继承是面向对象编程的核心特性之一。与Java、Python、C#等典型的面向对象语言不同,JavaScript采用基于原型 的继承机制。在《JS核心知识-原型和原型链》中我们已经探讨了原型的基本概念,本文将重点解析如何通过原型和原型链实现对象继承,并详细介绍各种继承方式及其应用场景。
面向对象编程核心概念
本文主要讲对象的继承,它是面向对象中核心特征之一。那什么是面向对象编程呢?
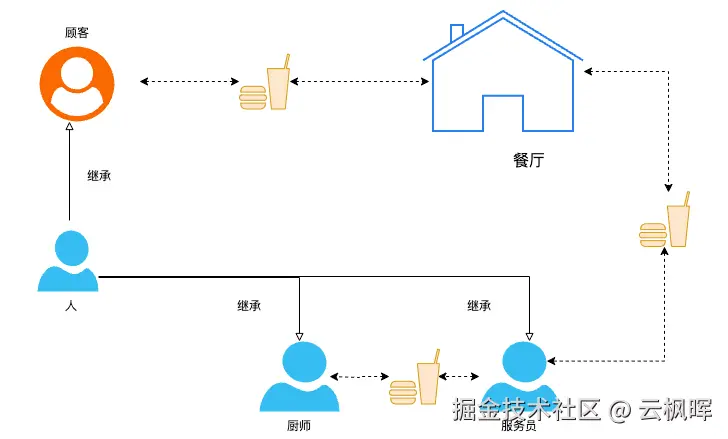
面向对象编程(OOP)将现实世界的事物抽象为程序中的对象,通过对象间的交互解决问题。以餐厅运营为例:
- 将"人"抽象为Person对象,包含姓名、技能等属性和方法
- 通过继承Person实例化出顾客、厨师、服务员等不同角色
- 按照"顾客点餐 → 服务员接单 → 厨师烹饪 → 服务员上菜 → 顾客用餐"的流程协同工作
面向对象三大特征
面向对象编程都基本具有以下特性:
1. 封装
将数据和操作数据的方法捆绑成独立单元,隐藏内部细节,仅暴露必要接口。
示例: 手机对象提供打电话、发短信等功能,用户无需了解内部实现细节。
例如: 把手机看做对象,提供了打电话、发短信、安装应用的功能,这些功能的细节我们并不知道。
2. 继承
子对象自动获取父对象的属性和方法,实现代码复用和层次关系构建。
JavaScript通过原型实现继承:
js
function Animal(name) {
this.name = name || 'animal';
}
Animal.prototype.speak = function() {
console.log(`${this.name} makes a sound`);
};
function Cat(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 设置原型继承
Cat.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat;
const cat = new Cat('Fluffy');
cat.speak(); // "Fluffy makes a sound"3. 多态
同一方法在不同对象上产生不同行为,提升代码灵活性和扩展性。。
js
class Animal {
speak() {
console.log("Animal makes a sound");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
speak() {
console.log("Woof! Woof!");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
speak() {
console.log("Meow!");
}
}
function makeAnimalSpeak(animal) {
animal.speak(); // 同一方法,不同表现
}
makeAnimalSpeak(new Dog()); // "Woof! Woof!"
makeAnimalSpeak(new Cat()); // "Meow!"JavaScript继承方式详解
JavaScript的原型继承机制非常灵活,衍生出多种继承模式。
1. 原型链继承
js
function Person(name) {
this.name = name || 'father';
this.colors = ['red', 'blue'];
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function() {
return `Hello, I'm ${this.name}`;
};
function Student() {
this.name = 'student';
}
// 关键步骤:设置原型链
Student.prototype = new Person();
const student1 = new Student();
const student2 = new Student();
student1.colors.push('green');
console.log(student1.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green']
console.log(student2.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green'] - 共享问题!
console.log(student1.sayHello()); // "Hello, I'm student"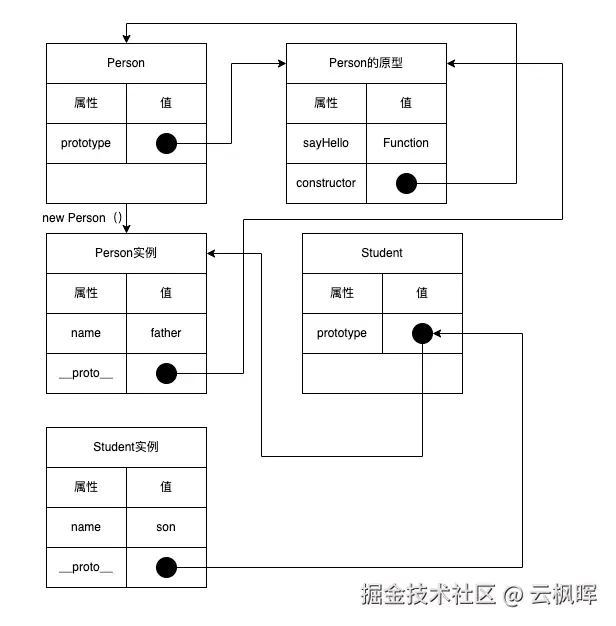 优缺点分析:
优缺点分析:
-
✅ 优点:实现简单,继承完整原型链
-
❌ 缺点:
- 引用类型属性被所有实例共享
- 无法向父构造函数传参
- 无法实现多继承
2. 构造函数继承
构造函数继承其实就是借用函数call方法改变了this的指向。从而继承其他构造函数中的属性和方法
js
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ['red', 'blue'];
this.sayHello = function() {
return `Hello, I'm ${this.name}`;
};
}
function Student(name) {
// 借用父类构造函数
Person.call(this, name);
}
const student1 = new Student('Alice');
const student2 = new Student('Bob');
student1.colors.push('green');
console.log(student1.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green']
console.log(student2.colors); // ['red', 'blue'] - 问题解决!
