目录
- 前言
- 一、知识铺垫
-
- [1. 回车换行](#1. 回车换行)
- [2. 缓冲区](#2. 缓冲区)
- 二、倒计时小程序
- 三、进度条小程序
-
- [1. 进度条理论代码](#1. 进度条理论代码)
- [2. 进度条实战版本](#2. 进度条实战版本)
前言
【Linux】自动化构建--make/Makefile详情请点击,今天继续介绍【Linux】倒计时小程序和进度条程序
一、知识铺垫
1. 回车换行
回车代表的意思是让光标回到当前行的起始位置,换行是换到下一行的意思
- 我们使用"\r"表示回车,"\n"表示换行
2. 缓冲区
- 我们在test.c中写入下面代码,sleep(2):休眠2秒,sleep头文件是#include< unistd.h >
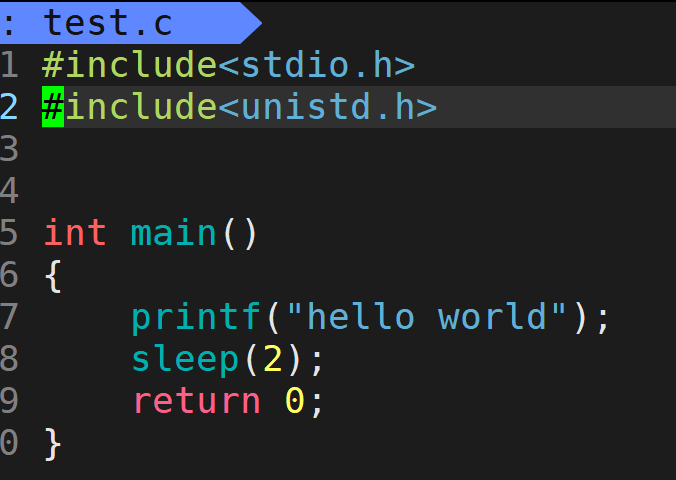
- 使用gcc编译链接再运行,发现开始的时候没有显示"hello world",等待2s后再显示屏上打印"hello world",按照我们正常C语言逻辑我们可以知道,程序是从上到下一条条执行的,按照正常逻辑应该先执行"hello world",在sleep 2s,然后程序结束,为什么会是我们看到的那样呢?
- 程序后面能打印出"hello world"说明字符串并没有丢失,而是先被保存起来了,这个保存的位置叫做缓冲区,当程序遇到"\n"或者程序结束时会将缓冲区的内容在显示屏显示出来,由于printf函数后面没有"\n",所以该语句暂时保存在缓冲区,sleep 2s后程序结束输出到显示屏上
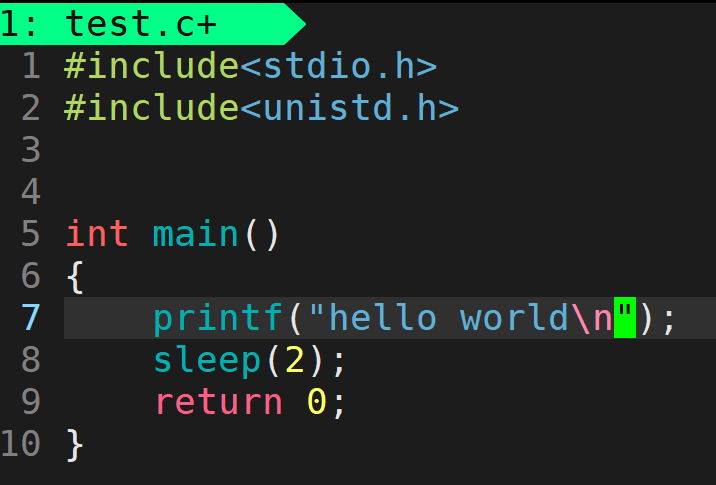
- 当在"hello world"语句后面加入"\n"后,先在显示屏输出"hello world",再sleep 2s,程序结束
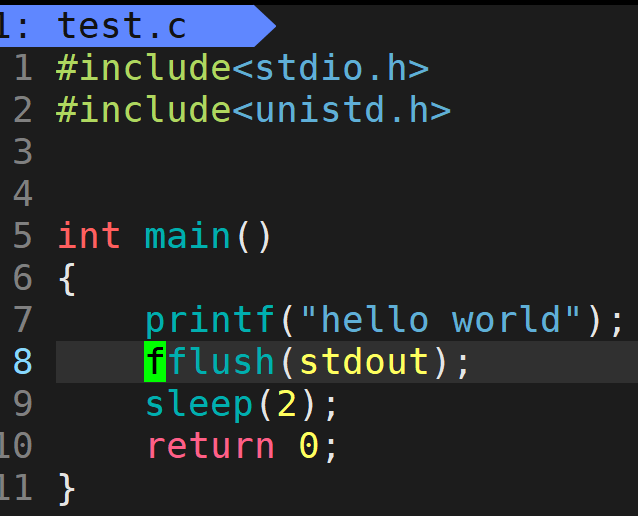
- 如果在不加"\n"的情况下,如何让程序立刻输出"hello world",再sleep 2s,程序结束?
