interface IUserService extends IService<User> {
Result login(LoginFormDTO loginForm, HttpSession session);
Result sedCode(String phone, HttpSession session);
Result sign();
}UserServiceImpl:
java
@Override
public Result sign() {
//1. 获取当前登录用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
//2. 获取日期
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
//3. 拼接key
String keySuffix = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(":yyyyMM"));
String key = USER_SIGN_KEY + userId + keySuffix;
//4. 获取今天是本月的第几天
int dayOfMonth = now.getDayOfMonth();
//5. 写入redis SETBIT key offset 1
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setBit(key,dayOfMonth-1,true);
return Result.ok();
}3. 统计连续签到
问题1:什么叫做连续签到天数?
从最后一次签到开始向前统计,直到遇到第一次未签到为止,计算总的签到次数,就是连续签到天数。

问题2:如何得到本月到今天为止的所有签到数据?
BITFIELD key GET u[dayOfMonth] 0
问题3:如何从后向前遍历每个bit位?
与1做与运算,就能得到最后一个bit位
随后右移1位,下一个bit位就成为了最后一个bit位。
需求:实现下面接口,统计当前用户截止当前时间在本月的连续签到天数
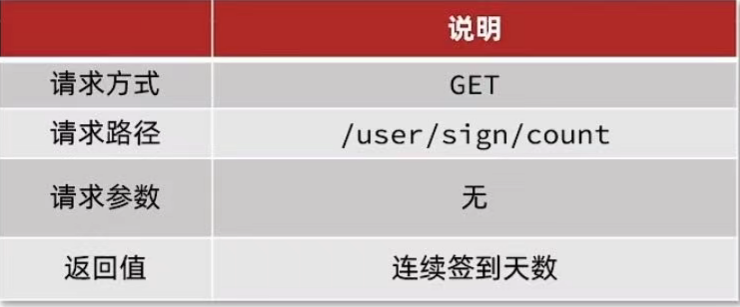
UserController:
java
@GetMapping("/sign/count")
public Result signCount(){
return userService.signCount();
}IUserService:
java
public interface IUserService extends IService<User> {
Result login(LoginFormDTO loginForm, HttpSession session);
Result sedCode(String phone, HttpSession session);
Result sign();
Result signCount();
}UserServiceImpl:
java
@Override
public Result signCount() {
//1. 获取当前登录用户
Long userId = UserHolder.getUser().getId();
//2. 获取日期
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
//3. 拼接key
String keySuffix = now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(":yyyyMM"));
String key = USER_SIGN_KEY + userId + keySuffix;
//4. 获取今天是本月的第几天
int dayOfMonth = now.getDayOfMonth();
