
Conference :34th USENIX Security Symposium
CCF level:CCF A
Year:2025
Conference time:August 13--15, 2025 Seattle, WA, USA
1
Title:
Auspex: Unveiling Inconsistency Bugs of Transaction Fee Mechanism in Blockchain
Auspex:揭秘区块链交易费机制的不一致漏洞
Authors:****

Abstract:****
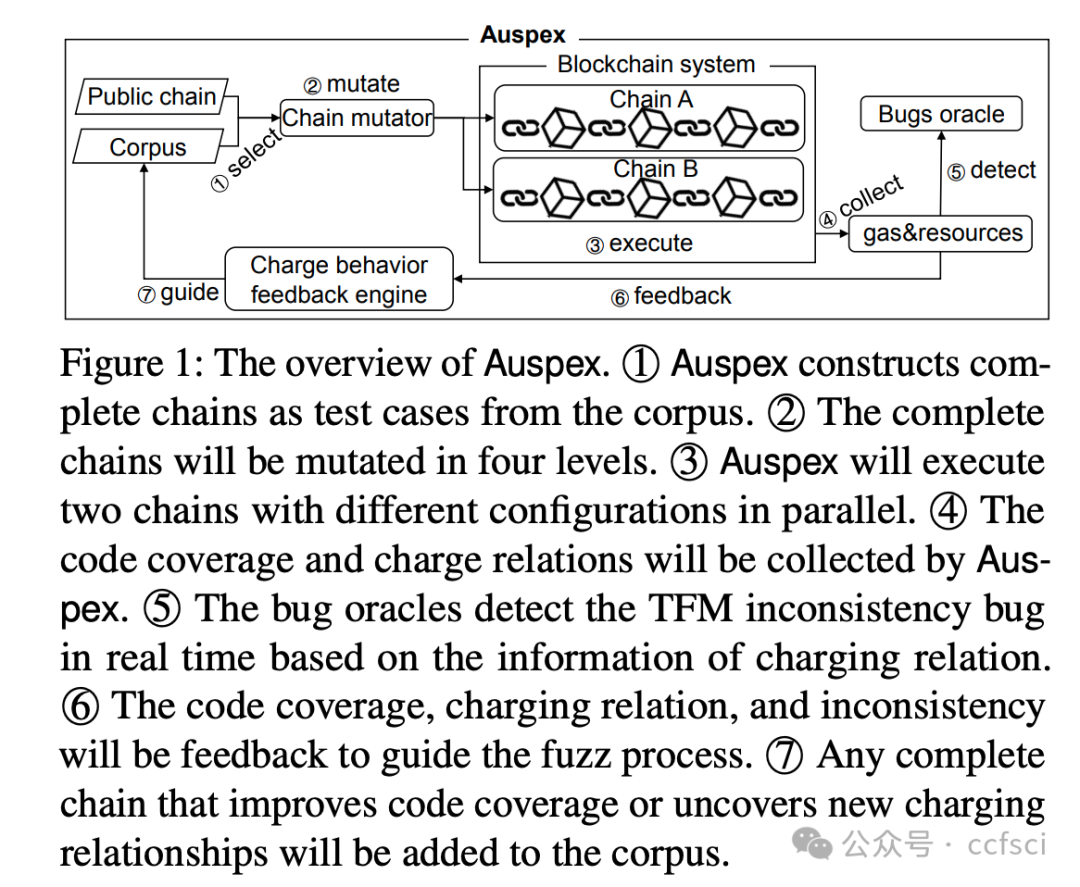
The transaction fee mechanism (TFM) in blockchain prevents resource abuse by charging users based on resource usage, but inconsistencies between charged fees and actual resource consumption, termed as TFM inconsistency bugs, introduce significant security and financial risks.
