Spring 中的 initializeBean 方法的内部逻辑小总结
背景
spring-beans 模块中的 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java 文件里有 initializeBean 方法,这个方法会负责 bean 的 initialization(初始化),本文会对其主要逻辑进行总结。
正文
该方法的代码复制如下 ⬇️
java
/**
* Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
* as well as init methods and bean post processors.
* <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans,
* and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
* @see #invokeInitMethods
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
// Skip initialization of a NullBean
if (bean.getClass() == NullBean.class) {
return bean;
}
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}其中的主要逻辑共有 4 步,可以简单概括如下
| 主要步骤 | 做了什么 | 核心代码 |
|---|---|---|
Step 1: 知 (Aware) |
处理与 3 个 XXXAware 接口 |
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); |
Step 2: 前 (Before) |
尝试在 initialization 之前 做点事情 |
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); |
Step 3: 中 (Init) |
initialization(初始化) |
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); |
Step 4: 后 (After) |
尝试在 initialization 之后 做点事情 |
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); |
为了便于查看,我把 4 个步骤的位置在下图中标出来了 ⬇️ 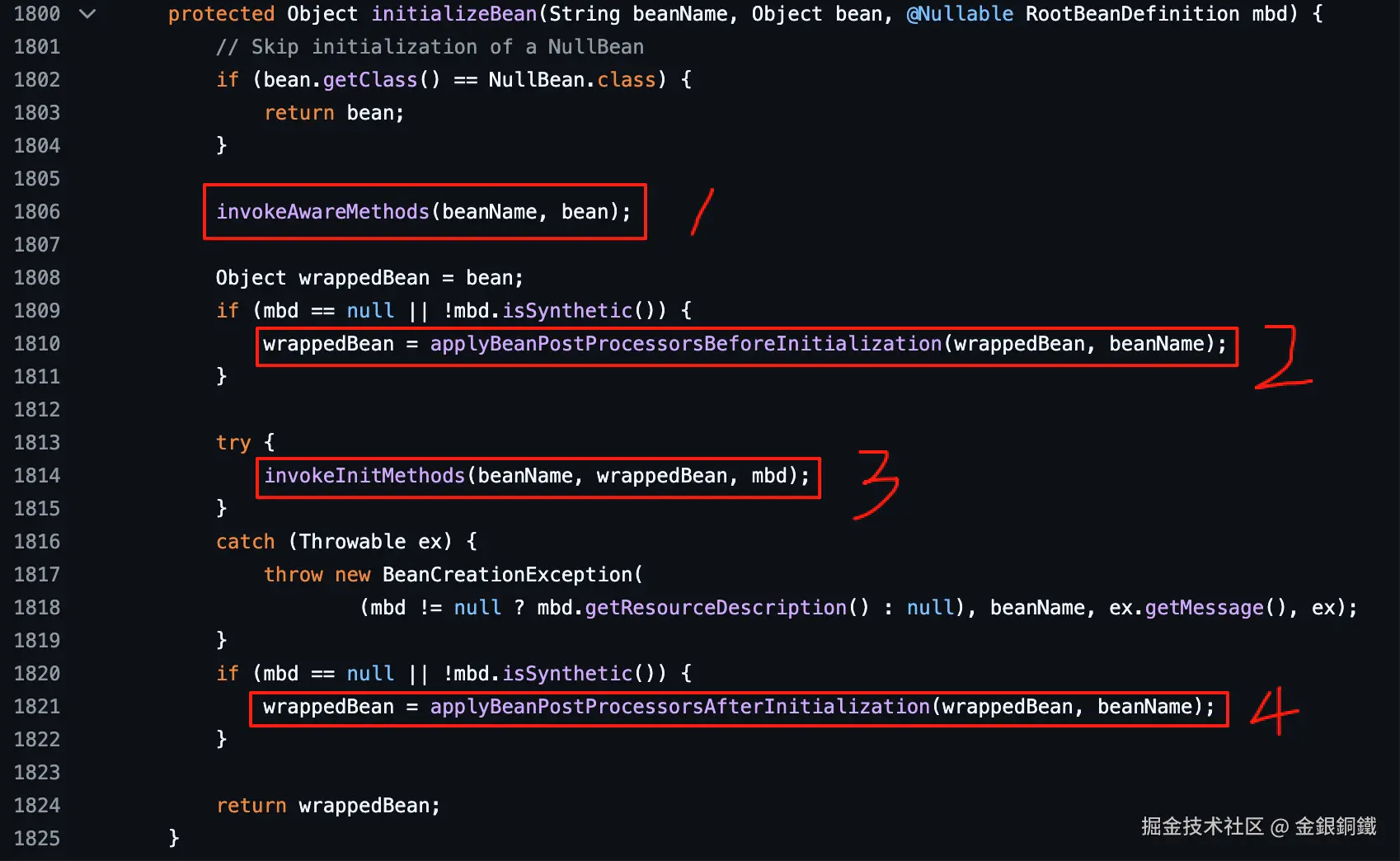
Step 1: 知 (Aware)
invokeAwareMethods(String, Object) 方法的代码复制如下 ⬇️
java
private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware beanNameAware) {
beanNameAware.setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware beanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
beanClassLoaderAware.setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware beanFactoryAware) {
beanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}如果当前的 bean implement 了以下 3 个 XXXAware 接口中的任意一个,在 invokeAwareMethods(String, Object) 方法中就会进行相应处理。
XXXAware 接口 |
例子 |
|---|---|
BeanNameAware |
假设一个 bean <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B 需要感知自身的 beanName,我们可以让 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B implement BeanNameAware 接口,那么在 invokeAwareMethods(String, Object) 方法中就会用 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B 来调用 setBeanName(...) 方法,从而将对应的 beanName 填进去 |
BeanClassLoaderAware |
略 |
BeanFactoryAware |
假设一个 bean <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B 需要感知 BeanFactory,我们可以让 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B implement BeanFactoryAware 接口,那么在 invokeAwareMethods(String, Object) 方法中就会用 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B 来调用 setBeanFactory(...) 方法,从而将 BeanFactory 填进去 |
