1.开机动画总体介绍
1.开机动画启动流程
代码路径
bootanimation frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/
surfaceflinger frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/
init system/core/init/启动流程详细分析:
内核起来后会启动第一个进程,即init进程。
init进程会根据init.rc配置启动surfaceflinger进程。
service surfaceflinger /system/bin/surfaceflinger
class core animation
user system
group graphics drmrpc readproc
capabilities SYS_NICE
onrestart restart --only-if-running zygote
task_profiles HighPerformance
socket pdx/system/vr/display/client stream 0666 system graphics u:object_r:pdx_display_client_endpoint_socket:s0
socket pdx/system/vr/display/manager stream 0666 system graphics u:object_r:pdx_display_manager_endpoint_socket:s0
socket pdx/system/vr/display/vsync stream 0666 system graphics u:object_r:pdx_display_vsync_endpoint_socket:s0surfaceflinger进程便启动了,跟着就会跑进程的main()函数。
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/main_surfaceflinger.cpp
cpp
int main(int, char**) {
...
...
// instantiate surfaceflinger 创建surfaceflinger实例
sp<SurfaceFlinger> flinger = surfaceflinger::createSurfaceFlinger();
...
...
// initialize before clients can connect
flinger->init();
// publish surface flinger 注册服务
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
sm->addService(String16(SurfaceFlinger::getServiceName()), flinger, false,
IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
// publish gui::ISurfaceComposer, the new AIDL interface
sp<SurfaceComposerAIDL> composerAIDL = new SurfaceComposerAIDL(flinger);
sm->addService(String16("SurfaceFlingerAIDL"), composerAIDL, false,
IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
startDisplayService(); // dependency on SF getting registered above
if (SurfaceFlinger::setSchedFifo(true) != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGW("Couldn't set to SCHED_FIFO: %s", strerror(errno));
}
// run surface flinger in this thread 开始运行
flinger->run();
return 0;
}这段代码主要是为了获取一个SurfaceFlinger实例,然后init,然后run
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
cpp
// Inform native graphics APIs whether the present timestamp is supported:
const bool presentFenceReliable =
!getHwComposer().hasCapability(Capability::PRESENT_FENCE_IS_NOT_RELIABLE);
mStartPropertySetThread = getFactory().createStartPropertySetThread(presentFenceReliable);
if (mStartPropertySetThread->Start() != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGE("Run StartPropertySetThread failed!");
}init函数中有段代码是和StartPropertySetThread有关,这里面主要做的是初始化某些属性值,可以看到注释里面写的,ctl.start这个属性值是为了start BootAnimation的。
cpp
namespace android {
StartPropertySetThread::StartPropertySetThread(bool timestampPropertyValue):
Thread(false), mTimestampPropertyValue(timestampPropertyValue) {}
status_t StartPropertySetThread::Start() {
return run("SurfaceFlinger::StartPropertySetThread", PRIORITY_NORMAL);
}
bool StartPropertySetThread::threadLoop() {
// Set property service.sf.present_timestamp, consumer need check its readiness
property_set(kTimestampProperty, mTimestampPropertyValue ? "1" : "0");
// Clear BootAnimation exit flag
property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "0");
property_set("service.bootanim.progress", "0");
// Start BootAnimation if not started
property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim");
// Exit immediately
return false;
}
} // namespace android这里bootanim的启动流程为什么可以被prop控制,下面继续分析
/system/core/init/init.cpp
system/core/init/property_service.cpp
在init进程启动的SecondStageMain过程中,会去调用 StartPropertyService
cpp
void StartPropertyService(int* epoll_socket) {
InitPropertySet("ro.property_service.version", "2");
int sockets[2];
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0, sockets) != 0) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Failed to socketpair() between property_service and init";
}
*epoll_socket = from_init_socket = sockets[0];
init_socket = sockets[1];
StartSendingMessages();
if (auto result = CreateSocket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
false, 0666, 0, 0, {});
result.ok()) {
property_set_fd = *result;
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "start_property_service socket creation failed: " << result.error();
}
listen(property_set_fd, 8);
auto new_thread = std::thread{PropertyServiceThread};
property_service_thread.swap(new_thread);
}
static void PropertyServiceThread() {
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd);
!result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(init_socket, HandleInitSocket); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
while (true) {
auto pending_functions = epoll.Wait(std::nullopt);
if (!pending_functions.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << pending_functions.error();
} else {
for (const auto& function : *pending_functions) {
(*function)();
}
}
}
}在StartPropertyService中会中国epoll来监听事件和fd的变化,其中handle_property_set_fd这里专门监听prop的变化。
如果有fd的变化, 该函数会进一步执行handle_control_message(),在/system/core/init/init.cpp,传入的参数msg.name=ctl.start,msg.value=bootanim,最后通过匹配ctl.来匹配prop,然后获取服务,ServiceList::GetInstance().FindInterface(name);
调用服务中特定函数来启动服务。到这里,bootanim启动服务就被正式启动,在这之前是空有进程,但无服务。
cpp
static void handle_property_set_fd() {
......
