1. 引言
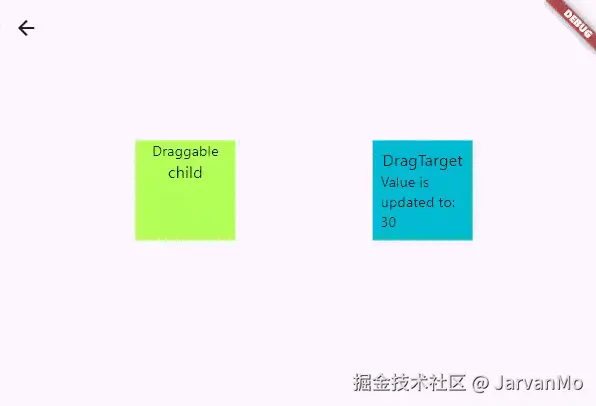
Draggable 是一个可以被拖动到 DragTarget 上的 Widget。
以下是一些最常用的属性。
Draggable:
child、childWhenDragging、data、feedback、onDragCompleted、onDragEnd、onDragStarted、onDragUpdate
 DragTarget:
DragTarget:
builder、onAcceptWithDetails
我稍微修改了官方示例,以突出显示上述属性的用法。
下面的代码展示了我们如何定义 Draggable and DragTarget.
less
Draggable<int>(
// Data 是当前 Draggable 要存储的值.
data: 10,
onDragStarted: controller.onDragStarted,
onDragUpdate: (details) {
controller.onDragUpdate(details);
},
onDragEnd: (details) {
controller.onDragEnd(details);
} ,
onDragCompleted: controller.onDragCompleted,
feedback: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Container(
color: Colors.deepOrange.shade300,
height: 100,
width: 100,
child: Column(
children: [
Text('Draggable').withStyle(fontSize: 12, color: Colors.black),
Text('feedback').withStyle(fontSize: 16, color: Colors.black),
],
)
),
),
childWhenDragging: Container(
height: 100.0,
width: 100.0,
color: Colors.pink.shade200,
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Center(child: Column(
children: [
Text('Draggable'),
Text('Child When Dragging'),
],
)),
),
),
child: Padding(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Container(
height: 100.0,
width: 100.0,
color: Colors.lightGreenAccent,
child: Center(child: Column(
children: [
Text('Draggable'),
Text ('child').withStyle(fontSize: 16),
],
)),
),
),
),
DragTarget<int>(
builder: (BuildContext context, List<dynamic> accepted, List<dynamic> rejected) {
return Container(
height: 100.0,
width: 100.0,
color: Colors.cyan,
child: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(8.0),
child: Center(child: Column(
children: [
Text('DragTarget').withStyle(fontSize: 16),
Text('Value is updated to: ${controller.acceptedData}'),
],
)),
),
);
},
onAcceptWithDetails: (DragTargetDetails<int> details) {
controller.onAcceptWithDetails(details);
},
),Draggable 是一个非常特殊的 Widget,因为它除了 child 属性之外,还有 childWhenDragging 和 feedback 属性。
child是在拖动开始前显示的不可移动的 Widget。- 当拖动开始时,
child会被childWhenDragging替换。 feedback是跟着你的指针(手指或鼠标)移动的可移动的 Widget。
DragTarget 只有 builder 属性,它会根据 Draggable 传递过来的数据来构建子 Widget。
事件会按照以下顺序触发:
DragStart--- 拖动开始时,只会触发一次;DragUpdate--- 在feedback改变位置时,会多次触发;AcceptWithDetails--- 当Draggable被DragTarget接受时,只会触发一次;DragEnd--- 当Draggable被放下时(任何地方),只会触发一次;DragCompleted--- 当Draggable被放到DragTarget上时,只会触发一次。
以下是这些事件的处理程序。
View:
dart
//Draggable
onDragStarted: controller.onDragStarted,
onDragUpdate: (details) {
controller.onDragUpdate(details);
},
onDragEnd: (details) {
controller.onDragEnd(details);
} ,
onDragCompleted: controller.onDragCompleted,
...
