六、关联关系查询
1. 关联关系查询
当查询内容涉及到具有关联关系的多个表的时候,就需要使用关联查询,根据表之间的关联关系不同,关联查询分为四种:
(1) 一对一关联查询:例如电影院的座位和观众,一人一座,是多对一的关联查询的特例。
(2) 一对多关联查询:例如一个国家包含多个城市。
(3) 多对一关联查询:例如多个城市对应一个国家。
(4) 多对多关联查询:例如学生和课程,一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程又可以由多个学生来选修。
注意:关联关系反应到数据库表中,就是存在主外键关系,这个外键放在多方表中,对于多对多,会创建一个中间表,来记录两张表的外键信息。
(1) 一对多关联查询
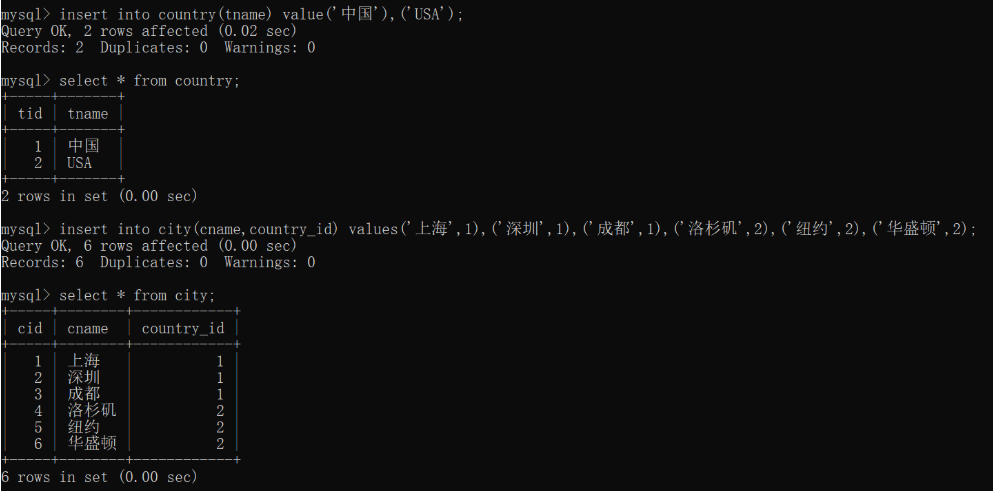
我们以国家和城市(1:n)为例:
1) 创建数据库表,先创建主键表:country,一方
2) 创建外键表:city,多方
录入数据:
3) 准备实体类
a. Country.java
package com.edu.beans;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//国家,一方
public class Country {
private int tid;
private String tname;
/**
* 由于一个国家对应多个城市,反应到 JavaBean 中就存在一个集合类型的属性,这样我们在封装 Country 对象的时候,同时也封装了 Country
* 对应多个 City,我们称这个集合属性为关联属性
*/
private List<City> cities;//关联属性
public Country() {
cities = new ArrayList<>();//在构造函数中初始化关联属性
}
public Country(String tname) {
this();//调用上面的默认构造函数完成关联属性初始化
this.tname = tname;
}
public Country(int tid, String tname) {
this();//调用上面的默认构造函数完成关联属性初始化
this.tid = tid;
this.tname = tname;
}
public int getTid() {
return tid;
}
public void setTid(int tid) {
this.tid = tid;
}
public String getTname() {
return tname;
}
public void setTname(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
public List<City> getCities() {
return cities;
}
public void setCities(List<City> cities) {
this.cities = cities;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Country{" +
"tid=" + tid +
", tname='" + tname + '\'' +
", cities=" + cities +
'}';
}
}
b. City.jav
package com.edu.beans;
//城市,多方
public class City {
private int cid;
private String cname;
public City() {
}
public City(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public City(int cid, String cname) {
this.cid = cid;
this.cname = cname;
}
public int getCid() {
return cid;
}
public void setCid(int cid) {
this.cid = cid;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "City{" +
"cid=" + cid +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
4) 多表连接查询方式
a. 定义 Dao 层接口:ICountryDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Country;
public interface ICountryDao {
Country selectCountryById(int tid);
}
b. 映射文件:ICountryDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.ICountryDao">
<!--<resultMap> 除了可以完成表字段到 bean 属性的映射之外,还可以完成关联关系映射-->
<resultMap id="countryMapper" type="Country">
<!--对一方 Country 进行表字段到 bean 属性的映射-->
<id column="tid" property="tid"/>
<result column="tname" property="tname"/>
<!--对 Country 中包含的关联属性进行映射-->
<!--
<collection>:关联关系映射,由于一个 Country 对应多个 City,所以这里用了一个 <collection> 标签来表示关联属性,属性有:
property="cities":关联属性的名字
ofType="City":关联属性中的每个元素的类型
-->
<collection property="cities" ofType="City">
<!--完成关联属性的表字段到 bean 属性的映射-->
<id column="cid" property="cid"/>
<result column="cname" property="cname"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectCountryById" resultMap="countryMapper">
select t.tid,t.tname,c.cid,c.cname from country t,city c where t.tid=c.country_id
and t.tid = #{xxx}
</select>
</mapper>
c. 测试类 RelationTest.java
package com.edu.test;
import com.edu.beans.Country;
import com.edu.dao.ICountryDao;
import com.edu.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
//JUnit 的测试类
public class RelationTest {
private SqlSession session;
private ICountryDao countryDao;
@Before //被 @Before 注解的方法为初始化方法,它会在每次 @Test 修饰的方法执行之前执行一次,完成初始化工作
public void setUp(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象(Mapper 的动态代理)
countryDao = session.getMapper(ICountryDao.class);
}
@After //被 @After 注解的方法为销毁方法,它会在 @Test 修饰的方法执行之后执行一次,完成资源的销毁工作
public void tearDown(){
if(session != null){
session.close();
}
}
@Test