switch (cmd) {
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: {
char prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX];
char prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
if (!socket.RecvChars(prop_name, PROP_NAME_MAX, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvChars(prop_value, PROP_VALUE_MAX, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP): error while reading name/value from the socket";
return;
}
prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX-1] = 0;
prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX-1] = 0;
std::string source_context;
if (!socket.GetSourceContext(&source_context)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << prop_name << "': getpeercon() failed";
return;
}
const auto& cr = socket.cred();
std::string error;
uint32_t result =
HandlePropertySet(prop_name, prop_value, source_context, cr, nullptr, &error);
if (result != PROP_SUCCESS) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to set property '" << prop_name << "' from uid:" << cr.uid
<< " gid:" << cr.gid << " pid:" << cr.pid << ": " << error;
}
break;
}
......
}
static bool HandleControlMessage(std::string_view message, const std::string& name,
pid_t from_pid) {
std::string cmdline_path = StringPrintf("proc/%d/cmdline", from_pid);
std::string process_cmdline;
if (ReadFileToString(cmdline_path, &process_cmdline)) {
std::replace(process_cmdline.begin(), process_cmdline.end(), '\0', ' ');
process_cmdline = Trim(process_cmdline);
} else {
process_cmdline = "unknown process";
}
Service* service = nullptr;
auto action = message;
if (ConsumePrefix(&action, "interface_")) {
service = ServiceList::GetInstance().FindInterface(name);
} else {
service = ServiceList::GetInstance().FindService(name);
}
if (service == nullptr) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Control message: Could not find '" << name << "' for ctl." << message
<< " from pid: " << from_pid << " (" << process_cmdline << ")";
return false;
}
const auto& map = GetControlMessageMap();
const auto it = map.find(action);
if (it == map.end()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unknown control msg '" << message << "'";
return false;
}
const auto& function = it->second;
if (auto result = function(service); !result.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Control message: Could not ctl." << message << " for '" << name
<< "' from pid: " << from_pid << " (" << process_cmdline
<< "): " << result.error();
return false;
}
LOG(INFO) << "Control message: Processed ctl." << message << " for '" << name
<< "' from pid: " << from_pid << " (" << process_cmdline << ")";
return true;
}2.开机动画的播放过程
frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/bootanimation_main.cpp
frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/BootAnimation.cpp
cpp
int main()
{
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
// create the boot animation object (may take up to 200ms for 2MB zip)
//创建BootAnimation实例
sp<BootAnimation> boot = new BootAnimation(audioplay::createAnimationCallbacks());
waitForSurfaceFlinger();//等待surfaceflinger启动成功
boot->run("BootAnimation", PRIORITY_DISPLAY);
ALOGV("Boot animation set up. Joining pool.");
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();//binder线程池,与surfaceflinger通信用的。
return 0;
}接下来到BootAnimation的构造函数中
cpp
BootAnimation::BootAnimation(sp<Callbacks> callbacks)
