Spring AI Alibaba
官方文档:java2ai.com/docs/
关于
Java大模型应用开发的生态目前有:
- SpringAI
- Spring AI Alibaba (国内阿里巴巴做的,基于阿里云的生态)
- LangChain4j(python的LangChain的Java版本,适合做一些复杂的工作流版本)
Spring AI Alibaba的技术生态
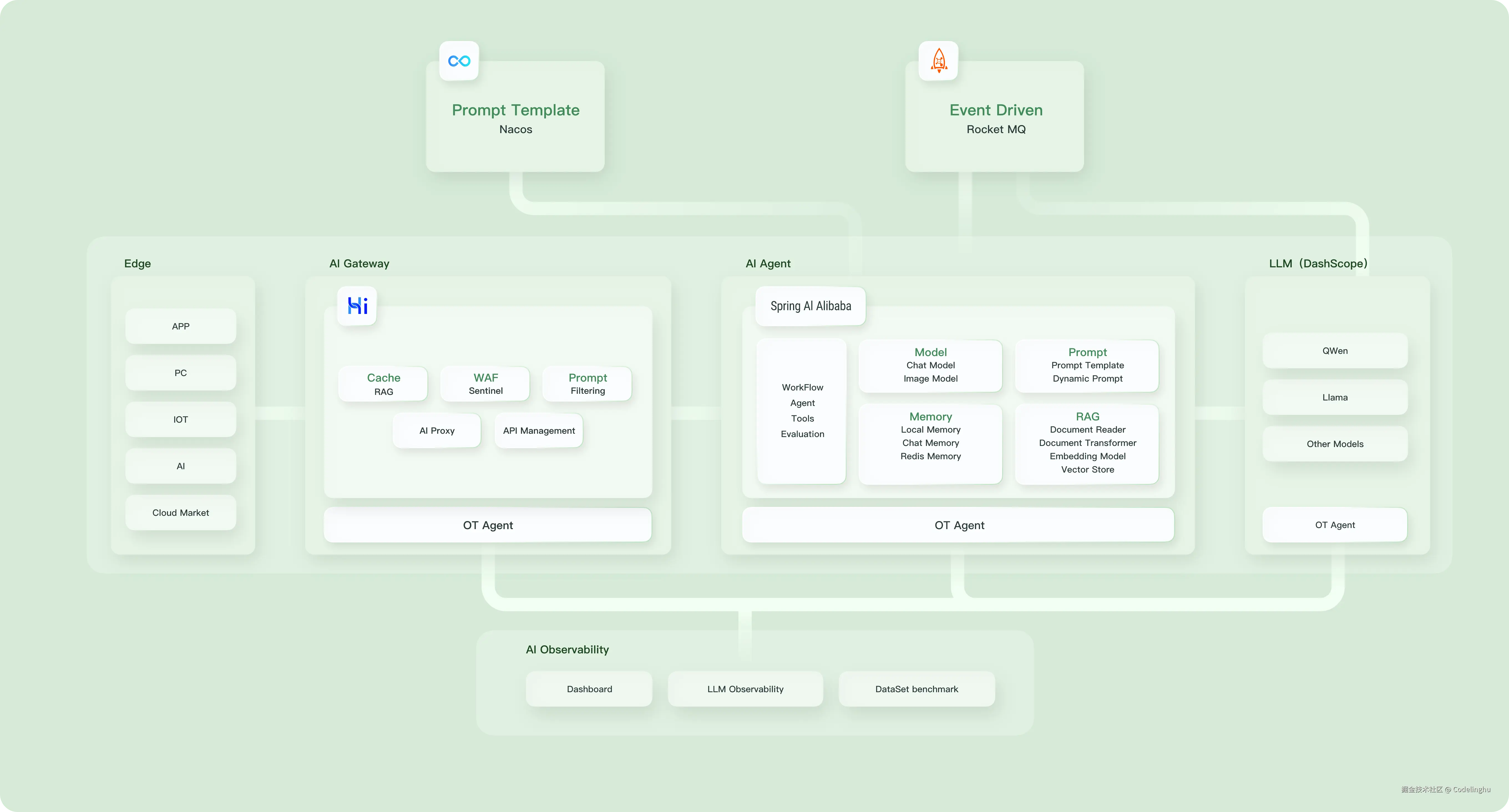
核心概念
-
模型model
大模型、学霸的大脑
-
提示词prompt
提问的问题
-
嵌入Embedding
把概念文字转换为向量、数字
-
Token
把提问的文章拆分成一段段的文字
-
结构化输出Structured output
规范大模型回答的内容格式
-
微调Fine Tuning
让学霸专注攻坚某一科,给它某一领域的数据集训练它。
-
检索增强RAG
给大模型外挂一个知识库,让它回答问题的时候去先根据知识库来回答
-
函数调用Function Calling
大模型调用工具(高德,天气)
-
评估人工智能的回答Evaluation
环境搭建与快速入门
版本
- JDK17
- SpringBoot3.4.0
- SpringAI 1.0.0-M6
- SpringAI aliba 1.0.0-M6.1
大模型选型
Ollama本地部署大模型
其实很简单,可以搭配cherrystudio来使用
云端大模型配置
- 阿里云百炼
- 硅基流动平台
- ...
