大家好,我是前端西瓜哥。
今天来看看如何对多边线进行光滑处理。
多边线光滑化,指的是提供一个多边形和圆角半径值,将多边线的角点转换为圆弧,如下图所示。
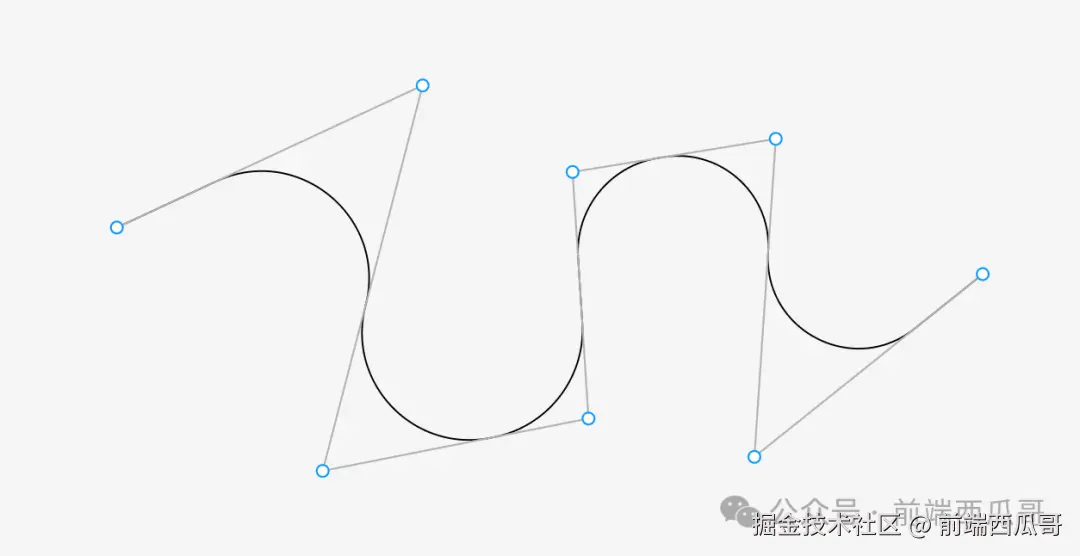
image-20251012165457385
之前写过一篇文章,是关于 在两条直线相交处添加圆角 的算法,这其实就是我们今天要讲的多边线光滑化中的核心算法。
相比两条线段,多边线只是维度更高一点,需要做遍历,细节也多一些。
两直线相交处添加圆角
先回顾下之前文章写的 在两条直线相交处添加圆角算法。
原理是:
-
两条线段往内做距离为 radius 的偏移,求出交点;
-
交点到两条边做垂线,得到两个垂点,这两个点是圆角圆弧的起点和终点;
-
求出圆弧。
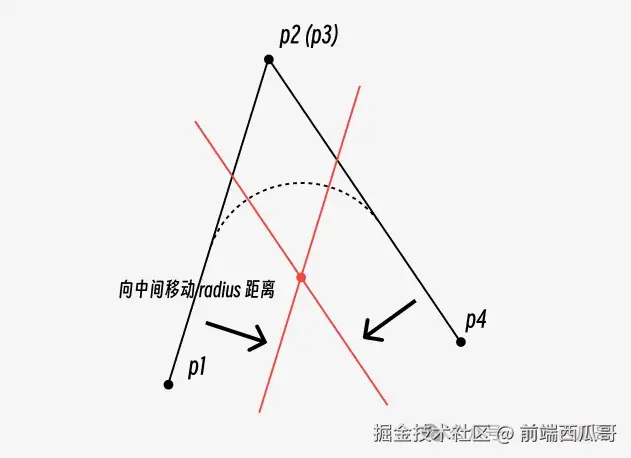
不过对于多段线,是多条线段组成的,radius 是受限的,不能无限大。
对此我们需要确定角点的可用圆角值 maxRadius。
maxRadius 确定
两条线段的情况下,一条线相邻边只有一条,它可以提供充分的空间给圆角线。
-
求相邻两条线段各自能支持的最大圆角半径,取其中较小的,作为半径的最大值 maxRadius;
-
将传入的 radius 限定在 [0, maxRadius] 范围;
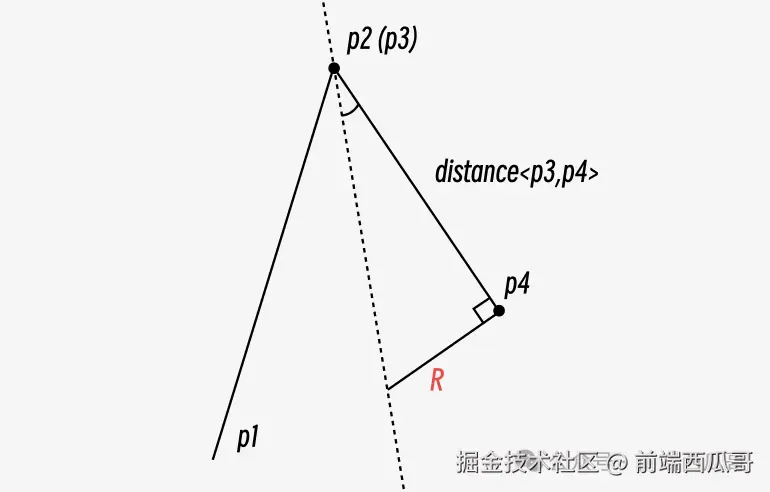
而在多边线场景下,一条线相邻边有两条边,这条边的两侧都要做圆角化。这就存在分配问题了,两边应分别分配多少空间?