: Thread(false), mLooper(new Looper(false)), mClockEnabled(true), mTimeIsAccurate(false),
mTimeFormat12Hour(false), mTimeCheckThread(nullptr), mCallbacks(callbacks) {
//mSession属于与SurfaceFlinger通信的Client端对象,通过这个对象来进行对应的Surface创建与申请
mSession = new SurfaceComposerClient();
std::string powerCtl = android::base::GetProperty("sys.powerctl", "");
if (powerCtl.empty()) {
mShuttingDown = false;
} else {
mShuttingDown = true;
}
ALOGD("%sAnimationStartTiming start time: %" PRId64 "ms", mShuttingDown ? "Shutdown" : "Boot",
elapsedRealtime());
}
//因为在创建BootAnimation时使用强引用计数,所以第一个引用时会调用这个函数
void BootAnimation::onFirstRef() {
//在preload函数中会根据设备的不同状态(加密、关机、用户空间重启等)来选择对应的动画文件
preloadAnimation();
}在main函数中调用run函数后就进入readyToRun函数,这里面主要是为了获取一块画布,初始化opengl
cpp
status_t BootAnimation::readyToRun() {
mAssets.addDefaultAssets();
mDisplayToken = SurfaceComposerClient::getInternalDisplayToken();
if (mDisplayToken == nullptr)
return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
DisplayMode displayMode;
const status_t error =
SurfaceComposerClient::getActiveDisplayMode(mDisplayToken, &displayMode);
if (error != NO_ERROR)
return error;
mMaxWidth = android::base::GetIntProperty("ro.surface_flinger.max_graphics_width", 0);
mMaxHeight = android::base::GetIntProperty("ro.surface_flinger.max_graphics_height", 0);
ui::Size resolution = displayMode.resolution;
resolution = limitSurfaceSize(resolution.width, resolution.height);
// create the native surface
sp<SurfaceControl> control = session()->createSurface(String8("BootAnimation"),
resolution.getWidth(), resolution.getHeight(), PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565);
SurfaceComposerClient::Transaction t;
// this guest property specifies multi-display IDs to show the boot animation
// multiple ids can be set with comma (,) as separator, for example:
// setprop persist.boot.animation.displays 19260422155234049,19261083906282754
Vector<PhysicalDisplayId> physicalDisplayIds;
char displayValue[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX] = "";
property_get(DISPLAYS_PROP_NAME, displayValue, "");
bool isValid = displayValue[0] != '\0';
if (isValid) {
char *p = displayValue;
while (*p) {
if (!isdigit(*p) && *p != ',') {
isValid = false;
break;
}
p ++;
}
if (!isValid)
SLOGE("Invalid syntax for the value of system prop: %s", DISPLAYS_PROP_NAME);
}
if (isValid) {
std::istringstream stream(displayValue);
for (PhysicalDisplayId id; stream >> id.value; ) {
physicalDisplayIds.add(id);
if (stream.peek() == ',')
stream.ignore();
}
// In the case of multi-display, boot animation shows on the specified displays
// in addition to the primary display
const auto ids = SurfaceComposerClient::getPhysicalDisplayIds();
for (const auto id : physicalDisplayIds) {
if (std::find(ids.begin(), ids.end(), id) != ids.end()) {
if (const auto token = SurfaceComposerClient::getPhysicalDisplayToken(id)) {
t.setDisplayLayerStack(token, ui::DEFAULT_LAYER_STACK);
}
}
}
t.setLayerStack(control, ui::DEFAULT_LAYER_STACK);
}
t.setLayer(control, 0x40000000)
.apply();
sp<Surface> s = control->getSurface();
// initialize opengl and egl
EGLDisplay display = eglGetDisplay(EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
eglInitialize(display, nullptr, nullptr);
EGLConfig config = getEglConfig(display);
EGLSurface surface = eglCreateWindowSurface(display, config, s.get(), nullptr);
// Initialize egl context with client version number 2.0.