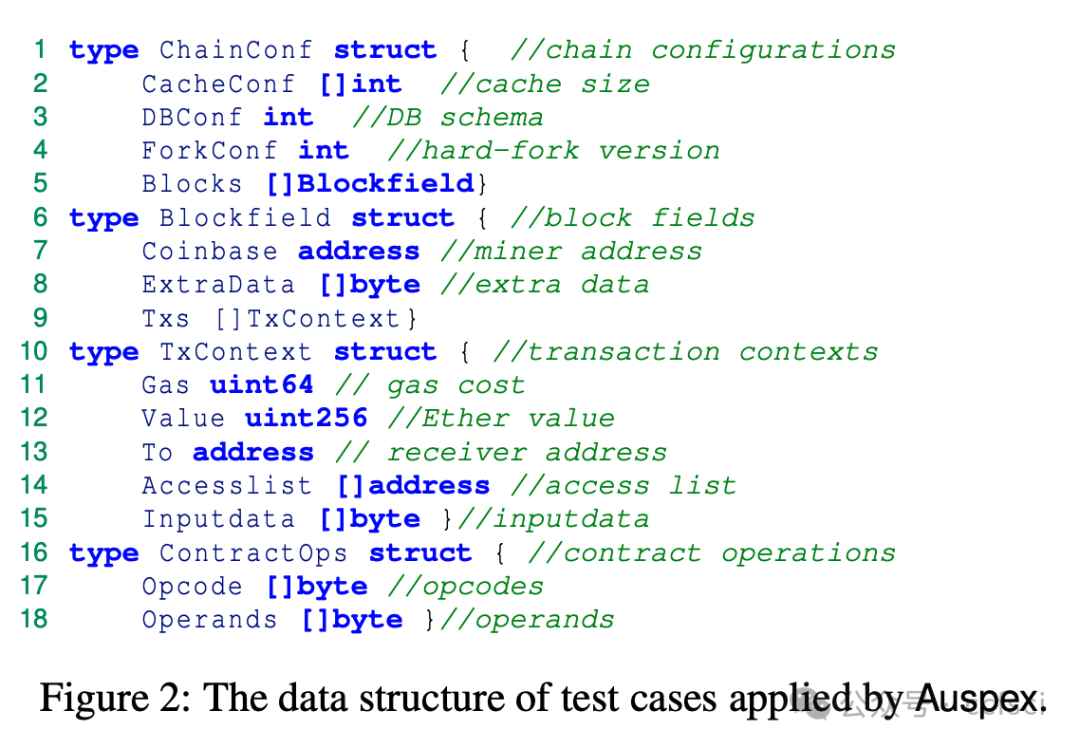
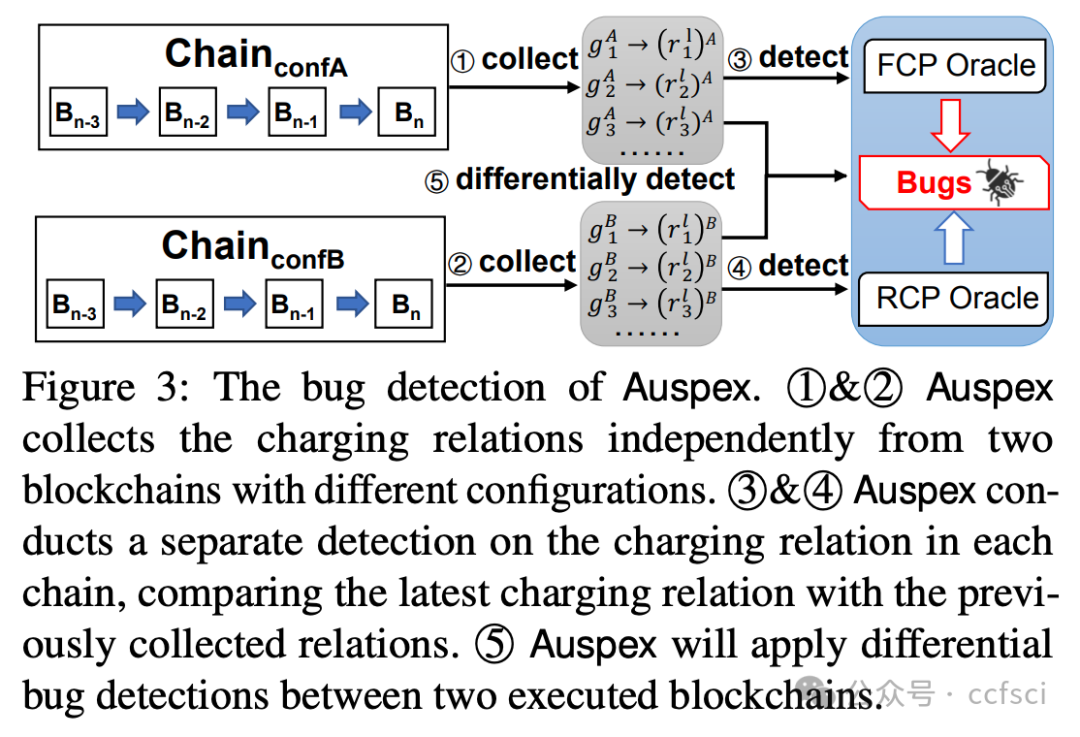
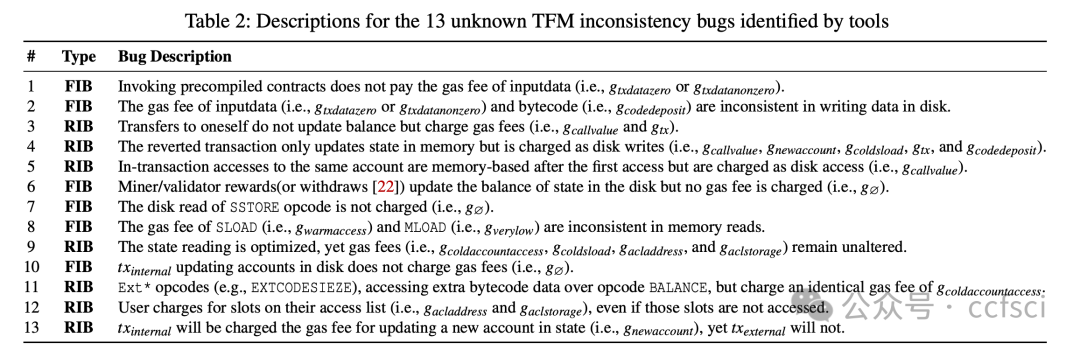
In this paper, we present Auspex, the first tool that automatically detects TFM inconsistency bugs in Ethereum ecosystem by leveraging fuzzing technology. To efficiently trigger and identify TFM inconsistency bugs, Auspex introduces three novel technologies: (i) a chain-based test case generation strategy that enables Auspex to efficiently generate the test cases; (ii) a charging-guided fuzzing approach that guides Auspex to explore more code logic; and (iii) fee consistency property and resource consistency property, two general bug oracles for automatically detecting bugs. We evaluate Auspex on Ethereum and demonstrate its effectiveness by discovering 13 previously unknown TFM inconsistency bugs, and achieving 3.5 times more code branches than state-of-the-art tools. We further explore the financial and security impact of the bugs. On one hand, these bugs have caused losses exceeding millions of dollars for users on both Ethereum and BSC. On the other hand, the denial-of-service (DoS) attack exploiting these bugs can prolong transaction wait time by 4.5 times during the attack period.