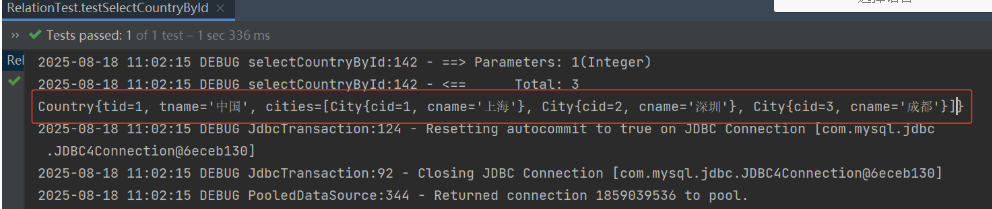
public void testSelectCountryById(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
}
5) 多表单独查询方式
多表的连接查询方式是将多张表进行连接,连接为一张表后进行查询,其本质是一张表,而多表单独查询方式是多张表各自查询各自的内容,而需要多张表联合数据了,则将主表的查询结果联合其他表的查询结果,封装为一个对象。
这种多表查询方式可以跨越多个映射文件的,即可以跨越多个 namespace ,使用时加上其 namespace 的前缀即可。
a. 修改 ICountryDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Country;
public interface ICountryDao {
Country selectCountryById(int tid);
Country selectCountryById2(int tid);
}
b. 修改 ICountryDao.xml
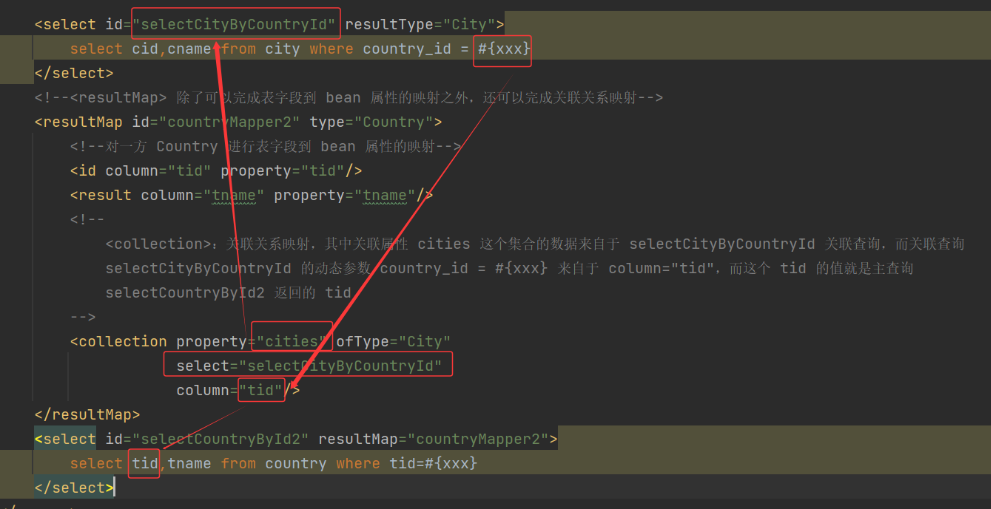
c. 测试类 RelationTest.java
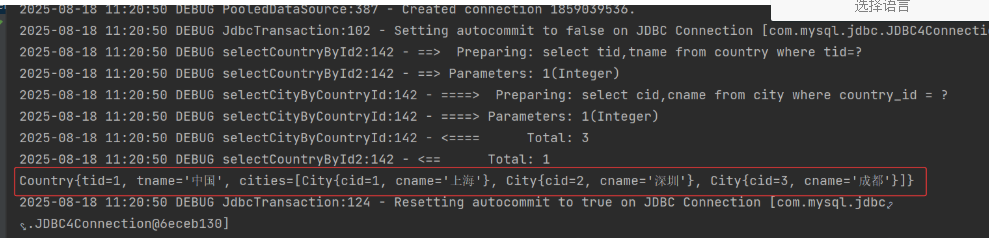
@Test
public void testSelectCountryById2(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById2(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
(2) 多对一(n:1)关联查询
这里的多对一关联查询是指,在查询多方对象的时候,同时将其关联的一方对象也查询出来。
由于在查询多方对象的时候也是一个一个的查询,所以一对一关联查询,其实就是多对一关联查询的特例,即一对一关联查询也当成多对一关联查询处理。
以多个城市对应一个国家为例,开发步骤:
1) 准备数据库表 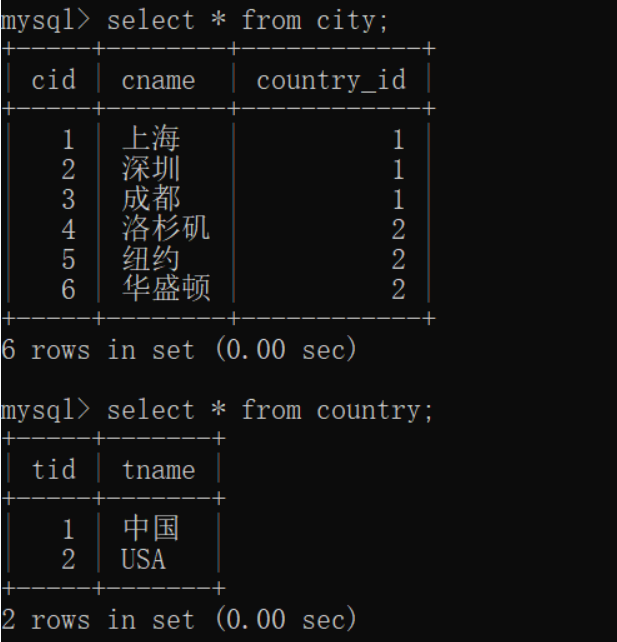
2) 实体类
多方 City:
package com.edu.beans;
//城市,多方
public class City {
private int cid;
private String cname;
//由于多个城市对应一个国家,即一个城市看到的国家是一个,所以这里就用了一个 Country 的对象来作为关联属性
private Country country;//关联属性
public City() {
}
public City(String cname, Country country) {
this.cname = cname;
this.country = country;
}
public City(int cid, String cname, Country country) {
this.cid = cid;
this.cname = cname;
this.country = country;
}
public int getCid() {
return cid;
}
public void setCid(int cid) {
this.cid = cid;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public Country getCountry() {
return country;
}
public void setCountry(Country country) {
this.country = country;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "City{" +
"cid=" + cid +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
", country=" + country +
'}';
}
}
一方 Country:
package com.edu.beans;
//国家,一方
public class Country {
private int tid;
private String tname;
public Country() {
}
public Country(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
public Country(int tid, String tname) {
this.tid = tid;
this.tname = tname;
}
public int getTid() {
return tid;
}
public void setTid(int tid) {
this.tid = tid;
}
public String getTname() {
return tname;
}
public void setTname(String tname) {
this.tname = tname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Country{" +
"tid=" + tid +
", tname='" + tname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
3) 定义 Dao 接口:ICityDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.City;
public interface ICityDao {
City selectCityById(int cid);
}
4) 映射文件 ICityDao.xml
a. 多表连接查询方式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.ICityDao">
<!--<resultMap> 除了可以完成表字段到 bean 属性的映射之外,还可以完成关联关系映射-->
<resultMap id="cityMapper" type="City">
<!--对多方 City 进行表字段到 bean 属性的映射-->
<id column="cid" property="cid"/>
<result column="cname" property="cname"/>
<!--对 City 中包含的关联属性进行映射-->
<!--
<association>:关联关系映射,由于一个 City 看到的国家是一个,所以这里用 <association> 来指明关联关系映射,属性:
property="country":关联属性的名称
javaType="Country":关联属性的类型
-->
<association property="country" javaType="Country">
<!--对一方 Country 完成表字段到 bean 属性的映射-->
<id column="tid" property="tid"/>
<result column="tname" property="tname"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectCityById" resultMap="cityMapper">
select c.cid,c.cname,t.tid,t.tname from city c,country t where c.country_id = t.tid
and c.cid = #{xxx}
</select>
</mapper>
b. 测试类:
package com.edu.test;
import com.edu.beans.City;
import com.edu.beans.Country;
import com.edu.dao.ICityDao;
import com.edu.dao.ICountryDao;
import com.edu.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
