文章目录
- 说明和参考资料
- [MCP 异地部署](#MCP 异地部署)
- 补充:@click.option核心参数
- [流式HTTP MCP服务器开发和测试](#流式HTTP MCP服务器开发和测试)
- [流式HTTP MCP服务器发布(未实践)](#流式HTTP MCP服务器发布(未实践))
说明和参考资料
- 说明:本文学习自赋范开源社区公开资料,结合本身实践总结而来,仅供学习和交流使用,最终著作权归九天老师及其团队所有!
- 参考文档:流式HTTP MCP服务器开发指南
MCP 异地部署
- MCP采用客户端服务器架构,支持异地部署,SSE通信方式只支持SSE单向通信,无多通道并发,稳定新不足,不适用于企业场景。HTTP流式传输拥有更高的并发、更稳定的通信、更低难度的集成和部署成本。

- 目前SDK中已加入HTTP流式MCP服务器的相关功能支持(自SDK1.8.0版本开始支持streamable http)。开发者可以通过MCP SDK,高效快速开发HTTP SDK MCP服务器,并通过多通多并发的企业级MCP工具部署。
- MCP python SDK streamable http guide docs
补充:@click.option核心参数
核心参数速查表
| 分类 | 参数 | 类型 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基础控制 | default |
Any | 未提供参数时的默认值 | default=3000 |
type |
Click Type | 参数类型(自动转换) | type=click.INT / type=click.Path(exists=True) |
|
required |
bool | 是否必须提供参数(默认False) |
required=True |
|
help |
str | 帮助文本(支持中文) | help="监听端口号" |
|
| 交互增强 | prompt |
bool/str | 未提供时交互式提示(可自定义提示文本) | prompt="请输入API密钥" |
confirmation_prompt |
bool | 需要二次确认(如密码) | confirmation_prompt=True |
|
hide_input |
bool | 隐藏输入内容(用于密码等敏感信息) | hide_input=True |
|
| 输入验证 | callback |
Callable | 自定义验证函数 | callback=validate_api_key |
metavar |
str | 帮助信息中的参数占位符 | metavar="PORT" → --port PORT |
|
nargs |
int | 指定参数值的个数(如2表示接收两个值) |
nargs=2 → --file a.txt b.txt |
|
| 特殊类型 | is_flag |
bool | 作为布尔标志(无需值,存在即为True) |
is_flag=True → --enable |
multiple |
bool | 允许重复参数(收集为列表) | multiple=True → --tag python --tag cli |
|
count |
bool | 统计参数出现次数(如-vvv) |
count=True → -v=1, -vv=2 |
|
| 环境集成 | envvar |
str/list | 从环境变量读取值(支持多个变量名) | envvar="API_KEY" 或 envvar=["API_KEY", "TOKEN"] |
show_envvar |
bool | 在帮助信息中显示支持的环境变量 | show_envvar=True → [env var: API_KEY] |
|
| 显示控制 | show_default |
bool/str | 显示默认值(可自定义文本) | show_default="默认3000" |
hidden |
bool | 隐藏该选项(不在帮助信息显示) | hidden=True |
|
| 选择限制 | choice |
list/click.Choice |
限定参数可选值 | choice=["DEBUG", "INFO"] 或 type=click.Choice(["A", "B"]) |
常用组合示例
- 必填参数+环境变量
python
@click.option("--api-key", envvar="API_KEY", required=True, help="API密钥")- 布尔标志+默认值
python
@click.option("--verbose", is_flag=True, default=False, help="启用详细输出")- 多值参数+验证
python
@click.option("--files", multiple=True, type=click.Path(exists=True))- 交互式密码输入
python
@click.option("--password", prompt=True, hide_input=True, confirmation_prompt=True)- 表格中的参数均为常用配置,实际使用时可根据需求组合。
流式HTTP MCP服务器开发和测试
项目开发
-
安装uv工具
pythonconda install uv -
创建项目,并创建、激活虚拟环境。
pythoncd /xxx/code uv init mcp-weather-http cd mcp-weather-http uv venv source .venv/bin/activate -
在虚拟环境中,安装所需依赖。
bashuv add mcp httpx -
采用
src_layer的风格进行项目文件编排,因此需要删除main.py,并创建mcp_weather_http目录。pythonrm main.py mkdir -p ./src/mcp_weather_http cd ./src/mcp_weather_http -
在
src/mcp_weather_http文件中创建__init__.py、__main__.py、server.py,具体文件内容如下:python(mcp-weather-http) (base) [root@yang mcp_weather_http]# vim __init__.py (mcp-weather-http) (base) [root@yang mcp_weather_http]# vim __main__.py (mcp-weather-http) (base) [root@yang mcp_weather_http]# vim server.py
-
__init__.pypythonfrom .server import main -
__main__.pypythonfrom mcp_weather_http import main main() -
server.pypython# 引入各种功能组件 import contextlib import logging # 日志 from collections.abc import AsyncIterator import anyio import click # 命令行参数 --api-key=xxx import httpx # 提供让大模型调用工具的能力 # mcp提供让大模型调用工具的能力 import mcp.types as types from mcp.server.lowlevel import Server from mcp.server.streamable_http_manager import StreamableHTTPSessionManager # 搭建http网络服务 from starlette.applications import Starlette from starlette.routing import Mount from starlette.types import Receive, Scope, Send # --------------------------------------------------------------------------- # 查询天气的函数 # --------------------------------------------------------------------------- OPENWEATHER_URL = "https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather" # openweather接口地址 DEFAULT_UNITS = "metric" # 默认使用摄氏温度 DEFAULT_LANG = "zh_cn" # 中文 async def fetch_weather(city: str, api_key: str) -> dict[str, str]: """ 调用OpenWeather API并返回一个简化的天气字典。 Raises: httpx.HTTPStatusError: if the response has a non-2xx status. """ # 设置请求参数 params = { "q": city, "appid": api_key, "units": DEFAULT_UNITS, "lang": DEFAULT_LANG, } # 异步网络请求 async with httpx.AsyncClient(timeout=10) as client: r = await client.get(OPENWEATHER_URL, params=params) r.raise_for_status() data = r.json() # 获取返回结果中的参数 weather_main = data["weather"][0]["main"] description = data["weather"][0]["description"] temp = data["main"]["temp"] feels_like = data["main"]["feels_like"] humidity = data["main"]["humidity"] # 函数返回结果 字典类型 return { "city": city, "weather": weather_main, "description": description, "temp": f"{temp}°C", "feels_like": f"{feels_like}°C", "humidity": f"{humidity}%", } # 命令函参数 @click.command() @click.option( "--port", default=3000, help="HTTP服务监听的端口号", type=int, # 参数类型 show_default=True # 显示默认值 ) @click.option( "--api-key", envvar="OPENWEATHER_API_KEY", # 支持从环境变量读取 required=True, # 强制要求必须提供 help="OpenWeather API密钥(也可以通过设置OPENWEATHER_API_KEY环境变量提供)", metavar="KEY" # 帮助信息中的参数占位符 ) @click.option( "--log-level", default="INFO", help="日志级别 (DEBUG, INFO, WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL)", type=click.Choice(["DEBUG", "INFO", "WARNING", "ERROR", "CRITICAL"], case_sensitive=False) # 限定可选值 ) @click.option( "--json-response", is_flag=True, # 标记为布尔标志 default=False, help="启用JSON响应格式(默认使用SSE流式传输)", show_default=True ) def main(port: int, api_key: str, log_level: str, json_response: bool) -> int: """使用流式传输协议运行一个天气查询MCP服务""" # ----------------------日志配置 ---------------------- logging.basicConfig( level=getattr(logging, log_level.upper()), format="%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s", ) logger = logging.getLogger("weather-server") # ---------------------- 创建mcp服务 ---------------------- app = Server("mcp-streamable-http-weather") # ---------------------- 工具实现 ------------------- # MCP工具注册:让大模型能调用 get-weather @app.call_tool() # 装饰器声明这是一个工具调用端点 # 异步设计:async def 支持非阻塞IO(如网络请求) # 输入参数 # name:工具名称(如"get-weather") # arguments:大模型传入的参数字典(如{"location": "北京"}) # 返回值:标准化返回TextContent类型列表(兼容多模态扩展) async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[types.TextContent]: """Handle the 'get-weather' tool call.""" # 获取当前请求的上下文对象(request context) ctx = app.request_context city = arguments.get("location") if not city: raise ValueError("'location' is required in arguments") # 发送初始日志消息,以便客户端尽早看到流。 await ctx.session.send_log_message( level="info", data=f"Fetching weather for {city}...", logger="weather", # # 日志分类 related_request_id=ctx.request_id, # 关联请求ID ) try: weather = await fetch_weather(city, api_key) except Exception as err: # 将错误信息流式传输至客户端并重新抛出异常,以便MCP协议能够返回错误状态。 ''' raise 重新抛出当前捕获的异常 双重处理:实现「日志记录 + 协议层错误处理」的分离: 本地处理:先通过send_log_message将错误详情流式传输给客户端 全局处理:再通过raise让MCP协议层捕获并返回标准化错误响应 ''' await ctx.session.send_log_message( level="error", data=str(err), logger="weather", related_request_id=ctx.request_id, ) raise # 流式传输成功状态通知(可选) await ctx.session.send_log_message( level="info", data="Weather data fetched successfully!", logger="weather", related_request_id=ctx.request_id, ) # 为最终返回值编写可读的总结 summary = ( f"{weather['city']}:{weather['description']},温度 {weather['temp']}," f"体感 {weather['feels_like']},湿度 {weather['humidity']}。" ) return [ types.TextContent(type="text", text=summary), ] # ---------------------- 工具注册 ------------------------- @app.list_tools() async def list_tools() -> list[types.Tool]: """保留可用的工具给大模型""" return [ types.Tool( name="get-weather", description="查询指定城市的实时天气(OpenWeather 数据)", inputSchema={ "type": "object", "required": ["location"], "properties": { "location": { "type": "string", "description": "城市的英文名称,如 'Beijing'", } }, }, ) ] # ---------------------- 会话管理 ----------------------- # 创建MCP的"HTTP 会话处理中心",负责处理所有/mcp 路由的请求 # json_response=False 表示用流式 SSE(也可以改成一次性 JSON 响应)。 session_manager = StreamableHTTPSessionManager( app=app, event_store=None, # 无状态;不保存历史事件 json_response=json_response, stateless=True, ) # 实现ASGI(Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface)服务的核心生命周期管理 async def handle_streamable_http(scope: Scope, receive: Receive, send: Send) -> None: await session_manager.handle_request(scope, receive, send) # ---------------------- Lifespan Management 生命周期管理 -------------------- @contextlib.asynccontextmanager async def lifespan(app: Starlette) -> AsyncIterator[None]: async with session_manager.run(): logger.info("Weather MCP server started! 🚀") try: yield finally: logger.info("Weather MCP server shutting down...") # ---------------------- ASGI app + Uvicorn --------------------- # ASGI 应用的最终组装和服务器启动 starlette_app = Starlette( debug=False, # 禁用调试模式(生产环境) routes=[Mount("/mcp", app=handle_streamable_http)], # 路由挂载 lifespan=lifespan, # 注入生命周期管理器 ) import uvicorn uvicorn.run( starlette_app, # ASGI应用实例 host="0.0.0.0", # 监听所有网络接口 port=port # 使用参数传入的端口号 ) return 0 if __name__ == "__main__": main()
-
查询当前环境中的
setuotools版本bash(mcp-weather-http) (base) [root@yang mcp_weather_http]# pip show setuptools Name: setuptools Version: 78.1.1 -
回到项目主目录
/mnt/code/mcp-weather-http,修改project.tomlpython# # [build-system] 部分指定了构建项目所需的工具和构建后端 [build-system] # # requires 列出了构建依赖,这些包会在构建时自动安装 requires = ["setuptools>=78.1.1", "wheel"] # 指定构建后端,这里使用 setuptools 的构建系统 build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta" # 项目描述部分只需要修改description部分 [project] name = "mcp-weather-http" version = "0.1.0" description = "输入OpenWeather-API-KEY,获取天气信息。" readme = "README.md" requires-python = ">=3.13" dependencies = [ "httpx>=0.28.1", "mcp>=1.13.1", ] # [project.scripts] 定义了项目安装后要创建的可执行脚本 [project.scripts] # 格式为 "命令名 = "模块路径:函数名"" mcp-weather-http = "mcp_weather_http:main" # [tool.setuptools] 部分提供 setuptools 特定的配置 [tool.setuptools] # 指定包目录的映射关系,这里表示根目录 ("") 映射到 "src" 目录 package-dir = {"" = "src"} # [tool.setuptools.packages.find] 配置 setuptools 如何查找包 [tool.setuptools.packages.find] # 指定在哪些目录中查找 Python 包,这里只在 src 目录中查找 where = ["src"]
server文件关键代码解释
python
def main(port: int, api_key: str, log_level: str, json_response: bool) -> int:
"""使用流式传输协议运行一个天气查询MCP服务"""
# ----------------------日志配置 ----------------------
logging.basicConfig(
level=getattr(logging, log_level.upper()),
format="%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s",
)
logger = logging.getLogger("weather-server")
# ---------------------- 创建mcp服务 ----------------------
app = Server("mcp-streamable-http-weather")
# ---------------------- 工具实现 -------------------
# MCP工具注册:让大模型能调用 get-weather
@app.call_tool() # 装饰器声明这是一个工具调用端点
python
# 异步设计:async def 支持非阻塞IO(如网络请求)
# 输入参数
# name:工具名称(如"get-weather")
# arguments:大模型传入的参数字典(如{"location": "北京"})
# 返回值:标准化返回TextContent类型列表(兼容多模态扩展)
async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[types.TextContent]:
"""Handle the 'get-weather' tool call."""