EGLint contextAttributes[] = {EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION, 2, EGL_NONE};
EGLContext context = eglCreateContext(display, config, nullptr, contextAttributes);
EGLint w, h;
eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_WIDTH, &w);
eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_HEIGHT, &h);
if (eglMakeCurrent(display, surface, surface, context) == EGL_FALSE)
return NO_INIT;
mDisplay = display;
mContext = context;
mSurface = surface;
mInitWidth = mWidth = w;
mInitHeight = mHeight = h;
mFlingerSurfaceControl = control;
mFlingerSurface = s;
mTargetInset = -1;
projectSceneToWindow();
// Register a display event receiver
mDisplayEventReceiver = std::make_unique<DisplayEventReceiver>();
status_t status = mDisplayEventReceiver->initCheck();
SLOGE_IF(status != NO_ERROR, "Initialization of DisplayEventReceiver failed with status: %d",
status);
mLooper->addFd(mDisplayEventReceiver->getFd(), 0, Looper::EVENT_INPUT,
new DisplayEventCallback(this), nullptr);
return NO_ERROR;
}BootAnimation类的成员函数session用来返回BootAnimation类的成员变量mSession所描述的一个SurfaceComposerClient对象。通过调用SurfaceComposerClient对象mSession的成员函数createSurface可以获得一个SurfaceControl对象control。
SurfaceComposerClient类的成员函数createSurface首先调用内部的Binder代理对象mClient来请求SurfaceFlinger返回一个类型为SurfaceLayer的Binder代理对象,接着再使用这个Binder代理对象来创建一个SurfaceControl对象。创建出来的SurfaceControl对象的成员变量mSurface就指向了从SurfaceFlinger返回来的类型为SurfaceLayer的Binder代理对象。有了这个Binder代理对象之后,SurfaceControl对象就可以和SurfaceFlinger服务通信了。
调用SurfaceControl对象control的成员函数getSurface会返回一个Surface对象s。这个Surface对象s内部也有一个类型为SurfaceLayer的Binder代理对象mSurface,这个Binder代理对象与前面所创建的SurfaceControl对象control的内部的Binder代理对象mSurface引用的是同一个SurfaceLayer对象。这样,Surface对象s也可以通过其内部的Binder代理对象mSurface来和SurfaceFlinger服务通信。
Surface类继承了ANativeWindow类。ANativeWindow类是连接OpenGL和Android窗口系统的桥梁,即OpenGL需要通过ANativeWindow类来间接地操作Android窗口系统。这种桥梁关系是通过EGL库来建立的,所有以egl为前缀的函数名均为EGL库提供的接口。
为了能够在OpenGL和Android窗口系统之间的建立一个桥梁,我们需要一个EGLDisplay对象display,一个EGLConfig对象config,一个EGLSurface对象surface,以及一个EGLContext对象context,其中,EGLDisplay对象display用来描述一个EGL显示屏,EGLConfig对象config用来描述一个EGL帧缓冲区配置参数,EGLSurface对象surface用来描述一个EGL绘图表面,EGLContext对象context用来描述一个EGL绘图上下文(状态),它们是分别通过调用egl库函数eglGetDisplay、EGLUtils::selectConfigForNativeWindow、eglCreateWindowSurface和eglCreateContext来获得的。注意,EGLConfig对象config、EGLSurface对象surface和EGLContext对象context都是用来描述EGLDisplay对象display的。有了这些对象之后,就可以调用函数eglMakeCurrent来设置当前EGL库所使用的绘图表面以及绘图上下文。
还有另外一个地方需要注意的是,每一个EGLSurface对象surface有一个关联的ANativeWindow对象。这个ANativeWindow对象是通过函数eglCreateWindowSurface的第三个参数来指定的。在我们这个场景中,这个ANativeWindow对象正好对应于前面所创建的 Surface对象s。每当OpenGL需要绘图的时候,它就会找到前面所设置的绘图表面,即EGLSurface对象surface。有了EGLSurface对象surface之后,就可以找到与它关联的ANativeWindow对象,即Surface对象s。有了Surface对象s之后,就可以通过其内部的Binder代理对象mSurface来请求 SurfaceFlinger服务返回帧缓冲区硬件设备的一个图形访问接口。这样,OpenGL最终就可以将要绘制的图形渲染到帧缓冲区硬件设备中去,即显示在实际屏幕上。屏幕的大小,即宽度和高度,可以通过函数eglQuerySurface来获得。
在一系列的准备工作后,最后进入开机动画的播放流程,这里默认走android()流程播放开机动画
cpp
bool BootAnimation::threadLoop() {
bool result;
initShaders();
// We have no bootanimation file, so we use the stock android logo
// animation.