//JUnit 的测试类
public class RelationTest {
private SqlSession session;
private ICountryDao countryDao;
private ICityDao cityDao;
@Before //被 @Before 注解的方法为初始化方法,它会在每次 @Test 修饰的方法执行之前执行一次,完成初始化工作
public void setUp(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象(Mapper 的动态代理)
countryDao = session.getMapper(ICountryDao.class);
cityDao = session.getMapper(ICityDao.class);
}
@After //被 @After 注解的方法为销毁方法,它会在 @Test 修饰的方法执行之后执行一次,完成资源的销毁工作
public void tearDown(){
if(session != null){
session.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectCountryById(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCountryById2(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById2(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCityById(){
City city = cityDao.selectCityById(3);
System.out.println(city);
}
}
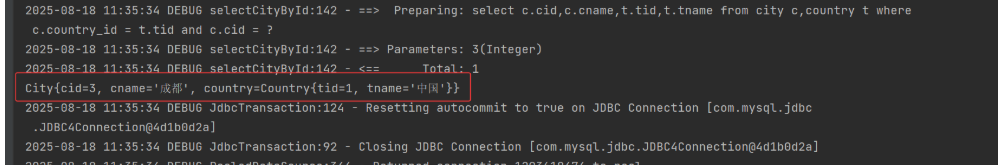
c. 多表单独查询方式
a) 修改 ICityDao.java:
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.City;
public interface ICityDao {
City selectCityById(int cid);
City selectCityById2(int cid);
}
b) 修改 ICityDao.xml
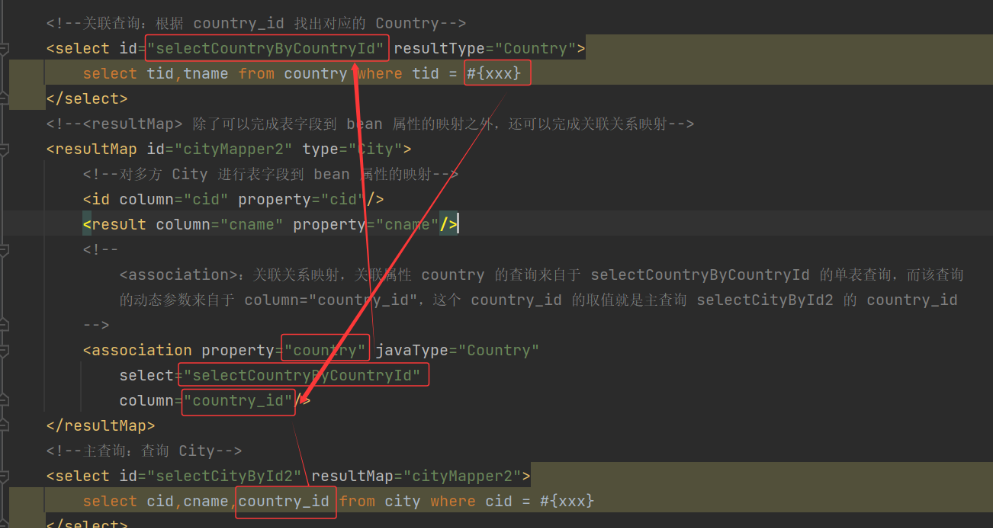
c) 测试类
@Test
public void testSelectCityById2(){
City city = cityDao.selectCityById2(3);
System.out.println(city);
}
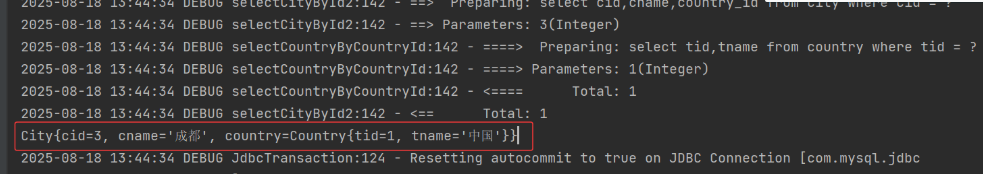
(3) 自关联查询
所以自关联,是指自己既可以充当一方,又可以充当多方,是 1:n 或 n:1 的变形,比如新闻栏目 NewsColumn,可以充当一方,即父栏目,又可以充当多方,即子栏目,反应到数据库表中,只有一张表,这张表有一个外键,用于表示该栏目的父栏目,一级栏目没有父栏目,它的外键值就是 null,其他子栏目就有外键值。
我们的自关联分为两种情况:一种是当做 1:n 关系处理,另一种是当成 n:1 关系处理
开发步骤:
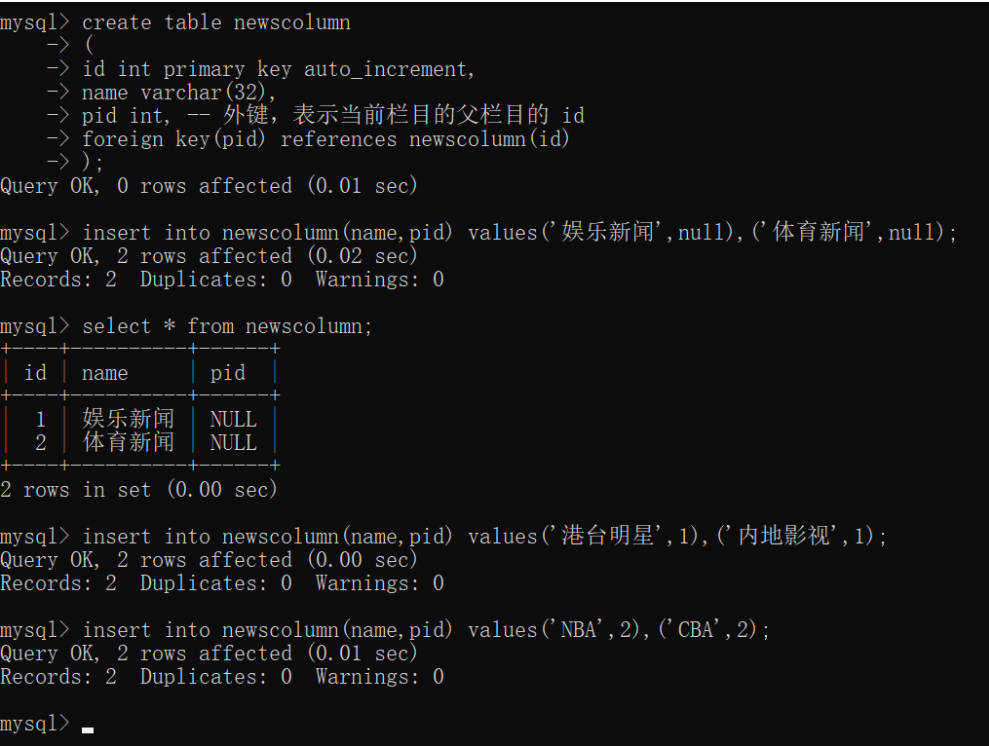
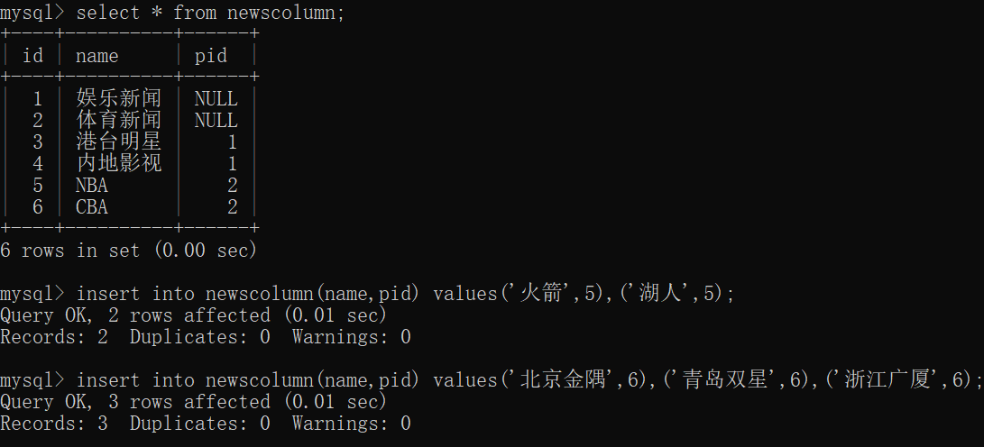
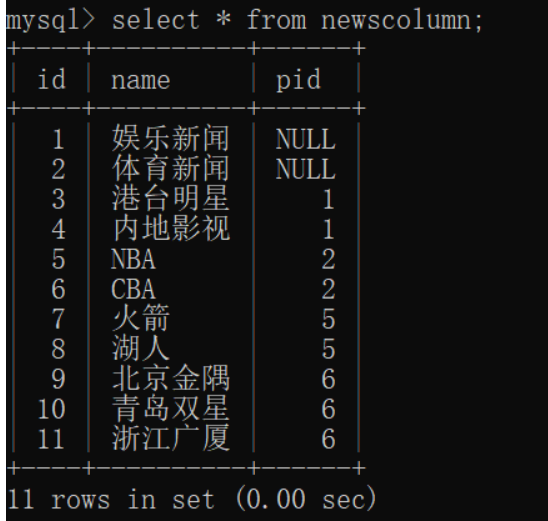
- 定义数据库表,并插入记录
2) 以一对多 (1:n) 的方式处理
这种方式是指一方可以看到多方,应用场景也比较多,例如在页面上点击父栏目显示出子栏目,又比如电商网站选择商品一级分类,显示出二级分类,选择二级分类又显示出三级分类,例如:
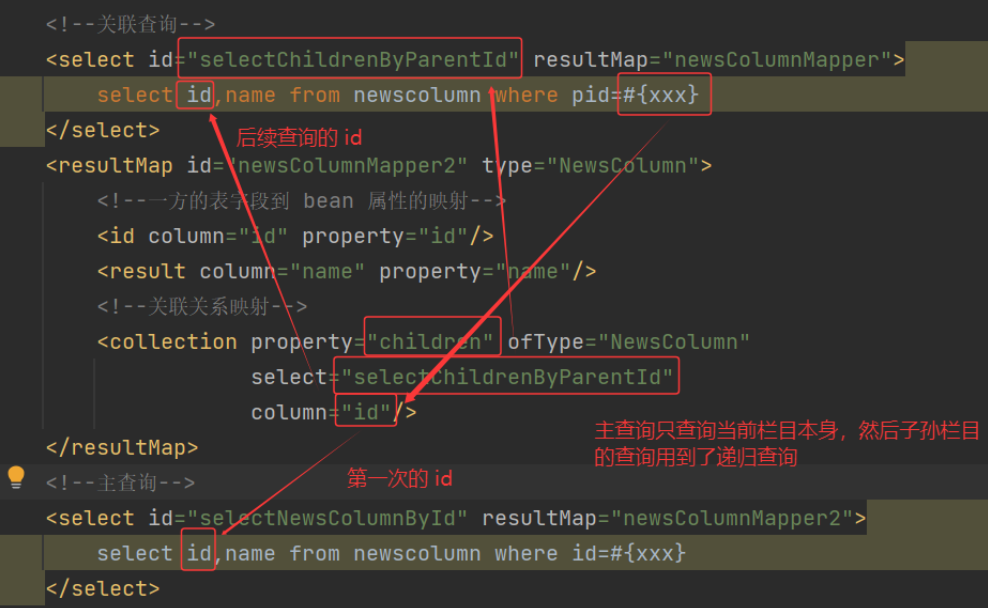
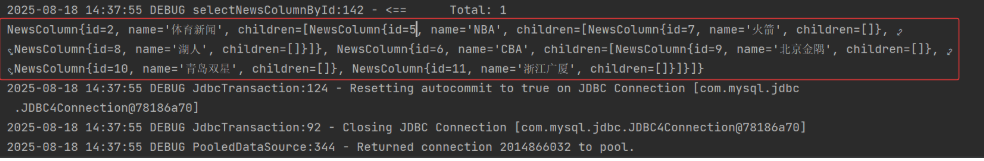
根据查询需求不同,又分为两种:查询出指定栏目的所有子孙栏目,还有一种查询出指定栏目及其子孙栏目
a. 查询出指定栏目的所有子孙栏目
a) 定义实体类
package com.edu.beans;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//以一对多方式处理
public class NewsColumn {
private int id;
private String name;
//由于是 1:n,所以一个父栏目看到的子栏目有多个,对应的关联属性就是集合
private List<NewsColumn> children;//关联属性,表示所有的子孙栏目
public NewsColumn() {
children = new ArrayList<>();//初始化关联属性
}
public NewsColumn(String name) {
this();//调用上面无参构造器,完成关联属性初始化
this.name = name;
}
public NewsColumn(int id, String name) {
this();//调用上面无参构造器,完成关联属性初始化
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<NewsColumn> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List<NewsColumn> children) {
this.children = children;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NewsColumn{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", children=" + children +
'}';
}
}
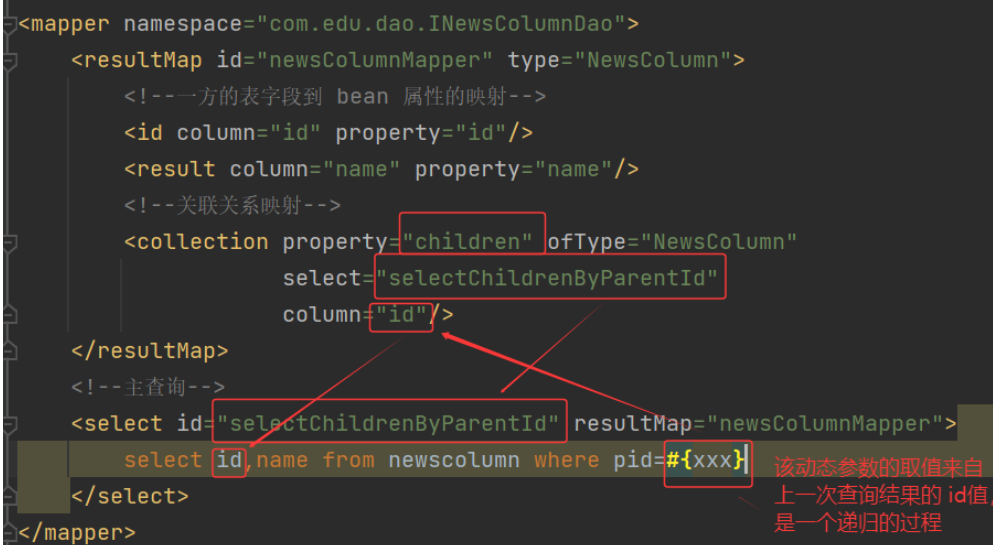
b) 定义 Dao 层接口:INewsColumnDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.NewsColumn;
import java.util.List;
public interface INewsColumnDao {
List<NewsColumn> selectChildrenByParentId(int pid);//根据父栏目的 id 找出所有的子孙栏目,不包含父栏目本身
}
c) 映射文件 INewsColumnDao.xml:
d) 测试类
package com.edu.test;
import com.edu.beans.City;
import com.edu.beans.Country;
import com.edu.beans.NewsColumn;
import com.edu.dao.ICityDao;
import com.edu.dao.ICountryDao;
import com.edu.dao.INewsColumnDao;
import com.edu.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.List;
//JUnit 的测试类
public class RelationTest {
private SqlSession session;
private ICountryDao countryDao;
private ICityDao cityDao;
private INewsColumnDao newsColumnDao;
@Before //被 @Before 注解的方法为初始化方法,它会在每次 @Test 修饰的方法执行之前执行一次,完成初始化工作
public void setUp(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象(Mapper 的动态代理)