- 可以使用fflush函数强制刷新缓冲区内容,fflush需要传对应的流,流分为:标准输入流(stdin)、标准输出流(stdout)、标准错误流
- "hello world"是要输出到显示屏上,因此传入标准输出流,使用fflush后先输出"hello world",再sleep 2s后程序结束,且没有换行

二、倒计时小程序
- 我们默认生成10s倒计时
- 使用while循环来打印的倒计时数字并设置sleep,这样才能看到倒计时效果,注意这里需要使用fflush函数强制刷新缓冲区内容到显示屏上
- 数字是以字符显示到显示屏上的,数字10在显示屏打印出来时是字符1和字符0打印到显示屏上,当倒计时数字是9时,是一个字符,那么0那个字符并不会被覆盖,因此我们要使用%-2d让数字打印占两个字符,且左对齐打印
- 最后倒计时完毕后加入换行符,防止倒计时的0被命令行覆盖
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main()
{
int cnt = 10;
while(cnt >= 0)
{
printf("%-2d\r", cnt);
fflush(stdout);
sleep(1);
cnt--;
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}三、进度条小程序
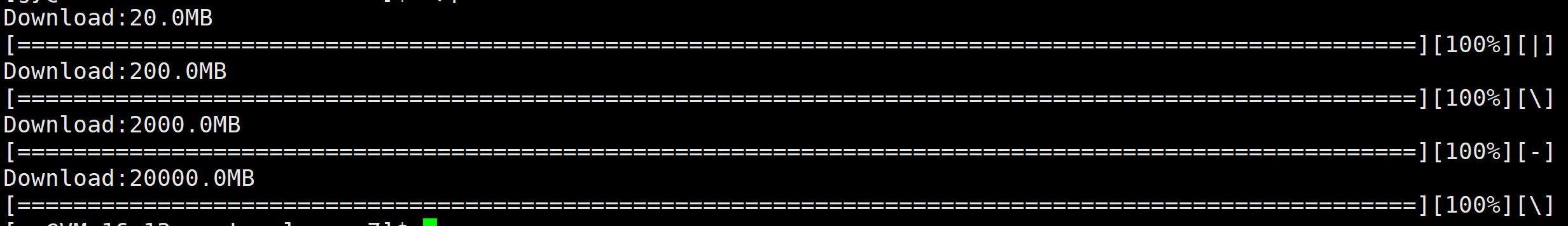
进度条样例
1. 进度条理论代码
- 我们创建processBar.c文件编写进度条代码的实现,main.c文件编写进度条函数和基本的框架,processBar.h声明进度条函数。同时使用make/makefile自动化构建
- processBar.h中,为了防止头文件被重复包含,使用#pragma once,同时声明进度条函数
void Process() - 包含头文件#include<string.h>和#include<unistd.h>,在初始化processbuff时使用memset需要string头文件,使用usleep时需要unistd头文件
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
void Process();- processBar.c中,包含#include<processBar.h>,宏定义数组大小和加载符号
- 根据上面进度条实例,我们需要打印processbuff、进度百分比和加载符,同时要使用fflush函数强制缓冲区刷新,实时将进度更新到显示屏上,再useep(50000)
- 最后进度条更新到100%后换行,防止命令行覆盖进度条
cpp
#include"processBar.h"
#define SIZE 101
#define STYLE '='
void Process()
{
const char* label = "|/-\\";
int len = strlen(label);
char processbuff[101];
memset(processbuff, '\0', SIZE);
int cnt = 0;
while(cnt <= 100)
{
printf("[%-100s][%d%%][%c]\r", processbuff, cnt, label[cnt%len]);
fflush(stdout);
processbuff[cnt++] = STYLE;
usleep(50000);
}
printf("\n");
} - main.c中,也需要包含#include<processBar.h>,直接调用Process函数
cpp
#include"processBar.h"
int main()
{
Process();
return 0;
}2. 进度条实战版本
生活中,进度条往往运用在软件下载过程中,由于网速和软件包大小不同软件下载时间也是不同的,进度条速度也在实时变化
- processBar.h中,为了防止头文件被重复包含,使用#pragma once,同时声明进度条函数
void FlashProcess(double total,double cur) - 包含头文件#include<string.h>和#include<unistd.h>,在初始化processbuff时使用memset需要string头文件,使用usleep时需要unistd头文件,使用#include<time.h>和#include<stdlib.h>生成随机数来模拟下载网速波动
cpp
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void FlashProcess(double total,double cur); // 更新进度,按照实时下载进度更新进度条- processBar.c中,包含#include<processBar.h>,宏定义数组大小和加载符号
- 对于进度条进度'='的更新问题,由于等号不可能出现0.13等小数个等号,所以取整
- 对于进度条的旋转光标的实现,在正常下如果下载较慢(进度条不更新,rate也没有更新),怎么判断是否还在下载,还是说只是下载较慢,暂时没有更新。通过旋转光标是否转动来判断,所以旋转光标的转换不能和total和cur挂钩,而是和调用FlashProcess函数的次数来更新,只要还在调用该函数说明还在下载中
