map
1 数据结构
go
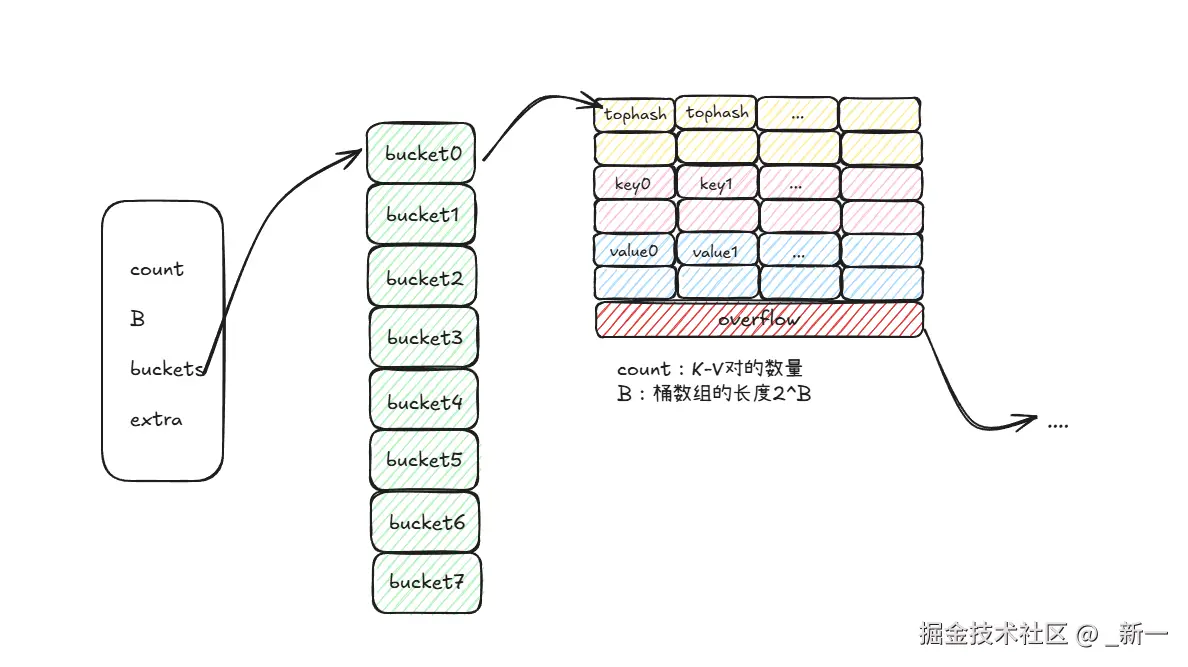
type hmap struct {
count int
flags uint8
B uint8
noverflow uint16
hash0 uint32
buckets unsafe.Pointer
oldbuckets unsafe.Pointer
nevacuate uintptr
extra *mapextra
}-
count: map 中 key-value 对的总数;
-
flags: map 的状态标识符;
goconst ( // flags iterator = 1 // there may be an iterator using buckets // 有迭代器可能正在使用 buckets oldIterator = 2 // there may be an iterator using oldbuckets // 有迭代器可能正在使用 oldbuckets hashWriting = 4 // a goroutine is writing to the map // 有协程在写 map sameSizeGrow = 8 // the current map growth is to a new map of the same size // 等量扩容的标记 ) -
B: 桶数组长度的指数,桶数组长度为
2^B; -
noverflow: map 中溢出桶的数量;
-
hash0: 随机因子;
-
buckets: 桶数组,是一个指针指向的连续内存块;
-
oldbuckets: 扩容过程中老的桶数组;
-
nevacuate: 扩容过程中的进度标识符,小于此下标的 buckets 都已迁移完成;
-
extra: 预申请的溢出桶;
go
type bmap struct {
tophash [abi.MapBucketCount]uint8
}- bmap 就是 map 中桶的具体数据结构,是上图中 bucket0 指向的内存块,一个桶可以存储8组 key-value 对,以及一个指向下一个 bmap的指针;
- 每组 bmap 包含 key 高8为哈希值
tophash和对应8为key和value组成; - 数据结构中只记录了
tophash,因为是连续的内存块,所以通过内存偏移就可以直接找到key和value的位置;
2 创建
go
//m := make(map[keyType]valType, hint)时触发创建逻辑
func makemap(t *maptype, hint int, h *hmap) *hmap {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(uintptr(hint), t.Bucket.Size_)
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc {
hint = 0
}
if h == nil {
h = new(hmap)
}
h.hash0 = uint32(rand()) // 取随机因子
// 计算实际需要的最小桶数组长度
B := uint8(0)
for overLoadFactor(hint, B) {
B++
}
h.B = B
if h.B != 0 {
var nextOverflow *bmap
// 初始化 buckets(分配 buckets 所需要的内存), 同时会检查是否需要提前分配一些空闲的溢出桶
h.buckets, nextOverflow = makeBucketArray(t, h.B, nil)