countryDao = session.getMapper(ICountryDao.class);
cityDao = session.getMapper(ICityDao.class);
newsColumnDao = session.getMapper(INewsColumnDao.class);
}
@After //被 @After 注解的方法为销毁方法,它会在 @Test 修饰的方法执行之后执行一次,完成资源的销毁工作
public void tearDown(){
if(session != null){
session.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectCountryById(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCountryById2(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById2(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCityById(){
City city = cityDao.selectCityById(3);
System.out.println(city);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCityById2(){
City city = cityDao.selectCityById2(3);
System.out.println(city);
}
@Test
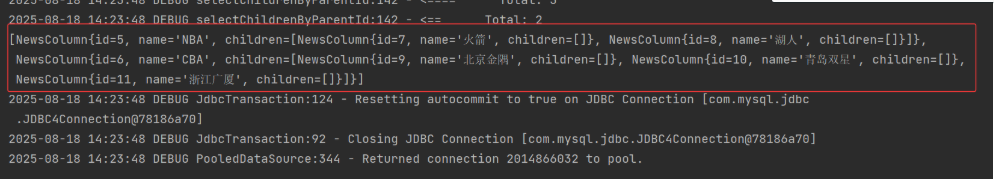
public void testSelectChildrenByParentId(){
List<NewsColumn> newsColumns = newsColumnDao.selectChildrenByParentId(2);
System.out.println(newsColumns);
}
}
b. 查询指定栏目以及子孙栏目
a) 修改 INewsColumnDao.java
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.NewsColumn;
import java.util.List;
public interface INewsColumnDao {
List<NewsColumn> selectChildrenByParentId(int pid);//根据父栏目的 id 找出所有的子孙栏目,不包含父栏目本身
NewsColumn selectNewsColumnById(int id);//根据 id 找出当前栏目以及子孙栏目
}
b) 修改 INewsColumnDao.xml:
c) 测试类
@Test
public void testSelectNewsColumnById(){
NewsColumn newsColumn = newsColumnDao.selectNewsColumnById(2);
System.out.println(newsColumn);
}
- 以多对一(n:1)的方式处理
以多对一方式处理,即多方可以看到一方,该处理方式的应用场景,比如在页面上显示当前页面的位置:
a. 修改实体类
package com.edu.beans;
//以多对弈方式处理
public class NewsColumn {
private int id;
private String name;
//由于是 n:1,所以一个子栏目看到的父栏目有以个,对应的关联属性就是一个对象
private NewsColumn parent;//关联属性,多个子栏目可以看到一个父栏目
public NewsColumn() {
}
public NewsColumn(String name, NewsColumn parent) {
this.name = name;
this.parent = parent;
}
public NewsColumn(int id, String name, NewsColumn parent) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.parent = parent;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public NewsColumn getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(NewsColumn parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NewsColumn{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", parent=" + parent +
'}';
}
}
b. 创建 Dao 层接口:
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.NewsColumn;
import java.util.List;
public interface INewsColumnDao {
List<NewsColumn> selectChildrenByParentId(int pid);//根据父栏目的 id 找出所有的子孙栏目,不包含父栏目本身
NewsColumn selectNewsColumnById(int id);//根据 id 找出当前栏目以及子孙栏目
NewsColumn selectParentById(int id);//根据 id 找出当前栏目的所有父栏目
}
c. 修改映射文件 INewsColumnDao.xml:
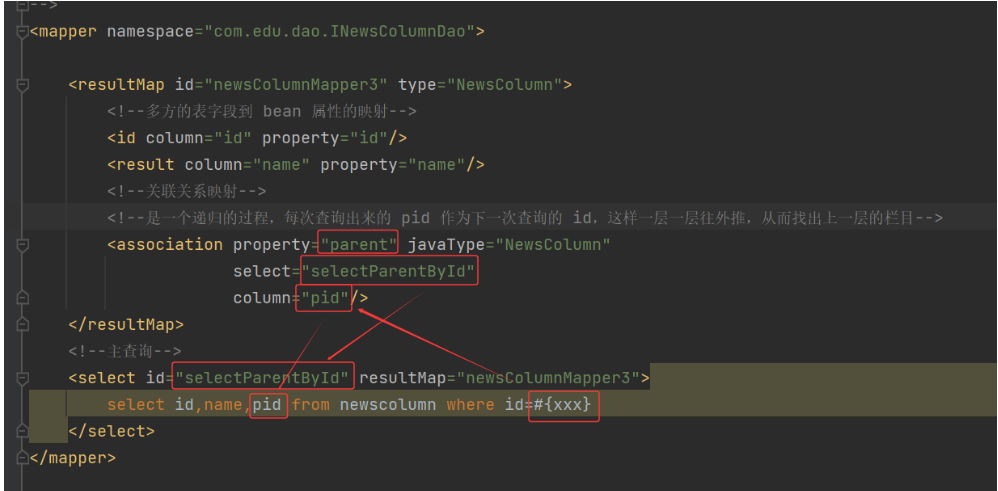
d. 测试类
@Test
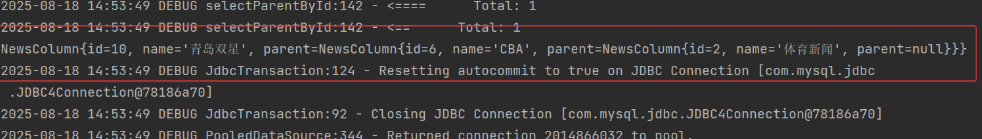
public void testSelectParentById(){
NewsColumn newsColumn = newsColumnDao.selectParentById(10);
System.out.println(newsColumn);
}
(4) 多对多关联关系
例如学生和课程,一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程又可以由多个学生来选修,学生和课程就存在多对多关系,多对多关系,反应到数据库中,就会存在一个中间表,用于记录两个多方的外键信息,开发步骤:
- 定义数据库表
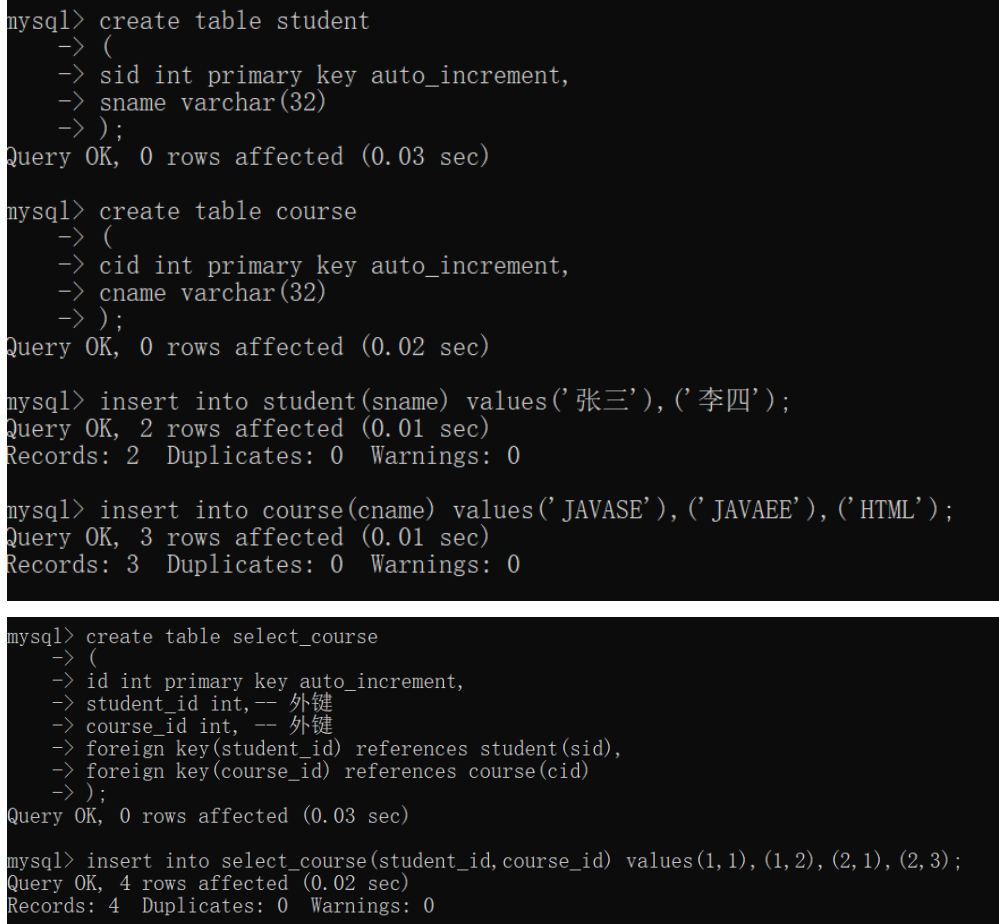
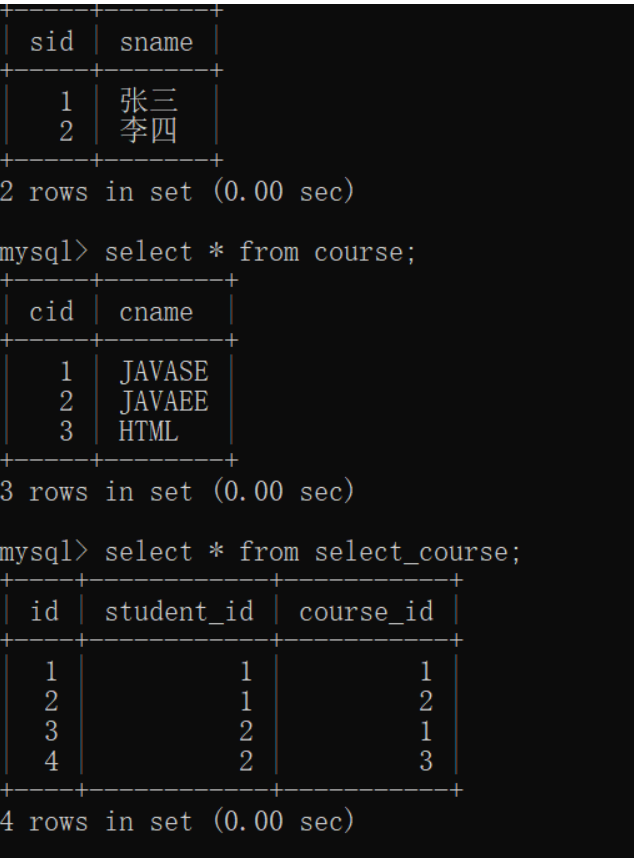
2) 定义实体类
Student.java:多方
package com.edu.beans;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Student {
private Long sid;
private String sname;
private List<Course> courses;//关联属性,一个学生可以看到多个课程,所以关联属性是一个集合
public Student() {
courses = new ArrayList<>();
}
public Student(String sname) {
this();
this.sname = sname;
}
public Student(Long sid, String sname) {
this();
this.sid = sid;
this.sname = sname;
}
public Long getSid() {
return sid;
}
public void setSid(Long sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public List<Course> getCourses() {