一个简单且有效的策略是:平分。(多边线第一条边和最后一条边不需要做平分,因为它们只有一条相邻边。如果做了闭合,变成多边形的话,也是要平分的)
但是它是有个问题的,就是 不能充分利用空间。比如一个三角形,因为卡着边的中点的位置,所以大概率不能圆滑为这个三角形的内接圆。
如果希望想要充分利用空间,就需要类似三角形求圆心一样,求出 "圆心",再去计算对应的利用空间。
如下图,要求 P 点圆角化最大半径,我们要先基于 P 和 Q 画出两条中线,求出 "圆心",圆心对 PQ 线做垂线得到垂点 T,PT 就是给 P 的可用空间,另一边 QT 是 Q 的可用空间。
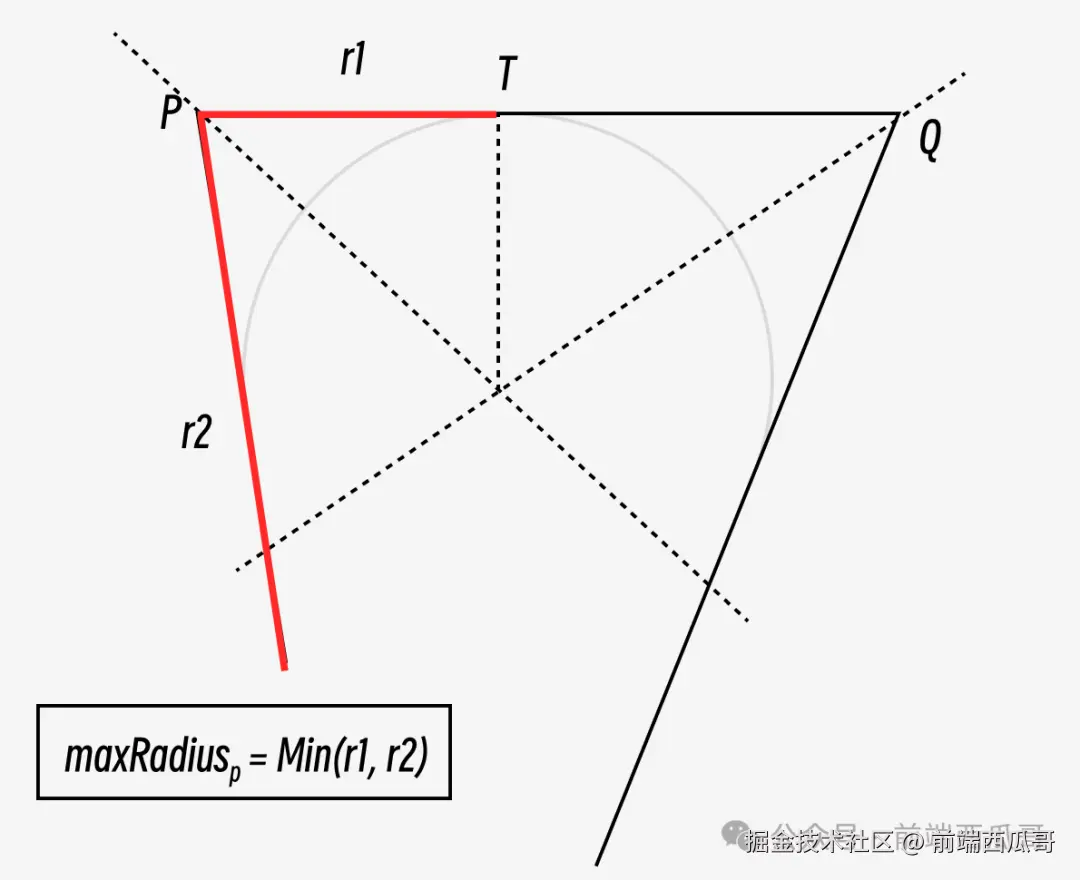
有个特殊情况,可能线不在相同方向,这时候需要将其中一条线翻转过来,这样才好求出 "圆心"。
这个还挺复杂的,我的需求也没这么高,所以这里我还是 继续用平分的方案。
这里只是稍微扩展一下,同时让读者理解为什么后面的实现 radius 开得很大,中间还是有直线的存在。感兴趣的读者可自行实现。
核心算法
ts
const roundPolyline = (polyline: Point[], radius: number) => {
let path: IPathCommand[] = [];
// 半径为 0 不做圆角化,以及小于 2 的话没有角点做圆角化
if (radius === 0 || polyline.length <= 2) {
path = polyline.map((p) => ({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...p }],
}));
} else {
// 从索引为 1 开始,到倒数第 2 个点结束
for (let i = 1; i < polyline.length - 1; i++) {
const p1Index = i - 1;
const p3Index = i + 1;
const p1 = polyline[p1Index];
const p2 = polyline[i];
const p3 = polyline[p3Index];
// 将 r 设置到正确的区间内
const left = p1Index === 0 ? p1 : pointMid(p1, p2);
const right = p3Index === polyline.length - 1 ? p3 : pointMid(p2, p3);
const r = getCorrectedRadius(left, p2, right, radius);
// 拿到圆角化数据,将它添加到 path 上
const data = calcRoundCorner(p1, p2, p2, p3, r);
if (data) {
path.push({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...data.start }],
});
const bezier = arcToBezier({
center: data.circleCenter,
r,
startAngle: data.startAngle,
endAngle: data.endAngle,
angleDir: data.angleDir,
});
path.push({
type: 'C',
points: [bezier[1], bezier[2], bezier[3]],
});
}
// data 为 null,无法生成圆角
else {
path.push({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...p2 }],
});
}
}
}
// 补充起点
if (!isPointEqual(path[0].points[0], polyline[0])) {
path.unshift({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...polyline[0] }],
});
}
if (
!isPointEqual(
path[path.length - 1].points.at(-1)!,
polyline[polyline.length - 1],
)
) {
path.push({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...polyline[polyline.length - 1] }],
});
}
path[0].type = 'M';
return path;
};效果
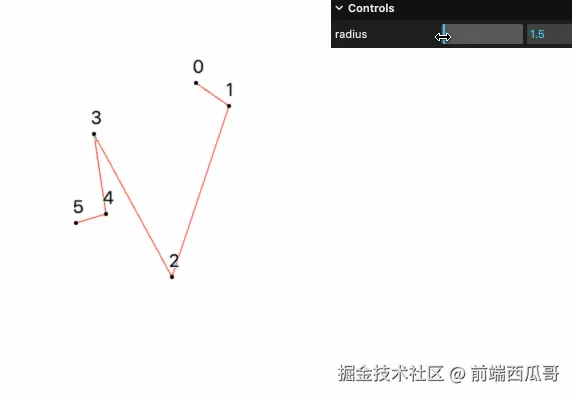
完整算法
核心算法调用的一些底层的基础几何方法,还挺多的。复杂算法本质就是一个个小的算法组合而成。
不过这些算法我在以前的文章都讲过,这里就不一一讲解了,具体哪些文章可以看文末的相关阅读。
ts
import { Matrix } from'pixi.js';
interface Point {
x: number;
y: number;
}
interface IPathCommand {
type: string;
points: Point[];
}
exportconst roundPolyline = (polyline: Point[], radius: number) => {