if nextOverflow != nil { // 如果预分配了空闲的溢出桶数组, 则初始化extra字段
h.extra = new(mapextra)
h.extra.nextOverflow = nextOverflow
}
}
return h
}
// 检查kv对的数量是否大于8, 若不大于则用一个桶就可以存下 2^0=1
// kv对 / 桶数量(2^B) > 负载因子(6.5) => 需要扩容 B++
func overLoadFactor(count int, B uint8) bool {
return count > abi.MapBucketCount && uintptr(count) > loadFactorNum*(bucketShift(B)/loadFactorDen)
}初始化 map buckets 的函数实现,makeBucketArray :
go
func makeBucketArray(t *maptype, b uint8, dirtyalloc unsafe.Pointer) (buckets unsafe.Pointer, nextOverflow *bmap) {
base := bucketShift(b)
nbuckets := base
// go的设计者认为 b>=4 时桶溢出概率会变大, 这个时候需要预分配溢出桶的内存
if b >= 4 {
// 实际桶的数量是: 已分配桶的数量 + 溢出桶的数量(2^(b-4))
nbuckets += bucketShift(b - 4)
// sz为加上溢桶后存储桶所需的内存
sz := t.Bucket.Size_ * nbuckets
// 内存对齐下
up := roundupsize(sz, !t.Bucket.Pointers())
// 若内存对齐后和实际计算的不一致, 则根据内存对齐后所需的内存空间大小计算出实际桶的数量
if up != sz {
nbuckets = up / t.Bucket.Size_
}
}
if dirtyalloc == nil { // 以nbuckets为桶数组分配大小
buckets = newarray(t.Bucket, int(nbuckets))
} else { // 清空原来的buckets内存空间
buckets = dirtyalloc
size := t.Bucket.Size_ * nbuckets
if t.Bucket.Pointers() {
memclrHasPointers(buckets, size)
} else {
memclrNoHeapPointers(buckets, size)
}
}
// 需要分配溢出桶的情况
if base != nbuckets {
nextOverflow = (*bmap)(add(buckets, base*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
last := (*bmap)(add(buckets, (nbuckets-1)*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
last.setoverflow(t, (*bmap)(buckets))
}
return buckets, nextOverflow
}3 读取
go
func mapaccess1(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
...