if (mZipFileName.isEmpty()) {
ALOGD("No animation file");
result = android();
} else {
result = movie();
}
mCallbacks->shutdown();
eglMakeCurrent(mDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
eglDestroyContext(mDisplay, mContext);
eglDestroySurface(mDisplay, mSurface);
mFlingerSurface.clear();
mFlingerSurfaceControl.clear();
eglTerminate(mDisplay);
eglReleaseThread();
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
return result;
}
bool BootAnimation::android() {
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
SLOGD("%sAnimationShownTiming start time: %" PRId64 "ms", mShuttingDown ? "Shutdown" : "Boot",
elapsedRealtime());
initTexture(&mAndroid[0], mAssets, "images/android-logo-mask.png");
initTexture(&mAndroid[1], mAssets, "images/android-logo-shine.png");
mCallbacks->init({});
// clear screen
glDisable(GL_DITHER);
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glUseProgram(mImageShader);
glClearColor(0,0,0,1);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
// Blend state
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
const nsecs_t startTime = systemTime();
do {
processDisplayEvents();
const GLint xc = (mWidth - mAndroid[0].w) / 2;
const GLint yc = (mHeight - mAndroid[0].h) / 2;
const Rect updateRect(xc, yc, xc + mAndroid[0].w, yc + mAndroid[0].h);
glScissor(updateRect.left, mHeight - updateRect.bottom, updateRect.width(),
updateRect.height());
nsecs_t now = systemTime();
double time = now - startTime;
float t = 4.0f * float(time / us2ns(16667)) / mAndroid[1].w;
GLint offset = (1 - (t - floorf(t))) * mAndroid[1].w;
GLint x = xc - offset;
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glDisable(GL_BLEND);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mAndroid[1].name);
drawTexturedQuad(x, yc, mAndroid[1].w, mAndroid[1].h);
drawTexturedQuad(x + mAndroid[1].w, yc, mAndroid[1].w, mAndroid[1].h);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mAndroid[0].name);
drawTexturedQuad(xc, yc, mAndroid[0].w, mAndroid[0].h);
EGLBoolean res = eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
if (res == EGL_FALSE)
break;
// 12fps: don't animate too fast to preserve CPU
const nsecs_t sleepTime = 83333 - ns2us(systemTime() - now);
if (sleepTime > 0)
usleep(sleepTime);
checkExit();
} while (!exitPending());
glDeleteTextures(1, &mAndroid[0].name);
glDeleteTextures(1, &mAndroid[1].name);
return false;
}3.开机动画的结束源码分析
这里还有一点就是开机动画的退出流程检测
cpp
static const char EXIT_PROP_NAME[] = "service.bootanim.exit";
void BootAnimation::checkExit() {
// Allow surface flinger to gracefully request shutdown
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get(EXIT_PROP_NAME, value, "0");
int exitnow = atoi(value);
if (exitnow) {
requestExit();
}
}这里可以看到是通过检测prop service.bootanim.exit来判断是否申请退出的。那么这个prop的值是由谁设置的呢?
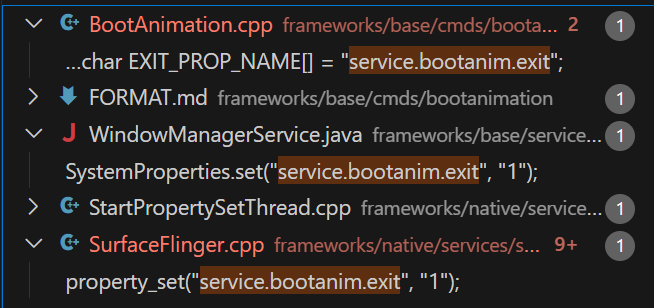
通过搜索框架中的代码可以看到,这个prop在 WindowManagerService.java 和 SurfaceFlinger.cpp 中都有设置。
先分析WindowManagerService.java 中这个prop的设置流程
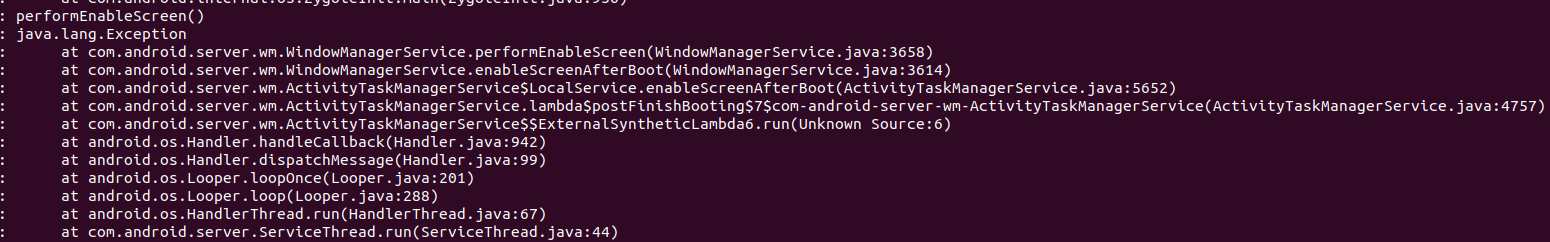
通过堆栈打印,可以分析到一部分流程,下面会反向贴出一层层调用流程的代码
cpp
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
private void performEnableScreen() {
android.util.Log.i("test1", "performEnableScreen() ", new Exception());
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
......