实现一个AI应用聊天机器人
这个案例是基于云端大模型做的,是基于阿里云百炼平台调用大模型API。
ChatController:
java
@RestController
public class ChatController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatController(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
this.chatClient = builder
.build();
}
//同步输出
@GetMapping("/chat")
public String chat(@RequestParam(value = "input") String input) {
return this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(input)
.call()
.content();
}
//流式输出
@GetMapping(value = "/stream", produces = MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM_VALUE)
public Flux<String> stream(String input) {
return this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(input)
.stream()
.content();
}
}application.yaml
yaml
spring:
application:
name: alibaba-ai-demo
ai:
dashscope:
api-key: xxxxxxPOM
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.fox</groupId>
<artifactId>ai-demo</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>alibaba-ai-demo</artifactId>
<version>${revision}</version>
<name>alibaba-ai-demo</name>
<description>alibaba-ai-demo</description>
<properties>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<-- 加这个依赖!-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-alibaba-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>ChatClient返回实体类型
其实ChatClient就是对操作大模型的一个底层封装,使得开发者能够专注于业务逻辑而非底层开发。
您经常希望返回一个预先定义好的实体类型响应,Spring AI 框架可以自动替我们完成从 String 到实体类的转换,调用entity() 方法可完成响应数据转换。
java
@RestController
public class ChatController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatController(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
this.chatClient = builder
.build();
}
/**
* 演员电影信息类
*/
static class ActorFilms {
private final String actor;
private final List<String> movies;
public ActorFilms(String actor, List<String> movies) {
this.actor = actor;
this.movies = movies;
}
public String getActor() {
return actor;
}
public List<String> getMovies() {
return movies;
}
}
@GetMapping("/movies")
public ActorFilms movies(@RequestParam(value = "input") String input) throws Exception {
ActorFilms films = chatClient.prompt()
.user(input)
.call()
.entity(ActorFilms.class);
return films;
}
//entity 还有一种带有参数的重载方法 entity(ParameterizedTypeReference<T> type),可让您指定如泛型 List 等类型:
@GetMapping("/movies2")
public List<ActorFilms> movies2(@RequestParam(value = "input") String input) throws Exception {
List<ActorFilms> filmsList = chatClient.prompt()
.user(input)
.call()
.entity(new ParameterizedTypeReference<List<ActorFilms>>() {
});
return filmsList;
}
}使用ChatClient指定系统角色
设置默认 System Message,其实就是设置一个系统角色!给我们的AI一个人设!
java
public ChatController(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
this.chatClient = builder
.defaultSystem("你是一个演员,请列出你所参演的电影")
.build();
}给系统角色绑定变量
java
@RestController
public class AIController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public AIController(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
this.chatClient = builder
.defaultSystem("你是一个友好的聊天机器人,回答问题时要使用{voice}的语气")
.build();
}
@GetMapping("/ai")
Map<String, String> completion(@RequestParam(value = "message", defaultValue = "说一个笑话") String message, String voice) {
return Map.of(
"completion",
this.chatClient.prompt()
.system(sp -> sp.param("voice", voice))//系统角色绑定变量
.user(message)
.call()
.content());
}
}让大模型具有记忆功能
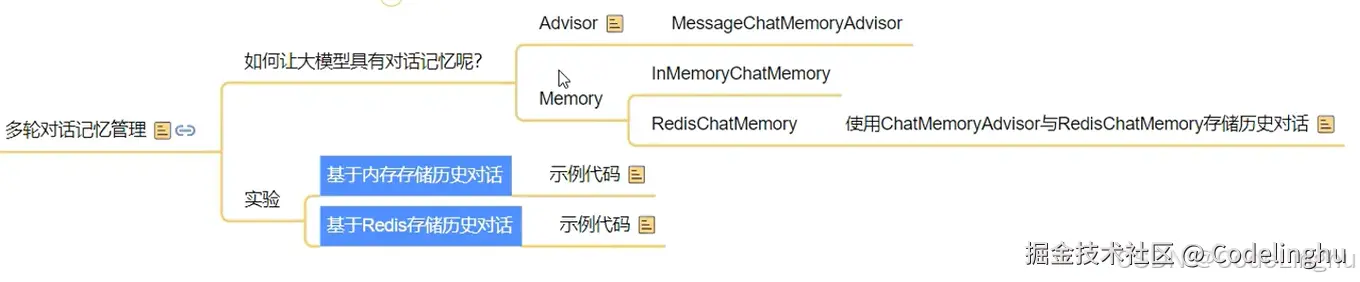
基于内存存储的历史对话
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/chat-memory")
public class ChatMemoryController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatMemoryController(ChatModel chatModel) {
this.chatClient = ChatClient
.builder(chatModel)
.defaultSystem("你是一个旅游规划师,请根据用户的需求提供旅游规划建议。")
.defaultAdvisors(new MessageChatMemoryAdvisor(new InMemoryChatMemory()))//这是基于内存存储,实则是一个拦截器
// .defaultAdvisors(new MessageChatMemoryAdvisor(new RedisChatMemory(
// "127.0.0.1",
// 6379,
// null
// )))
.build();
}
/**
* 获取内存中的聊天内容
* 根据提供的prompt和chatId,从内存中获取相关的聊天内容,并设置响应的字符编码为UTF-8。
*
* @param prompt 用于获取聊天内容的提示信息
* @param chatId 聊天的唯一标识符,用于区分不同的聊天会话
* @param response HTTP响应对象,用于设置响应的字符编码
* @return 返回包含聊天内容的Flux<String>对象
*/
@GetMapping("/in-memory")
public Flux<String> memory(
@RequestParam("prompt") String prompt,
@RequestParam("chatId") String chatId,
HttpServletResponse response
