📖 故事背景:内存王国的两个重要区域
在Android王国里,有两个重要的存储区域:
- 栈(Stack) :像一叠盘子,后进先出,存储方法调用和局部变量
- 堆(Heap) :像一个大仓库,存储对象实例和数组
让我们跟随主角"小方法"的冒险来理解这两个错误!
🏰 栈(Stack)的奇妙世界
栈中存储什么?
java
public class StackStory {
public void heroJourney() {
int health = 100; // 局部基本类型变量
String weapon = "宝剑"; // 局部引用变量(引用在栈,对象在堆)
boolean hasMagic = true; // 局部基本类型变量
fightDragon(health, weapon); // 方法调用
}
private void fightDragon(int hp, String wpn) {
int damage = 50;
// ... 战斗逻辑
}
}栈中存储内容:
- 方法调用的栈帧(Stack Frame)
- 局部变量(基本类型和对象引用)
- 方法参数
- 返回地址
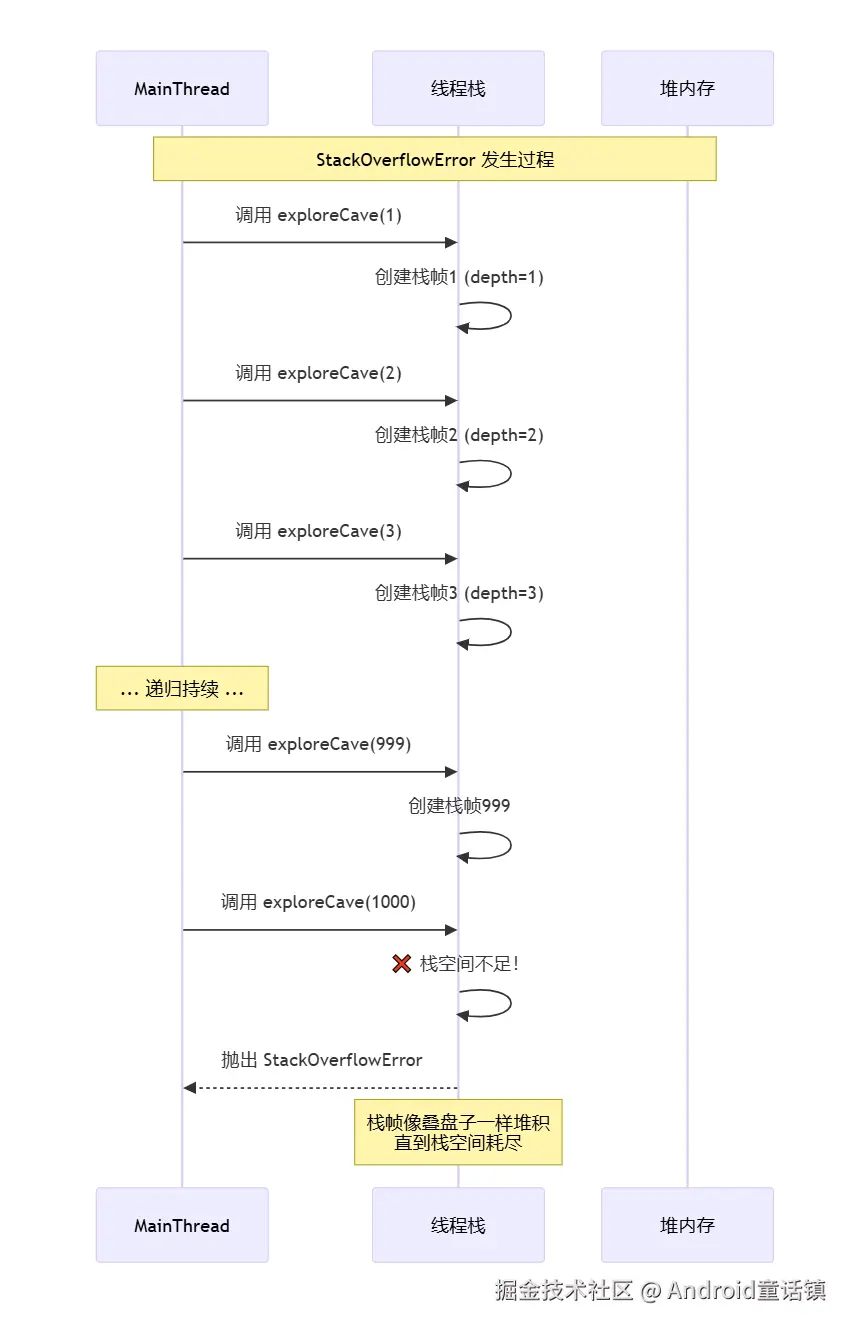
🎭 StackOverflowError的故事:无限递归的陷阱
java
public class InfiniteAdventure {
private int stepCount = 0;
// 🚨 危险!没有终止条件的递归!
public void exploreCave() {
stepCount++;
System.out.println("探索第 " + stepCount + " 步");
// 递归调用自己,没有退出条件!
exploreCave(); // 这里会导致StackOverflowError!