if (!mBootAnimationStopped) {
Trace.asyncTraceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "Stop bootanim", 0);
// stop boot animation
// formerly we would just kill the process, but we now ask it to exit so it
// can choose where to stop the animation.
SystemProperties.set("service.bootanim.exit", "1");
mBootAnimationStopped = true;
}
......
try {
IBinder surfaceFlinger = ServiceManager.getService("SurfaceFlinger");
if (surfaceFlinger != null) {
ProtoLog.i(WM_ERROR, "******* TELLING SURFACE FLINGER WE ARE BOOTED!");
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken("android.ui.ISurfaceComposer");
surfaceFlinger.transact(IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION, // BOOT_FINISHED
data, null, 0);
data.recycle();
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
ProtoLog.e(WM_ERROR, "Boot completed: SurfaceFlinger is dead!");
}
EventLogTags.writeWmBootAnimationDone(SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
Trace.asyncTraceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "Stop bootanim", 0);
mDisplayEnabled = true;
ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_SCREEN_ON, "******************** ENABLING SCREEN!");
// Enable input dispatch.
mInputManagerCallback.setEventDispatchingLw(mEventDispatchingEnabled);
}
try {
mActivityManager.bootAnimationComplete();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
mPolicy.enableScreenAfterBoot();
// Make sure the last requested orientation has been applied.
updateRotationUnchecked(false, false);
}
public void enableScreenAfterBoot() {
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_BOOT, "enableScreenAfterBoot: mDisplayEnabled=%b "
+ "mForceDisplayEnabled=%b mShowingBootMessages=%b mSystemBooted=%b. "
+ "%s",
mDisplayEnabled, mForceDisplayEnabled, mShowingBootMessages, mSystemBooted,
new RuntimeException("here").fillInStackTrace());
if (mSystemBooted) {
return;
}
mSystemBooted = true;
hideBootMessagesLocked();
// If the screen still doesn't come up after 30 seconds, give
// up and turn it on.
mH.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(H.BOOT_TIMEOUT, 30 * 1000);
}
mPolicy.systemBooted();
performEnableScreen();
}
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityTaskManagerService.java
public void enableScreenAfterBoot(boolean booted) {
writeBootProgressEnableScreen(SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
mWindowManager.enableScreenAfterBoot();
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
updateEventDispatchingLocked(booted);
}
}
void postFinishBooting(boolean finishBooting, boolean enableScreen) {
mH.post(() -> {
if (finishBooting) {
mAmInternal.finishBooting();
}
if (enableScreen) {
mInternal.enableScreenAfterBoot(isBooted());
}
});
}
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityTaskSupervisor.java
/**
* Called when all resumed tasks/root-tasks are idle.
*/
@GuardedBy("mService")
private void checkFinishBootingLocked() {
final boolean booting = mService.isBooting();
boolean enableScreen = false;
mService.setBooting(false);
if (!mService.isBooted()) {
mService.setBooted(true);
enableScreen = true;
}
if (booting || enableScreen) {
mService.postFinishBooting(booting, enableScreen);
}
}
void activityIdleInternal(ActivityRecord r, boolean fromTimeout,
boolean processPausingActivities, Configuration config) {
......