// ①
if h == nil || h.count == 0 {
if err := mapKeyError(t, key); err != nil {
panic(err) // see issue 23734
}
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}
// ②
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map read and map write")
}
// ③
hash := t.Hasher(key, uintptr(h.hash0))
m := bucketMask(h.B)
b := (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, (hash&m)*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
// ④
if c := h.oldbuckets; c != nil {
if !h.sameSizeGrow() {
m >>= 1
}
oldb := (*bmap)(add(c, (hash&m)*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
if !evacuated(oldb) {
b = oldb
}
}
// ⑤
top := tophash(hash)
bucketloop:
for ; b != nil; b = b.overflow(t) {
for i := uintptr(0); i < abi.MapBucketCount; i++ {
if b.tophash[i] != top {
if b.tophash[i] == emptyRest {
break bucketloop
}
continue
}
k := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+i*uintptr(t.KeySize))
if t.IndirectKey() {
k = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(k))
}
if t.Key.Equal(key, k) {
e := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize)+i*uintptr(t.ValueSize))
if t.IndirectElem() {
e = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(e))
}
return e
}
}
}
return unsafe.Pointer(&zeroVal[0])
}- ①:若 map 未初始化或 map 中元素为空,则直接返回 map 的零值;
- ②:若此时有 goroutine 在并发写 map,则直接抛出 fatal;
- ③:根据 key 计算出对应的哈希值,然后对当前桶数组进行取模和偏移找到实际桶数组的下标;
- ④:这里需要判断下当前 map 是否处于扩容阶段,若是:
- 判断当前 map 是否为增量扩容,若是的话取老桶数组需要桶数组长度除2减1
- 然后根据老桶数组的指针进行取模偏移找到对应的桶数组下标
- 通过 evacuated 方法判断数据是否已迁移到新桶中,若还没有则需要取老桶进行遍历:
b = oldb
- ⑤:到了遍历桶数组内部结构的模块了:
- 先取哈希值的高8位
- 两层循环遍历,外层循环为当前桶数组位置的桶链表;内存循环为遍历8位的 tophash 值
- 检查每个位置上 tophash 值,看看是否和当前哈希值的高8位值匹配,若不匹配有个小技巧:不匹配且当前位置 tophash 未放过元素,则判定后续也无匹配项,可以直接打破循环,返回零值
- 倘若找到了相等的 key,则通过地址偏移的方式取到对应位置上的 key,再检查下 key 坐标中存的值是否真的和查询的相等,若相等则通过地址偏移的方式找到对应位置上的 value 返回即可
读流程核心的点就一个:在扩容的过程中查找时,需要注意 buckets 是否已经迁移,若未迁移需要在旧桶当中进行读取;
4 写入&更新
go
func mapassign(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
// map 为空, 触发panic
if h == nil {
panic(plainError("assignment to entry in nil map"))
}
...
// 并发写, 直接fatal
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
// 计算key的哈希值, 然后将当前map标记为正在写map
hash := t.Hasher(key, uintptr(h.hash0))
h.flags ^= hashWriting
// 如果buckets为nil, 则分配个内存块
if h.buckets == nil {
h.buckets = newobject(t.Bucket)
}
// ①
again:
bucket := hash & bucketMask(h.B)
if h.growing() {
growWork(t, h, bucket)
}
b := (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, bucket*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
top := tophash(hash)
// ②
var inserti *uint8
var insertk unsafe.Pointer
var elem unsafe.Pointer
// ③
bucketloop:
for {
for i := uintptr(0); i < abi.MapBucketCount; i++ {
// Ⅰ
if b.tophash[i] != top {
if isEmpty(b.tophash[i]) && inserti == nil {
inserti = &b.tophash[i]