区块链中的交易费用机制 (TFM) 通过根据资源使用情况向用户收费来防止资源滥用,但收取的费用与实际资源消耗之间的不一致(称为 TFM 不一致漏洞)会带来严重的安全和财务风险。
本文介绍了 Auspex,这是首个利用模糊测试技术自动检测以太坊生态系统中 TFM 不一致漏洞的工具。为了高效地触发和识别 TFM 不一致漏洞,Auspex 引入了三项新技术:(i) 基于链的测试用例生成策略,使 Auspex 能够高效地生成测试用例;(ii) 收费引导的模糊测试方法,引导 Auspex 探索更多代码逻辑;(iii) 费用一致性属性和资源一致性属性,这两个通用的漏洞预言机可用于自动检测漏洞。我们在以太坊上对 Auspex 进行了评估,并通过发现 13 个先前未知的 TFM 不一致漏洞证明了其有效性,并且其代码分支数量是现有工具的 3.5 倍。我们进一步探讨了这些漏洞带来的财务和安全影响。一方面,这些漏洞已给以太坊和BSC用户造成了超过数百万美元的损失。另一方面,利用这些漏洞发起的拒绝服务 (DoS) 攻击,在攻击期间可将交易等待时间延长 4.5 倍。
Pdf下载链接:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/usenixsecurity25-he-zheyuan.pdf
2
Title:
Blockchain Address Poisoning
区块链地址中毒
Authors:****
Abstract:****
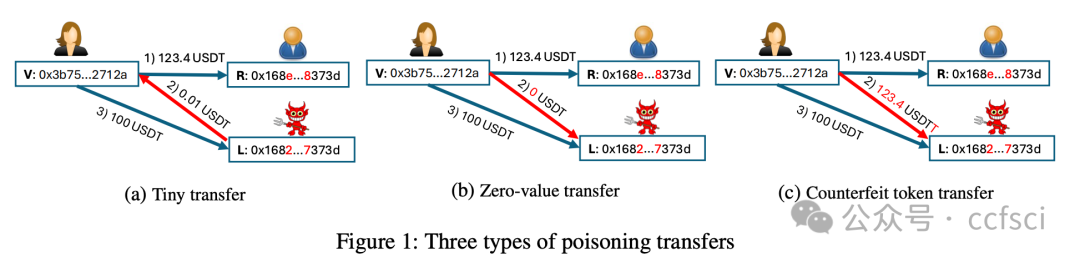
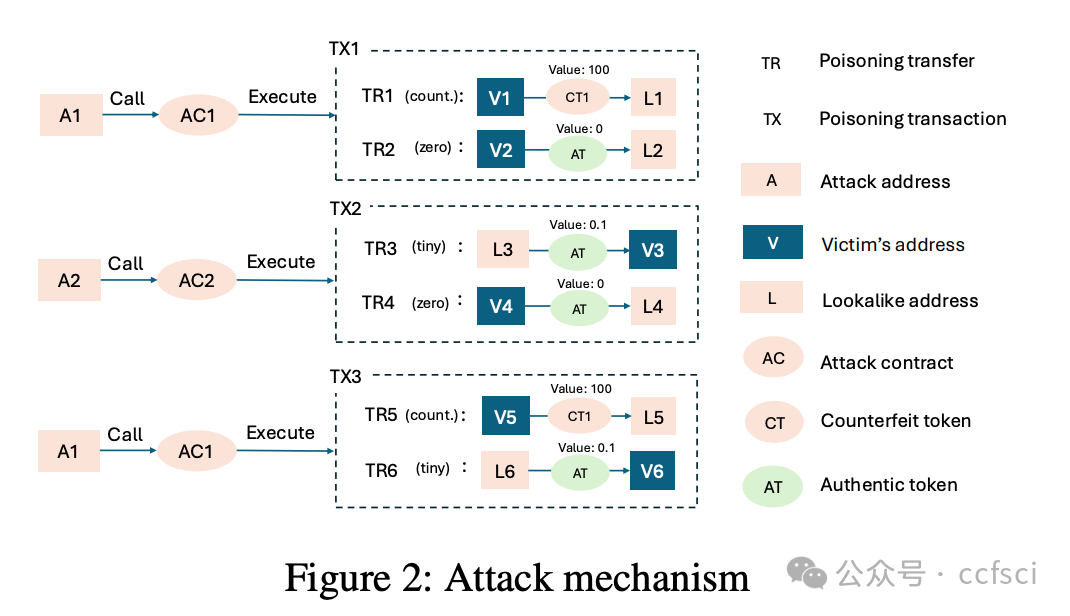
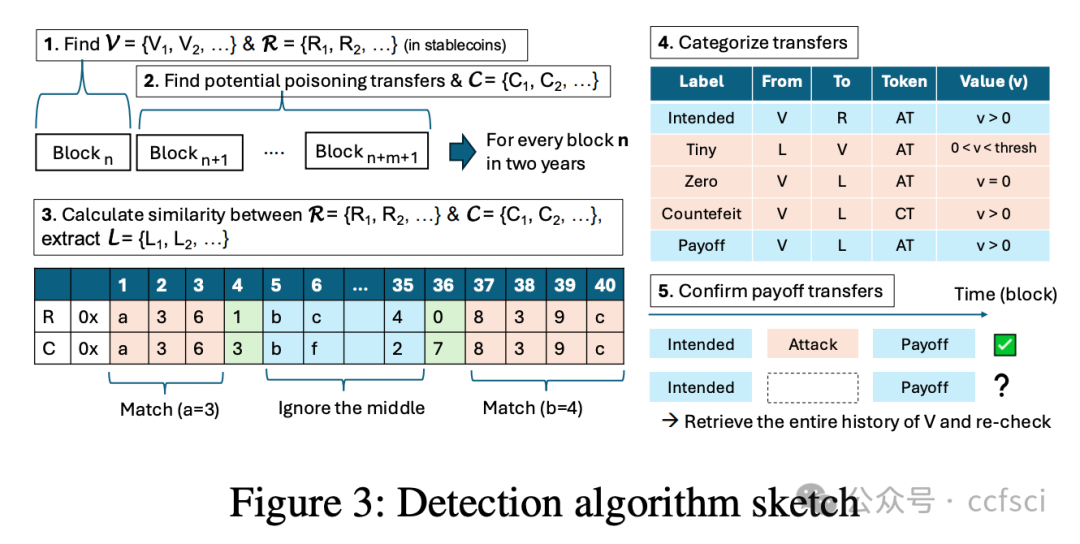
In many blockchains, e.g., Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain (BSC), the primary representation used for wallet addresses is a hardly memorable 40-digit hexadecimal string. As a result, users often select addresses from their recent transaction history, which enables blockchain address poisoning. The adversary first generates lookalike addresses similar to one with which the victim has previously interacted, and then engages with the victim to "poison" their transaction history. The goal is to have the victim mistakenly send tokens to the lookalike address, as opposed to the intended recipient. Compared to contemporary studies, this paper provides four notable contributions. First, we develop a detection system and perform measurements over two years on both Ethereum and BSC. We identify 13~times more attack attempts than reported previously---totaling 270M on-chain attacks targeting 17M victims. 6,633 incidents have caused at least 83.8M USD in losses, which makes blockchain address poisoning one of the largest cryptocurrency phishing schemes observed in the wild. Second, we analyze a few large attack entities using improved clustering techniques, and model attacker profitability and competition. Third, we reveal attack strategies---targeted populations, success conditions (address similarity, timing), and cross-chain attacks. Fourth, we mathematically define and simulate the lookalike address generation process across various software- and hardware-based implementations, and identify a large-scale attacker group that appears to use GPUs. We also discuss defensive countermeasures.
