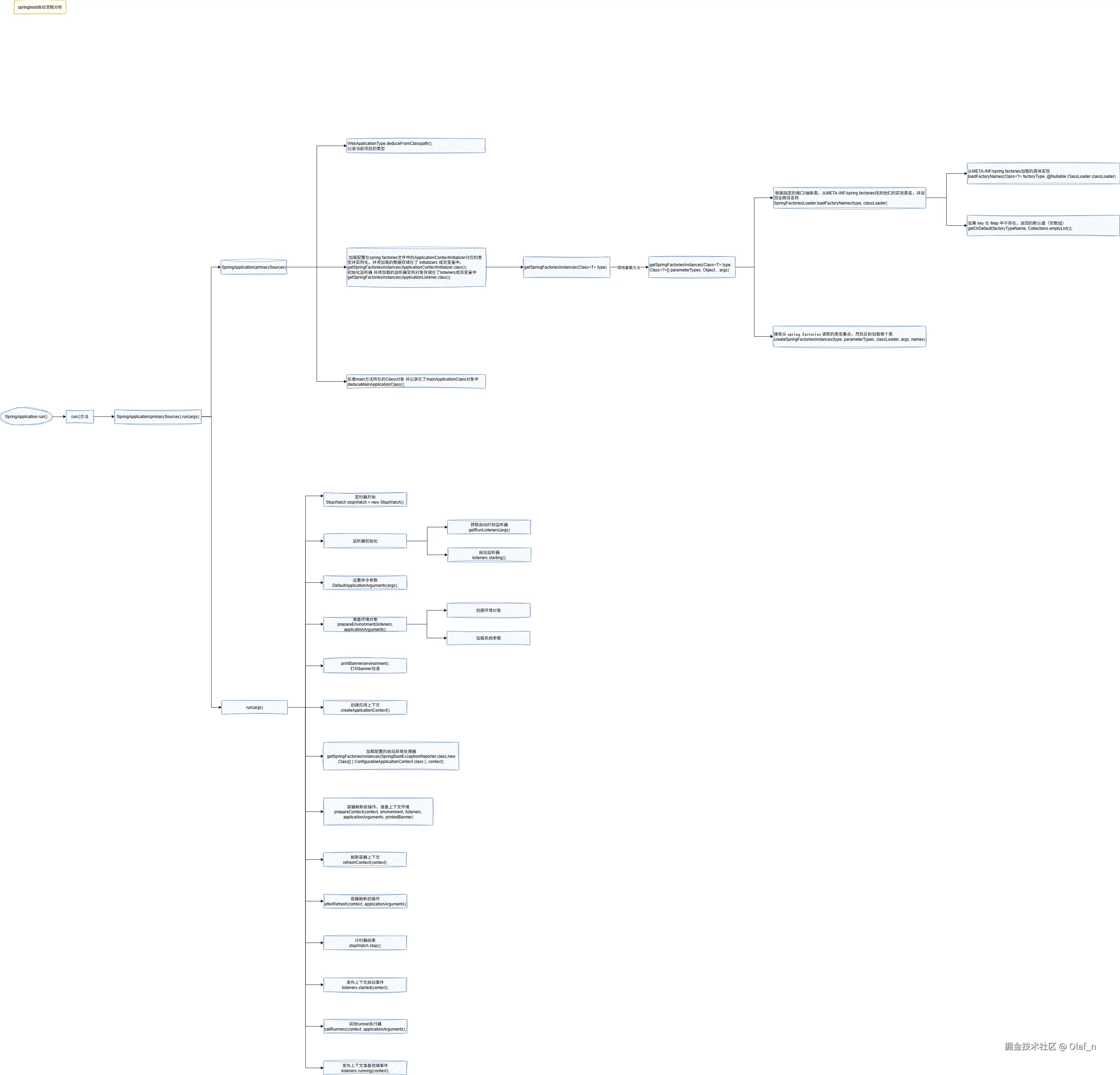
SpringBoot启动流程
SpringBoot启动入口
typescript
@SpringBootApplication
public class StartApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(StartApp.class);
}
}run方法
run方法里面的内容
typescript
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
// 调用重载的run方法,将传递的Class对象封装为了一个数组
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}run方法里面重载了一个run方法
typescript
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}重载后的Run方法里面又调用了SpringApplication构造器和另外一个Run方法,将这两个方法拆开来看
SpringApplication 构造器
scss
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 传递的resourceLoader为null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 记录主方法的配置类名称
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 记录当前项目的类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 加载配置在spring.factories文件中的ApplicationContextInitializer对应的类型并实例化
// 并将加载的数据存储在了 initializers 成员变量中。
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 初始化监听器 并将加载的监听器实例对象存储在了listeners成员变量中
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 反推main方法所在的Class对象 并记录在了mainApplicationClass对象中
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}这个构造器做了以下几个操作
- 记录项目的类型
- 加载配置在spring.factories文件中的ApplicationContextInitializer
- 加载配置在spring.factories文件中的ApplicationListener
- 反推main方法所在的Class对象是在那个类里面
webApplicationType
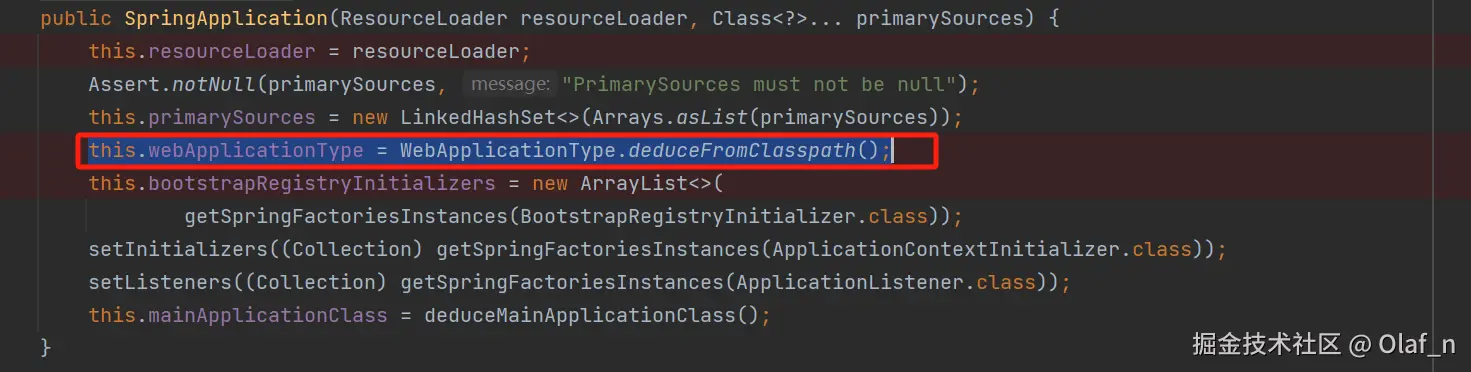
发现这个是一个枚举类
arduino
public enum WebApplicationType {
/**
* The application should not run as a web application and should not start an
* embedded web server.
*/
NONE,
/**
* The application should run as a servlet-based web application and should start an
* embedded servlet web server.
*/
SERVLET,
/**
* The application should run as a reactive web application and should start an
* embedded reactive web server.
*/
REACTIVE;
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet";
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer";
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
// 存在webflux 并且不存在webmvc和jersey,返回reactive