console.log(student1.sayHello()); // "Hello, I'm Alice"优缺点分析:
-
✅ 优点:
- 解决引用类型共享问题
- 支持向父类传参
- 可实现多继承(多个call调用)
-
❌ 缺点:
- 无法继承原型方法
- 方法需在构造函数中定义,内存占用大
3. 组合继承(经典继承)
组合继承结合了原型
js
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ['red', 'blue'];
}
Person.prototype.sayHello = function() {
return `Hello, I am ${this.name}`;
};
function Student(name, grade) {
// 1. 构造函数继承 - 继承实例属性
Person.call(this, name);
this.grade = grade;
}
// 2. 原型链继承 - 继承原型方法
Student.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
// 修复constructor指向
Student.prototype.constructor = Student;
const student = new Student('Alice', 5);
console.log(student.sayHello()); // "Hello, I am Alice"
console.log(student instanceof Student); // true
console.log(student instanceof Person); // true优缺点分析:
- ✅ 优点:结合两种模式优点,是常用继承方式
- ❌ 缺点:父类构造函数被调用两次,轻微性能损耗
4. 原型式继承
适用于基于现有对象创建新对象。
js
function createObject(obj) {
function F() {}
F.prototype = obj;
return new F();
}
const parent = {
name: 'Parent',
colors: ['red', 'blue'],
getName: function() {
return this.name;
}
};
const child1 = createObject(parent);
const child2 = createObject(parent);
child1.name = 'Child1';
child1.colors.push('green'); // 影响所有实例!
console.log(child1.getName()); // "Child1"
console.log(child2.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green'] - 共享问题ES5中的Object.create()可替代此模式:
js
const child = Object.create(parent);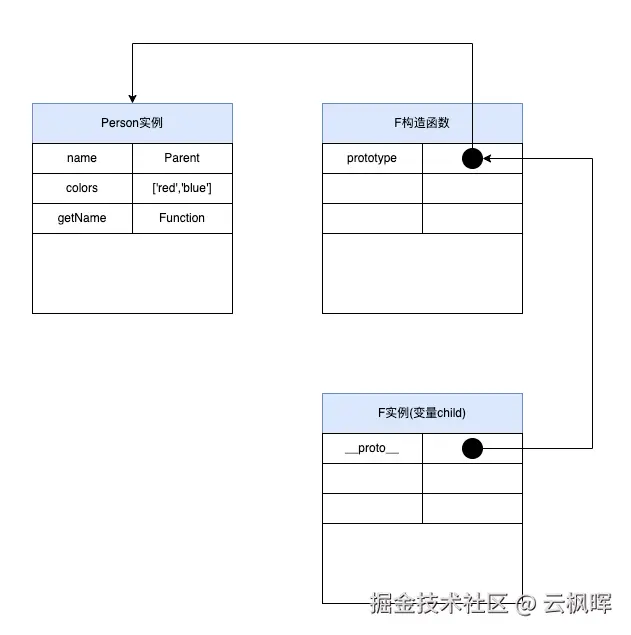 原型式继承适用于不需要构造函数创建对象的情况,但是它仍然存在原型链继承的问题(
原型式继承适用于不需要构造函数创建对象的情况,但是它仍然存在原型链继承的问题(数据存在污染)
5. 寄生式继承
在原型式继承基础上增强对象功能。
js
function createEnhancedObject(obj) {
const clone = Object.create(obj);
// 增强对象功能
clone.getColor = function(index) {
return this.colors[index];
};
clone.introduce = function() {
return `I'm ${this.name}`;
};
return clone;
}
const parent = {
name: 'Parent',
colors: ['red', 'blue'],
getName: function() {
return this.name;
}
};
const child = createEnhancedObject(parent);
child.name = 'Child';
console.log(child.introduce()); // "I'm Child"
console.log(child.getColor(0)); // "red"适用场景:主要关注对象而非类型构造函数的场景。
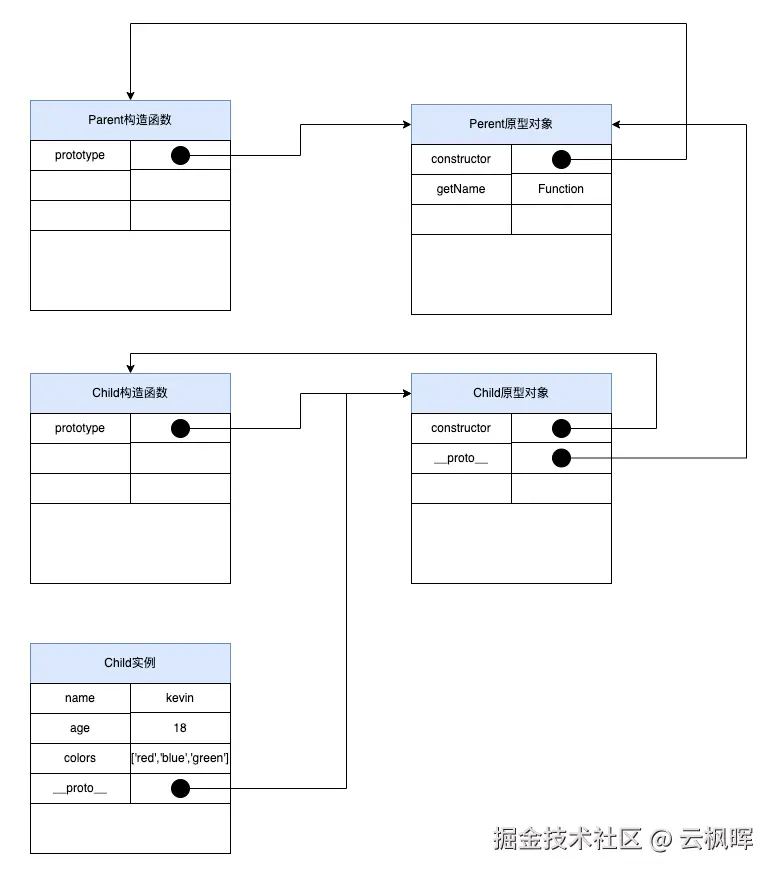
6. 寄生组合式继承(最优方案)
js