return courses;
}
public void setCourses(List<Course> courses) {
this.courses = courses;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sid=" + sid +
", sname='" + sname + '\'' +
", courses=" + courses +
'}';
}
}
Course.java:多方
package com.edu.beans;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Course {
private Long cid;
private String cname;
private List<Student> students;//关联属性,一个课程看到的学生也是多个,所以关联属性也是一个集合
public Course() {
students = new ArrayList<>();
}
public Course(String cname) {
this();
this.cname = cname;
}
public Course(Long cid, String cname) {
this();
this.cid = cid;
this.cname = cname;
}
public Long getCid() {
return cid;
}
public void setCid(Long cid) {
this.cid = cid;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public List<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
public void setStudents(List<Student> students) {
this.students = students;
}
//注意,这里的 toString(0 不能再将 students 输出,因为 Student 中已经将 courses 集合输出了,如果这里再输出,就会形成递归调用,最后栈溢出
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Course{" +
"cid=" + cid +
", cname='" + cname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
3) 定义 Dao 层接口
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
public interface IStudentDao {
Student selectStudentById(long id);//根据学生 id 找出学生信息以及关联的课程信息
}
4) 映射文件 IStudentDao.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IStudentDao">
<resultMap id="studentMapper" type="Student">
<!--多方 Student 的表字段到 bean 属性的映射-->
<id column="sid" property="sid"/>
<result column="sname" property="sname"/>
<!--关联关系映射-->
<collection property="courses" ofType="Course">
<!--多方 Course 的表字段到 bean 属性的映射-->
<id column="cid" property="cid"/>
<result column="cname" property="cname"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectStudentById" resultMap="studentMapper">
<!--三表的连接查询-->
select s.sid,s.sname,c.cid,c.cname from student s,course c,select_course sc where
sc.student_id = s.sid and sc.course_id = c.cid and s.sid=#{xxx}
</select>
</mapper>
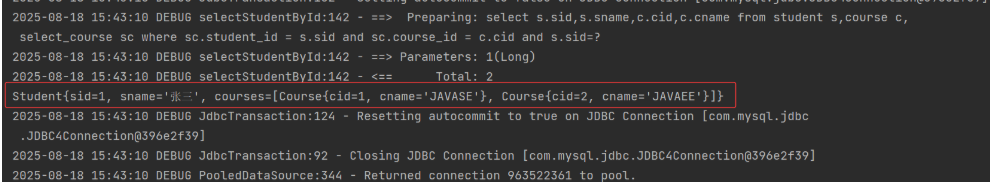
5) 测试类
package com.edu.test;
import com.edu.beans.City;
import com.edu.beans.Country;
import com.edu.beans.NewsColumn;
import com.edu.beans.Student;
import com.edu.dao.ICityDao;
import com.edu.dao.ICountryDao;
import com.edu.dao.INewsColumnDao;
import com.edu.dao.IStudentDao;
import com.edu.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.List;
//JUnit 的测试类
public class RelationTest {
private SqlSession session;
private ICountryDao countryDao;
private ICityDao cityDao;
private INewsColumnDao newsColumnDao;
private IStudentDao studentDao;
@Before //被 @Before 注解的方法为初始化方法,它会在每次 @Test 修饰的方法执行之前执行一次,完成初始化工作
public void setUp(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象(Mapper 的动态代理)
countryDao = session.getMapper(ICountryDao.class);
cityDao = session.getMapper(ICityDao.class);
newsColumnDao = session.getMapper(INewsColumnDao.class);
studentDao = session.getMapper(IStudentDao.class);
}
@After //被 @After 注解的方法为销毁方法,它会在 @Test 修饰的方法执行之后执行一次,完成资源的销毁工作
public void tearDown(){
if(session != null){
session.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectCountryById(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCountryById2(){
Country country = countryDao.selectCountryById2(1);
System.out.println(country);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCityById(){
City city = cityDao.selectCityById(3);
System.out.println(city);
}
@Test
public void testSelectCityById2(){
City city = cityDao.selectCityById2(3);
System.out.println(city);
}
@Test