在许多区块链中,例如以太坊、币安智能链 (BSC),钱包地址的主要表示形式是一个难以记忆的 40 位十六进制字符串。因此,用户经常从最近的交易历史记录中选择地址,从而导致区块链地址中毒。攻击者首先生成与受害者之前交互过的地址类似的地址,然后与受害者互动,以"毒害"他们的交易历史记录。其目标是让受害者错误地将代币发送到类似的地址,而不是预期的接收者。与当代研究相比,本文提供了四个显著的贡献。首先,我们开发了一个检测系统,并在两年内对以太坊和 BSC 进行了测量。我们发现的攻击尝试比之前报告的多 13 倍左右------总计 2.7 亿次链上攻击,针对 1700 万受害者。6,633 起事件造成了至少 8,380 万美元的损失,这使得区块链地址中毒成为目前观察到的最大的加密货币网络钓鱼诈骗之一。其次,我们使用改进的聚类技术分析了一些大型攻击实体,并模拟了攻击者的盈利能力和竞争情况。第三,我们揭示了攻击策略------目标人群、成功条件(地址相似性、时机)以及跨链攻击。第四,我们以数学方式定义并模拟了跨各种软件和硬件实现的相似地址生成过程,并识别出一个似乎使用 GPU 的大规模攻击者群体。我们还讨论了防御对策。
Pdf下载链接:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/usenixsecurity25-tsuchiya.pdf