) {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
return chatClient.prompt(prompt).advisors(
a -> a
.param(CHAT_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_ID_KEY, chatId)
.param(CHAT_MEMORY_RETRIEVE_SIZE_KEY, 100)
).stream().content();
}
}基于Redis内存存储的历史对话
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/chat-memory")
public class ChatMemoryController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatMemoryController(ChatModel chatModel) {
this.chatClient = ChatClient
.builder(chatModel)
.defaultSystem("你是一个旅游规划师,请根据用户的需求提供旅游规划建议。")
.defaultAdvisors(new MessageChatMemoryAdvisor(new RedisChatMemory(
"127.0.0.1",
6379,
"lilishop"
)))
.build();
}
/**
* 从Redis中获取聊天内容
* 根据提供的prompt和chatId,从Redis中检索聊天内容,并以Flux<String>的形式返回
*
* @param prompt 聊天内容的提示或查询关键字
* @param chatId 聊天的唯一标识符,用于从Redis中检索特定的聊天内容
* @param response HttpServletResponse对象,用于设置响应的字符编码为UTF-8
* @return Flux<String> 包含聊天内容的反应式流
*/
@GetMapping("/redis")
public Flux<String> redis(
@RequestParam("prompt") String prompt,
@RequestParam("chatId") String chatId,
HttpServletResponse response
) {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
return chatClient.prompt(prompt)
.advisors(
a -> a
.param(CHAT_MEMORY_CONVERSATION_ID_KEY, chatId)
.param(CHAT_MEMORY_RETRIEVE_SIZE_KEY, 10)
)
.stream().content();
}
}需要maven打包下面这个类文件,引入到上一个文件中。
java
/**
*
* 基于Redis的聊天记忆实现。
* 该类实现了ChatMemory接口,提供了将聊天消息存储到Redis中的功能。
*
* @author Fox
*/
public class RedisChatMemory implements ChatMemory, AutoCloseable {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisChatMemory.class);
private static final String DEFAULT_KEY_PREFIX = "chat:";
private static final String DEFAULT_HOST = "127.0.0.1";
private static final int DEFAULT_PORT = 6379;
private static final String DEFAULT_PASSWORD = null;
private final JedisPool jedisPool;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
public RedisChatMemory() {
this(DEFAULT_HOST, DEFAULT_PORT, DEFAULT_PASSWORD);
}
public RedisChatMemory(String host, int port, String password) {
JedisPoolConfig poolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
this.jedisPool = new JedisPool(poolConfig, host, port, 2000, password);
this.objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
logger.info("Connected to Redis at {}:{}", host, port);
}
@Override
public void add(String conversationId, List<Message> messages) {
String key = DEFAULT_KEY_PREFIX + conversationId;
AtomicLong timestamp = new AtomicLong(System.currentTimeMillis());
try (Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource()) {
// 使用pipeline批量操作提升性能
var pipeline = jedis.pipelined();
messages.forEach(message ->
pipeline.hset(key, String.valueOf(timestamp.getAndIncrement()), message.toString())
);
pipeline.sync();
}
logger.info("Added messages to conversationId: {}", conversationId);
}
@Override
public List<Message> get(String conversationId, int lastN) {
String key = DEFAULT_KEY_PREFIX + conversationId;
try (Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource()) {
Map<String, String> allMessages = jedis.hgetAll(key);
if (allMessages.isEmpty()) {
return List.of();
}
return allMessages.entrySet().stream()
.sorted((e1, e2) ->
Long.compare(Long.parseLong(e2.getKey()), Long.parseLong(e1.getKey()))
)
.limit(lastN)
.map(entry -> new UserMessage(entry.getValue()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
@Override
public void clear(String conversationId) {
String key = DEFAULT_KEY_PREFIX + conversationId;
try (Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource()) {
jedis.del(key);
}
logger.info("Cleared messages for conversationId: {}", conversationId);
}
@Override
public void close() {
try (Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource()) {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
logger.info("Redis connection closed.");
}
if (jedisPool != null) {
jedisPool.close();
logger.info("Jedis pool closed.");
}
}
}
public void clearOverLimit(String conversationId, int maxLimit, int deleteSize) {
try {
String key = DEFAULT_KEY_PREFIX + conversationId;
try (Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource()) {
List<String> all = jedis.lrange(key, 0, -1);
if (all.size() >= maxLimit) {
all = all.stream().skip(Math.max(0, deleteSize)).toList();
}
this.clear(conversationId);