public void testSelectChildrenByParentId(){
List<NewsColumn> newsColumns = newsColumnDao.selectChildrenByParentId(2);
System.out.println(newsColumns);
}
@Test
public void testSelectNewsColumnById(){
NewsColumn newsColumn = newsColumnDao.selectNewsColumnById(2);
System.out.println(newsColumn);
}
@Test
public void testSelectParentById(){
NewsColumn newsColumn = newsColumnDao.selectParentById(10);
System.out.println(newsColumn);
}
@Test
public void testSelectStudentById(){
Student student = studentDao.selectStudentById(1L);
System.out.println(student);
}
}
七、延迟加载
Mybatis 的延迟加载,也称为懒加载,指进行关联查询时,按照延迟规则推迟对关联对象的select查询,延迟加载可以有效的减少数据库压力,提高性能。
注意,延迟加载只是对关联对象延迟加载,对于主加载对象都是直接 select 的。
1. 关联对象加载的时机
Mybatis 根据关联对象 的 select 语句执行的时机,分为三种:直接加载,侵入式延迟加载,深度延迟加载
(1) 直接加载
执行完主加载对象的 select 语句后,马上执行对关联对象的 select 查询。
(2) 侵入式延迟加载
执行完主加载对象的 select 语句后,不会执行关联对象的 select 查询,但是要访问主加载对象的详情的时候,就会马上执行关联对象的 select 查询,即侵入到了主加载对象的详情访问中。
(3) 深度延迟加载
执行完主加载对象的 select 语句后,不会执行关联对象的 select 查询,当访问主加载对象的详情时,也不会执行关联对象的 select 查询,只有真正访问到关联对象的详情时,才会执行关联对象的 select 查询。
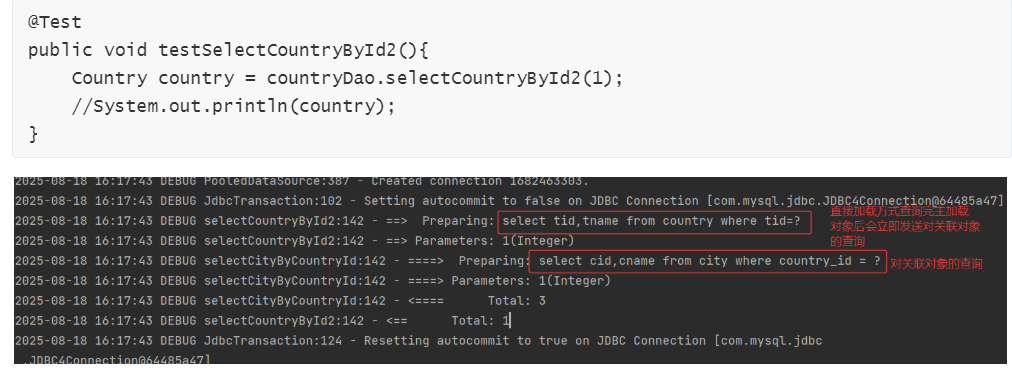
注意, 延迟加载必须是主加载对象和关联对象分别进行单表的 select 查询,不能是多表连接查询,因为多表连接查询本质上是把多张表连接成一张表来查询。
2. 直接加载
(1) 修改主配置文件
在主配置文件的 <properties> 与 <typeAliases> 标签之间,添加 <settings> 标签,用于完成全局参数设置,可以在 Mybatis 的帮助文档中搜索 lazy,可以查询出延迟加载的相关参数:
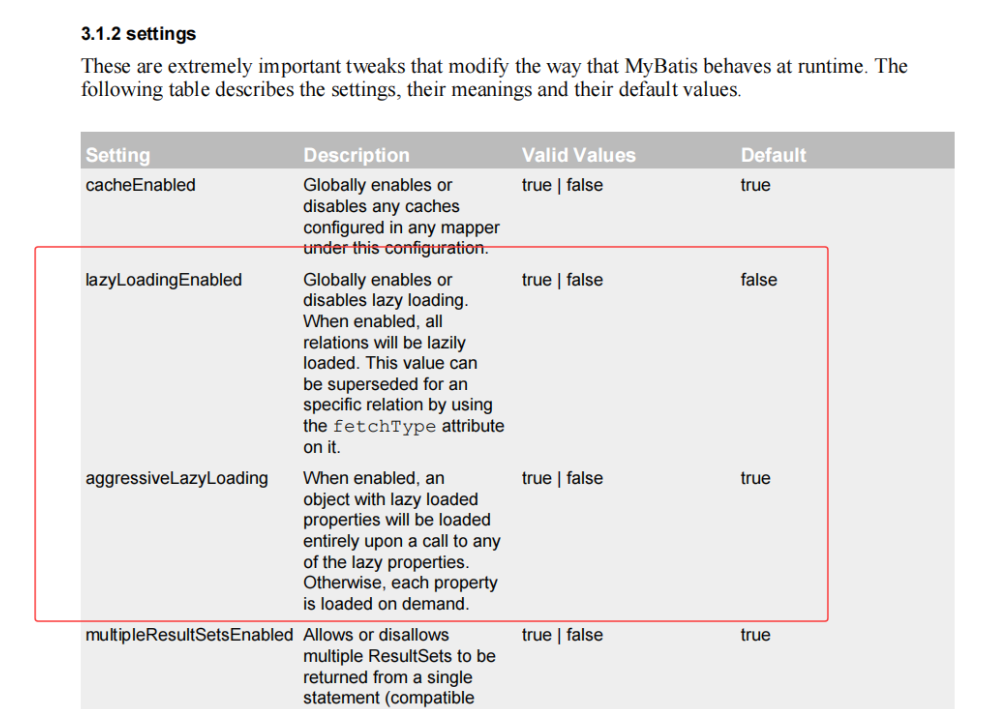
全局属性 lazyLoadingEnabled 的值是 false,那么对关联对象的查询采用的就是直接加载,是默认情况。
示例:
- 修改主配置文件 mybatis.xml
- 映射文件 ICountryDao.xml
- 测试类
3. 深度延加载
(1) 修改主配置文件 mybatis.xml
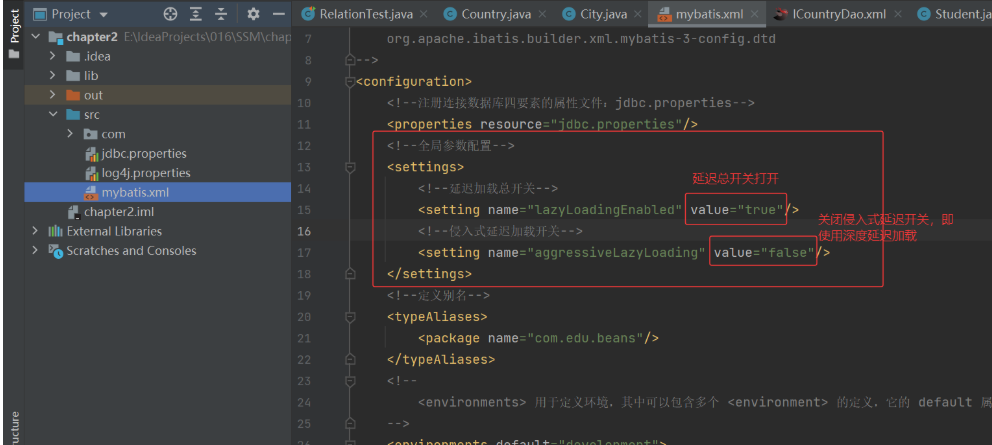
(2) 映射文件,同上
(3) 测试类 RelationTest
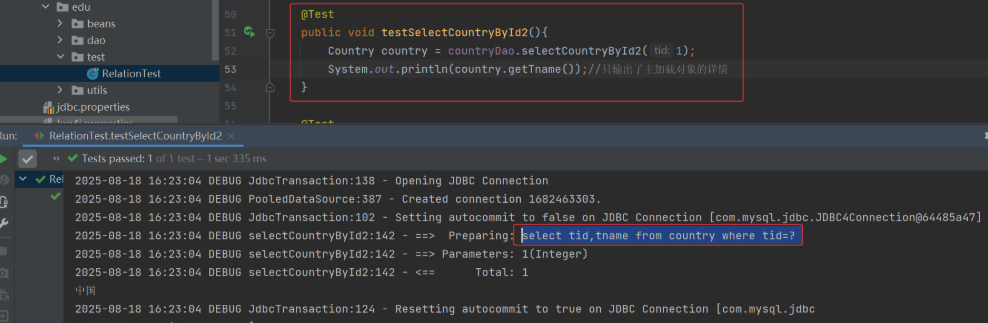
从上可知,我们只输出了主加载对象 Country 详情,就只会发送对主加载对象的 select 查询,不会执行对关联对象的 select 语句,我们修改代码,输出关联对象详情:
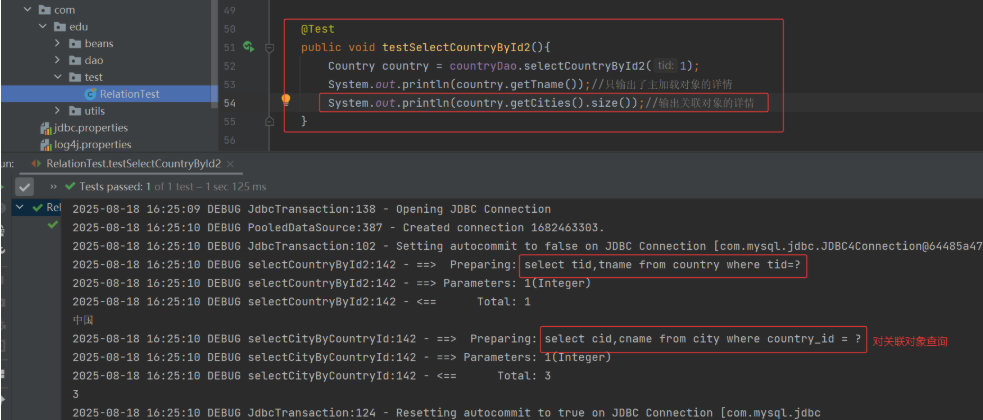
只有当我们用到了关联对象详情的时候,才会发送对关联对象的 select 查询,是深度延迟加载。
4. 侵入式延迟加载
(1) 主配置文件:
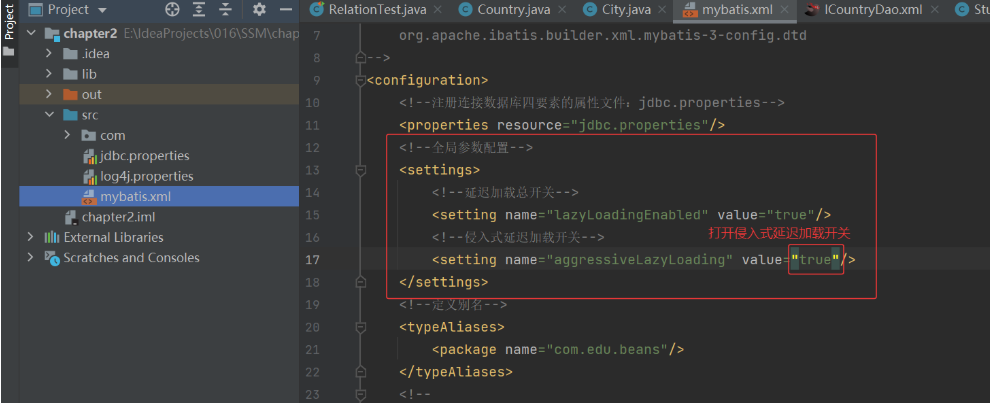
(2) 映射文件同上
(3) 测试类 RelationTest
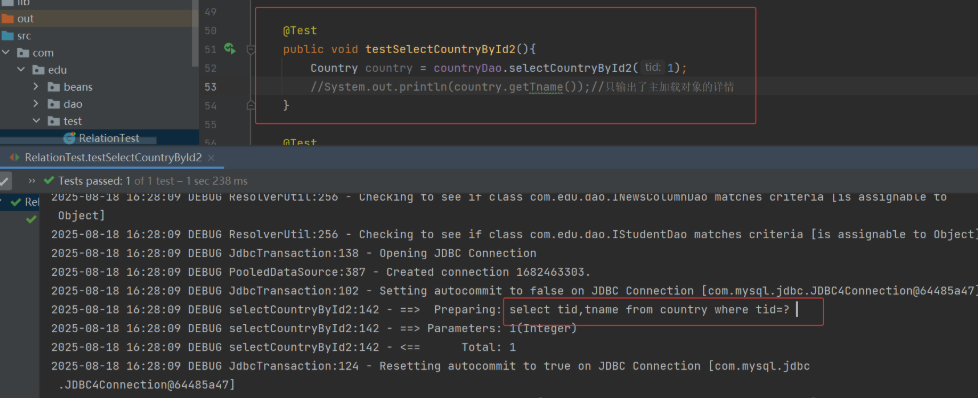
由上可知,侵入式延迟加载方式在没有输出任何对象时,不会发送对关联对象的 select 查询。
修改代码,只输出主加载对象,不输出关联对象:
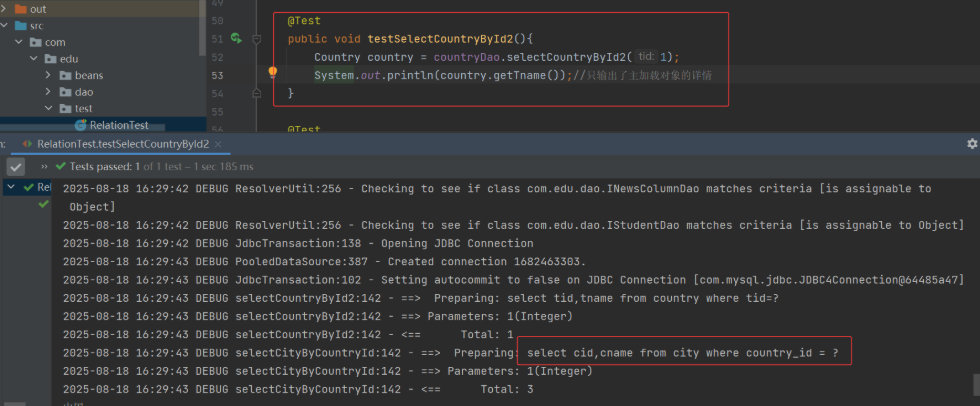
由上可知,我们只是输出了主加载对象,但是也发送了对关联对象的 select 查询,属于侵入式延迟加载,即关联对象侵入到了主加载对象的数据中了。
八、查询缓存
查询缓存的作用,主要是为了提高查询的速度,将用户对同一数据的重复查询过程简化,不再每次都从数据库中获取结果,而是从缓存中获取数据,从而提高查询效率。
Mybatis 根据缓存的作用域(生命周期)分为两种:一级查询缓存和二级查询缓存
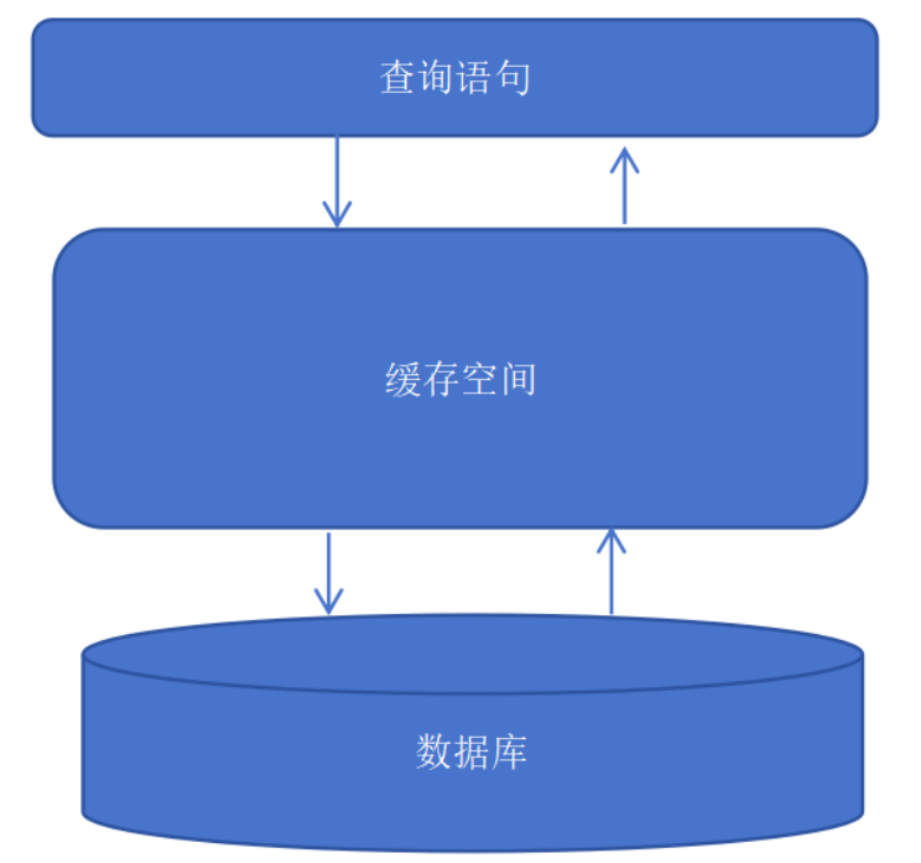
1. 一级查询缓存
Mybatis 的一级查询缓存是基于 org.apache.ibatis.cache.impl.PerpentualCache 类的 HashMap 类型的本地缓存,其作用域是 SqlSession,在同一个 SqlSession 中执行两次相同的 sql 查询,第一次查询后,会将结果放入缓存,第二次查询就直接从缓存中获取数据,不再从数据库中去数据,从而提高了查询效率。
当一个 SqlSession 关闭后,对应的一级缓存就不存在了,Mybatis 默认情况下是开启一级缓存的,并且不能关闭。
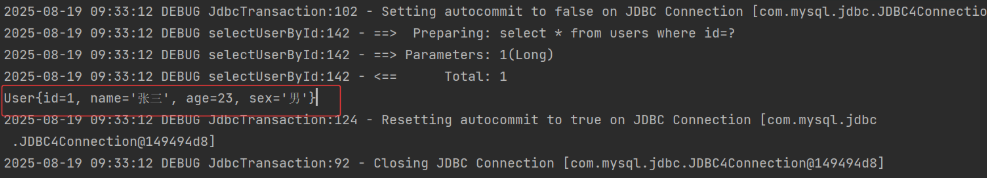
2. 一级缓存的存在性证明
(1) 创建数据库表
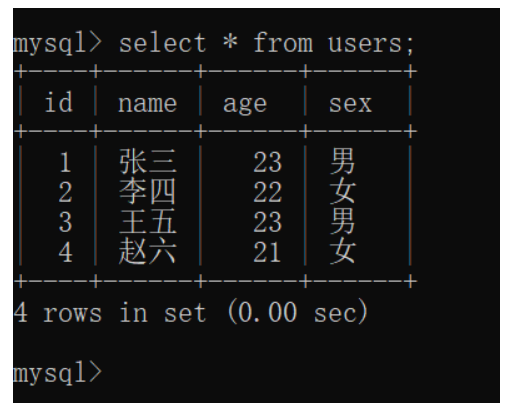
(2) 创建实体类
package com.edu.beans;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public User(Long id, String name, int age, String sex) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
(3) Dao 层接口
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.User;
public interface IUserDao {
User selectUserById(Long id);
}
(4) 映射文件 IUserDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="selectUserById" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
</mapper>
(5) 测试类 UserTest
package com.edu.test;
import com.edu.beans.User;
import com.edu.dao.*;
import com.edu.utils.MybatisUtils;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class UserTest {
private SqlSession session;
private IUserDao userDao;
@Before //被 @Before 注解的方法为初始化方法,它会在每次 @Test 修饰的方法执行之前执行一次,完成初始化工作
public void setUp(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//获取 Dao 层接口的动态代理对象(Mapper 的动态代理)
userDao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
}
