文章目录
- 一、线程间通信概述
- 二、线程间通信对象
-
- 1、普通对象
- 2、ArrayBuffer对象
- 3、SharedArrayBuffer对象
- 4、Transferable对象(NativeBinding对象)
- 5、Sendable对象
-
- [5.1 实现原理](#5.1 实现原理)
- [5.2 异步锁](#5.2 异步锁)
- [5.3 异步等待](#5.3 异步等待)
- [5.4 ASON解析与生成](#5.4 ASON解析与生成)
- [5.5 共享容器](#5.5 共享容器)
- [5.6 共享模块](#5.6 共享模块)
- [5.7 Sendable对象冻结](#5.7 Sendable对象冻结)
- 三、线程间通信场景
- 四、应用多线程开发
-
- 1、耗时任务并发场景
-
- [1.1 CPU密集型](#1.1 CPU密集型)
- [1.2 I/O密集型](#1.2 I/O密集型)
- [1.3 同步任务](#1.3 同步任务)
- 2、长时任务并发场景
- 3、常驻任务并发场景
一、线程间通信概述
线程间通信指并发多线程间的数据交换行为。
在ArkTS线程间通信中,不同数据对象的行为存在差异。例如,普通JS对象、ArrayBuffer对象和SharedArrayBuffer对象在跨线程时的处理方式不同,涉及序列化、反序列化、数据转移和数据共享等操作。
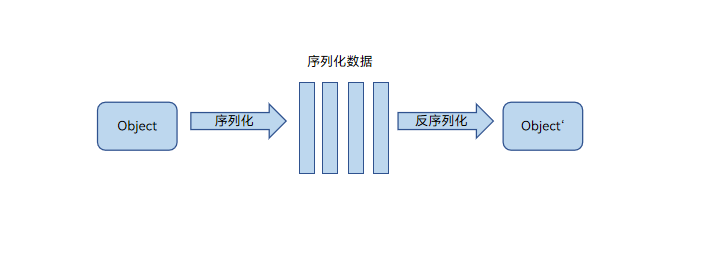
以JS对象为例,其在并发任务间的通信采用了标准的Structured Clone算法(序列化和反序列化)。该算法通过序列化将JS对象转换为与引擎无关的数据(如字符串或内存块),在另一个并发任务中通过反序列化还原成与原JS对象内容一致的新对象。因此,需要进行深拷贝,效率较低。除了支持JS标准的序列化和反序列化能力,还支持绑定Native的JS对象的传输,以及Sendable对象的共享能力。
ArkTS目前主要提供两种并发能力支持线程间通信:TaskPool和Worker。
Worker是Actor并发模型标准的跨线程通信API,与Web Worker或者Node.js Worker的使用方式基本一致。TaskPool提供了功能更强、并发编程更简易的任务池API。其中TaskPool涉及跨并发任务的对象传递行为与Worker一致,还是采用了标准的Structured Clone算法,并发通信的对象越大,耗时就越长。
基于ArkTS提供的TaskPool和Worker并发接口,支持多种线程间通信能力,可以满足不同线程间通信场景。如独立的耗时任务、多个耗时任务、TaskPool线程与宿主线程通信、Worker线程与宿主线程的异步通信、Worker同步调用宿主线程的接口等。
二、线程间通信对象
在多线程并发场景中,例如通过TaskPool或Worker创建后台线程,不同线程间需要进行数据交互。由于线程间内存隔离,线程间通信对象必须通过序列化实现值拷贝或内存共享。
1、普通对象
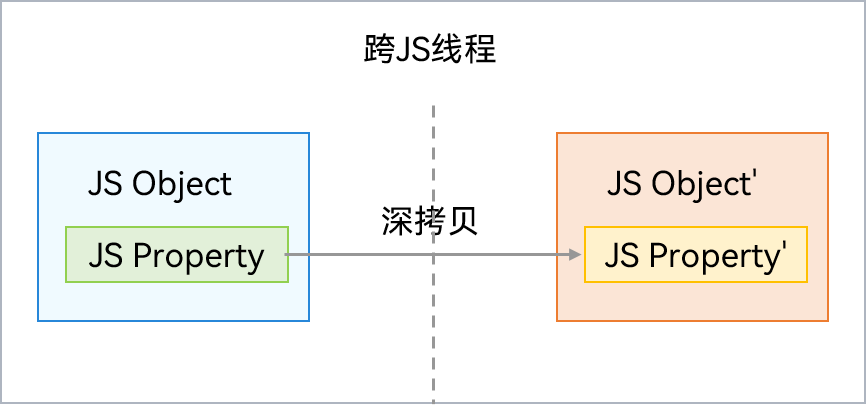
普通对象跨线程时通过拷贝(序列化)形式传递,两个线程的对象内容一致,但指向各自线程的隔离内存区间,被分配在各自线程的虚拟机本地堆(LocalHeap)。
序列化支持类型包括:除Symbol之外的基础类型、Date、String、RegExp、Array、Map、Set、Object(仅限简单对象,比如通过"{}"或者"new Object"创建,普通对象仅支持传递属性,不支持传递其原型及方法)、ArrayBuffer、TypedArray。
普通类实例对象跨线程通过拷贝形式传递,只能传递数据,类实例上的方法会丢失。可以使用@Sendable装饰器标识为Sendable类,类实例对象跨线程传递后,可携带类方法。
2、ArrayBuffer对象
ArrayBuffer包含两部分:底层存储数据的Native内存区域,以及封装操作的JS对象壳。JS对象壳分配在虚拟机的本地堆(LocalHeap)中。
跨线程传递时,JS对象壳需要序列化和反序列化拷贝传递,而Native内存区域可以通过拷贝或转移的方式传递。
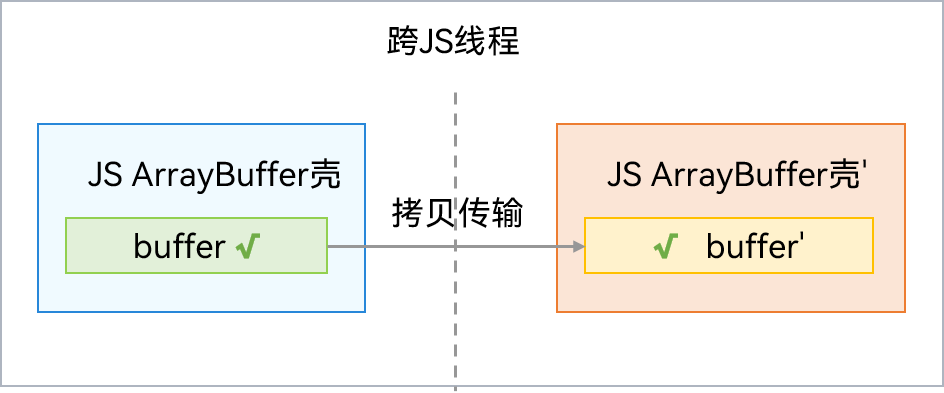
Native内存使用**拷贝方式(递归遍历)**传输时,传输后两个线程可以独立访问ArrayBuffer。此方式需要重建JS壳和拷贝Native内存,传输效率较低。通信过程如下图所示:
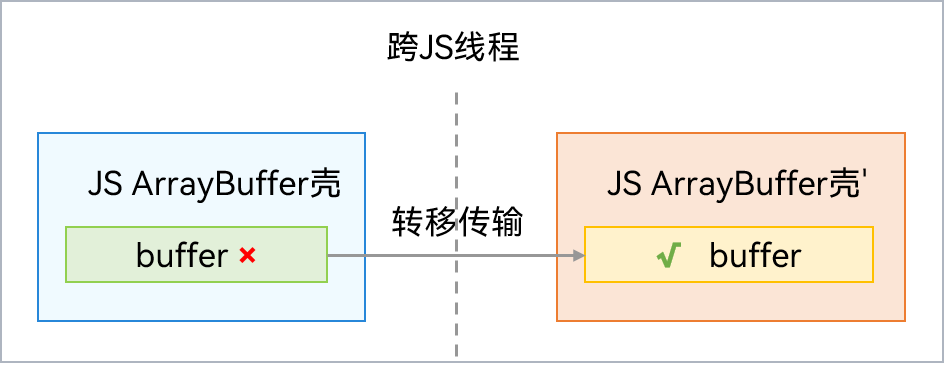
Native内存使用转移方式 传输时,传输后原线程将无法使用此ArrayBuffer对象。跨线程时只需重建JS壳,Native内存无需拷贝,从而提高效率。通信过程如下图所示
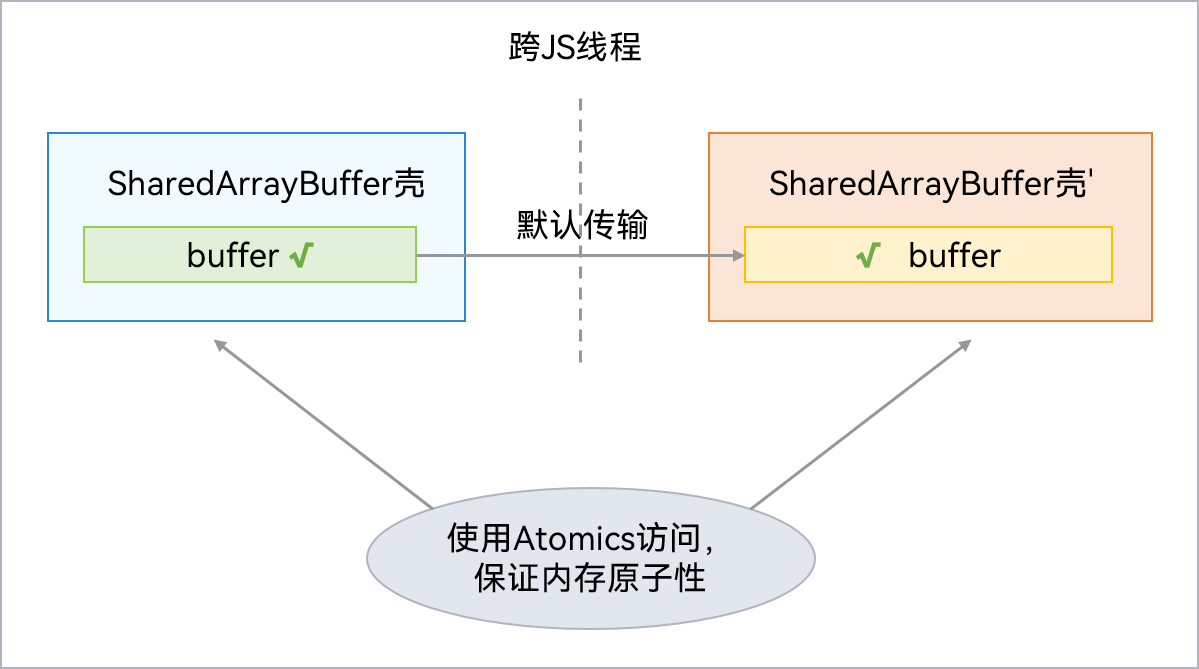
3、SharedArrayBuffer对象
SharedArrayBuffer内部包含一块Native内存,其JS对象壳被分配在虚拟机本地堆(LocalHeap)。支持跨并发实例间共享Native内存,但是对共享Native内存的访问及修改需要采用Atomics类,防止数据竞争。SharedArrayBuffer可用于多个并发实例间的状态或数据共享。
4、Transferable对象(NativeBinding对象)
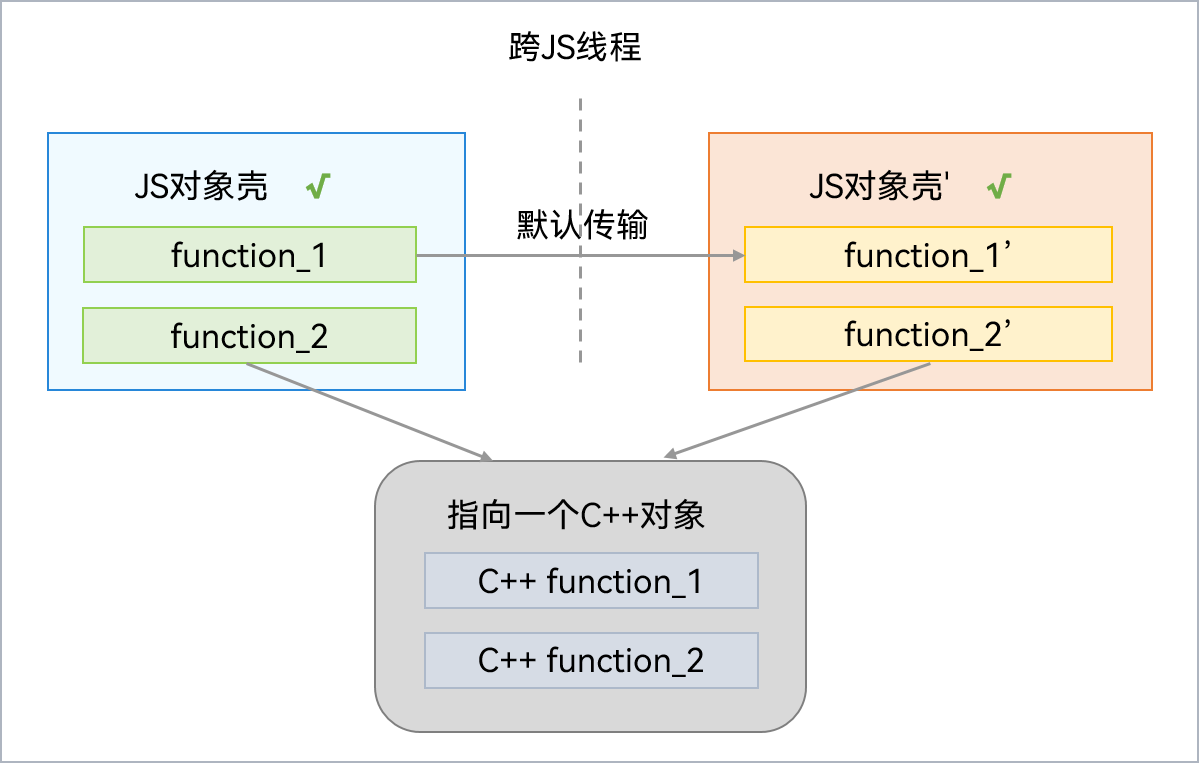