// We are now idle. If someone is waiting for a thumbnail from
// us, we can now deliver.
r.idle = true;
// Check if able to finish booting when device is booting and all resumed activities
// are idle.
if ((mService.isBooting() && mRootWindowContainer.allResumedActivitiesIdle())
|| fromTimeout) {
checkFinishBootingLocked();
}
......
// When activity is idle, we consider the relaunch must be successful, so let's clear
// the flag.
r.mRelaunchReason = RELAUNCH_REASON_NONE;
}
}
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/ActivityClientController.java
public void activityIdle(IBinder token, Configuration config, boolean stopProfiling) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
Trace.traceBegin(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "activityIdle");
final ActivityRecord r = ActivityRecord.forTokenLocked(token);
if (r == null) {
return;
}
mTaskSupervisor.activityIdleInternal(r, false /* fromTimeout */,
false /* processPausingActivities */, config);
if (stopProfiling && r.hasProcess()) {
r.app.clearProfilerIfNeeded();
}
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
}
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
private class Idler implements MessageQueue.IdleHandler {
@Override
public final boolean queueIdle() {
ActivityClientRecord a = mNewActivities;
boolean stopProfiling = false;
if (mBoundApplication != null && mProfiler.profileFd != null
&& mProfiler.autoStopProfiler) {
stopProfiling = true;
}
if (a != null) {
mNewActivities = null;
final ActivityClient ac = ActivityClient.getInstance();
ActivityClientRecord prev;
do {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Reporting idle of " + a +
" finished=" +
(a.activity != null && a.activity.mFinished));
if (a.activity != null && !a.activity.mFinished) {
ac.activityIdle(a.token, a.createdConfig, stopProfiling);
a.createdConfig = null;
}
prev = a;
a = a.nextIdle;
prev.nextIdle = null;
} while (a != null);
}
if (stopProfiling) {
mProfiler.stopProfiling();
}
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void handleResumeActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, boolean finalStateRequest,
boolean isForward, String reason) {
......
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new Idler());
}在Activity resume函数中注册空闲处理任务,空闲处理在activity空闲时会进入系统流程,最后走到performEnableScreen 中设置prop。
SurfaceFlinger.cpp中的流程如下
cpp
void SurfaceFlinger::bootFinished() {
......
// stop boot animation
// formerly we would just kill the process, but we now ask it to exit so it
// can choose where to stop the animation.
property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "1");
......
}
frameworks/native/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.cpp
status_t BnSurfaceComposer::onTransact(
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
switch(code) {
......
case BOOT_FINISHED: {
CHECK_INTERFACE(ISurfaceComposer, data, reply);
bootFinished();
return NO_ERROR;
}
......
}
}
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
status_t SurfaceFlinger::onTransact(uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags) {
......
status_t err = BnSurfaceComposer::onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
......
}
class BnSurfaceComposer: public BnInterface<ISurfaceComposer> {
public:
enum ISurfaceComposerTag {
// Note: BOOT_FINISHED must remain this value, it is called from
// Java by ActivityManagerService.
BOOT_FINISHED = IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION,
......
}
}
private void performEnableScreen() {
android.util.Log.i("test1", "performEnableScreen() ", new Exception());
try {
IBinder surfaceFlinger = ServiceManager.getService("SurfaceFlinger");
if (surfaceFlinger != null) {
ProtoLog.i(WM_ERROR, "******* TELLING SURFACE FLINGER WE ARE BOOTED!");
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken("android.ui.ISurfaceComposer");
surfaceFlinger.transact(IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION, // BOOT_FINISHED
data, null, 0);
data.recycle();
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
ProtoLog.e(WM_ERROR, "Boot completed: SurfaceFlinger is dead!");
}
EventLogTags.writeWmBootAnimationDone(SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
Trace.asyncTraceEnd(TRACE_TAG_WINDOW_MANAGER, "Stop bootanim", 0);
mDisplayEnabled = true;
ProtoLog.i(WM_DEBUG_SCREEN_ON, "******************** ENABLING SCREEN!");
// Enable input dispatch.