//DragTarget
onAcceptWithDetails: (DragTargetDetails<int> details) {
controller.onAcceptWithDetails(details);
},Controller:
dart
void onDragStarted() {
_isDragging = true;
Get.snackbar('onDragStart', '', duration: Duration(seconds: 1));
}
void onDragUpdate(DragUpdateDetails details) {
_position = details.globalPosition;
update();
}
void onDragEnd(DraggableDetails details) {
_isDragging = false;
Get.snackbar('onDragEnd', 'wasAccepted: ${details.wasAccepted}',
duration: Duration(seconds: 1));
update();
}
void onDragCompleted() {
_isDragging = false;
Get.snackbar('onDragComplete', '', duration: Duration(seconds: 1));
}
void onAcceptWithDetails(DragTargetDetails<int> details) {
acceptedData += details.data;
Get.snackbar('onAcceptWithDetails', 'data:${details.data}', duration: Duration(seconds: 1));
}onDragUpdate 会接收 DragUpdateDetails,可用于检索位置。
onDragEnd 会接收 DraggableDetails,其中有一个 wasAccepted 属性。实际上,onDragEnd 在 Draggable 被拖放到 DragTarget 之外时很有用。
onAcceptWithDetails 会接收 DragTargetDetails,可用于检索 data(它被定义为 Draggable 的属性)。
我希望以上的解释足够清晰。😎
完整的代码在这里。
让我们看看一些使用 Draggable 的实用例子。
2. 可重新排序的任务列表

这个例子有意思的地方在于,任务 Widget 被放到了它自己身上。
这通过将 DragTarget 作为 Draggable 的 child 来实现。
dart
Draggable<int>(
data: index,
onDragStarted: () => controller.onDragStarted(index),
onDragEnd: (_) => controller.onDragEnded(),
feedback: Material(
elevation: 4,
child: Container(
width: MediaQuery.of(context).size.width - 32,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(16),
color: Colors.blue.shade200,
child: Text(
task,
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 16),
),
),
),
childWhenDragging: Opacity(
opacity: 0.3,
child: TaskItem(task: task),
),
child: DragTarget<int>( //<-!
builder: (context, candidateData, rejectedData) {
return TaskItem(
task: task,
isDragging: isDragging,
isHighlighted: candidateData.isNotEmpty,
);
},
onAcceptWithDetails: (details) {
controller.reorderTask(details.data, index);
},
),
);完整的代码在这里
3. 带有分类的任务面板

 在这里,(与上一个例子相反),我们有的是在
在这里,(与上一个例子相反),我们有的是在 DragTargets 内部的一个 Draggable 列表。每个分类(待办、进行中、已完成)都是一个 DragTarget,而每个任务则是一个 Draggable。
dart
DragTarget<Map<String, dynamic>>(
builder: (context, candidateData, rejectedData) {
return Container(
color:
candidateData.isNotEmpty ? category.color.withValues(alpha: 0.3) : null,
padding: EdgeInsets.all(8),
child: ListView.builder(
padding: EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 100),
itemCount: category.tasks.length,
itemBuilder: (context, taskIndex) {
return DraggableTask(
context: context,
taskName: category.tasks[taskIndex],
categoryIndex: categoryIndex,
);
},
),
);
},
onAcceptWithDetails: (details) {
controller.moveTask(
details.data['taskName'],
details.data['fromCategoryIndex'],
categoryIndex,
);
},
),完整的代码在这里
4. 拼图游戏模板
在这里,我们使用 onWillAcceptWithDetails 来检查 Draggable 是否会被 DragTarget 接受。
dart
return DragTarget<int>(
builder: (context, candidateData, rejectedData) {
return Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(
color:
candidateData.isNotEmpty ? Colors.green.withValues(alpha: .3) : Colors.white,
borderRadius: BorderRadius.circular(12),
border: Border.all(
color: isPlaced ? Colors.green : Colors.blue.shade200,
width: 2,
),
),
child: isPlaced
? Center(
child: PlaceholderPuzzlePiece(
id: targetId,
isPlaced: true,
),
)
: Center(
child: Text(
'$targetId',
style: TextStyle(
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold,
color: Colors.blue.shade200,
),
),
),
);
},
onWillAcceptWithDetails: (details) { //<-!
// Only accept if this is the correct target for this piece
return controller.isPieceCorrect(targetId, details.data);
},
onAcceptWithDetails: (details) {
controller.placePiece(details.data);
},
);完整的代码在这里
5. Draggable vs LongPressDraggable
Flutter 还有一个类,叫 LongPressDraggable,它和 Draggable 很像,但拖动会在一个延迟后才发生。也就是说,在拖动开始之前,设备必须先识别到长按手势。
我修改了第一个官方示例,用 LongPressDraggable 替代了 Draggable。
它的行为开始变得不一样。如果我们立即开始拖动,什么都不会发生。我们必须在一个点上先长按,当 feedback Widget 出现后,才能开始拖动。
我不太确定为什么或者在什么时候会用 LongPressDraggable 来代替 Draggable,但我确信肯定存在合理的用例。
6. Draggable vs GestureDetector
GestureDetector 可以(除其他外)检测到 HorizontalDrag(水平拖动)、VerticalDrag(垂直拖动)和 Pan(任意方向的自由拖动)。
一些功能既可以用 Draggable 实现,也可以用 GestureDetector 实现。最终的选择取决于具体的用例和/或开发者的偏好。
7. 结论
Draggable 是最实用的 Flutter Widget 之一,每个开发者都应该熟悉它。😉