let path: IPathCommand[] = [];
if (radius === 0 || polyline.length <= 2) {
path = polyline.map((p) => ({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...p }],
}));
} else {
for (let i = 1; i < polyline.length - 1; i++) {
const p1Index = i - 1;
const p3Index = i + 1;
const p1 = polyline[p1Index];
const p2 = polyline[i];
const p3 = polyline[p3Index];
// 将 r 设置到正确的区间内
const left = p1Index === 0 ? p1 : pointMid(p1, p2);
const right = p3Index === polyline.length - 1 ? p3 : pointMid(p2, p3);
const r = getCorrectedRadius(left, p2, right, radius);
const data = calcRoundCorner(p1, p2, p2, p3, r);
// data 为 null,说明无法生成圆角
if (data) {
path.push({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...data.start }],
});
const bezier = arcToBezier({
center: data.circleCenter,
r,
startAngle: data.startAngle,
endAngle: data.endAngle,
angleDir: data.angleDir,
});
path.push({
type: 'C',
points: [bezier[1], bezier[2], bezier[3]],
});
} else {
path.push({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...p2 }],
});
}
}
}
// 补充起点
if (!isPointEqual(path[0].points[0], polyline[0])) {
path.unshift({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...polyline[0] }],
});
}
if (
!isPointEqual(
path[path.length - 1].points.at(-1)!,
polyline[polyline.length - 1],
)
) {
path.push({
type: 'L',
points: [{ ...polyline[polyline.length - 1] }],
});
}
path[0].type = 'M';
return path;
};
const calcRoundCorner = (
p1: Point,
p2: Point,
p3: Point,
p4: Point,
radius: number,
) => {
// p2 到 p1 向量
const v1 = {
x: p1.x - p2.x,
y: p1.y - p2.y,
};
// p2 到 p3 的向量
const v2 = {
x: p4.x - p3.x,
y: p4.y - p3.y,
};
// 求叉积
const cp = v1.x * v2.y - v2.x * v1.y;
if (cp === 0) {
// 平行,无法生成圆角
returnnull;
}
let normalVec1: Point;
let normalVec2: Point;
// v2 在 v1 的左边
if (cp < 0) {
// 求 v1 向左法向量
normalVec1 = {
x: v1.y,
y: -v1.x,
};
// 求 v2 向右法向量
normalVec2 = {
x: -v2.y,
y: v2.x,
};
}
// v2 在 v1 的右边
else {
normalVec1 = {
x: -v1.y,
y: v1.x,
};
normalVec2 = {
x: v2.y,
y: -v2.x,
};
}
// 求沿法向量偏移半径长度的 line1
const t1 = radius / distance(p1, p2);
const d = {
x: normalVec1.x * t1,
y: normalVec1.y * t1,
};
const offsetLine1 = [
{
x: p1.x + d.x,
y: p1.y + d.y,
},
{
x: p2.x + d.x,
y: p2.y + d.y,
},
];
// 求沿法向量偏移半径长度的 line1
const t2 = radius / distance(p3, p4);
const d2 = {
x: normalVec2.x * t2,
y: normalVec2.y * t2,
};
const offsetLine2 = [
{
x: p3.x + d2.x,
y: p3.y + d2.y,