Transferable对象,也称为NativeBinding对象,是指绑定C++对象的JS对象,其主要功能由C++提供,JS对象壳则分配在虚拟机的本地堆(LocalHeap)中。跨线程传输时复用同一个C++对象,相比JS对象的拷贝模式,传输效率更高。因此,可共享或转移的NativeBinding对象被称为Transferable对象。
如果C++实现能够确保线程安全性,则NativeBinding对象的C++部分支持跨线程共享。NativeBinding对象跨线程传输后,只需重新创建JS壳即可桥接到同一个C++对象上,实现C++对象的共享。
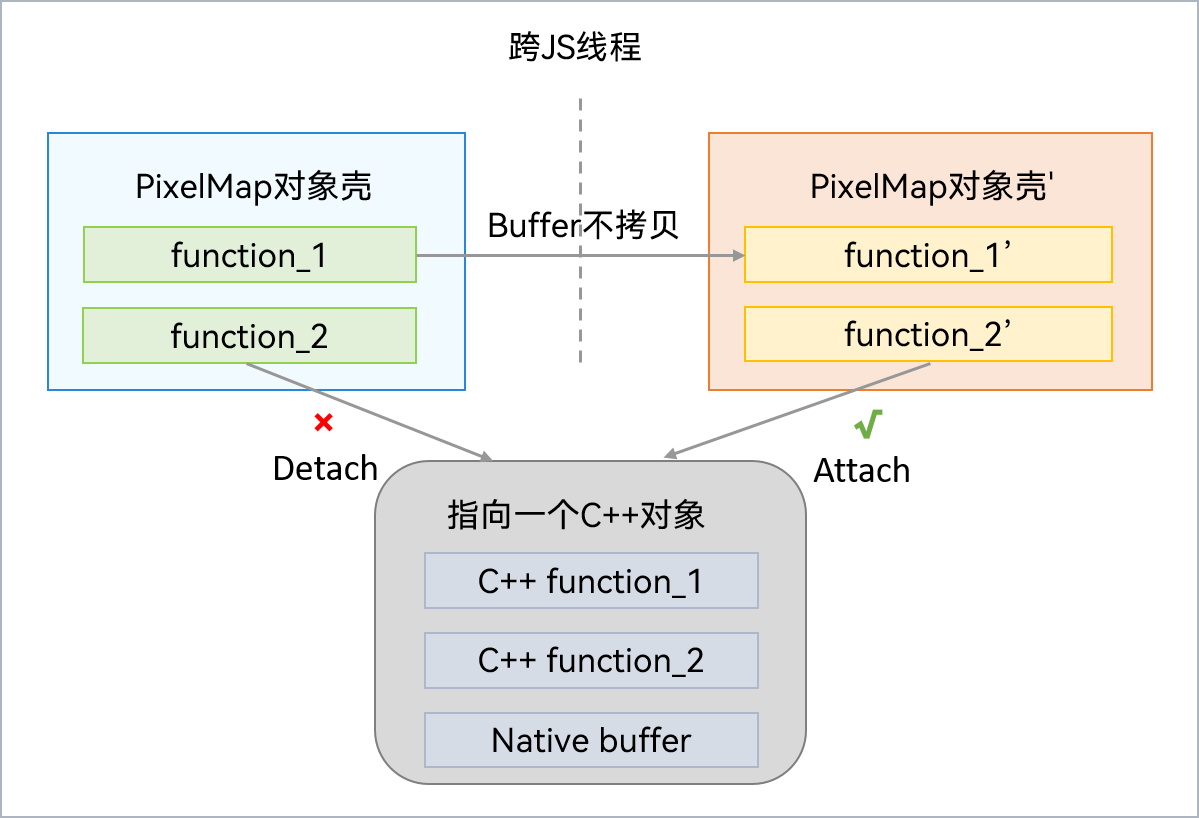
如果C++实现包含数据且无法保证线程安全性,则NativeBinding对象的C++部分需要采用转移方式传输 。NativeBinding对象跨线程传输后,重新创建JS壳可桥接到C++对象上,但需移除原JS壳与C++对象的绑定关系。
5、Sendable对象
Sendable对象可共享,跨线程前后指向同一个JS对象。如果包含JS或Native内容,可以直接共享。如果底层是Native实现,则需要确保线程安全性。
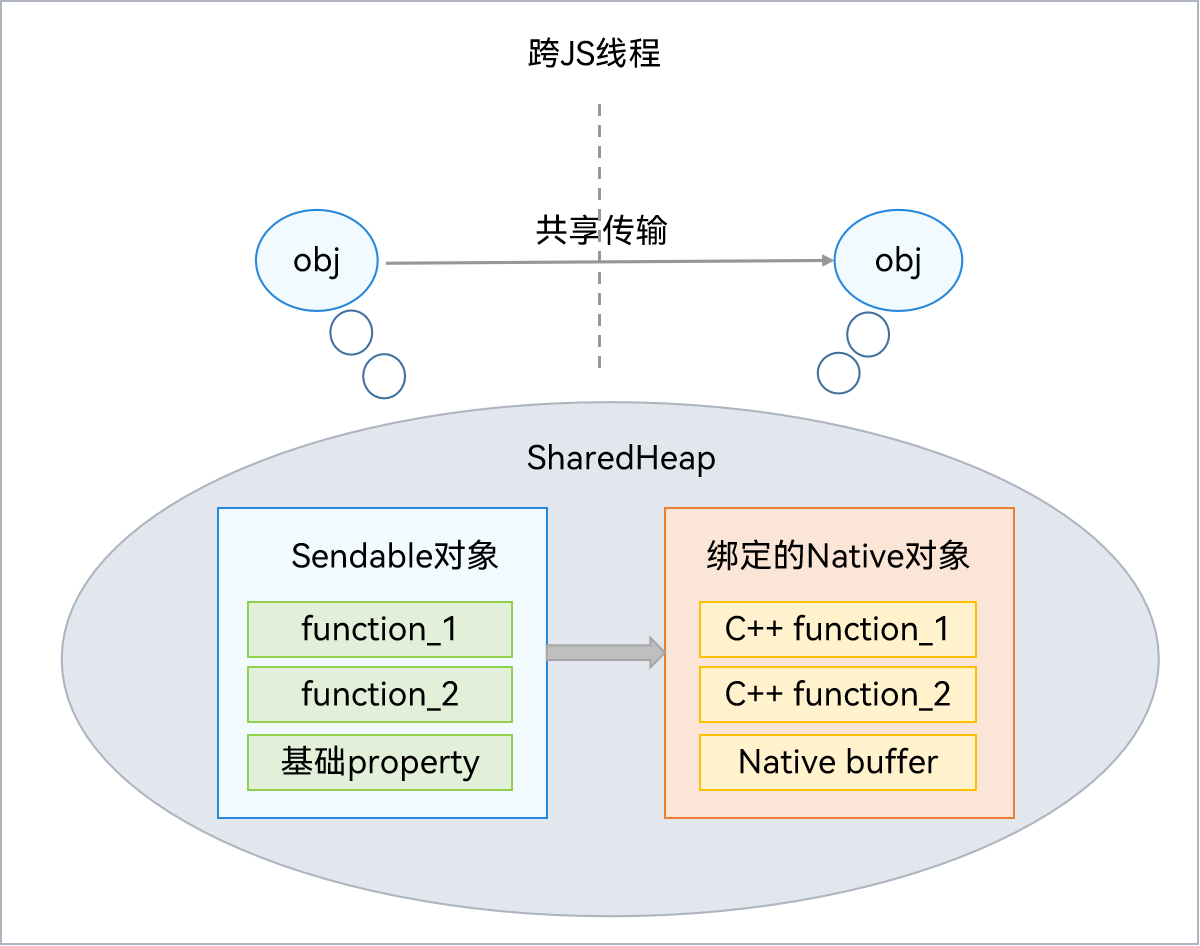
5.1 实现原理
共享堆(SharedHeap)是进程级别的堆空间,与虚拟机本地堆(LocalHeap)不同,LocalHeap仅限单个并发实例访问,而SharedHeap可被所有线程访问。Sendable对象的跨线程行为为引用传递,因此,一个Sendable对象可能被多个并发实例引用。判断该Sendable对象是否存活,取决于所有并发实例是否存在对此Sendable对象的引用。
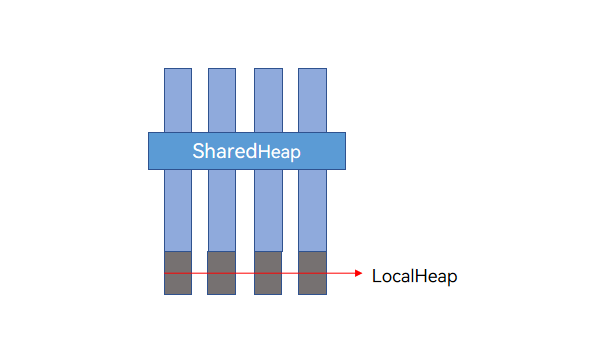
各个并发实例的LocalHeap是隔离的。SharedHeap是进程级别的堆,可以被所有并发实例共享,但SharedHeap不能引用LocalHeap中的对象。
5.2 异步锁
为了解决数据竞争问题,ArkTS引入了异步锁能力。异步锁可能会被类对象持有,因此为了更方便地在并发实例间获取同一个异步锁对象。
由于ArkTS语言支持异步操作,阻塞锁容易产生死锁问题,因此在ArkTS中仅支持异步锁(非阻塞式锁)。同时,异步锁还可以用于保证单线程内的异步任务时序一致性,防止异步任务时序不确定导致的同步问题。
5.3 异步等待
ArkTS引入了异步任务的等待和被唤醒能力,以解决多线程任务时序控制问题。异步任务的等待和被唤醒ConditionVariable对象支持跨线程引用传递。
5.4 ASON解析与生成
ASON工具与JS提供的JSON工具类似。ASON提供了Sendable对象的序列化、反序列化能力。使用ASON.stringify方法可将对象转换为字符串,使用ASON.parse方法可将字符串转换为Sendable对象,从而实现对象在并发任务间的高性能引用传递。
ASON.parse默认生成的对象为Sendable对象,布局不可变,不支持增删属性。如果返回的对象需要支持增删属性,可以指定返回类型为collections.Map对象。
5.5 共享容器
ArkTS共享容器在多个并发实例间传递时,默认采用引用传递,允许多个并发实例操作同一容器实例。此外,还支持拷贝传递,即每个并发实例拥有独立的ArkTS容器实例。
ArkTS共享容器不是线程安全的,内部使用了fail-fast(快速失败)机制,即当检测到多个并发实例同时对容器进行结构性修改时,会触发异常。
5.6 共享模块
共享模块是进程内只会加载一次的模块,使用"use shared"这一指令来标记一个模块是否为共享模块。
非共享模块在同一线程内只加载一次,而在不同线程中会多次加载,每个线程都会生成新的模块对象。因此,目前只能使用共享模块实现进程单例。
5.7 Sendable对象冻结
Sendable对象支持冻结操作。冻结后,对象变为只读,不能修改属性。因此,多个并发实例间访问时无需加锁。可以通过调用Object.freeze接口冻结对象。
三、线程间通信场景
1、使用TaskPool执行独立的耗时任务
对于独立运行的耗时任务,任务完成后将结果返回给宿主线程。
-
实现子线程需要执行的任务。
typescript// IconItemSource.ets export class IconItemSource { image: string | Resource = ''; text: string | Resource = ''; constructor(image: string | Resource = '', text: string | Resource = '') { this.image = image; this.text = text; } }typescript// IndependentTask.ets import { IconItemSource } from './IconItemSource'; // 在TaskPool线程中执行的方法,需要添加@Concurrent注解,否则无法正常调用。 @Concurrent export function loadPicture(count: number): IconItemSource[] { let iconItemSourceList: IconItemSource[] = []; // 遍历添加6*count个IconItem的数据 for (let index = 0; index < count; index++) { const numStart: number = index * 6; // 此处循环使用6张图片资源 iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:startIcon', `item${numStart + 1}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:background', `item${numStart + 2}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:foreground', `item${numStart + 3}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:startIcon', `item${numStart + 4}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:background', `item${numStart + 5}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:foreground', `item${numStart + 6}`)); } return iconItemSourceList; } -
使用TaskPool的execute方法执行任务,加载图片。
typescript// Index.ets import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS'; import { IconItemSource } from './IconItemSource'; import { loadPicture } from './IndependentTask'; @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(() => { let iconItemSourceList: IconItemSource[] = []; // 创建Task let loadPictureTask: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(loadPicture, 30); // 执行Task,并返回结果 taskpool.execute(loadPictureTask).then((res: object) => { // loadPicture方法的执行结果 iconItemSourceList = res as IconItemSource[]; // 输出结果是:The length of iconItemSourceList is 180 console.info("The length of iconItemSourceList is " + iconItemSourceList.length); }) }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
2、使用TaskPool执行多个耗时任务
多个任务同时执行时,由于任务复杂度不同,执行时间和返回数据的时间也会不同。如果宿主线程需要所有任务执行完毕的数据,可以通过TaskGroup的方式实现。
-
实现子线程中需要执行的任务。
typescript// IconItemSource.ets export class IconItemSource { image: string | Resource = ''; text: string | Resource = ''; constructor(image: string | Resource = '', text: string | Resource = '') { this.image = image; this.text = text; } }typescript// IndependentTask.ets import { IconItemSource } from './IconItemSource'; // 在TaskPool线程中执行的方法,需要添加@Concurrent注解,否则无法正常调用 @Concurrent export function loadPicture(count: number): IconItemSource[] { let iconItemSourceList: IconItemSource[] = []; // 遍历添加6*count个IconItem的数据 for (let index = 0; index < count; index++) { const numStart: number = index * 6; // 此处循环使用6张预定义的图片资源(例如:startIcon、background、foreground等) iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:startIcon', `item${numStart + 1}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:background', `item${numStart + 2}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:foreground', `item${numStart + 3}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:startIcon', `item${numStart + 4}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:background', `item${numStart + 5}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:foreground', `item${numStart + 6}`)); } return iconItemSourceList; } -