for (String message : all) {
jedis.rpush(key, message);
}
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error clearing messages from Redis chat memory", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}对话模型ChatModel
java
@RestController
public class ChatModelController {
private final ChatModel chatModel;
public ChatModelController(@Qualifier("dashscopeChatModel") ChatModel chatModel) {
this.chatModel = chatModel;
}
@RequestMapping("/chat2")
public String chat2(String input) {
DashScopeChatOptions options = DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
.withTemperature(0.9)
.withMaxToken(1500)
// .withTopP(0.01)
.build();
Prompt prompt = new Prompt(input, options);
ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(prompt);
//ChatResponse response = chatModel.call(new Prompt(input));
return response.getResult().getOutput().getText();
}
@RequestMapping("/streamChat")
public Flux<String> streamChat(String input, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
response.setContentType("text/event-stream");
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
return chatModel.stream(input);
}
}文生图ImageModel
java
@RestController
public class ImageModelController {
private final ImageModel imageModel;
ImageModelController(@Qualifier("dashScopeImageModel") ImageModel imageModel) {
this.imageModel = imageModel;
}
@RequestMapping("/image")
public String image(String input) {
ImageOptions options = ImageOptionsBuilder.builder()
.model("wanx2.1-t2i-turbo")
.height(1024)
.width(1024)
.build();
ImagePrompt imagePrompt = new ImagePrompt(input, options);
ImageResponse response = imageModel.call(imagePrompt);
String imageUrl = response.getResult().getOutput().getUrl();
return "redirect:" + imageUrl;
}
}AudioModel文本转语音
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/audio")
public class AudioModelController {
private final SpeechSynthesisModel speechSynthesisModel;
@Autowired
public AudioModelController(SpeechSynthesisModel speechSynthesisModel) {
this.speechSynthesisModel = speechSynthesisModel;
}
@GetMapping("/synthesize")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> synthesizeSpeech(@RequestParam String text) throws IOException {
// 构建语音合成请求
SpeechSynthesisPrompt prompt = new SpeechSynthesisPrompt(text);
// 调用模型生成语音
SpeechSynthesisResponse response = speechSynthesisModel.call(prompt);
ByteBuffer audioData = response.getResult().getOutput().getAudio();
// 将 ByteBuffer 转换为字节数组
byte[] audioBytes = new byte[audioData.remaining()];
audioData.get(audioBytes);
// 返回音频流(MP3格式)
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM)
.header("Content-Disposition", "attachment; filename=output.mp3")
.body(audioBytes);
}
}AudioModel语音转文本
java
@RestController
public class AudioModelController2 {
private static final String AUDIO_RESOURCES_URL = "https://dashscope.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/samples/audio/paraformer/hello_world_female2.wav";
private final DashScopeAudioTranscriptionModel dashScopeAudioTranscriptionModel; //modelname:sensevoice-v1,paraformer-realtime-v2,paraformer-v2
AudioModelController2(DashScopeAudioTranscriptionModel dashScopeAudioTranscriptionModel){
this.dashScopeAudioTranscriptionModel = dashScopeAudioTranscriptionModel;
}
@GetMapping("/audio")
public String audio() throws MalformedURLException {
Resource resource =new UrlResource(AUDIO_RESOURCES_URL);
AudioTranscriptionPrompt prompt = new AudioTranscriptionPrompt(resource,
DashScopeAudioTranscriptionOptions.builder()
.withModel("sensevoice-v1")
.build());
return dashScopeAudioTranscriptionModel.call(prompt).getResult().getOutput();
}
}提示词的数据结构
Prompt中的主要角色Role包括:
- 系统角色System Role
- 用户角色User Role
- 助手角色Assistant Role
- 工具/功能角色Tool/Function Role
Prompt Template
动态提示词模板,可以按照自定义的提示词模版进行结构化输出。
- PromptTemplateStringActions 专注于创建和呈现提示字符串,代表提示生成的最基本形式。
- PromptTemplateMessageActions 专门用于通过生成和操作 Message 对象来创建提示。
- PromptTemplateActions 旨在返回 Prompt 对象,该对象可以传递给 ChatModel 以生成响应。
基于 ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory实现动态提示词模板
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/example/ai")
public class PromptTemplateController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private final ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory configurablePromptTemplateFactory;