}
// ✅ 正确的递归:有终止条件
public void exploreCaveSafely(int depth) {
if (depth >= 1000) { // 终止条件
System.out.println("到达洞穴底部!");
return;
}
System.out.println("探索深度:" + depth);
exploreCaveSafely(depth + 1); // 安全递归
}
}StackOverflowError发生时机:
- 无限递归调用
- 方法调用层次太深
- 栈空间被耗尽(通常每个线程栈大小约1-8MB)
🏗️ 堆(Heap)的宏大世界
堆中存储什么?
java
public class HeapStory {
public void createKingdom() {
// 这些对象都存储在堆中!
Castle castle = new Castle("王者城堡"); // 对象实例
Knight[] knights = new Knight[1000]; // 数组
List<Weapon> arsenal = new ArrayList<>(); // 集合
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
knights[i] = new Knight("骑士" + i); // 创建大量对象
arsenal.add(new Weapon("武器" + i));
}
}
}
class Castle {
private String name;
private List<Knight> residents;
public Castle(String name) {
this.name = name;
this.residents = new ArrayList<>(); // 对象在堆中
}
}堆中存储内容:
- 所有对象实例
- 数组
- 静态变量
- 被方法区加载的类信息
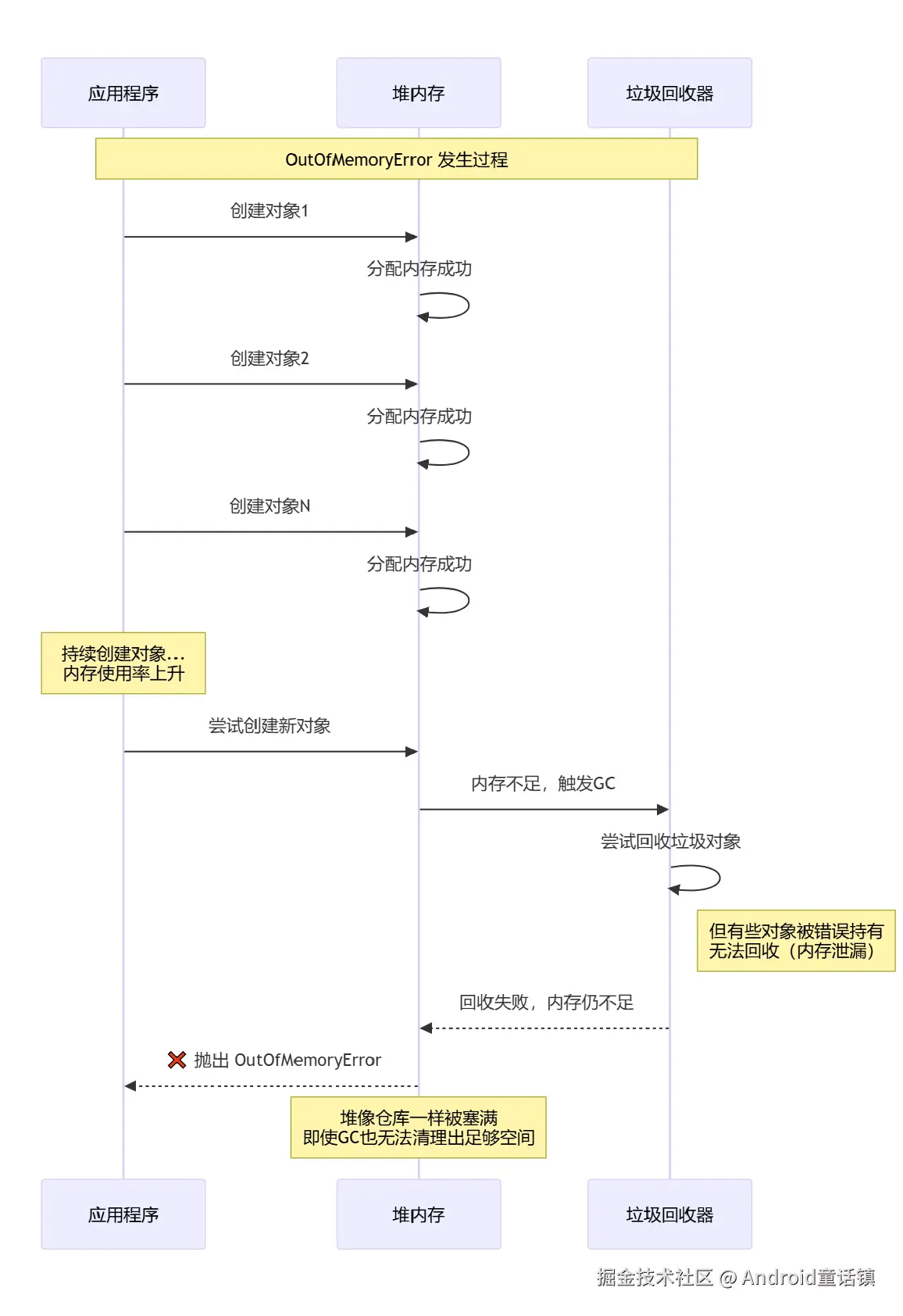
💥 OutOfMemoryError(OOM)的故事:仓库爆炸危机
java
public class KingdomBuilder {
private List<Castle> castles = new ArrayList<>();
// 🚨 危险!内存泄漏!
public void buildCastlesForever() {
int castleCount = 0;
while (true) {
Castle castle = new Castle("城堡" + castleCount++);
castles.add(castle); // 不断添加,从不移除!