将需要执行的Task放到一个TaskGroup里面,当TaskGroup中的所有Task执行完毕后,会将所有Task的结果都放在一个数组中并返回给宿主线程,而不是每执行完一个Task就返回一次,这样宿主线程就可以在返回的数据里拿到所有Task的执行结果,便于后续使用。
typescript// Index.ets import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS'; import { IconItemSource } from './IconItemSource'; import { loadPicture } from './IndependentTask'; @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(() => { let iconItemSourceList: IconItemSource[][] = []; let taskGroup: taskpool.TaskGroup = new taskpool.TaskGroup(); taskGroup.addTask(new taskpool.Task(loadPicture, 30)); taskGroup.addTask(new taskpool.Task(loadPicture, 20)); taskGroup.addTask(new taskpool.Task(loadPicture, 10)); taskpool.execute(taskGroup).then((ret: object) => { let tmpLength = (ret as IconItemSource[][]).length; for (let i = 0; i < tmpLength; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < ret[i].length; j++) { iconItemSourceList.push(ret[i][j]); } } // The length of iconItemSourceList is 360 console.info("The length of iconItemSourceList is " + iconItemSourceList.length); }) }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
3、TaskPool任务与宿主线程通信
如果Task不仅需要返回最终执行结果,还需定时通知宿主线程状态和数据变化,或分段返回大量数据(如从数据库读取大量数据)。
-
实现接收Task消息的方法。
typescript// TaskSendDataUsage.ets export function notice(data: number): void { console.info("子线程任务已执行完,共加载图片: ", data); } -
在需要执行的Task中,添加sendData()接口将消息发送给宿主线程。
typescript// IconItemSource.ets export class IconItemSource { image: string | Resource = ''; text: string | Resource = ''; constructor(image: string | Resource = '', text: string | Resource = '') { this.image = image; this.text = text; } }typescript// TaskSendDataUsage.ets import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS'; import { IconItemSource } from './IconItemSource'; // 通过Task的sendData方法,即时通知宿主线程信息 @Concurrent export function loadPictureSendData(count: number): IconItemSource[] { let iconItemSourceList: IconItemSource[] = []; // 遍历添加6*count个IconItem的数据 for (let index = 0; index < count; index++) { const numStart: number = index * 6; // 此处循环使用6张图片资源 iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:startIcon', `item${numStart + 1}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:background', `item${numStart + 2}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:foreground', `item${numStart + 3}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:startIcon', `item${numStart + 4}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:background', `item${numStart + 5}`)); iconItemSourceList.push(new IconItemSource('$media:foreground', `item${numStart + 6}`)); taskpool.Task.sendData(iconItemSourceList.length); } return iconItemSourceList; } -
最后,在宿主线程通过onReceiveData()接口接收消息。
这样宿主线程就可以通过notice()接口接收到Task发送的数据。
typescript// Index.ets import { taskpool } from '@kit.ArkTS'; import { IconItemSource } from './IconItemSource'; import { loadPictureSendData, notice } from './TaskSendDataUsage'; @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(async () => { let iconItemSourceList: IconItemSource[] = []; let loadPictureTask: taskpool.Task = new taskpool.Task(loadPictureSendData, 30); // 设置notice方法接收Task发送的消息 loadPictureTask.onReceiveData(notice); iconItemSourceList = await taskpool.execute(loadPictureTask) as IconItemSource[]; console.info("The length of iconItemSourceList is " + iconItemSourceList.length); }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
4、Worker和宿主线程的即时消息通信
在ArkTS中,Worker相对于Taskpool存在一定的差异性,有数量限制但是可以长时间存在。一个Worker中可能会执行多个不同的任务,每个任务的执行时长或返回结果可能都不同,宿主线程需要根据情况调用Worker中的不同方法,Worker则需要及时地将结果返回给宿主线程。
-
首先,创建一个执行任务的Worker。
typescript// Worker.ets import { ErrorEvent, MessageEvents, ThreadWorkerGlobalScope, worker } from '@kit.ArkTS'; const workerPort: ThreadWorkerGlobalScope = worker.workerPort; // Worker接收宿主线程的消息,做相应的处理 workerPort.onmessage = (e: MessageEvents): void => { if (e.data === 'hello world') { workerPort.postMessage('success'); } } -
这里的宿主线程是UI主线程,在宿主线程中创建Worker对象,当点击Button时调用postMessage方法向Worker线程发送消息,Worker线程将通过注册的onmessage回调处理宿主线程发送的消息。
typescript// Index.ets import { worker } from '@kit.ArkTS'; function promiseCase() { let p: Promise<void> = new Promise<void>((resolve: Function, reject: Function) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve(); }, 100); }); return p; } async function postMessageTest() { let ss = new worker.ThreadWorker("entry/ets/workers/Worker.ets"); let res = undefined; let flag = false; let isTerminate = false; ss.onexit = () => { isTerminate = true; } // 接收Worker线程发送的消息 ss.onmessage = (e) => { res = e.data; flag = true; console.info("worker:: res is " + res); } // 给Worker线程发送消息 ss.postMessage("hello world"); while (!flag) { await promiseCase(); } ss.terminate(); while (!isTerminate) { await promiseCase(); } } @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(() => { postMessageTest(); }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