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
// SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES这个里面没有发现servlet和configurableWebApplicationContext
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
// 不属于以上的几种情况统统返回servlet
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
}发现有一些静态变量,这些个静态变量绑定的就是一些java类的全路径
isPresent方法,通过反射获取对应的class对象,存在就返回true,不存在返回false
typescript
public static boolean isPresent(String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
forName(className, classLoader);
return true;
}
catch (IllegalAccessError err) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Readability mismatch in inheritance hierarchy of class [" +
className + "]: " + err.getMessage(), err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// Typically ClassNotFoundException or NoClassDefFoundError...
return false;
}
}setInitializers
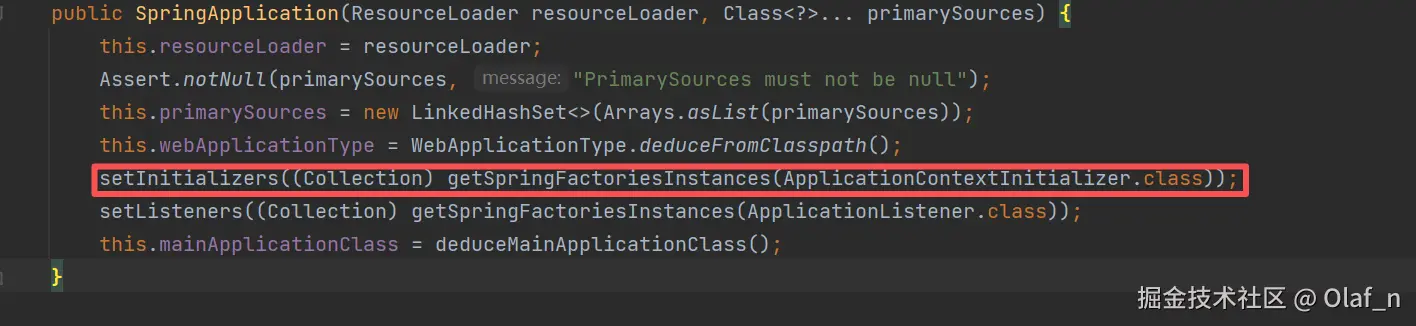
从spring-boot 和 springboot-autoconfigure包下的META-INF下的spring-factories下面读取org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer的内容
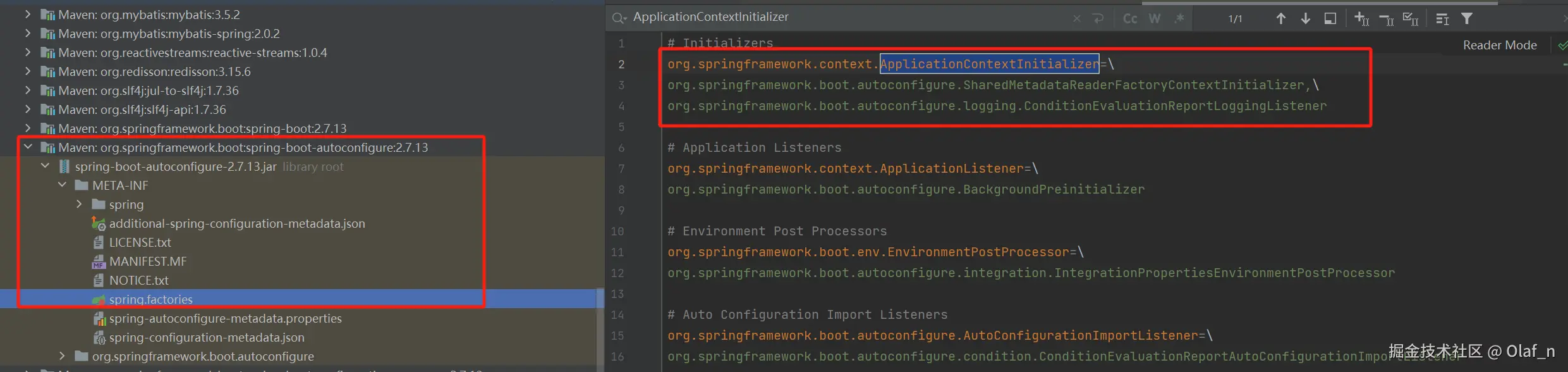
typescript
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactorieInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
// 获取类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// 从META-INF/spring.factories里面加载相关的配置类
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 根据从从META-INF/spring.factories读取出来的内容,初始化成对应的实例bean
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader) 方法
这个方法就是从 META-INF/spring.factories 配置文件中加载指定接口或抽象类对应的实现类全限定名,并返回实现类列表。
less
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}createSpringFactoriesInstances方法
通过反射创建对应的Bean实例,然后放到一个集合中进行返回。
ini
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}setListeners
读取过过程和setInitializers类似
只不过是换成了从META-INF下的spring-factories文件下读取org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener的内容
mainApplicationClass
StackTrace其实就是记录了程序方法执行的链路,然后找到main方法,它的一个目的就是帮助开发者快速定位异常的发生位置。因为main通常是方法的一个入口,肯定是在栈底。
scss