3
Title:
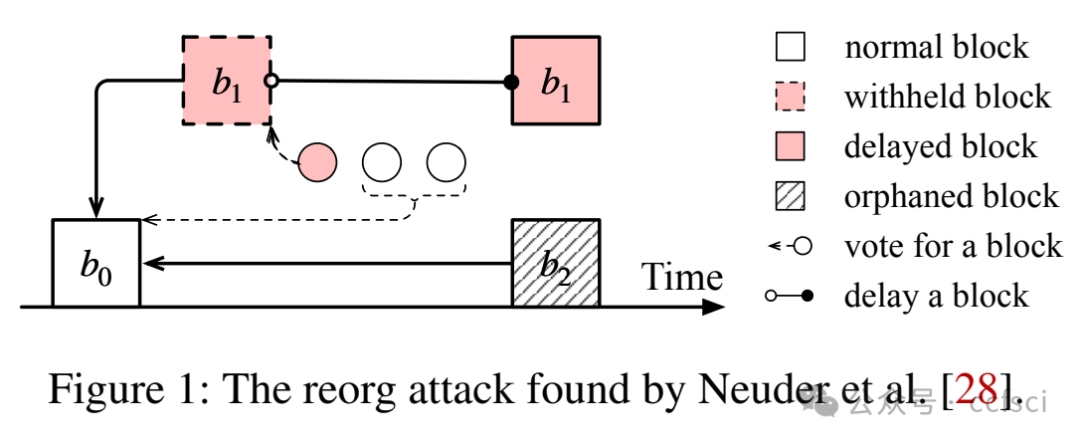
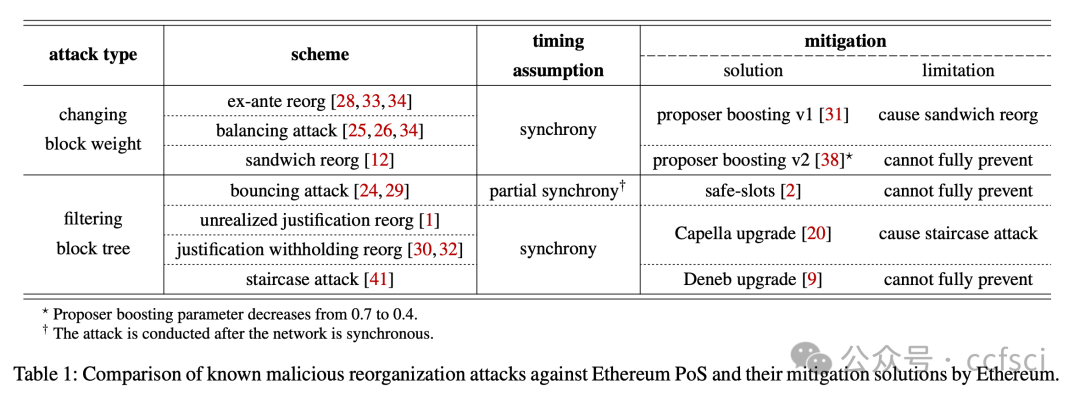
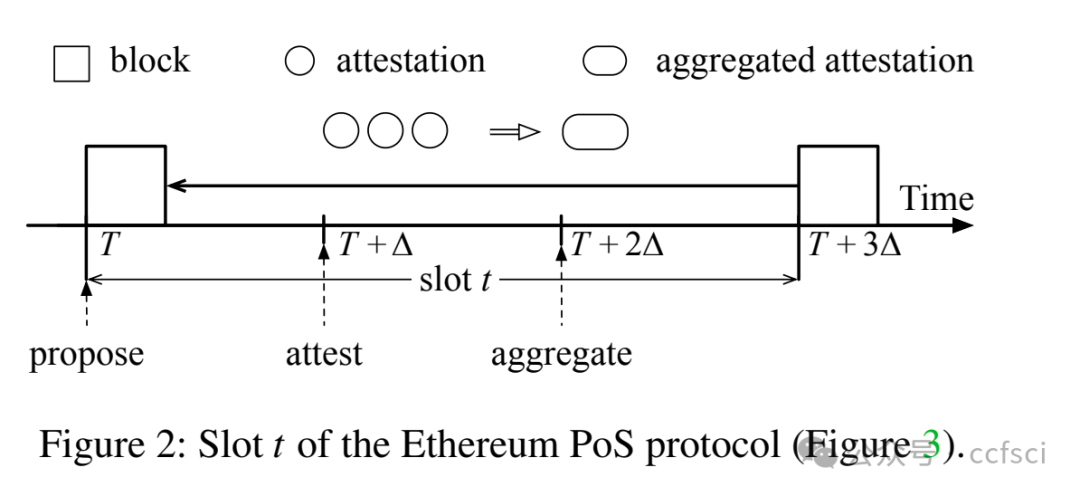
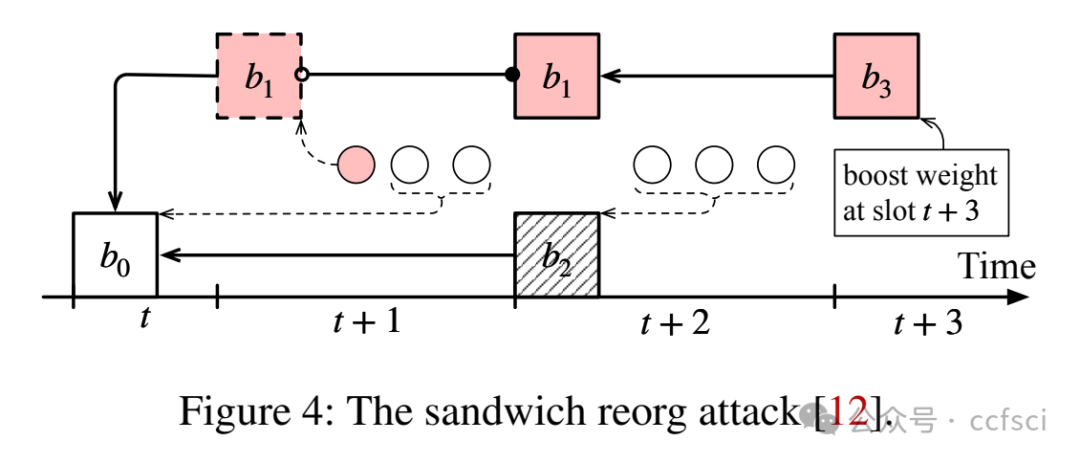
Available Attestation: Towards a Reorg-Resilient Solution for Ethereum Proof-of-Stake