5、Worker同步调用宿主线程的接口
如果一个接口已在宿主线程中实现,Worker可以通过以下方式调用该接口。
-
首先,在宿主线程实现需要调用的接口,并创建Worker对象,在Worker对象上注册需要调用的对象。
typescript// Index.ets import { MessageEvents, worker } from '@kit.ArkTS'; class TestObj { public getMessage(): string { return "this is a message from TestObj"; } static testObj: TestObj = new TestObj(); } @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(() => { // 创建Worker对象 const workerInstance: worker.ThreadWorker = new worker.ThreadWorker("entry/ets/workers/Worker.ets"); // 在Worker上注册需要调用的对象 workerInstance.registerGlobalCallObject("testObj", TestObj.testObj); workerInstance.postMessage("start"); workerInstance.onmessage = (e: MessageEvents): void => { // 接收Worker子线程的结果 console.info("mainThread: " + e.data); // 销毁Worker workerInstance.terminate(); } }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } } -
然后,在Worker中通过callGlobalCallObjectMethod接口可以调用宿主线程中的getMessage()方法。
typescript// Worker.ets import { ErrorEvent, MessageEvents, ThreadWorkerGlobalScope, worker } from '@kit.ArkTS'; const workerPort: ThreadWorkerGlobalScope = worker.workerPort; workerPort.onmessage = async (e: MessageEvents) => { if (e.data === 'start') { try { // 调用方法 let res: string = workerPort.callGlobalCallObjectMethod("testObj", "getMessage", 0) as string; console.info("worker: ", res); if (res === "this is a message from TestObj") { workerPort.postMessage("run function success."); } } catch (error) { // 异常处理 console.error("worker: error code is " + error.code + " error message is " + error.message); } } }
6、多级Worker间高性能消息通信
多级Worker(即通过父Worker创建子Worker的机制形成层级线程关系)间通信是一种常见的需求,由于Worker线程生命周期由用户自行管理,因此需要注意多级Worker生命周期的正确管理,建议开发者确保销毁父Worker前先销毁所有子Worker。
-
在ets文件夹下新建文件夹Sendable,并准备一个Sendable类CopyEntry,封装克隆任务数据。
typescript// CopyEntry.ets @Sendable export class CopyEntry { // 克隆类型 type: string; // 文件路径 filePath: string; constructor(type: string, filePath: string) { this.type = type; this.filePath = filePath; } } -
创建两个Worker文件,DevEco Studio支持一键生成Worker,在对应的{moduleName}目录下任意位置,单击鼠标右键 > New > Worker,即可自动生成Worker的模板文件及配置信息。本文以创建"ParentWorker"(父Worker)和"ChildWorker"(子Worker)为例。父Worker负责分发克隆任务并判断任务全部完成后关闭子Worker与父Worker;子Worker负责接收任务并执行数据克隆操作,并在任务完成后通知父Worker。