@After //被 @After 注解的方法为销毁方法,它会在 @Test 修饰的方法执行之后执行一次,完成资源的销毁工作
public void tearDown(){
if(session != null){
session.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testSelectUserById(){
User user1 = userDao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user1);
User user2 = userDao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user2);
}
}
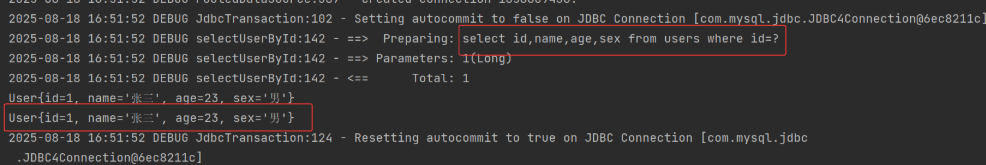
第二次执行相同的查询并没有向数据库发送 select 语句,证明一级缓存时存在的,因为第二次的查询就是从一级缓存中出来的。
3. 从缓存中读取数据的依据是映射文件中 SQL 的 id,不是缓存值
一级缓存缓存的是相同的 SQL 映射的 id 的查询结果,而不是相同的 SQL 语句的查询结果。因为 Mybatis 内部,无论一级缓存还是二级缓存,其底层都是用一个 HashMap 来实现的,其 key 就是映射文件中 SQL 语句的 id 值,value 就是从数据库中查询出来的结果。
示例:
(1) 修改 Dao 层接口
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.User;
public interface IUserDao {
User selectUserById(Long id);
User selectUserById2(Long id);
}
(2) 修改映射文件 IUserDao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="selectUserById" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<select id="selectUserById2" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
</mapper>
(3) 测试类 UserTest
@Test
public void testSelectUserById2(){
User user1 = userDao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user1);
User user2 = userDao.selectUserById2(1L);
System.out.println(user2);
}
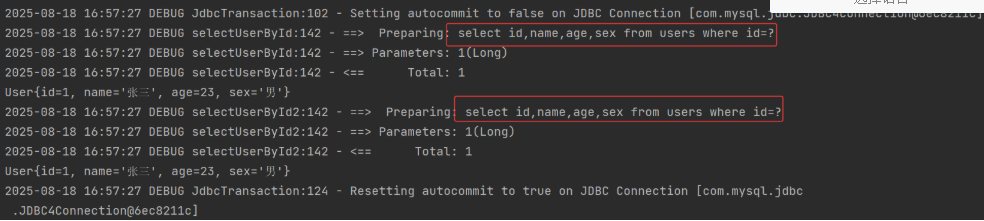
从上可知,虽然执行的是两个相同的 sql 语句,但是并没有从缓存中出来,而是 select 了两次数据库,证明Mybatis 缓存的是映射文件中 SQL 语句的 id 值,并不是缓存查询的结果。
4. 增删改对一级缓存的影响
增、删、改操作,无论是否提交事务(session.commit()),均会清空一级缓存,迫使查询再次从数据库中 select,这样就更新了缓存。
示例:
(1) 修改 Dao 层接口
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.User;
public interface IUserDao {
User selectUserById(Long id);
User selectUserById2(Long id);
void updateUser(User user);
}
(2) 修改 IUserDao.xml 映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="selectUserById" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<select id="selectUserById2" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<update id="updateUser">
update users set name=#{name},age=#{age},sex=#{sex} where id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
(3) 测试类 UserTest
@Test
public void testUpdateUser(){
User user1 = userDao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user1);
User user = new User(1L,"晓晓",23,"男");
userDao.updateUser(user);
User user2 = userDao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user2);
}
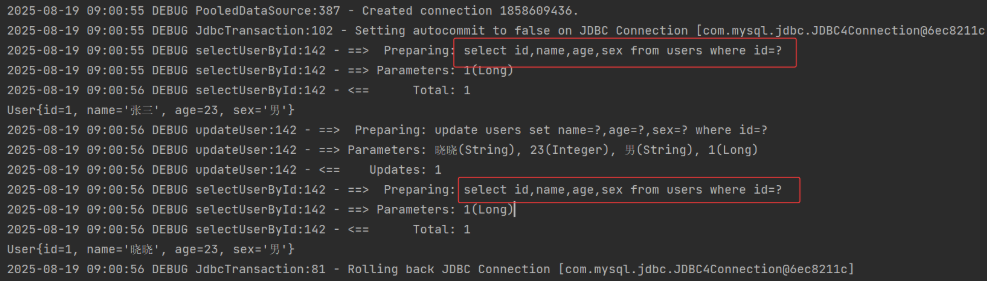
由上可知,增删改均会清空一级缓存,迫使 Mybatis 重新执行 select 查询让缓存中的数据更新。
5. 二级缓存
(1) 使用二级缓存的步骤:
- 实体类要实现 java.io.Serializable 接口(可序列化),如果实体类还包含父类或域属性(关联属性),则父类和域属性也要实现 java.io.Serializable 接口
package com.edu.beans;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class User implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public User(Long id, String name, int age, String sex) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2) 在映射文件 IUserDao.xml 中添加 <cache> 标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IUserDao">
<!--二级缓存-->
<cache/>
<select id="selectUserById" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<select id="selectUserById2" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<update id="updateUser">
update users set name=#{name},age=#{age},sex=#{sex} where id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
3) 证明二级缓存的存在性
@Test
public void testSecondCache(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
IUserDao dao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//第一次查询
User user1 = dao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user1);
session.close();//关闭 session,一级缓存就被清空了
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