mInputManagerCallback.setEventDispatchingLw(mEventDispatchingEnabled);
}
}可以看到,SurfaceFlinger中设置动画退出流程的prop其实也是performEnableScreen 发出去的。
4.开机动画opengl绘制分析
cpp
bool BootAnimation::android() {
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
SLOGD("%sAnimationShownTiming start time: %" PRId64 "ms", mShuttingDown ? "Shutdown" : "Boot",
elapsedRealtime());
//初始化两张开机图片
initTexture(&mAndroid[0], mAssets, "images/android-logo-mask.png");
initTexture(&mAndroid[1], mAssets, "images/android-logo-shine.png");
mCallbacks->init({});
// clear screen
//禁用一些GL功能(抖动和剪裁测试)
glDisable(GL_DITHER);
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glUseProgram(mImageShader);
//设置清屏颜色为黑色,清空颜色缓冲区,并交换缓冲区,从而将黑色屏幕显示出来
glClearColor(0,0,0,1);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
// Blend state
glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);
const nsecs_t startTime = systemTime();
do {
processDisplayEvents();
const GLint xc = (mWidth - mAndroid[0].w) / 2;
const GLint yc = (mHeight - mAndroid[0].h) / 2;
const Rect updateRect(xc, yc, xc + mAndroid[0].w, yc + mAndroid[0].h);
glScissor(updateRect.left, mHeight - updateRect.bottom, updateRect.width(),
updateRect.height());
nsecs_t now = systemTime();
double time = now - startTime;
float t = 4.0f * float(time / us2ns(16667)) / mAndroid[1].w;
GLint offset = (1 - (t - floorf(t))) * mAndroid[1].w;
GLint x = xc - offset;
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
glDisable(GL_BLEND);
//glBindTexture 绘制图片
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mAndroid[1].name);
drawTexturedQuad(x, yc, mAndroid[1].w, mAndroid[1].h);
drawTexturedQuad(x + mAndroid[1].w, yc, mAndroid[1].w, mAndroid[1].h);
glEnable(GL_BLEND);
//glBindTexture 绘制图片
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, mAndroid[0].name);
drawTexturedQuad(xc, yc, mAndroid[0].w, mAndroid[0].h);
EGLBoolean res = eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
if (res == EGL_FALSE)
break;
// 12fps: don't animate too fast to preserve CPU
//这里配置了帧率
const nsecs_t sleepTime = 83333 - ns2us(systemTime() - now);
if (sleepTime > 0)
usleep(sleepTime);
checkExit();
} while (!exitPending());
//如果动画结束,要对纹理进行删除
glDeleteTextures(1, &mAndroid[0].name);
glDeleteTextures(1, &mAndroid[1].name);
return false;
}初始化两张图片的样式

cpp
status_t BootAnimation::initTexture(Texture* texture, AssetManager& assets,
const char* name, bool premultiplyAlpha) {
//打开图片文件 并获取图片数据
Asset* asset = assets.open(name, Asset::ACCESS_BUFFER);
if (asset == nullptr)
return NO_INIT;
AndroidBitmapInfo bitmapInfo;
void* pixels = decodeImage(asset->getBuffer(false), asset->getLength(), &bitmapInfo,
premultiplyAlpha);
auto pixelDeleter = std::unique_ptr<void, decltype(free)*>{ pixels, free };
asset->close();
delete asset;
if (!pixels) {
return NO_INIT;
}
const int w = bitmapInfo.width;
const int h = bitmapInfo.height;
//从解码后的位图信息中获取宽高
texture->w = w;
texture->h = h;
//opengl 生成纹理
glGenTextures(1, &texture->name);
//绑定纹理
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture->name);
//根据不同的数据格式将数据放到纹理里面去
switch (bitmapInfo.format) {
case ANDROID_BITMAP_FORMAT_A_8:
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_ALPHA, w, h, 0, GL_ALPHA,
GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, pixels);
break;
case ANDROID_BITMAP_FORMAT_RGBA_4444:
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, w, h, 0, GL_RGBA,
GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_4_4_4_4, pixels);
break;
case ANDROID_BITMAP_FORMAT_RGBA_8888:
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, w, h, 0, GL_RGBA,
GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, pixels);
break;
case ANDROID_BITMAP_FORMAT_RGB_565:
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, w, h, 0, GL_RGB,
GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5, pixels);
break;
default:
break;
}
//设置纹理参数 设置纹理的过滤和环绕方式
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
return NO_ERROR;
}