# 获取当前请求的上下文对象(request context)
ctx = app.request_context
city = arguments.get("location")
if not city:
raise ValueError("'location' is required in arguments")
# 发送初始日志消息,以便客户端尽早看到流。
await ctx.session.send_log_message(
level="info",
data=f"Fetching weather for {city}...",
logger="weather", # # 日志分类
related_request_id=ctx.request_id, # 关联请求ID
)
try:
weather = await fetch_weather(city, api_key)
except Exception as err:
# 将错误信息流式传输至客户端并重新抛出异常,以便MCP协议能够返回错误状态。
'''
raise 重新抛出当前捕获的异常
双重处理:实现「日志记录 + 协议层错误处理」的分离:
本地处理:先通过send_log_message将错误详情流式传输给客户端
全局处理:再通过raise让MCP协议层捕获并返回标准化错误响应
'''
await ctx.session.send_log_message(
level="error",
data=str(err),
logger="weather",
related_request_id=ctx.request_id,
)
raise
# 流式传输成功状态通知(可选)
await ctx.session.send_log_message(
level="info",
data="Weather data fetched successfully!",
logger="weather",
related_request_id=ctx.request_id,
)
# 为最终返回值编写可读的总结
summary = (
f"{weather['city']}:{weather['description']},温度 {weather['temp']},"
f"体感 {weather['feels_like']},湿度 {weather['humidity']}。"
)
return [
types.TextContent(type="text", text=summary),
]- 功能定位:这是一个工具调用(Tool Call)的异步处理函数 ,核心功能是:
- 作为大模型(如ChatGPT)的扩展工具,处理
get-weather天气查询请求 - 通过OpenWeather API获取指定城市的天气数据
- 实现实时日志流式传输 (Streaming Logs)和结构化返回结果
- 作为大模型(如ChatGPT)的扩展工具,处理
-
函数定义
python@app.call_tool() async def call_tool(name: str, arguments: dict) -> list[types.TextContent]:
@app.call_tool():装饰器声明这是一个工具调用端点- 异步设计 :
async def支持非阻塞IO(如网络请求) - 输入参数 :
name:工具名称(如"get-weather")arguments:大模型传入的参数字典(如{"location": "北京"})