function inheritPrototype(SubType, SuperType) {
// 创建原型对象副本
const prototype = Object.create(SuperType.prototype);
// 修复constructor指向
prototype.constructor = SubType;
// 设置子类原型
SubType.prototype = prototype;
}
function Parent(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ['red', 'blue', 'green'];
}
Parent.prototype.getName = function() {
return this.name;
};
function Child(name, age) {
// 继承实例属性
Parent.call(this, name);
this.age = age;
}
// 继承原型方法(关键改进)
inheritPrototype(Child, Parent);
// 可添加子类特有方法
Child.prototype.getAge = function() {
return this.age;
};
const child1 = new Child('Kevin', 18);
const child2 = new Child('Daisy', 20);
child1.colors.push('black');
console.log(child1.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green', 'black']
console.log(child2.colors); // ['red', 'blue', 'green'] - 无共享问题
console.log(child1.getName()); // "Kevin"
console.log(child1.getAge()); // 18优势:
- 只调用一次父类构造函数
- 原型链保持完整
- 是最理想的继承方式
ES6的class方式继承
js
class Parent {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
this.colors = ['red', 'blue'];
}
getName() {
return this.name;
}
static staticMethod() {
return 'Parent static method';
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
constructor(name, age) {
super(name); // 相当于Parent.call(this, name)
this.age = age;
}
// 方法重写
getName() {
return `${super.getName()} (child)`;
}
getAge() {
return this.age;
}
}
const child = new Child('Alice', 10);
console.log(child.getName()); // "Alice (child)"
console.log(child.getAge()); // 10
console.log(Child.staticMethod()); // "Parent static method"底层原理:class本质仍是基于原型的语法糖,babel转译后其实就是寄生组合式继承。
总结与选择建议
| 继承方式 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原型链继承 | 实现简单 | 引用类型共享、无法传参 | 简单的原型扩展 |
| 构造函数继承 | 解决共享问题、支持传参 | 无法继承原型方法 | 需要属性隔离 |
| 组合继承 | 结合两者优点 | 父类调用两次 | 传统项目使用 |
| 原型式继承 | 轻量、灵活 | 共享问题依然存在 | 对象克隆扩展 |
| 寄生式继承 | 功能增强 | 方法难以复用 | 对象功能扩展 |
| 寄生组合继承 | 性能最优、完整继承 | 实现稍复杂 | 现代库和框架 |
| ES6 Class | 语法简洁、易维护 | 需要转译支持 | 现代开发 |
实践建议:
- 现代项目优先使用 ES6 Class
- 库/框架开发推荐 寄生组合式继承
- 简单对象扩展可使用 原型式继承
- 理解底层原理有助于应对复杂场景
掌握JavaScript继承机制,能够帮助开发者编写出更加优雅、可维护的面向对象代码,构建复杂的应用程序架构。希望此文能帮忙你!┏(^0^)┛