},
{
x: p4.x + d2.x,
y: p4.y + d2.y,
},
];
// 求偏移后两条直线的交点,这个交点就是圆心
const circleCenter = getLineIntersection(
offsetLine1[0],
offsetLine1[1],
offsetLine2[0],
offsetLine2[1],
)!;
// 求圆心到两条线的垂足
const { point: start } = closestPointOnLine(p1, p2, circleCenter, true);
const { point: end } = closestPointOnLine(p3, p4, circleCenter, true);
// 圆心到垂足的弧度
const angleBase = { x: 1, y: 0 };
const startAngle = getSweepAngle(angleBase, {
x: start.x - circleCenter.x,
y: start.y - circleCenter.y,
});
const endAngle = getSweepAngle(angleBase, {
x: end.x - circleCenter.x,
y: end.y - circleCenter.y,
});
return {
offsetLine1,
offsetLine2,
circleCenter,
start,
end,
startAngle,
endAngle,
angleDir: cp < 0, // 正 -> 顺时针
};
};
/** arc to cubic bezier */
const arcToBezier = ({
center,
r,
startAngle,
endAngle,
angleDir = true,
}: {
center: Point;
r: number;
startAngle: number;
endAngle: number;
angleDir: boolean;
}) => {
if (angleDir === false) {
[startAngle, endAngle] = [endAngle, startAngle];
}
const sweepAngle = (endAngle - startAngle + Math.PI * 2) % (Math.PI * 2);
const halfSweepAngle = sweepAngle / 2;
const k =
(4 * (1 - Math.cos(halfSweepAngle))) / (3 * Math.sin(halfSweepAngle));
const matrix = new Matrix()
.rotate(startAngle)
.scale(r, r)
.translate(center.x, center.y);
endAngle -= startAngle;
startAngle = 0;
const p1 = matrix.apply({
x: 1,
y: 0,
});
const p2 = matrix.apply({
x: 1,
y: k,
});
const p3 = matrix.apply({
x: Math.cos(sweepAngle) + k * Math.sin(sweepAngle),
y: Math.sin(sweepAngle) - k * Math.cos(sweepAngle),
});
const p4 = matrix.apply({
x: Math.cos(sweepAngle),
y: Math.sin(sweepAngle),
});
if (angleDir) {
return [p1, p2, p3, p4];
}
return [p4, p3, p2, p1];
};
/** 求两个向量的夹角 */
const getAngle = (a: Point, b: Point) => {
// 使用点乘求夹角
const dot = a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
const d = Math.sqrt(a.x * a.x + a.y * a.y) * Math.sqrt(b.x * b.x + b.y * b.y);
let cosTheta = dot / d;
// 修正精度问题导致的 cosTheta 超出 [-1, 1] 的范围
// 导致 Math.acos(cosTheta) 的结果为 NaN
if (cosTheta > 1) {
cosTheta = 1;
} elseif (cosTheta < -1) {
cosTheta = -1;
}
returnMath.acos(cosTheta);
};
/** 求两个点的中点 */
const pointMid = (p1: Point, p2: Point) => {
return {
x: (p1.x + p2.x) / 2,
y: (p1.y + p2.y) / 2,
};
};
/** 求纠正后的半径 */
const getCorrectedRadius = (
p1: Point,
p2: Point,
p3: Point,
radius: number,
) => {
const v1 = {
x: p2.x - p1.x,
y: p2.y - p1.y,
};