- 返回值 :标准化返回
TextContent类型列表(兼容多模态扩展)
-
参数验证
pythoncity = arguments.get("location") if not city: raise ValueError("'location' is required in arguments")
- 强制检查
location参数是否存在 - 缺失时抛出明确错误(大模型会捕获并提示用户)
-
实时日志流
pythonawait ctx.session.send_log_message( level="info", data=f"Fetching weather for {city}...", logger="weather", related_request_id=ctx.request_id, )
- 实时反馈机制:在API请求完成前,先发送"进行中"日志
- 关键字段 :
level:日志级别(info/error等)related_request_id:关联请求ID(用于链路追踪)
-
核心业务逻辑
pythonweather = await fetch_weather(city, api_key)
- 调用异步函数
fetch_weather(实际发起OpenWeather API请求)
-
异常处理
pythonawait ctx.session.send_log_message( level="error", data=str(err), logger="weather", related_request_id=ctx.request_id, ) raise# 继续向上抛出异常
- 错误流式传输:将异常信息实时发送给客户端。
raise的作用是重新抛出当前捕获的异常。- 双重处理:实现「日志记录 + 协议层错误处理」的分离:
- 本地处理:先通过send_log_message将错误详情流式传输给客户端。
- 全局处理:再通过raise让MCP协议层捕获并返回标准化错误响应。
失败 成功 调用 fetch_weather 是否成功? 捕获异常 Exception 发送错误日志到客户端 重新抛出异常 raise MCP协议层处理 继续后续逻辑
| 场景 | 客户端表现 | 服务端行为 |
|---|---|---|
| 有raise | 1. 实时看到错误日志2. 最终收到MCP错误响应 | 中断当前请求,MCP返回500状态码 |
| 无raise | 仅看到错误日志,但状态码为200 | 继续执行后续代码(可能逻辑异常) |
-
结果格式化
pythonsummary = ( f"{weather['city']}:{weather['description']},温度 {weather['temp']}," f"体感 {weather['feels_like']},湿度 {weather['humidity']}。" ) return [types.TextContent(type="text", text=summary)]
- 自然语言摘要:将API返回的JSON转换为人类可读文本
- 标准化返回 :包装为
TextContent类型(未来可扩展图片等内容)
- 完整工作流程