@Value("classpath:/prompts/joke-prompt.st")
private Resource jokeResource;
public PromptTemplateController(
ChatClient.Builder builder,
ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory configurablePromptTemplateFactory
) {
this.chatClient = builder.build();
this.configurablePromptTemplateFactory = configurablePromptTemplateFactory;
}
/**
* nacos template config [{"name:"test-template","template:"please list the most famous books by this {author}."}]
*/
@GetMapping("/prompt-template")
public AssistantMessage generate(
@RequestParam(value = "author", defaultValue = "鲁迅") String author
) {
ConfigurablePromptTemplate template = configurablePromptTemplateFactory.getTemplate("test-template");
if (template == null) {
template = configurablePromptTemplateFactory.create("test-template",
"请列出 {author} 最著名的三本书。");
}
Prompt prompt;
if (StringUtils.hasText(author)) {
prompt = template.create(Map.of("author", author));
} else {
prompt = template.create();
}
return chatClient.prompt(prompt)
.call()
.chatResponse()
.getResult()
.getOutput();
}
}
java
@Configuration
public class PromptTemplateConfig {
@Bean
public ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory configurablePromptTemplateFactory() {
// 这里假设ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory有一个无参构造函数
return new ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory();
// 如果需要配置参数,可以在这里进行配置
// return new ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory(param1, param2);
}
}基于 PromptTemplate实现动态提示词模板
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/example/ai")
public class PromptTemplateController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private final ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory configurablePromptTemplateFactory;
@Value("classpath:/prompts/joke-prompt.st")
private Resource jokeResource;
public PromptTemplateController(
ChatClient.Builder builder,
ConfigurablePromptTemplateFactory configurablePromptTemplateFactory
) {
this.chatClient = builder.build();
this.configurablePromptTemplateFactory = configurablePromptTemplateFactory;
}
@GetMapping("/prompt")
public AssistantMessage completion(
@RequestParam(value = "adjective", defaultValue = "有趣") String adjective,
@RequestParam(value = "topic", defaultValue = "奶牛") String topic
) {
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate(jokeResource);
Prompt prompt = promptTemplate.create(Map.of("adjective", adjective, "topic", topic));
return chatClient.prompt(prompt)
.call()
.chatResponse()
.getResult()
.getOutput();
}
}
structured
给我讲一个关于 {topic} 的 {adjective} 笑话基于SystemPromptTemplate实现动态提示词模板
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/example/ai")
public class RoleController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
@Value("classpath:/prompts/system-message.st")
private Resource systemResource;
@Autowired
public RoleController(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
this.chatClient = builder.build();
}
@GetMapping("/roles")
public AssistantMessage generate(
@RequestParam(value = "message",
defaultValue = "请介绍一下海盗黄金时代的三位著名海盗,以及他们为什么这样做。为每个海盗至少写一句话。") String message,
@RequestParam(value = "name", defaultValue = "Fox") String name,
@RequestParam(value = "voice", defaultValue = "海盗") String voice
) {
UserMessage userMessage = new UserMessage(message);
SystemPromptTemplate systemPromptTemplate = new SystemPromptTemplate(systemResource);
Message systemMessage = systemPromptTemplate.createMessage(Map.of("name", name, "voice", voice));
return chatClient.prompt(new Prompt(List.of(userMessage, systemMessage)))
.call()
.chatResponse()
.getResult()
.getOutput();
}
}
structured
你是一个有用的 AI 助手。
你是帮助人们查找信息的 AI 助手。
你的名字是 {name}
你应该使用你的姓名和 {voice} 的样式回复用户的请求。RAG(静态)
静态RAG和动态RAG不一样,动态RAG采用的是结合的向量数据库
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/example/ai")
public class StuffController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
@Value("classpath:/docs/bailian.md")
private Resource docsToStuffResource;
@Value("classpath:/prompts/qa-prompt.st")
private Resource qaPromptResource;
@Autowired
public StuffController(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
this.chatClient = builder.build();
}
@GetMapping(value = "/stuff")