const v2 = {
x: p2.x - p3.x,
y: p2.y - p3.y,
};
const angle = getAngle(v1, v2) / 2;
const r1 = Math.tan(angle) * distance(p1, p2);
const r2 = Math.tan(angle) * distance(p2, p3);
returnMath.min(radius, r1, r2);
};
const TOL = 0.00000001;
const isNumEqual = (a: number, b: number, tol = TOL) => {
returnMath.abs(a - b) <= tol;
};
const isPointEqual = (p1: Point, p2: Point, tol = TOL) => {
return isNumEqual(p1.x, p2.x, tol) && isNumEqual(p1.y, p2.y, tol);
};
const closestPointOnLine = (
p1: Point,
p2: Point,
p: Point,
/** 是否限制在在线段之内 */
canOutside = false,
) => {
if (p1.x === p2.x && p1.y === p2.y) {
return {
t: 0,
d: distance(p1, p),
point: { x: p1.x, y: p1.y },
};
}
const dx = p2.x - p1.x;
const dy = p2.y - p1.y;
let t = ((p.x - p1.x) * dx + (p.y - p1.y) * dy) / (dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (!canOutside) {
t = Math.max(0, Math.min(1, t));
}
const closestPt = {
x: p1.x + t * dx,
y: p1.y + t * dy,
};
return {
t,
d: distance(p, closestPt),
point: closestPt,
};
};
const distance = (p1: Point, p2: Point) => {
const dx = p2.x - p1.x;
const dy = p2.y - p1.y;
returnMath.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
};
/**
* 求向量 a 到向量 b 扫过的夹角
* 这里假设为 x时针方向为正
*/
const getSweepAngle = (a: Point, b: Point) => {
// 使用点乘求夹角
const dot = a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y;
const d = Math.sqrt(a.x * a.x + a.y * a.y) * Math.sqrt(b.x * b.x + b.y * b.y);
let cosTheta = dot / d;
// 修正精度问题导致的 cosTheta 超出 [-1, 1] 的范围
// 导致 Math.acos(cosTheta) 的结果为 NaN
if (cosTheta > 1) {
cosTheta = 1;
} elseif (cosTheta < -1) {
cosTheta = -1;
}
let theta = Math.acos(cosTheta);
// 通过叉积判断方向
// 如果 b 在 a 的左边,则取负值
if (a.x * b.y - a.y * b.x < 0) {
theta = -theta;
}
return theta;
};
/**
* 求两条直线交点
*/
const getLineIntersection = (
p1: Point,
p2: Point,
p3: Point,
p4: Point,
): Point | null => {
const { x: x1, y: y1 } = p1;
const { x: x2, y: y2 } = p2;
const { x: x3, y: y3 } = p3;
const { x: x4, y: y4 } = p4;
const a = y2 - y1;
const b = x1 - x2;
const c = x1 * y2 - x2 * y1;
const d = y4 - y3;
const e = x3 - x4;
const f = x3 * y4 - x4 * y3;
// 计算分母
const denominator = a * e - b * d;
// 判断分母是否为 0(代表平行)
if (Math.abs(denominator) < 0.000000001) {
// 这里有个特殊的重叠但只有一个交点的情况,可以考虑处理一下
returnnull;
}
const px = (c * e - f * b) / denominator;
const py = (a * f - c * d) / denominator;
return { x: px, y: py };
};线上 demo
结尾
我是前端西瓜哥,关注我,学习更多几何知识。
相关阅读,