用户 大模型 工具服务 客户端 OpenWeather 查询"北京天气" call_tool("get-weather", {"location":"北京"}) [日志流] "Fetching weather for 北京..." 异步API请求 返回JSON数据 [日志流] "Success!" ["北京:晴,温度 25℃,体感 26℃,湿度 60%"] 返回错误 [错误日志] "API请求失败" 抛出异常 alt [成功] [失败] 格式化响应 用户 大模型 工具服务 客户端 OpenWeather
python
# ---------------------- 工具注册 -------------------------
@app.list_tools()
async def list_tools() -> list[types.Tool]:
"""保留可用的工具给大模型"""
return [
types.Tool(
name="get-weather",
description="查询指定城市的实时天气(OpenWeather 数据)",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"required": ["location"],
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市的英文名称,如 'Beijing'",
}
},
},
)
]
python
# ---------------------- 会话管理 -----------------------
# 创建MCP的"HTTP 会话处理中心",负责处理所有/mcp 路由的请求
# json_response=False 表示用流式 SSE(也可以改成一次性 JSON 响应)。
session_manager = StreamableHTTPSessionManager(
app=app,
event_store=None, # 无状态;不保存历史事件
json_response=json_response,
stateless=True,
)
# 实现ASGI(Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface)服务的核心生命周期管理
async def handle_streamable_http(scope: Scope, receive: Receive, send: Send) -> None:
await session_manager.handle_request(scope, receive, send)
# ---------------------- Lifespan Management 生命周期管理 --------------------
@contextlib.asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app: Starlette) -> AsyncIterator[None]:
async with session_manager.run():
logger.info("Weather MCP server started! 🚀")
try:
yield
finally:
logger.info("Weather MCP server shutting down...")- 这段代码实现了一个 ASGI(Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface)服务的核心生命周期管理,分为两部分:HTTP请求处理和服务器启停管理。以下是详细解析:
-
HTTP请求处理 (
handle_streamable_http)pythonasync def handle_streamable_http(scope: Scope, receive: Receive, send: Send) -> None: await session_manager.handle_request(scope, receive, send)
- 功能 :
- 作为ASGI协议的入口点,处理所有HTTP请求
- 将请求委托给
session_manager进行实际处理
- 参数说明:
| 参数 | 类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
scope |
Scope |
包含请求的元数据(如HTTP方法、路径、headers等)的字典 |
receive |
Receive |
异步函数,用于接收请求体(如POST数据) |
send |
Send |
异步函数,用于发送响应(如status/headers/body) |
- 关键设计 :
- 委托模式 :将具体逻辑交给
session_manager实现解耦 - 流式支持 :函数名
streamable暗示支持流式传输(如SSE/WebSocket)
- 委托模式 :将具体逻辑交给
- 生命周期管理 (
lifespan)
python
@contextlib.asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app: Starlette) -> AsyncIterator[None]:
async with session_manager.run():
logger.info("Weather MCP server started! 🚀")
try:
yield
finally:
logger.info("Weather MCP server shutting down...")- 功能 :
- 使用异步上下文管理器管理服务启停
- 控制
session_manager的启动/清理逻辑
- 阶段分解:
- 启动阶段 (
async with session_manager.run())- 初始化连接池、加载配置等
- 打印启动日志(含火箭emoji增强可读性 🚀)
- 运行阶段 (
yield)- 保持服务运行状态
- 在此处可插入健康检查、指标上报等逻辑
- 关闭阶段 (
finally)- 无论服务是否异常都会执行
- 释放资源(如关闭数据库连接)
- 关键机制:
| 机制 | 作用 |
|---|---|
@contextlib.asynccontextmanager |
将普通函数转为异步上下文管理器 |
async with |
确保session_manager.run()的__aexit__一定会被调用(类似Java的try-with-resources) |
yield |
分隔启动和关闭逻辑(yield前为启动,后为关闭) |
- 完整生命周期流程
ASGI_Server Lifespan SessionManager 服务启动 run() 初始化完成 进入运行状态(yield) handle_request() 返回响应 loop [处理请求] 服务终止 清理资源 关闭确认 ASGI_Server Lifespan SessionManager