insertk = add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+i*uintptr(t.KeySize))
elem = add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize)+i*uintptr(t.ValueSize))
}
if b.tophash[i] == emptyRest {
break bucketloop
}
continue
}
// Ⅱ
k := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+i*uintptr(t.KeySize))
if t.IndirectKey() {
k = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(k))
}
if !t.Key.Equal(key, k) {
continue
}
// Ⅲ
if t.NeedKeyUpdate() {
typedmemmove(t.Key, k, key)
}
elem = add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize)+i*uintptr(t.ValueSize))
goto done
}
ovf := b.overflow(t)
if ovf == nil {
break
}
b = ovf
}
// ④ 这里是触发扩容的位置
if !h.growing() && (overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) || tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B)) {
hashGrow(t, h)
goto again
}
// ⑤
if inserti == nil {
newb := h.newoverflow(t, b)
inserti = &newb.tophash[0]
insertk = add(unsafe.Pointer(newb), dataOffset)
elem = add(insertk, abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize))
}
if t.IndirectKey() {
kmem := newobject(t.Key)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(insertk) = kmem
insertk = kmem
}
if t.IndirectElem() {
vmem := newobject(t.Elem)
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(elem) = vmem
}
typedmemmove(t.Key, insertk, key)
*inserti = top
h.count++
// ⑥
done:
if h.flags&hashWriting == 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
h.flags &^= hashWriting
if t.IndirectElem() {
elem = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(elem))
}
return elem
}- ①:获取桶数组的下标;检查当前map是否处于扩容的流程,若是的话则去协助进行渐进式扩容完成一部分扩容的工作;然后偏移得到当前这个桶节点的链表头节点位置,并且计算出高八位top的值;
- ②:定义三个指针容器:
inserti:tophash 要插入的地址insertk:key 要插入的地址elem: value 要插入的地址
- ③:还是双层遍历外层是当前桶节点的桶链表,内层是八位tophash地址:
- Ⅰ:这里是插入的逻辑:在遇到第一个空的凹槽的位置就将对应空凹槽的 tophash、key、value给记下来;
- Ⅱ:再根据偏移位置检查 key 是否为真的要找的
- Ⅲ:找到了对应的凹槽就将偏移后对应 value 的地址赋值给 elem,然后
goto done走收尾流程
- ④:触发扩容的时机:当前没有在扩容阶段 且 (满足开启增量扩容检查 或 满足开启等量扩容检查)
- ⑤:这里意味这整个已有桶节点链表遍历下来没有空位置可以插入,所以此时就需要申请新的溢出桶节点
- ⑥:首尾的操作,重置 map 的写标记,返回实际 value 的位置 elem
4.1 扩容机制
map 的扩容类型分为两类:
-
增量扩容
-
条件:kv对数量大于8 且 kv对数量 / 桶数量(2^B) > 负载因子(6.5)
-
表现:桶数组的长度增长为原来的 2 倍
-
目的:降低每个桶中 k-v 对的数量,优化 map 操作的时间复杂度
-
方式:
- key 的哈希值的最后 n 位决定这个 key 会被放到哪个桶节点上,那么在触发增量扩容后桶数组的长度扩大为原来的一倍;
- 这个时候就需要用哈希值的最后 n+1 位来确定 key 会被放到哪个桶节点上;
- 由于后 n 位都一样,所以最终的索引位置取决于哈希值第 n+1 位,若为 0 则新索引位较扩容前不变,若为 1 则新索引位为原索引位加上原桶数组长度(就是在原索引位的基础上加第 n+1 位的十进制数)
-
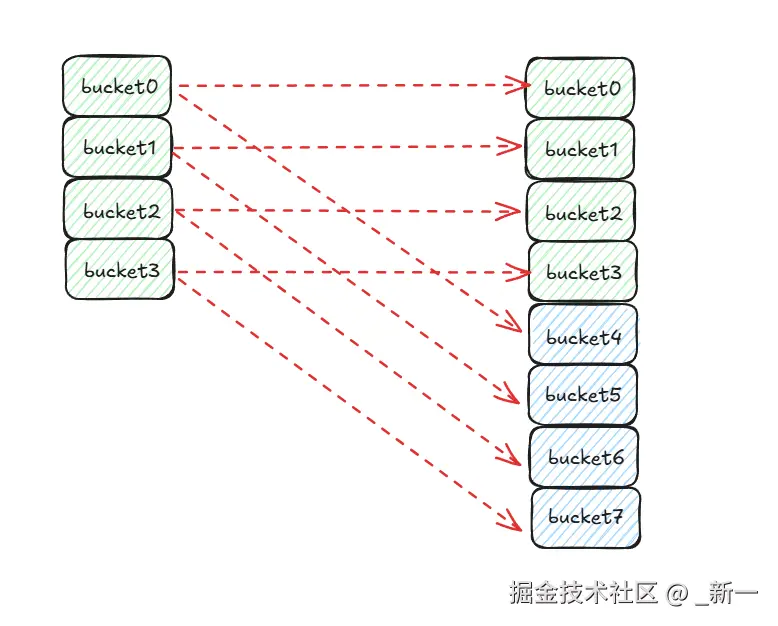
-
接下来就是遍历老桶数组的每个 k-v 对,根据正常的写流程取哈希值、计算索引、遍历溢出桶节点、放入对饮的桶节点中;
-
等量扩容:
- 条件:溢出桶的数量 >= 桶数量(2^B)
- 表现:桶数组的长度保持不变
- 目的:提高桶主体结构的填充率,使桶节点的填充密度更高,减少溢出桶节点的数量
- 方式:
- 由于是等量扩容,所以就正常遍历老桶数组,重新写入到新的桶数组中即可;
map 的扩容发生在什么时候:
扩容的条件一定是发生在写操作时的,更新操作也不会触发扩容;
写 map 新插入 k-v 对之前,会发起是否需要扩容的逻辑判断:
go
func mapassign(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) unsafe.Pointer {
// ...