dao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//第二次查询
User user2 = dao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user2);
}
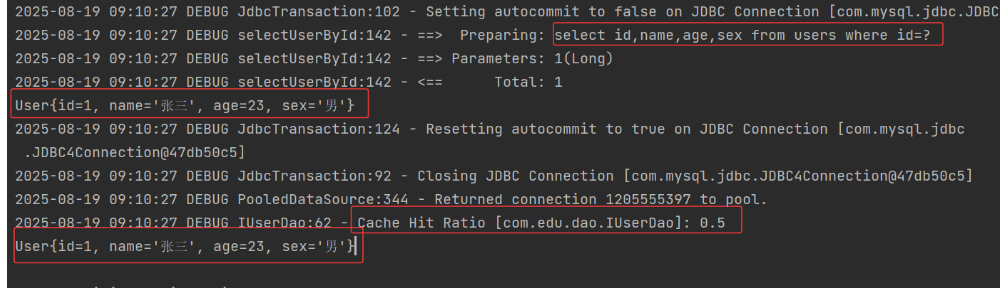
由上可知,只发送了一次 select 语句,证明二级缓存是存在的,日志中的 Cache Hit Ratio 表示缓存命中率,每一次执行查询,系统都会计算一次二级缓存命中率,第一次查询二级缓存中没有数据,所以命中率 0,第二次从二级缓存中出来,所以命中率为1/2=0.5,第三次就是1/3=0.33。
4) 我们还可以对二级缓存进行性能的配置,例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--
mybatis-3-mapper.dtd:是 mybatis 映射文件的约束文件,约束文件的位置在 mybatis 的核心jar包(mybatis-3.3.0.jar)
的这里:org.apache.ibatis.builder.xml.mybatis-3-mapper.dtd
-->
<mapper namespace="com.edu.dao.IUserDao">
<!--
eviction:逐出策略,当二级缓存对象达到最大值的时候,就需要通过逐出策略将缓存中数据移除,默认是LRU,取值为:
FIFO:先进先出
LRU:使用时间最长的先出
flushInterval:刷新缓存的时间间隔,单位为秒,刷新缓存就是情况缓存,迫使数据全部写出
readOnly:设置缓存是否只读
size:二级缓存中存放的对象的最大值,默认1024个
-->
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="10800000" readOnly="true" size="512"/>
<select id="selectUserById" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<select id="selectUserById2" resultType="User">
select id,name,age,sex from users where id=#{xxx}
</select>
<update id="updateUser">
update users set name=#{name},age=#{age},sex=#{sex} where id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
5) 增删改对二级缓存的影响
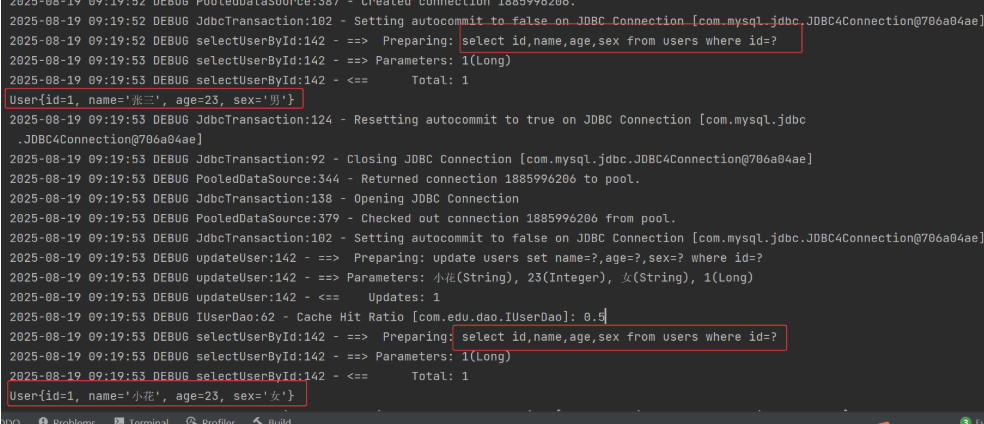
增删改操作,无论是否提交事务,均会清空一、二级缓存,迫使查询再次从数据库中 select,这样就可以更新缓存。
a. 修改测试类 UserTest
@Test
public void testUpdateSecondCache(){
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
IUserDao dao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//第一次查询
User user1 = dao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user1);
session.close();//关闭 session,一级缓存就被清空了
session = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
dao = session.getMapper(IUserDao.class);
//更新操作
User user = new User(1L,"小花",23,"女");
dao.updateUser(user);
//第二次查询
User user2 = dao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user2);
}
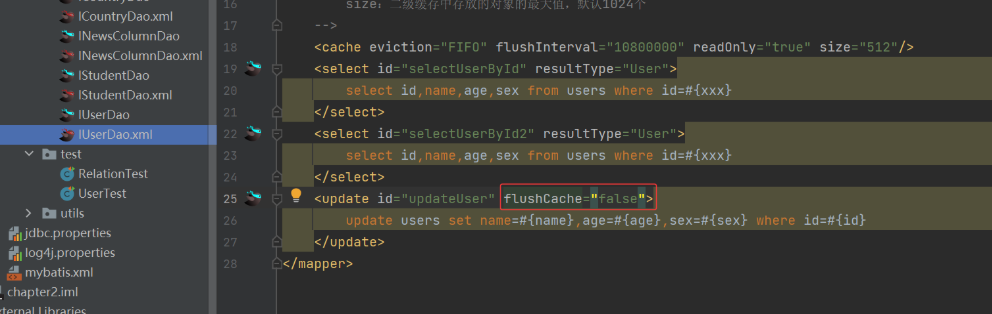
6) 我们还可以设置增删改时不刷新缓存
可以在 <insert>、<update>、<delete> 标签上添加 flushCache="false"
7) 二级缓存的关闭
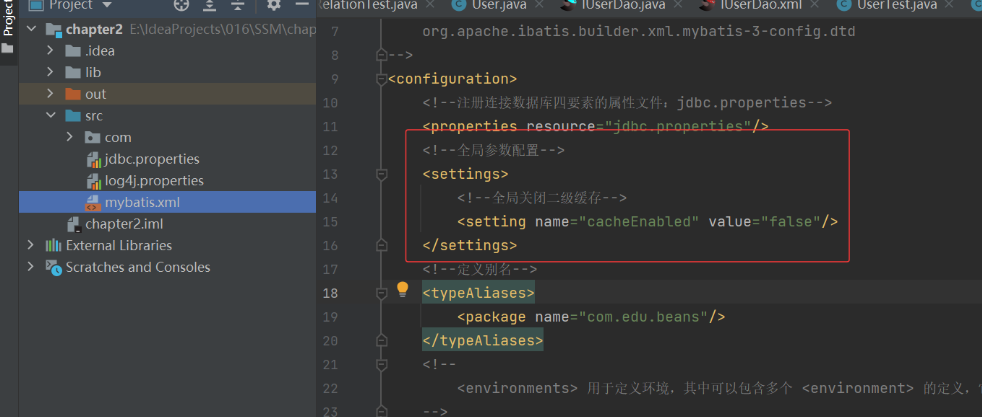
二级缓存默认情况下也是开启的,若要关闭它,需要进行配置
a. 全局关闭:指整个应用都不使用二级缓存,在 <settings>标签中配置:
b. 局部关闭:在需要关闭二级缓存的 <select> 标签中使用 useCache="false"
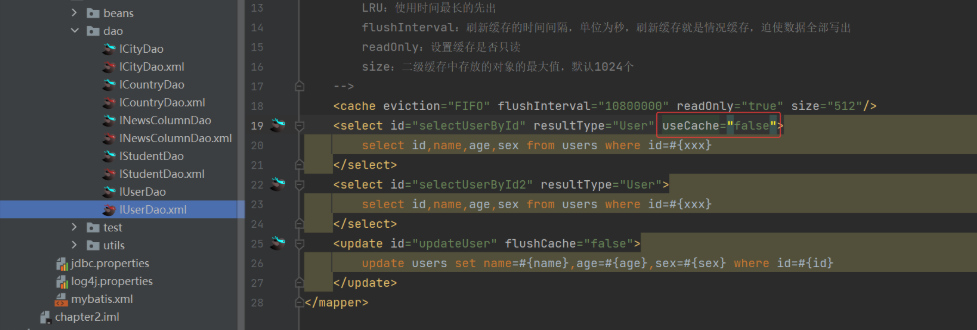
8)** 二级缓存的使用原则
a. 只能在一个命名空间下使用二级缓存
二级缓存的数据是基于 namespace 的,不同的 namespace 互不干扰,在多个 namespace 中若均存在对同一个表的操作,那么多个 namespace 中的数据就可能出现不一致的情况。
b. 在单表上使用二级缓存
如果一个表与其他表有关联关系,那么很有可能存在多个 namespace 对同一数据操作,就有可能出现 namespace 中数据不一致的情况。
c. 查询多于修改的情况使用二级缓存
因为增删改都会刷新二级缓存,对二级缓存频繁刷新会降低效率。
九、Mybatis 的注解式开发
Mybatis 的注解是开发就是使用注解替换掉 xml 形式的映射文件,使用注解来完成增删改查。
1. Mybatis 常用注解
@Insert:其 value 属性用于指定要执行的 insert 语句 @SelectKey:用于替换映射文件中的 <selectKey>,示例: @SelectKey(statement="select last_insert_id()", keyProperty="id", resultType=int.class, before=false) statement:获取新插入记录的主键值的 sql 语句 keyProperty:获取该主键值返回初始化对象的那个属性 resultType:返回值类型 before:指定主键的生成是在 insert 语句之前还是之后 @Delete:其value属性为要执行的 delete 语句 @Update:其value属性为要执行的 update语句 @Select:其value属性为要执行的 select 语句
示例:先删除映射文件 IUserDao.xml,然后在接口方法上添加Mybatis 的注解来替换掉映射文件
package com.edu.dao;
import com.edu.beans.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
public interface IUserDao {
@Insert("insert into users(name,age,sex) values(#{name},#{age},#{sex})")
void insertUser(User user);
@Delete("delete from users where id=#{xxx}")
void deleteUser(Long id);
@Update("update users set name=#{name},age=#{age},sex=#{sex} where id=#{id}")
void updateUser(User user);
@Select("select * from users where id=#{xxx}")
User selectUserById(Long id);
}
测试类:
@Test
public void testSelectUserById2(){
User user1 = userDao.selectUserById(1L);
System.out.println(user1);
}