typescript// ParentWorker.ets import { ErrorEvent, MessageEvents, ThreadWorkerGlobalScope, worker, collections, ArkTSUtils } from '@kit.ArkTS' import { CopyEntry } from '../Sendable/CopyEntry' const workerPort: ThreadWorkerGlobalScope = worker.workerPort; // 计算worker1的任务数量 let count1 = 0; // 计算worker2的任务数量 let count2 = 0; // 计算总任务数量 let sum = 0; // 异步锁 const asyncLock = new ArkTSUtils.locks.AsyncLock(); // 创建子Worker const copyWorker1 = new worker.ThreadWorker('entry/ets/workers/ChildWorker.ets'); const copyWorker2 = new worker.ThreadWorker('entry/ets/workers/ChildWorker.ets'); workerPort.onmessage = (e : MessageEvents) => { let array = e.data as collections.Array<CopyEntry>; sum = array.length; for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) { let entry = array[i]; if (entry.type === 'copy1') { count1++; // 如果是copy1类型,则将数据传递给 copyWorker1 copyWorker1.postMessageWithSharedSendable(entry); } else if (entry.type === 'copy2') { count2++; // 如果是copy2类型,则将数据传递给 copyWorker2 copyWorker2.postMessageWithSharedSendable(entry); } } } copyWorker1.onmessage = async (e : MessageEvents) => { console.info('copyWorker1 onmessage:' + e.data); await asyncLock.lockAsync(() => { count1--; if (count1 == 0) { // 如果copyWorker1的任务全部完成,则关闭copyWorker1 console.info('copyWorker1 close'); copyWorker1.terminate(); } sum--; if (sum == 0) { // 如果所有任务全部完成,则关闭父Worker workerPort.close(); } }) } copyWorker2.onmessage = async (e : MessageEvents) => { console.info('copyWorker2 onmessage:' + e.data); await asyncLock.lockAsync(() => { count2--; sum--; if (count2 == 0) { // 如果copyWorker2的任务全部完成,则关闭copyWorker2 console.info('copyWorker2 close') copyWorker2.terminate(); } if (sum == 0) { // 如果所有任务全部完成,则关闭父Worker workerPort.close(); } }) } workerPort.onmessageerror = (e : MessageEvents) => { console.error('onmessageerror:' + e.data); } workerPort.onerror = (e : ErrorEvent) => { console.error('onerror:' + e.message); }typescript// ChildWorker.ets import { ErrorEvent, MessageEvents, ThreadWorkerGlobalScope, worker} from '@kit.ArkTS' import { CopyEntry } from '../Sendable/CopyEntry' const workerPort: ThreadWorkerGlobalScope = worker.workerPort; workerPort.onmessage = (e : MessageEvents) => { let data = e.data as CopyEntry; // 中间copy操作省略 console.info(data.filePath); workerPort.postMessageWithSharedSendable("done"); } workerPort.onmessageerror = (e : MessageEvents) => { console.error('onmessageerror:' + e.data); } workerPort.onerror = (e : ErrorEvent) => { console.error('onerror:' + e.message); } -
在UI主线程页面,创建父Worker并准备克隆任务所需的数据,准备完成后将数据发送给父Worker。