- 这种模式是ASGI服务的标准实践,FastAPI/Starlette等框架均采用类似结构。
python
# ---------------------- ASGI app + Uvicorn ---------------------
# ASGI 应用的最终组装和服务器启动
starlette_app = Starlette(
debug=False, # 禁用调试模式(生产环境)
routes=[Mount("/mcp", app=handle_streamable_http)], # 路由挂载
lifespan=lifespan, # 注入生命周期管理器
)
import uvicorn
uvicorn.run(
starlette_app, # ASGI应用实例
host="0.0.0.0", # 监听所有网络接口
port=port # 使用参数传入的端口号
)
return 0- 这段代码完成了 ASGI 应用的最终组装和服务器启动,是服务端程序的入口点。以下是解析:
- Starlette 应用构造
python
starlette_app = Starlette(
debug=False,# 禁用调试模式(生产环境)
routes=[Mount("/mcp", app=handle_streamable_http)],# 路由挂载
lifespan=lifespan,# 注入生命周期管理器
)- 核心参数解析:
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
debug=False |
关闭调试模式,避免敏感信息泄漏(如堆栈跟踪) |
routes |
定义路由映射: - Mount("/mcp", ...) 将路径前缀/mcp下的所有请求路由到handle_streamable_http |
lifespan |
绑定之前定义的异步生命周期管理器 |
- 路由设计意图:
- 通过
/mcp路径前缀实现API版本隔离 (如未来可扩展/mcp/v2) - 所有匹配
/mcp/*的请求都会交由handle_streamable_http处理
- 通过
-
Uvicorn 服务器启动
pythonuvicorn.run( starlette_app,# ASGI应用实例 host="0.0.0.0",# 监听所有网络接口 port=port,# 使用参数传入的端口号 )
- 关键配置:
| 参数 | 典型值 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
host |
"0.0.0.0" |
监听所有可用网络接口(如需限制只允许本地访问则设为"127.0.0.1") |
port |
如3000 |
服务暴露的端口,通常通过外部参数传入 |
| 隐含配置 | workers=1 |
默认单进程运行(适合配合K8s/Docker的横向扩展) |
- 生产环境建议:
python
uvicorn.run(
starlette_app,
host="0.0.0.0",
port=port,
workers=4,# 根据CPU核心数调整
timeout_keep_alive=60,# 连接保活时间
access_log=False# 禁用访问日志提升性能
)-
返回状态码
pythonreturn 0# 表示正常退出
- 当服务器被手动停止(如Ctrl+C)时,返回
0表示正常退出 - 非零返回值通常表示错误(如端口冲突返回
98)