// 当堆内存耗尽时,抛出OutOfMemoryError
if (castleCount % 1000 == 0) {
System.out.println("已建造 " + castleCount + " 座城堡");
}
}
}
// ✅ 正确的做法:及时清理不需要的对象
public void buildCastlesSafely() {
List<Castle> temporaryCastles = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
Castle castle = new Castle("临时城堡" + i);
temporaryCastles.add(castle);
// 使用完及时清理
if (i % 10 == 0) {
temporaryCastles.clear(); // 释放对象引用
System.gc(); // 建议垃圾回收(实际开发中慎用)
}
}
}
// 🚨 另一个常见问题:大对象分配失败
public void createHugeArray() {
// 尝试分配超大数组
int[] hugeArray = new int[Integer.MAX_VALUE]; // 可能导致OOM
}
}OOM发生时机:
- 内存泄漏(对象无法被GC回收)
- 加载大图片/文件
- 创建超大数组/集合
- 堆内存耗尽(Android应用通常有内存上限)
🕰️ 时序图:两种错误的调用过程
StackOverflowError的调用时序图
OutOfMemoryError的调用时序图
🔧 实战代码:诊断和预防
诊断StackOverflowError
java
public class StackDebugger {
private static final int MAX_DEPTH = 1000;
private int currentDepth = 0;
public void safeRecursiveMethod() {
currentDepth++;
// 预防StackOverflow
if (currentDepth > MAX_DEPTH) {
throw new IllegalStateException("递归过深,可能存在问题!");
}
try {
// 业务逻辑
if (needMoreRecursion()) {
safeRecursiveMethod();
}
} finally {
currentDepth--; // 确保深度计数器正确递减
}
}
// 使用迭代替代深度递归
public void iterativeSolution() {
Stack<Task> taskStack = new Stack<>();
taskStack.push(initialTask);
while (!taskStack.isEmpty()) {
Task current = taskStack.pop();
processTask(current);
// 添加子任务
for (Task subtask : current.getSubtasks()) {
taskStack.push(subtask);
}
}
}
}预防OutOfMemoryError
java
public class MemoryManager {
// 1. 使用弱引用避免内存泄漏
private WeakReference<Context> contextRef;
// 2. 及时释放资源
public void loadImageSafely(String imagePath) {
BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options();
options.inJustDecodeBounds = true;
BitmapFactory.decodeFile(imagePath, options);
// 计算合适的采样率
options.inSampleSize = calculateInSampleSize(options, 100, 100);
options.inJustDecodeBounds = false;
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(imagePath, options);
// 使用完后及时回收
if (bitmap != null && !bitmap.isRecycled()) {
bitmap.recycle();
}
}
// 3. 使用对象池复用对象
private static class KnightPool {
private static final Queue<Knight> pool = new LinkedList<>();
public static Knight obtain() {
Knight knight = pool.poll();
return knight != null ? knight : new Knight();
}
public static void recycle(Knight knight) {
if (pool.size() < 10) { // 限制池大小
pool.offer(knight);
}
}
}
// 4. 监控内存使用
public void monitorMemory() {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory();
long usedMemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
double memoryUsage = (double) usedMemory / maxMemory;
if (memoryUsage > 0.8) { // 内存使用超过80%
// 触发内存清理
clearCaches();
System.gc();
}
}
}📊 对比总结表
| 特性 | StackOverflowError | OutOfMemoryError |
|---|---|---|
| 发生位置 | 栈(Stack) | 堆(Heap) |
| 存储内容 | 方法调用、局部变量 | 对象实例、数组 |
| 触发原因 | 递归过深、无限循环调用 | 内存泄漏、大对象分配 |
| 错误类型 | 线程私有 | 整个进程共享 |
| 典型场景 | 无终止条件的递归 | 加载大图片、内存泄漏 |
| 解决策略 | 限制递归深度、改用迭代 | 内存优化、及时释放 |
| 内存大小 | 通常1-8MB/线程 | 几十到几百MB |
💡 关键要点
- 栈是方法调用的工作区,堆是对象存储的仓库
- StackOverflowError是"调用链太长",OOM是"仓库装太满"
- 递归必须有终止条件,对象必须及时释放
- 使用内存分析工具(Profiler)定期检查内存使用
记住这个口诀:
栈短堆大要记牢,递归终止很重要
对象用完及时清,内存泄漏无处逃
通过这个故事,希望你能深刻理解Android中这两种常见的内存错误,并在实际开发中避免它们!