//5. 获取本月截止今天为止的所有的签到记录,返回的是一个十进制的数字
List<Long> result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().bitField(
key,
BitFieldSubCommands.create()
.get(BitFieldSubCommands.BitFieldType.unsigned(dayOfMonth)).valueAt(0)
);
if (result == null || result.isEmpty()){
//没有任何签到结果
return Result.ok(0);
}
Long num = result.get(0);
if (num == null || num == 0){
return Result.ok(0);
}
//6. 循环遍历
int count = 0;
while (true) {
//6.1 让这个数字与1做运算,得到数字的最后一个bit位 //判断这个bit位是否为0
if ((num & 1) == 0){
//6.2 如果为0,说明未签到,结束
break;
}else {
//6.3 如果不为0,说明已签到,计数器+1
count++;
}
//6.4 把数字右移一位,抛弃最后一个bit位,继续下一个bit位
num >>>= 1;
}
return Result.ok(count);
}UV统计
首先我们搞懂两个概念:
UV:全称Unique visitor,也叫独立访客量,是指通过互联网访问、浏览这个网页的自然人。1天内同一个用户多次访问该网站,只记录1次。
PV:全称Page View,也叫页面访问量或点击量,用户每访问网站的一个页面,记录1次PV,用户多次打开页面,则记录多次PV。往往用来衡量网站的流量。
UV统计在服务端做会比较麻烦,因为要判断该用户是否已经统计过了,需要将统计过的用户信息保存。但是如果每个访问的用户都保存到Redis中,数据量会非常恐怖。
1. HyperLogLog的用法
Hyperloglog(H|L)是从Loglog算法派生的概率算法,用于确定非常大的集合的基数,而不需要存储其所有值。相关算法原理大家可以参考:https://juejin,cn/post/6844903785744056333#heading-0
Redis中的HLL是基于string结构实现的,单个HLL的内存永远小于16kb,内存占用低的令人发指!作为代价,其测量结果是概率性的,有小于0.81%的误差。不过对于UV统计来说,这完全可以忽略。
2. 测试百万数据的统计
我们直接利用单元测试,向HyperLogLog中添加100万条数据,看看内存占用和统计效果如何:
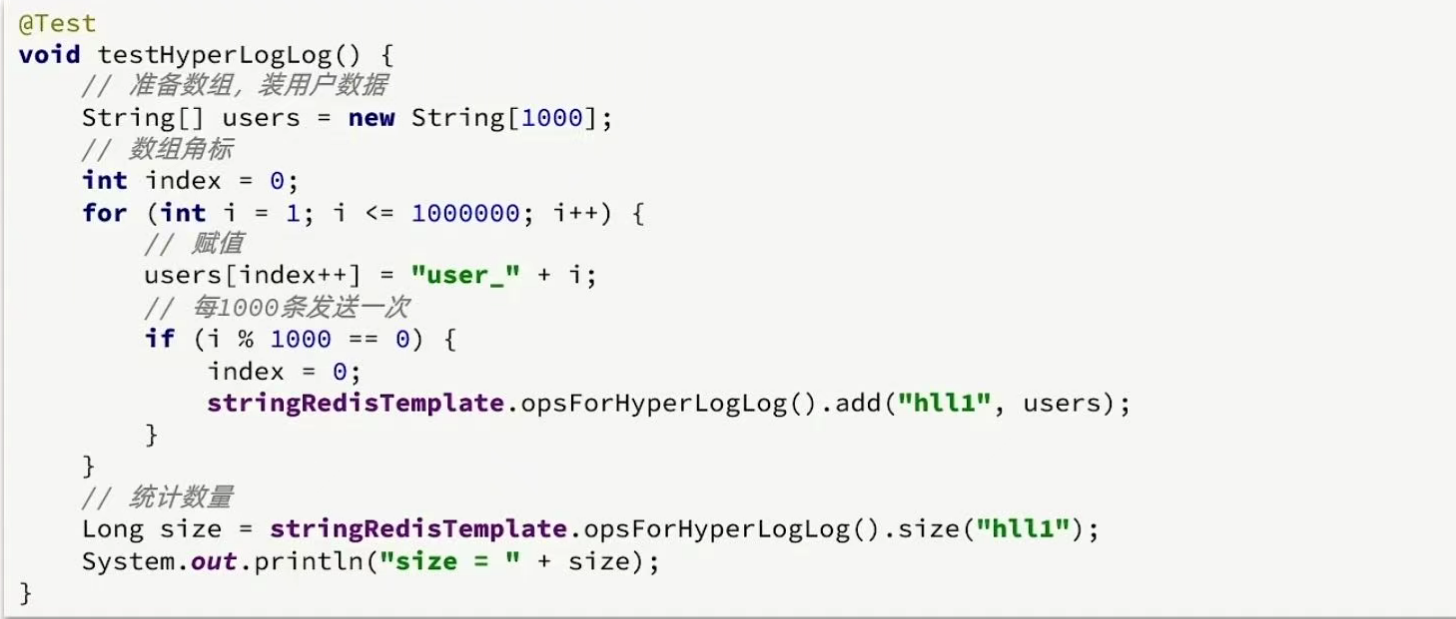
Test:
java
@Test
void testHyperLogLog(){
String[] values = new String[1000];
int j = 0 ;
for(int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++){
j = i % 1000;
values[j] = "user_"+ i;
if (j == 999){
//发送到redis
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().add("hl2",values);
}
}
//统计数量
Long count = stringRedisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog().size("hl2");
System.out.println("count = " + count);
}