if !h.growing() && (overLoadFactor(h.count+1, h.B) || tooManyOverflowBuckets(h.noverflow, h.B)) {
hashGrow(t, h)
goto again
}
/ ...
}
// map是否已经开启扩容模式
func (h *hmap) growing() bool {
return h.oldbuckets != nil
}
// 增量扩容判断条件
// kv对数量大于8 且 kv对数量 / 桶数量(2^B) > 负载因子(6.5)
func overLoadFactor(count int, B uint8) bool {
return count > abi.MapBucketCount && uintptr(count) > loadFactorNum*(bucketShift(B)/loadFactorDen)
}
// 等量扩容判断条件
// 溢出桶的数量 >= 桶数量(2^B)
func tooManyOverflowBuckets(noverflow uint16, B uint8) bool {
if B > 15 {
B = 15
}
return noverflow >= uint16(1)<<(B&15)
}map 在扩容阶段还会触发扩容吗:
不会
因为 map 不是并发安全的数据结构,所以不存在并发写的情况,那么在某次写操作时触发了扩容那么再次触发触发扩容操作就得是下次的写操作了;
又因为 map 的扩容是渐进式的借助写入、更新、删除操作进行扩容的,所以下次写操作要满足触发扩容的条件的数量级时,这些写操作已经完成了上次的扩容;
所以并不会发生在扩容阶段还会触发下次扩容;
map 哪些操作会去做渐进扩容:
写入 & 更新:mapassign
删除:mapdelete
map 扩容的具体流程:
map 采用渐进式扩容的方式,避免一次性数据迁移导致的性能问题;
go
func growWork(t *maptype, h *hmap, bucket uintptr) {
// make sure we evacuate the oldbucket corresponding
// to the bucket we're about to use
// 把即将使用的旧存储桶迁移到新桶
evacuate(t, h, bucket&h.oldbucketmask())
// evacuate one more oldbucket to make progress on growing
// 仍然处于扩容中, 则按顺序触发迁移
if h.growing() {
evacuate(t, h, h.nevacuate)
}
}
go
func evacuate(t *maptype, h *hmap, oldbucket uintptr) {
b := (*bmap)(add(h.oldbuckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
newbit := h.noldbuckets()
if !evacuated(b) {
var xy [2]evacDst
x := &xy[0]
x.b = (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
x.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(x.b), dataOffset)
x.e = add(x.k, abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize))
if !h.sameSizeGrow() {
y := &xy[1]
y.b = (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, (oldbucket+newbit)*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
y.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(y.b), dataOffset)
y.e = add(y.k, abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize))
}
for ; b != nil; b = b.overflow(t) {
k := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset)
e := add(k, abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize))
for i := 0; i < abi.MapBucketCount; i, k, e = i+1, add(k, uintptr(t.KeySize)), add(e, uintptr(t.ValueSize)) {
top := b.tophash[i]
if isEmpty(top) {
b.tophash[i] = evacuatedEmpty
continue
}
if top < minTopHash {
throw("bad map state")
}
k2 := k
if t.IndirectKey() {
k2 = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(k2))
}
var useY uint8
if !h.sameSizeGrow() {
hash := t.Hasher(k2, uintptr(h.hash0))
if h.flags&iterator != 0 && !t.ReflexiveKey() && !t.Key.Equal(k2, k2) {
useY = top & 1
top = tophash(hash)
} else {
if hash&newbit != 0 {
useY = 1
}
}
}
if evacuatedX+1 != evacuatedY || evacuatedX^1 != evacuatedY {
throw("bad evacuatedN")
}
b.tophash[i] = evacuatedX + useY
dst := &xy[useY]
if dst.i == abi.MapBucketCount {
dst.b = h.newoverflow(t, dst.b)