typescript// Index.ets import { worker, collections } from '@kit.ArkTS'; import { CopyEntry } from '../Sendable/CopyEntry' function promiseCase() { let p: Promise<void> = new Promise<void>((resolve: Function, reject: Function) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve(); }, 100); }); return p; } async function postMessageTest() { let ss = new worker.ThreadWorker("entry/ets/workers/ParentWorker.ets"); let isTerminate = false; ss.onexit = () => { isTerminate = true; } let array = new collections.Array<CopyEntry>(); // 准备数据 for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) { if (i % 2 == 0) { array.push(new CopyEntry("copy1", "file://copy1.txt")); } else { array.push(new CopyEntry("copy2", "file://copy2.txt")); } } // 给Worker线程发送消息 ss.postMessageWithSharedSendable(array); while (!isTerminate) { await promiseCase(); } console.info("Worker线程已退出"); } @Entry @Component struct Index { @State message: string = 'Hello World'; build() { Row() { Column() { Text(this.message) .fontSize(50) .fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold) .onClick(() => { postMessageTest(); }) } .width('100%') } .height('100%') } }
四、应用多线程开发
在ArkTS应用开发中,不同业务场景需要不同的并发能力和任务类型。
常见的业务场景分为三种并发任务:
-
耗时任务:业务逻辑包含较大计算量或多次I/O读写等需要长时间执行的任务。
-
长时任务:业务逻辑包含监听或定期采集数据等需要长时间保持运行的任务。
-
常驻任务:业务逻辑跟随主线程生命周期或与主线程绑定的任务。
1、耗时任务并发场景
耗时任务是指需要较长时间执行的任务,如果在UI主线程执行,可能导致应用卡顿、掉帧或响应延迟。典型的耗时任务包括CPU密集型任务、I/O密集型任务和同步任务。
常见业务有:图片,视频的编解码;压缩,解压缩;JSON解析;网络下载;模型运算;数据库操作。
1.1 CPU密集型
CPU密集型任务是指需要占用系统资源进行大量计算的任务,这类任务需要长时间运行,会阻塞线程中其他事件的处理,因此不适合在UI主线程中执行。
当任务不需要长时间(3分钟)占用后台线程,而是一个个独立的任务时,推荐使用TaskPool,反之推荐使用Worker。
1.2 I/O密集型
使用异步并发可以解决单次I/O任务阻塞的问题。对于I/O密集型任务,若线程中的其他任务仍可能被阻塞,建议采用多线程并发来处理。
I/O密集型任务的性能关键在于I/O操作的速度和效率,而非CPU的处理能力。这类任务需要频繁进行磁盘读写和网络通信。此处通过频繁读写系统文件来模拟I/O密集型并发任务的处理。
1.3 同步任务
同步任务用于在多个线程间协调执行,确保任务按特定顺序和规则进行(如使用锁防止数据竞争)。
同步任务的实现需要考虑多个线程之间的协作和同步,以确保数据的正确性和程序的正确执行。
当同步任务之间相对独立时,推荐使用TaskPool,例如一系列导入的静态方法或单例实现的方法。如果同步任务之间有关联性,则需要使用Worker。
由于Actor模型不同线程间内存隔离的特性,普通单例无法在不同线程间使用。可通过共享模块导出单例解决此问题。
2、长时任务并发场景
在应用业务实现过程中,需要较长时间不定时运行的任务称为长时任务。如果在UI主线程中执行这些长时任务,会阻塞UI业务,导致卡顿和丢帧等问题,影响用户体验。因此,通常需要将这些独立的长时任务放到单独的子线程中执行。
长时任务,任务执行周期长,与外部交互简单。分发到后台线程后,这些任务需要不定期响应以获取结果。使用TaskPool可以简化开发工作量,避免管理复杂的生命周期,避免线程泛滥。开发者只需要将上述独立的长时任务放入TaskPool队列,再等待结果即可。
3、常驻任务并发场景
在应用业务实现中,对于耗时较长(超过3分钟)且并发量较小的常驻任务,建议使用Worker在后台线程中执行这些操作,以避免阻塞UI主线程,防止出现丢帧、卡顿等影响用户体验的问题。
常驻任务是指相比于短时任务,时间更长的任务,可能跟UI主线程生命周期一致。相比于长时任务,常驻任务更倾向于跟线程绑定的任务,单次运行时间更长(比如超过3分钟)。