- 完整启动流程
User Uvicorn Starlette SessionManager OS 启动命令(含port参数) 初始化应用 调用lifespan启动 初始化完成 应用就绪 绑定端口 0.0.0.0:{port} 端口监听成功 服务运行中(阻塞主线程) HTTP请求 GET /mcp/weather 传递ASGI事件 handle_streamable_http() 生成响应 ASGI响应 返回HTTP响应 loop [请求处理] SIGTERM终止信号 触发lifespan关闭 清理资源 清理完成 释放端口 退出码 0 User Uvicorn Starlette SessionManager OS
MCP服务器开启与测试
-
开启流式HTTP MCP服务器
python# 回到项目主目录 # cd ../../ uv run ./src/mcp_weather_http/server.py --api-key xxxx -
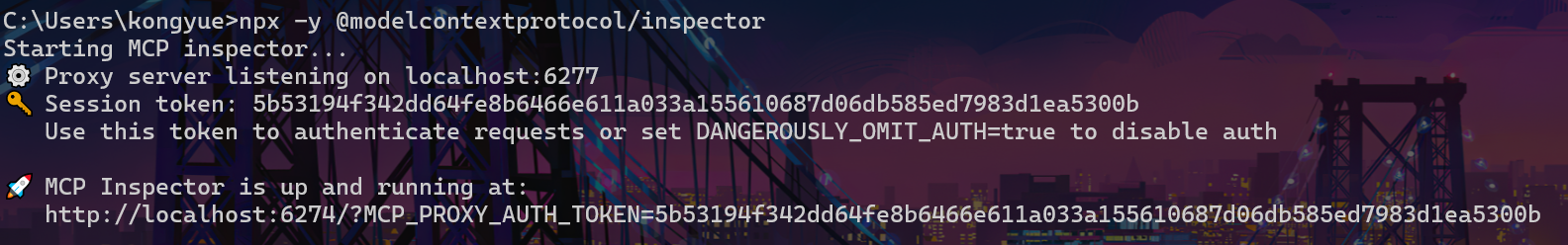
开启Inspector:可以在本地主机上运行,连接公网或局域网内的MCP服务器。
pythonnpx -y @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
- 打开Inspector,网址在终端中显示
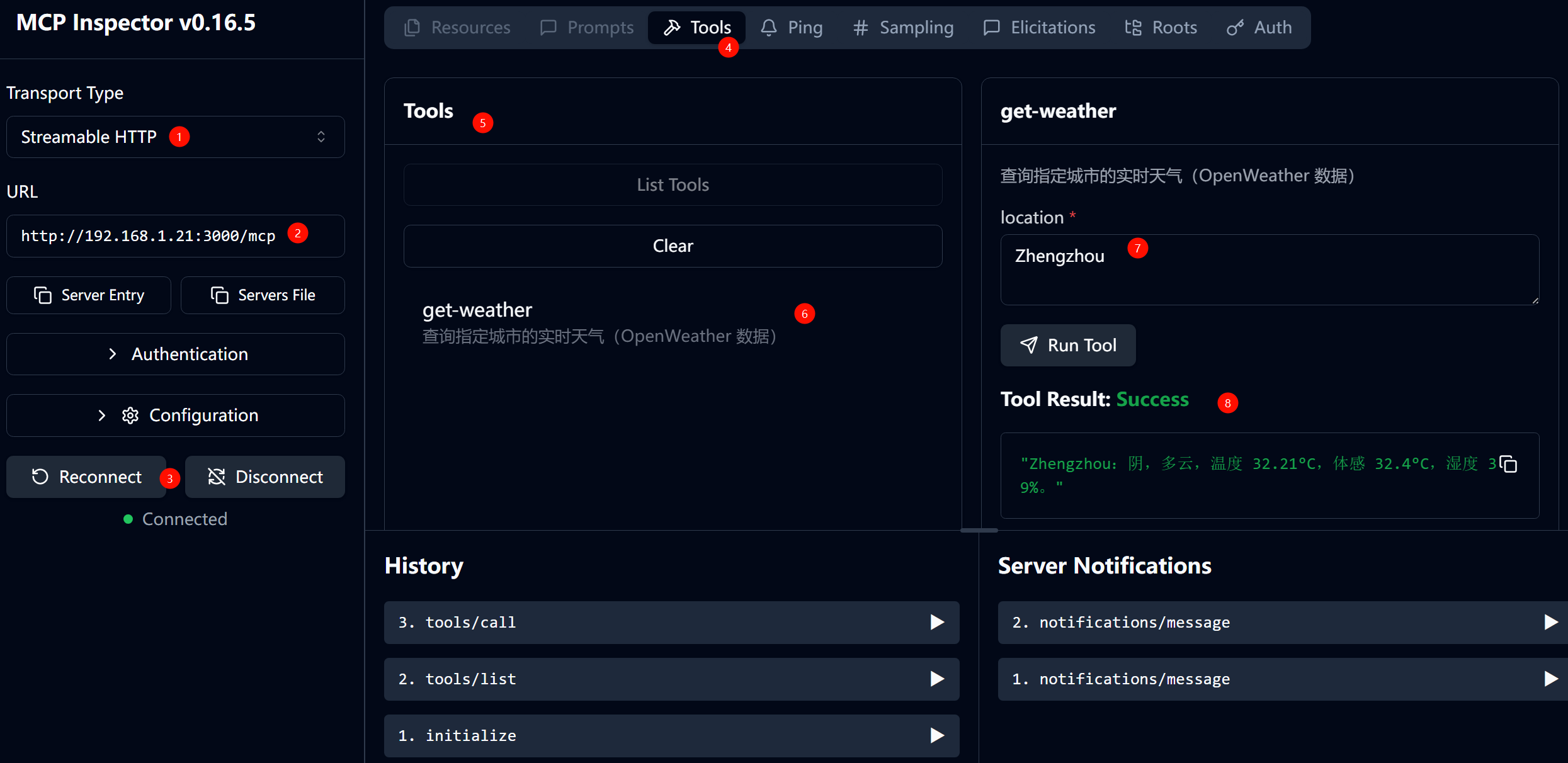
- 选择HTTP流式模式,选择运行地址:
http://192.168.1.21:3000/mcp,然后点击connect、点击List Tools、点击get-weather、输入地名进行测试
MCP客户端连接
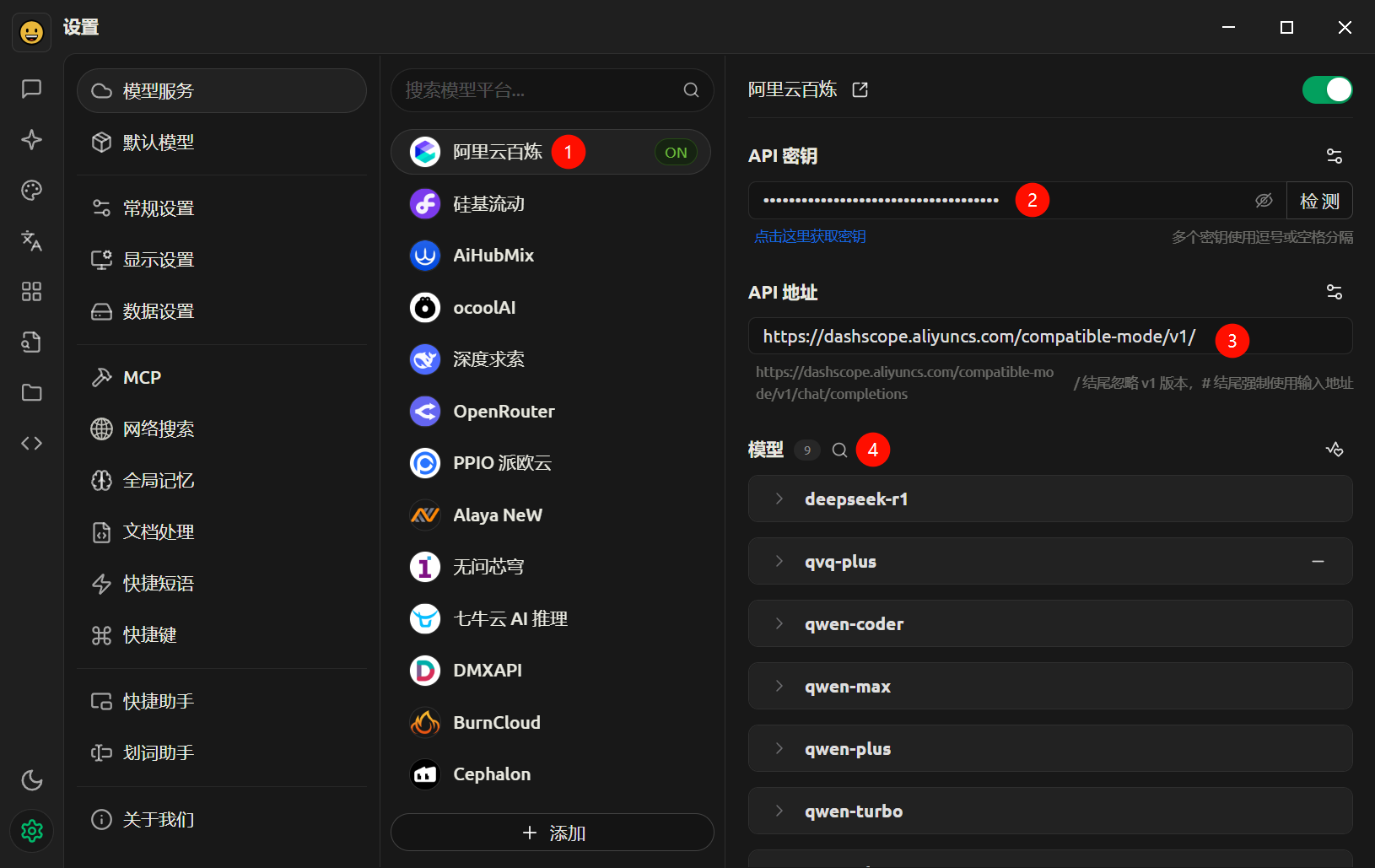
- 安装cherry studio,配置模型和MCP服务。
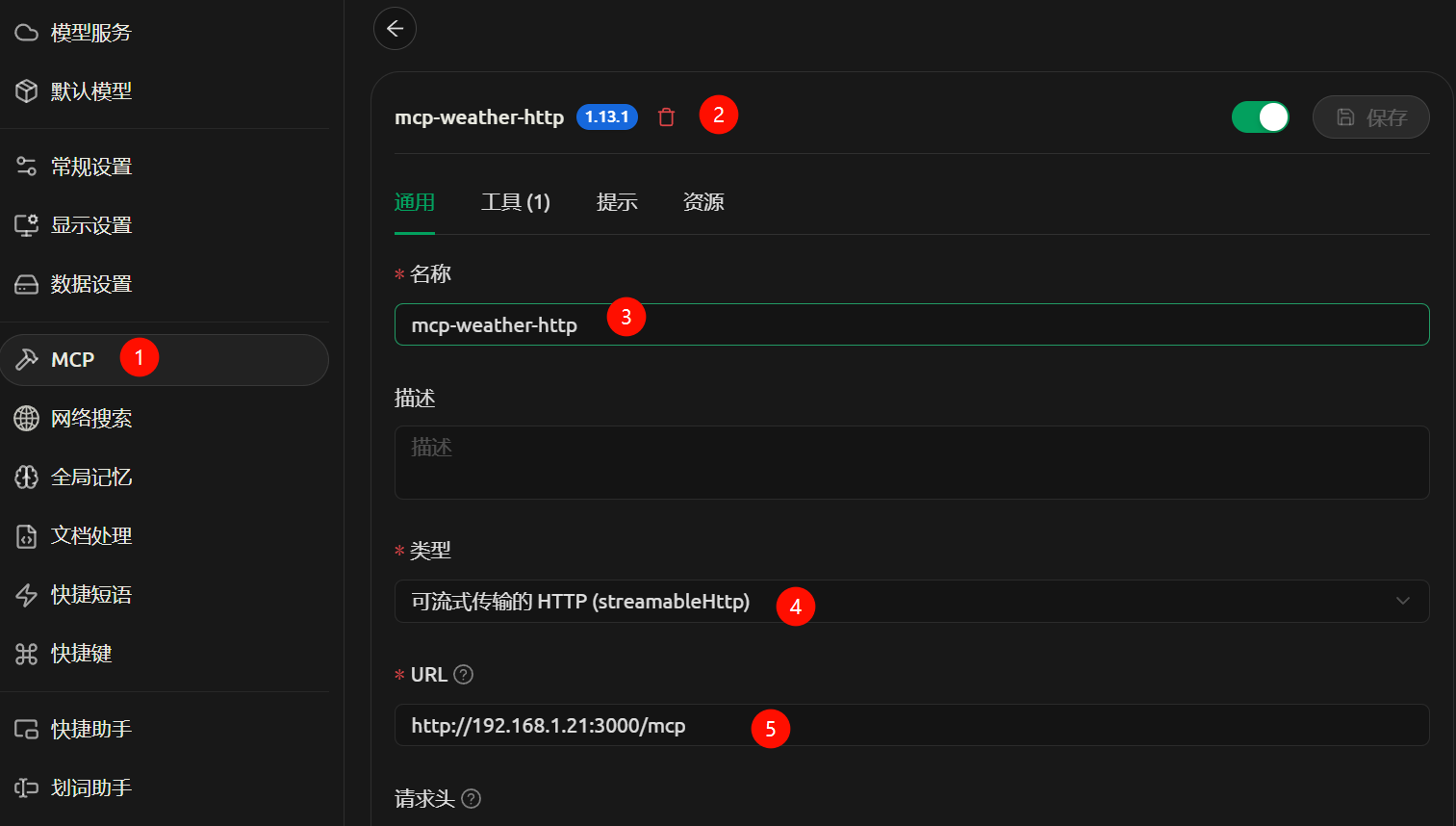
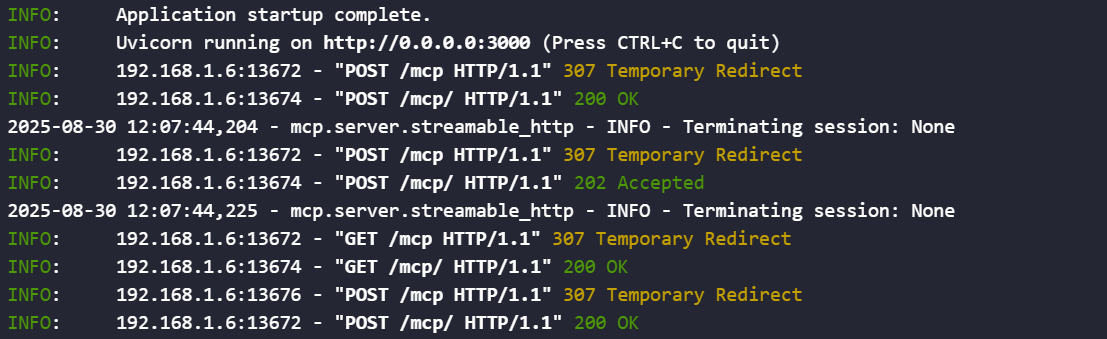
- 服务器终端中可以查看到连接日志。
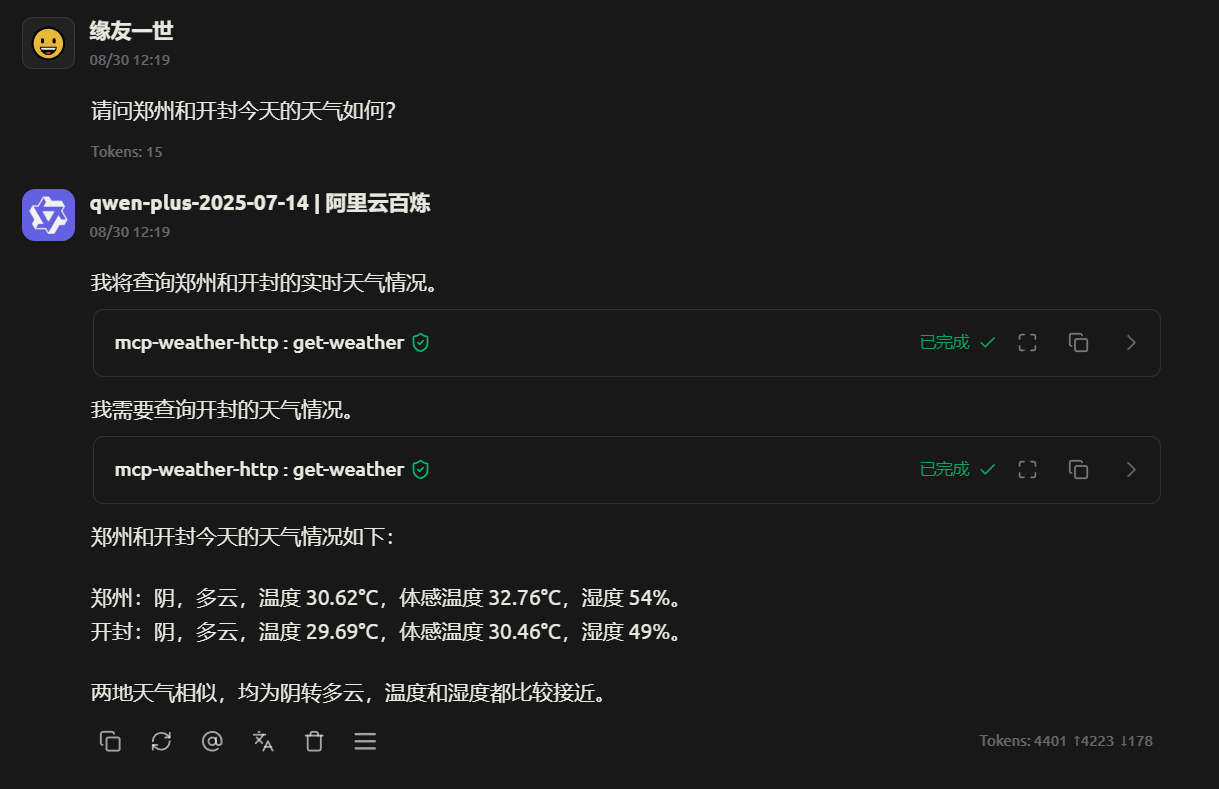
- 创建对话,选择模型和MCP服务器进行对话测试。
流式HTTP MCP服务器发布(未实践)
-
测试完成后,即可上线发布。可以考虑发布到pypi平台。
bash# 回到项目主目录 # cd /xxx/mcp-weather-http uv pip install build twine python -m build python -m twine upload dist/* -
本地安装
bashpip install mcp-weather-http -
开启服务
pythonuv run mcp-weather-http --api-key YOUR_API_KEY -
然后,即可使用
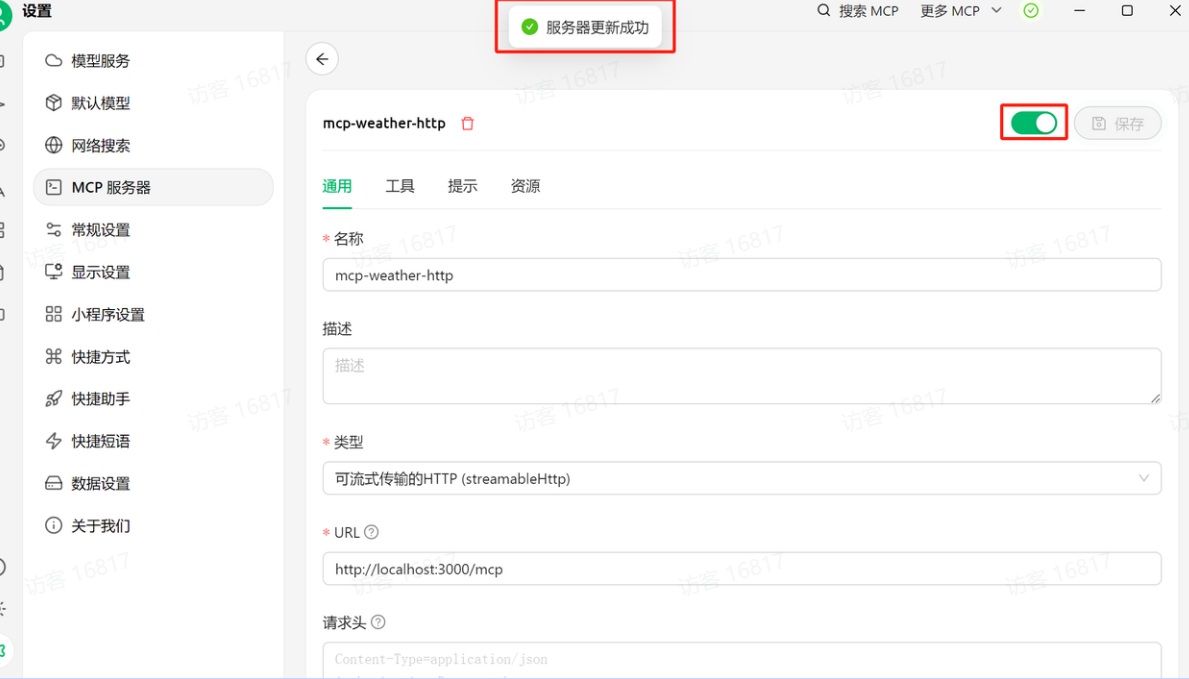
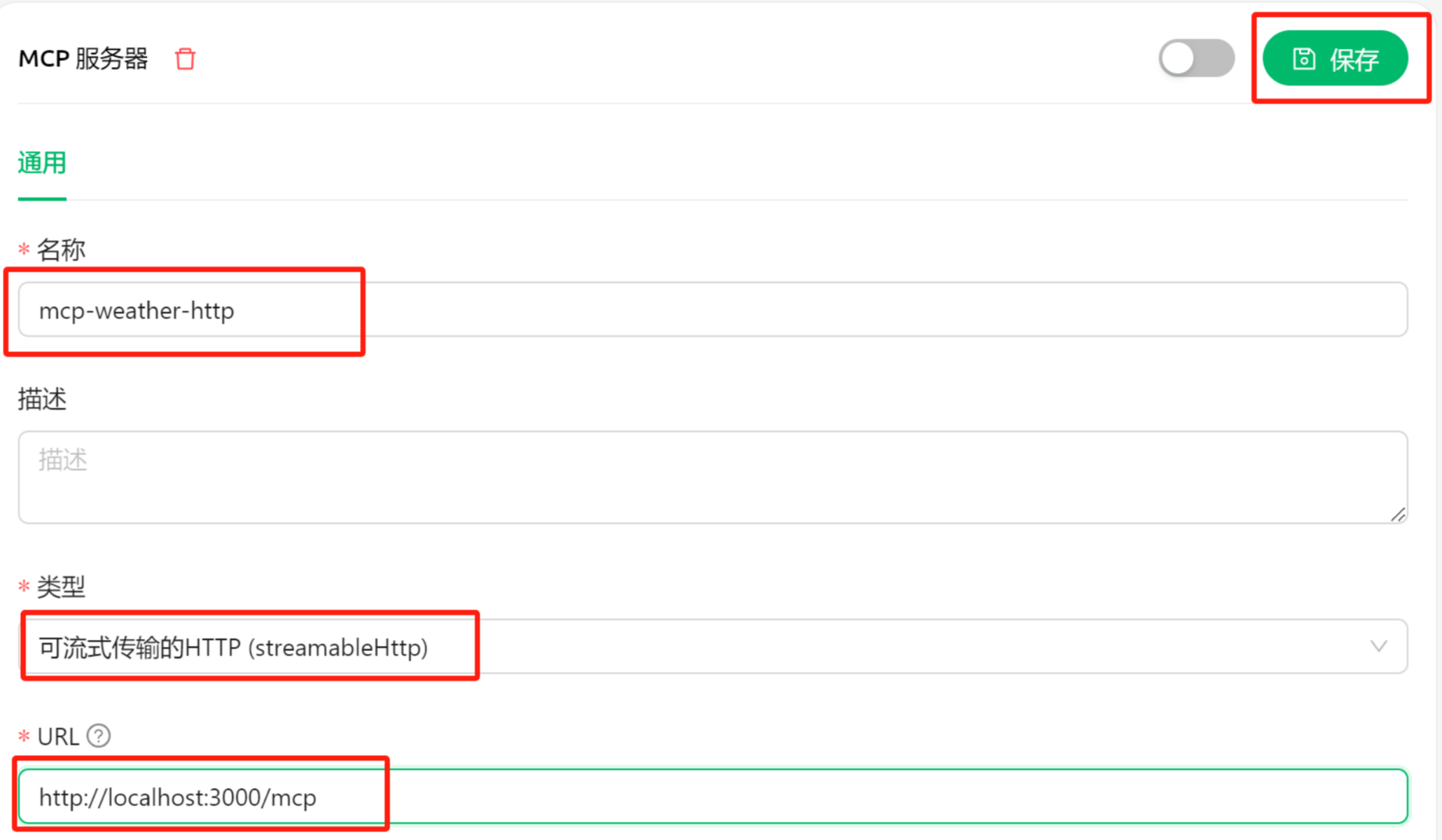
Cherry studio连接流式HTTP模式下的MCP服务器,还是和此前一样的连接流程,输入服务器名称mcp-weather-http,并选择流式传输类型,并选择服务器地址:http://localhost:3000/mcp,然后点击保存。
-
若显示服务器更新成功,则表示已经连接上MCP服务器。