- 再将进度条实时刷新到显示屏上,而不是等函数调用完成之后自动刷新到显示屏上,所以使用
fflush(stdout); - 当进度条到达100%之后,还需要换行,避免命令行覆盖进度条
cpp
1 #include"processBar.h"
2
3
4 #define SIZE 101
5 #define STYLE '='
8 void FlashProcess(double total,double cur)
9 {
10 if(cur > total)
11 cur = total;
12 double rate = cur / total * 100; //转化为0.1->10%这样的形式
13 int cnt = (int) rate;// 10.4->10
14 char processbuff[SIZE];
15 memset(processbuff, '\0', SIZE);
16 int i = 0;
17 for(; i < cnt; i++)
18 {
19 processbuff[i] = STYLE;
20 }
21 static const char* label = "|/-\\";
22 static int index = 0;
23 printf("[%-100s][%.lf%%][%c]\r",processbuff, rate, label[index++]);
24 index %= strlen(label);
25 fflush(stdout);
26 if(cur >= total)
27 printf("\n");
28 }- main.c中,也需要包含#include<processBar.h>,需要一个下载函数,当
cur > total时,将cur = total,再刷新到显示屏上跳出循环 - 模拟实现网速波动使用函数SpeedFloat,限制网速波动范围
cpp
1 #include"processBar.h"
5 double SpeedFloat(double start, double range)
6 {
7 int int_range = (int)range;
8 return start + rand() % int_range + (range - int_range);
9
10 }
11 void Download(double total)
12 {
13 srand(time(NULL));
14 double cur = 0.0;
15 while(1)
16 {
17 if(cur > total)
18 {
19 cur = total;
20 FlashProcess(total, cur);
21 break;
22 }
23 FlashProcess(total, cur); // 更新进度,按照实时下载进度更新进度条
25 cur += SpeedFloat(speed, 20.3);
26 usleep(30000);
27 }
28 }
30 int main()
31 {
32 printf("Download:20.0MB\n");
33 Download(20.0);
34 printf("Download:200.0MB\n");
35 Download(200.0);
36 printf("Download:2000.0MB\n");
37 Download(2000.0);
38 printf("Download:20000.0MB\n");
39 Download(20000.0);
40 return 0;
41 }- 我们还可以定义函数指针在调用Download函数的时候直接调用进度条更新函数
Download(double total, callback_t cb)
cpp
5 //函数指针类型
6 typedef void (* callback_t)(double, double);
14 //cb:回调函数
15 void Download(double total, callback_t cb)
16 {
17 srand(time(NULL));
18 double cur = 0.0;
19 while(1)
20 {
21 if(cur > total)
22 {
23 cur = total;
24 cb(total, cur);
25 break;
26 }
27 cb(total, cur); // 更新进度,按照实时下载进度更新进度条
28 // cur += speed; //模拟下载
29 cur += SpeedFloat(speed, 20.3);
30 usleep(30000);
31 }
32 }
34 int main()
35 {
36 printf("Download:20.0MB\n");
37 Download(20.0, FlashProcess);
38 printf("Download:200.0MB\n");
39 Download(200.0, FlashProcess);
40 printf("Download:2000.0MB\n");
41 Download(2000.0, FlashProcess);
42 printf("Download:20000.0MB\n");
43 Download(20000.0, FlashProcess);
44 return 0;
45 }运行结果如下:模拟实现了不同网速下的进度条下载过程