dst.i = 0
dst.k = add(unsafe.Pointer(dst.b), dataOffset)
dst.e = add(dst.k, abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize))
}
dst.b.tophash[dst.i&(abi.MapBucketCount-1)] = top
if t.IndirectKey() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(dst.k) = k2
} else {
typedmemmove(t.Key, dst.k, k)
}
if t.IndirectElem() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(dst.e) = *(*unsafe.Pointer)(e)
} else {
typedmemmove(t.Elem, dst.e, e)
}
dst.i++
dst.k = add(dst.k, uintptr(t.KeySize))
dst.e = add(dst.e, uintptr(t.ValueSize))
}
}
if h.flags&oldIterator == 0 && t.Bucket.Pointers() {
b := add(h.oldbuckets, oldbucket*uintptr(t.BucketSize))
ptr := add(b, dataOffset)
n := uintptr(t.BucketSize) - dataOffset
memclrHasPointers(ptr, n)
}
}
if oldbucket == h.nevacuate {
advanceEvacuationMark(h, t, newbit)
}
}5 删除
go
func mapdelete(t *maptype, h *hmap, key unsafe.Pointer) {
...
if h == nil || h.count == 0 {
if err := mapKeyError(t, key); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
return
}
if h.flags&hashWriting != 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
hash := t.Hasher(key, uintptr(h.hash0))
h.flags ^= hashWriting
bucket := hash & bucketMask(h.B)
if h.growing() {
growWork(t, h, bucket)
}
b := (*bmap)(add(h.buckets, bucket*uintptr(t.BucketSize)))
bOrig := b
top := tophash(hash)
search:
for ; b != nil; b = b.overflow(t) {
for i := uintptr(0); i < abi.MapBucketCount; i++ {
if b.tophash[i] != top {
if b.tophash[i] == emptyRest {
break search
}
continue
}
k := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+i*uintptr(t.KeySize))
k2 := k
if t.IndirectKey() {
k2 = *((*unsafe.Pointer)(k2))
}
if !t.Key.Equal(key, k2) {
continue
if t.IndirectKey() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(k) = nil
} else if t.Key.Pointers() {
memclrHasPointers(k, t.Key.Size_)
}
e := add(unsafe.Pointer(b), dataOffset+abi.MapBucketCount*uintptr(t.KeySize)+i*uintptr(t.ValueSize))
if t.IndirectElem() {
*(*unsafe.Pointer)(e) = nil
} else if t.Elem.Pointers() {
memclrHasPointers(e, t.Elem.Size_)
} else {
memclrNoHeapPointers(e, t.Elem.Size_)
}
b.tophash[i] = emptyOne
if i == abi.MapBucketCount-1 {
if b.overflow(t) != nil && b.overflow(t).tophash[0] != emptyRest {
goto notLast
}
} else {
if b.tophash[i+1] != emptyRest {
goto notLast
}
}
for {
b.tophash[i] = emptyRest
if i == 0 {
if b == bOrig {
break
}
c := b
for b = bOrig; b.overflow(t) != c; b = b.overflow(t) {
}
i = abi.MapBucketCount - 1
} else {
i--
}
if b.tophash[i] != emptyOne {
break
}
}
notLast:
h.count--
if h.count == 0 {
h.hash0 = uint32(rand())
}
break search
}
}
if h.flags&hashWriting == 0 {
fatal("concurrent map writes")
}
h.flags &^= hashWriting
}6 常见的几个问题
- 可以通过定义 value 为 struct 节约内存,也可以用这种方式实现 set 结构
- map 底层通过哈希值的高八位来做桶内定位;通过低
2^B-1位来决定桶索引 - map 的扩容细节
- map rehash的过程
- map 循环是有序的还是无序的
- map 如何顺序读取
- map 中删除一个 key,它的内存会释放吗
- 怎么处理对 map 进行并发访问