public Completion completion(@RequestParam(value = "message", defaultValue = "给我推荐一款百炼系列的手机?") String message, @RequestParam(value = "stuffit", defaultValue = "false") boolean stuffit) {
PromptTemplate promptTemplate = new PromptTemplate(qaPromptResource);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("question", message);
if (stuffit) {
map.put("context", docsToStuffResource);
} else {
map.put("context", "");
}
return new Completion(chatClient.prompt(promptTemplate.create(map)).call().content());
}
}
markdown
# **百炼手机产品介绍**
欢迎来到未来科技的前沿,探索我们精心打造的智能手机系列,每一款都是为了满足您对科技生活的无限遐想而生。
**百炼X1** ------ 畅享极致视界:搭载6.7英寸1440 x 3200像素超清屏幕,搭配120Hz刷新率,流畅视觉体验跃然眼前。256GB海量存储空间与12GB RAM强强联合,无论是大型游戏还是多任务处理,都能轻松应对。5000mAh电池长续航,加上超感光四摄系统,记录生活每一刻精彩。参考售价:4599 - 4999
**通义Vivid 7** ------ 智能摄影新体验:拥有6.5英寸1080 x 2400像素全面屏,AI智能摄影功能让每一张照片都能展现专业级色彩与细节。8GB RAM与128GB存储空间确保流畅操作,4500mAh电池满足日常所需。侧面指纹解锁,便捷又安全。参考售价:2999 - 3299
**星尘S9 Pro** ------ 创新视觉盛宴:突破性6.9英寸1440 x 3088像素屏下摄像头设计,带来无界视觉享受。512GB存储与16GB RAM的顶级配置,配合6000mAh电池与100W快充技术,让性能与续航并驾齐驱,引领科技潮流。参考售价:5999 - 6499。
**百炼Ace Ultra** ------ 游戏玩家之选:配备6.67英寸1080 x 2400像素屏幕,内置10GB RAM与256GB存储,确保游戏运行丝滑无阻。5500mAh电池搭配液冷散热系统,长时间游戏也能保持冷静。高动态双扬声器,沉浸式音效升级游戏体验。参考售价:3999 - 4299。
**百炼Zephyr Z9** ------ 轻薄便携的艺术:轻巧的6.4英寸1080 x 2340像素设计,搭配128GB存储与6GB RAM,日常使用游刃有余。4000mAh电池确保一天无忧,30倍数字变焦镜头捕捉远处细节,轻薄而不失强大。参考售价:2499 - 2799。
**百炼Flex Fold+** ------ 折叠屏新纪元:集创新与奢华于一身,主屏7.6英寸1800 x 2400像素与外屏4.7英寸1080 x 2400像素,多角度自由悬停设计,满足不同场景需求。512GB存储、12GB RAM,加之4700mAh电池与UTG超薄柔性玻璃,开启折叠屏时代新篇章。此外,这款手机还支持双卡双待、卫星通话,帮助您在世界各地都能畅联通话。参考零售价:9999 - 10999。
每一款手机都是匠心独运,只为成就您手中的科技艺术品。选择属于您的智能伙伴,开启未来科技生活的新篇章。
structured
使用以下上下文来回答最后的问题。
如果你不知道答案,就说你不知道,不要试图编造答案。
{context}
问题: {question}
有用的答案:如何实现结构化输出
结构化输出就是返回特定的格式,返回Java对象还是json格式的问题。
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/example/stream")
public class StreamToBeanController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StreamToBeanController.class);
public StreamToBeanController(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
// 使用builder对象构建ChatClient实例
this.chatClient = builder.build();
}
/**
* @return {@link com.fox.structureddemo.stream.StreamToBeanEntity}
*/
@GetMapping("/play")
public StreamToBeanEntity simpleChat(HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
var converter = new BeanOutputConverter<>(
new ParameterizedTypeReference<StreamToBeanEntity>() { }
);
Flux<String> flux = this.chatClient.prompt()
.user(u -> u.text("""
requirement: 请用大概 120 字,作者为 Fox ,为计算机的发展历史写一首现代诗;
format: 以纯文本输出 json,请不要包含任何多余的文字------包括 markdown 格式;
outputExample: {
"title": {title},
"author": {author},
"date": {date},
"content": {content}
};
"""))
.stream()
.content();
String result = String.join("\n", Objects.requireNonNull(flux.collectList().block()))
.replaceAll("\\n", "")
.replaceAll("\\s+", " ")
.replaceAll("\"\\s*:", "\":")
.replaceAll(":\\s*\"", ":\"");
log.info("LLMs 响应的 json 数据为:{}", result);
return converter.convert(result);
}
}StreamToBeanEntity:
java
public class StreamToBeanEntity {
private String title;
private String author;
private String date;
private String content;
public StreamToBeanEntity() {
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(String date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StreamToBeanEntity{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", date='" + date + '\'' +
", content='" + content + '\'' +
'}';
}
}还有一种方法来实现这种转换:
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/example/stream/json")
public class StreamToJsonController {
private static final String DEFAULT_PROMPT = "你好,请以JSON格式介绍你自己!";
private final ChatClient dashScopeChatClient;
public StreamToJsonController(ChatModel chatModel) {
DashScopeResponseFormat responseFormat = new DashScopeResponseFormat();
responseFormat.setType(DashScopeResponseFormat.Type.JSON_OBJECT);
this.dashScopeChatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultOptions(
DashScopeChatOptions.builder()
.withTopP(0.7)
.withResponseFormat(responseFormat)
.build()
)
.build();
}
/**
* @return {@link String}
*/
@GetMapping("/play")
public String simpleChat(HttpServletResponse response) {
response.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
return dashScopeChatClient.prompt(DEFAULT_PROMPT)
.call()
.content();
}
}大模型是如何工作的?