Step 2: 前 (Before)
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object, String) 方法的代码复制如下 ⬇️
java
@Deprecated(since = "6.1")
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}这里的逻辑是遍历所有的 BeanPostProcessor,依次调用它们的 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法(可能会提前结束)
例如我们平时用的 @PostConstruct 注解,它对应的 BeanPostProcessor 是 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor。而对 @PostConstruct 的支持,就体现在 Step 2 里(可以打断点进行验证,这里就不展开说了)。
Step 3: 中 (Init)
invokeInitMethods(String, Object, RootBeanDefinition) 方法的代码复制如下 ⬇️
java
/**
* Give a bean a chance to initialize itself after all its properties are set,
* and a chance to know about its owning bean factory (this object).
* <p>This means checking whether the bean implements {@link InitializingBean}
* or defines any custom init methods, and invoking the necessary callback(s)
* if it does.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the merged bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @throws Throwable if thrown by init methods or by the invocation process
* @see #invokeCustomInitMethod
*/
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.hasAnyExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String[] initMethodNames = mbd.getInitMethodNames();
if (initMethodNames != null) {
for (String initMethodName : initMethodNames) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.hasAnyExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd, initMethodName);
}
}
}
}
}这个方法会处理以下 2 种情况
- 如果当前
bean<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>Bimplement了InitializingBean接口,则尝试通过 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B 来调用InitializingBean接口中的afterPropertiesSet()方法 - 如果当前
bean<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B 指定了init method(例如可以在xml文件里指定init method),则尝试通过 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> B B </math>B 来调用这些init method
Step 4: 后 (After)
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object, String) 方法的代码复制如下 ⬇️
java
@Deprecated(since = "6.1")
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}这一步和 Step 2 的代码类似,其逻辑是遍历所有的 BeanPostProcessor,依次调用它们的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法(可能会提前结束)