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args)方法
构建完成以后调用的run方法
scss
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 创建一个任务执行观察器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
// 开始执行记录执行时间
stopWatch.start();
// 声明 ConfigurableApplicationContext 对象
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 声明集合容器用来存储 SpringBootExceptionReporter 启动错误的回调接口
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 设置了一个名为java.awt.headless的系统属性
// 其实是想设置该应用程序,即使没有检测到显示器,也允许其启动.
//对于服务器来说,是不需要显示器的,所以要这样设置.
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 获取 SpringApplicationRunListener 加载的是 EventPublishingRunListener
// 获取启动时到监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 触发启动事件
listeners.starting();
try {
// 构造一个应用程序的参数持有类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 创建并配置环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 配置需要忽略的BeanInfo信息
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 输出的Banner信息
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建应用上下文对象
context = createApplicationContext();
// 加载配置的启动异常处理器
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 刷新前操作
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新应用上下文 完成Spring容器的初始化
refreshContext(context);
// 刷新后操作
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 结束记录启动时间
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 事件广播 启动完成了
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 事件广播启动出错了
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 监听器运行中
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 返回上下文对象--> Spring容器对象
return context;
}针对以上的步骤进行总结
- 创建了一个任务执行的观察器,统计启动的时间
- 声明ConfigurableApplicationContext对象
- 声明集合容器来存储SpringBootExceptionReporter即启动错误的回调接口
- 设置java.awt.headless的系统属性
- 获取我们之间初始化的监听器(EventPublishingRunListener),并触发starting事件
- 创建ApplicationArguments这是一个应用程序的参数持有类
- 创建ConfigurableEnvironment这时一个配置环境的对象
- 配置需要忽略的BeanInfo信息
- 配置Banner信息对象
- 创建对象的上下文对象
- 加载配置的启动异常的回调异常处理器
- 刷新应用上下文,本质就是完成Spring容器的初始化操作
- 启动结束记录启动耗时
- 完成对应的事件广播
- 返回应用上下文对象。