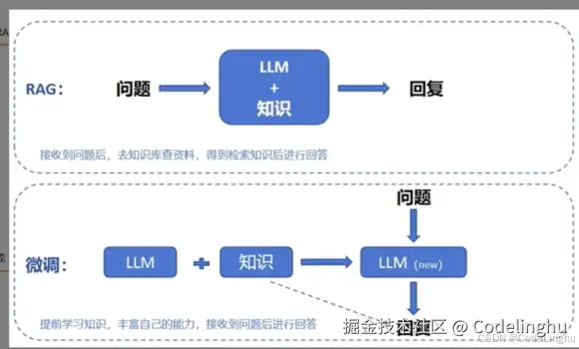
RAG和微调
RAG就是给大模型外挂一个知识库,检索知识库再回答问题;微调的话是真正的在训练大模型具备回答知识的能力。
RAG适合那种经常变化的知识:比如政策性的;微调适合那种静态知识,比如医疗领域的知识,这种知识变化不大。
RagConfig:
java
@Configuration
public class RagConfig {
@Bean
ChatClient chatClient(ChatClient.Builder builder) {
return builder.defaultSystem("你将作为一名机器人产品的专家,对于用户的使用需求作出解答")
.build();
}
@Bean
VectorStore vectorStore(EmbeddingModel embeddingModel) {
SimpleVectorStore simpleVectorStore = SimpleVectorStore.builder(embeddingModel)
.build();
// 生成一个机器人产品说明书的文档
List<Document> documents = List.of(
new Document("产品说明书:产品名称:智能机器人\n" +
"产品描述:智能机器人是一个智能设备,能够自动完成各种任务。\n" +
"功能:\n" +
"1. 自动导航:机器人能够自动导航到指定位置。\n" +
"2. 自动抓取:机器人能够自动抓取物品。\n" +
"3. 自动放置:机器人能够自动放置物品。\n"));
simpleVectorStore.add(documents);
return simpleVectorStore;
}
}RagController:
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/ai")
public class RagController {
@Autowired
private ChatClient chatClient;
@Autowired
private VectorStore vectorStore;
@GetMapping(value = "/chat", produces = "text/plain; charset=UTF-8")
public String generation(String userInput) {
// 发起聊天请求并处理响应
return chatClient.prompt()
.user(userInput)
.advisors(new QuestionAnswerAdvisor(vectorStore))//这个是关键,向量数据库的开启
.call()
.content();
}
}其实可以直接利用百炼平台创建智能体应用,通过应用关联向量数据库,再在业务系统中通过api调用百炼平台的智能体应用。
Function calling
这是一个让大模型调用外部工具能力的一个工具。
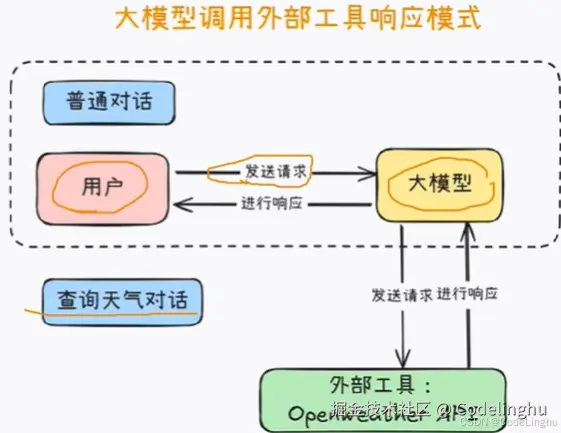
其实这个Function你可以理解成我们自己写的一个函数工具,也可以是第三方提供的一个函数工具。
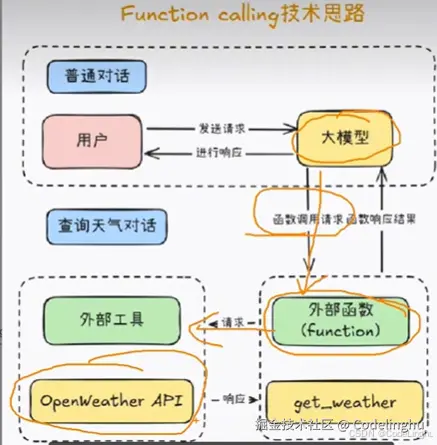
我们接下来实现一个天气预报获取的案例。
天气预报获取案例
我们我们可以用Function calling和method两种方法来实现。
第一种方法:Function calling
构造获取天气预报信息的函数
java
public class WeatherFunction implements Function<WeatherFunction.WeatherRequest, String> {
@Override
public String apply(WeatherRequest request) {
// 此处省略了实际的天气查询逻辑,直接返回一个示例字符串
// 实际应用中需要根据请求参数调用天气API获取天气信息
return "The weather in " + request.getCity() + " is sunny.";
}
public static class WeatherRequest {
private String city;
public String getCity() { return city; }
public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; }
}
}
java
@Configuration
public class FunctionConfig {
@Bean
@Description("获取指定城市的天气信息")
public Function<WeatherFunction.WeatherRequest, String> weatherFunction() {
return new WeatherFunction();
}
}Controller:
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/weather")
public class WeatherController {
private final ChatClient dashScopeChatClient;
public WeatherController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.dashScopeChatClient = chatClientBuilder
.defaultFunctions("weatherFunction")//把这里打开
.build();
}
/**
* 调用工具版 - function
*/
@GetMapping("/chat-tool-function")
public String chatTranslateFunction(@RequestParam(value = "query", defaultValue = "北京今天的天气") String query) {
return dashScopeChatClient.prompt(query).functions("weatherFunction").call().content();
}
}第二种方法:Tool Calling
首先定义接口:
java
public interface WeatherTool {
String getWeather(String city);
}用 @Tool(description = "获取指定城市的天气信息。")来描述函数的功能作用。
@Tool的好处就是你的工具拿到结果以后不需要在交给大模型,而是直接返回给客户端。
java
public class WeatherToolImpl implements WeatherTool {
@Override
@Tool(description = "获取指定城市的天气信息。")
public String getWeather(String city) {
return "The weather in " + city + " is sunny.";
}
}
java
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/weather")
public class WeatherController {
private final ChatClient dashScopeChatClient;
public WeatherController(ChatClient.Builder chatClientBuilder) {
this.dashScopeChatClient = chatClientBuilder
.defaultTools(new WeatherToolImpl())
.build();
}
/**
* 无工具版
*/
@GetMapping("/chat")
public String simpleChat(@RequestParam(value = "query", defaultValue = "北京今天的天气") String query) {
return dashScopeChatClient.prompt(query).call().content();
}
/**
* 调用工具版 - method
*/
@GetMapping("/chat-tool-method")
public String chatTranslateMethod(@RequestParam(value = "query", defaultValue = "北京今天的天气") String query) {
return dashScopeChatClient.prompt(query).tools(new WeatherToolImpl()).call().content();
}
}MCP
MCP我以前的文章都讲过。
直接点开:都说MCP牛B,牛刀小试了一下,代码案例自取_java mcp代码案例-CSDN博客
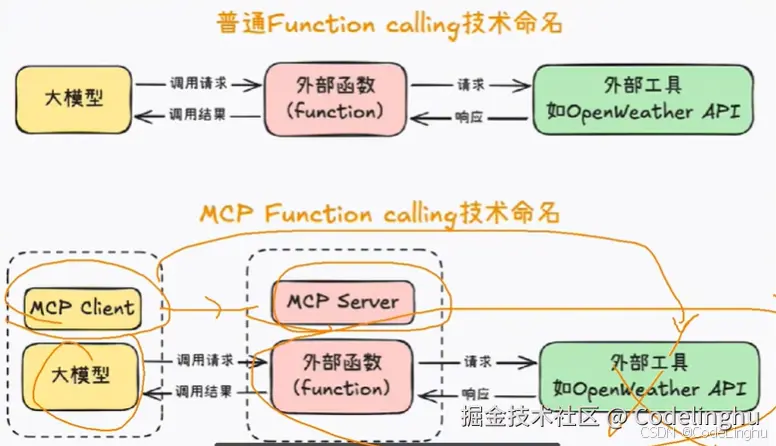
Function calling和MCP的区别就是:
- Function calling 的外部工具一般都是我们自己写、自己封装的
- MCP的外部工具都是别人写好的,第三方提供的。