可用证明:迈向以太坊权益证明的重组弹性解决方案
Authors:****

Abstract:****
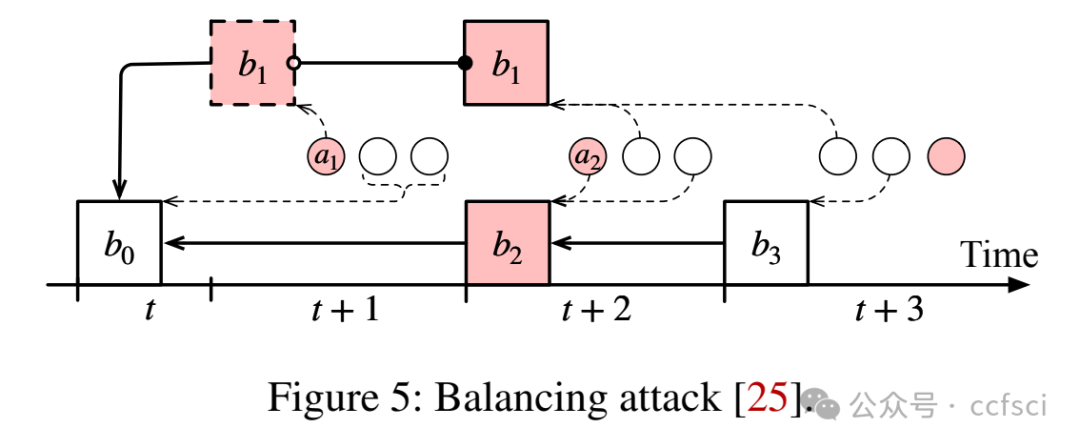
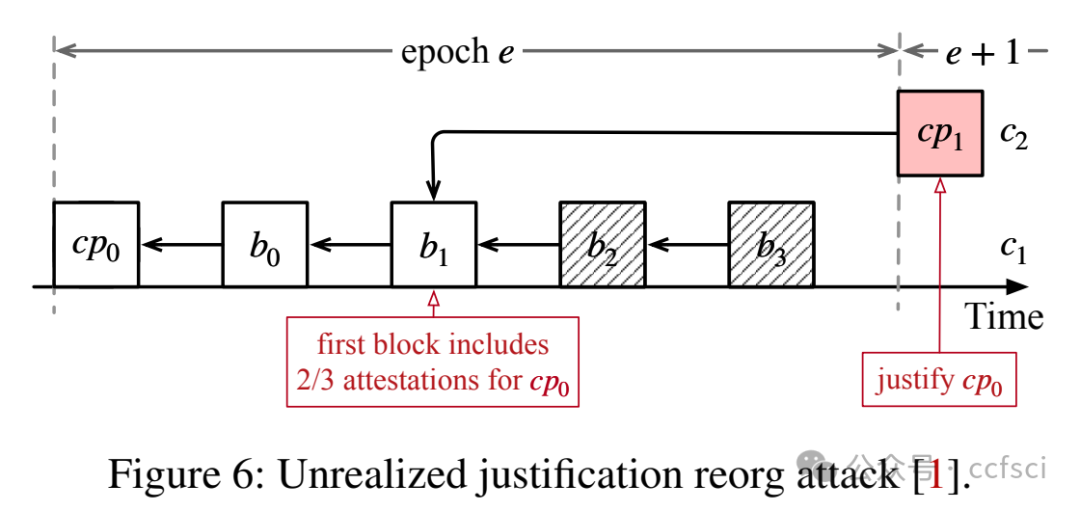
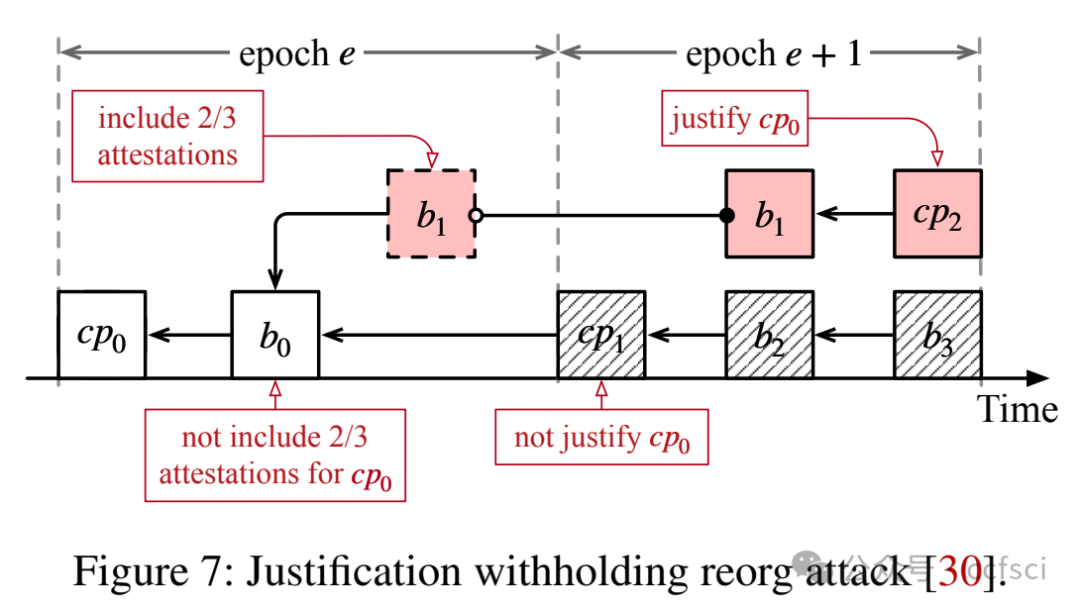
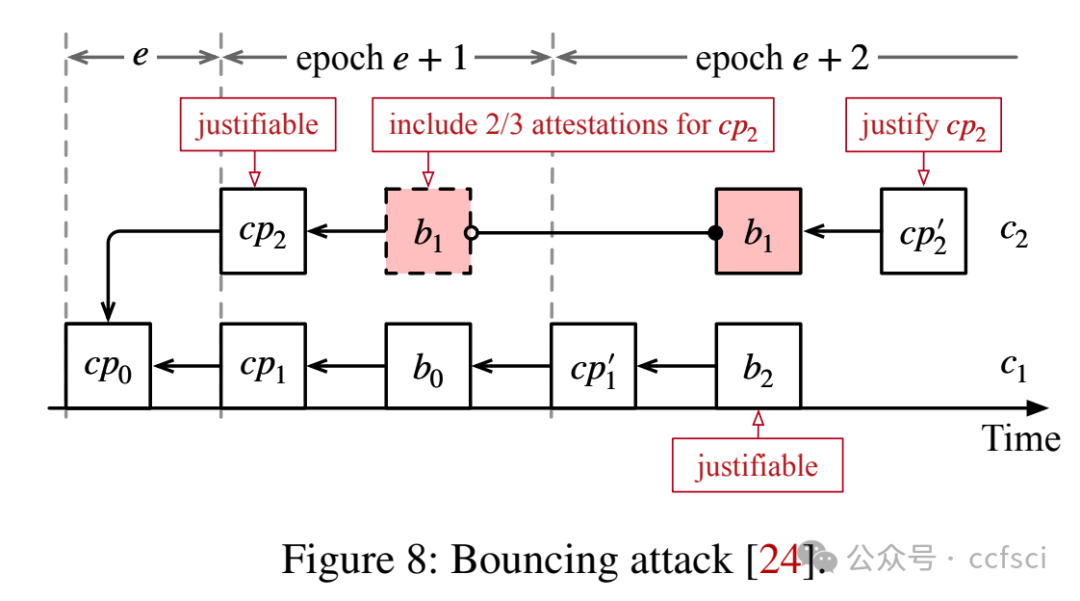
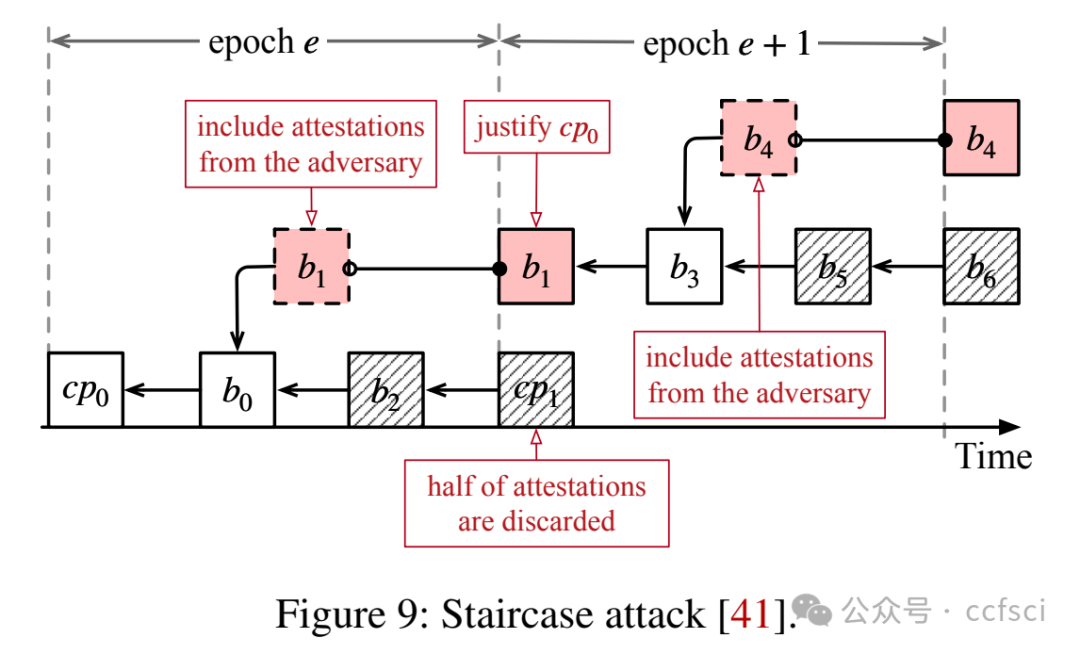
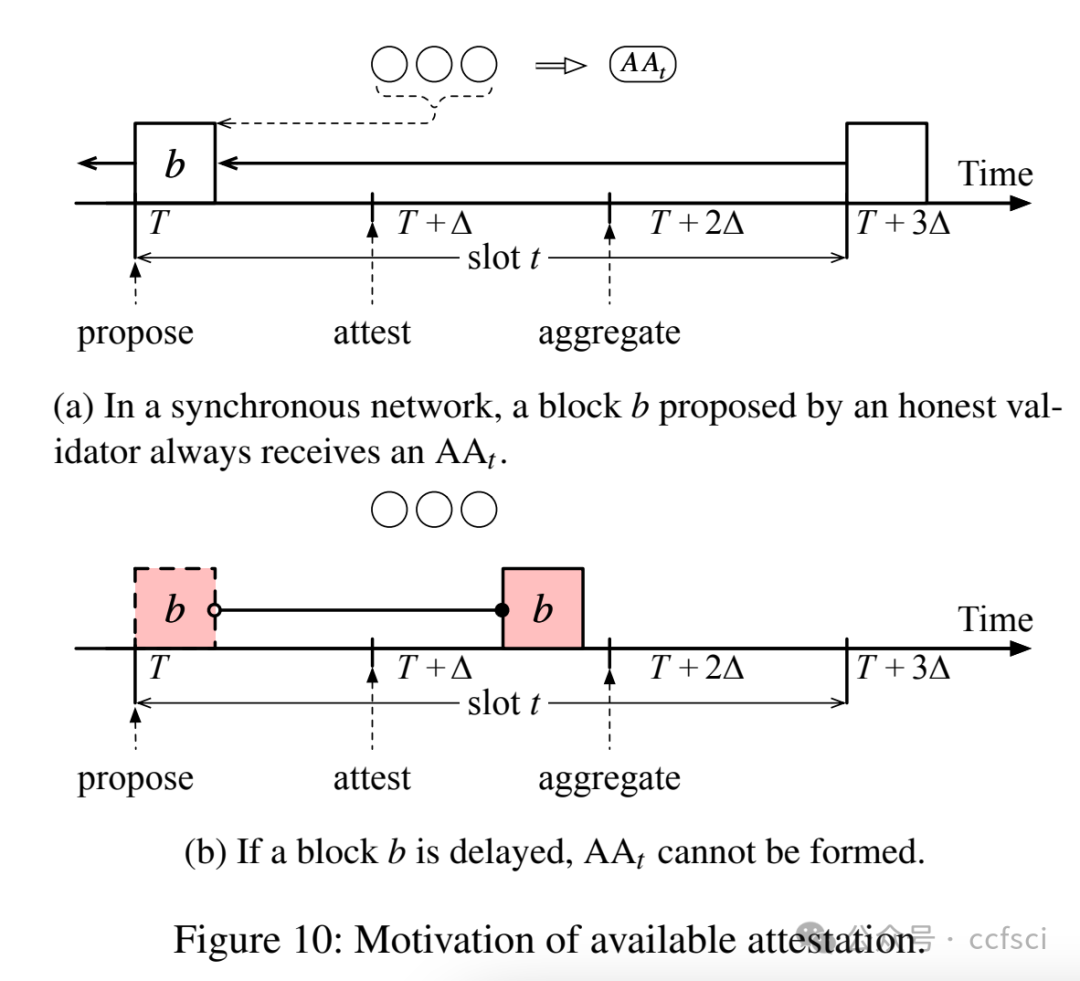
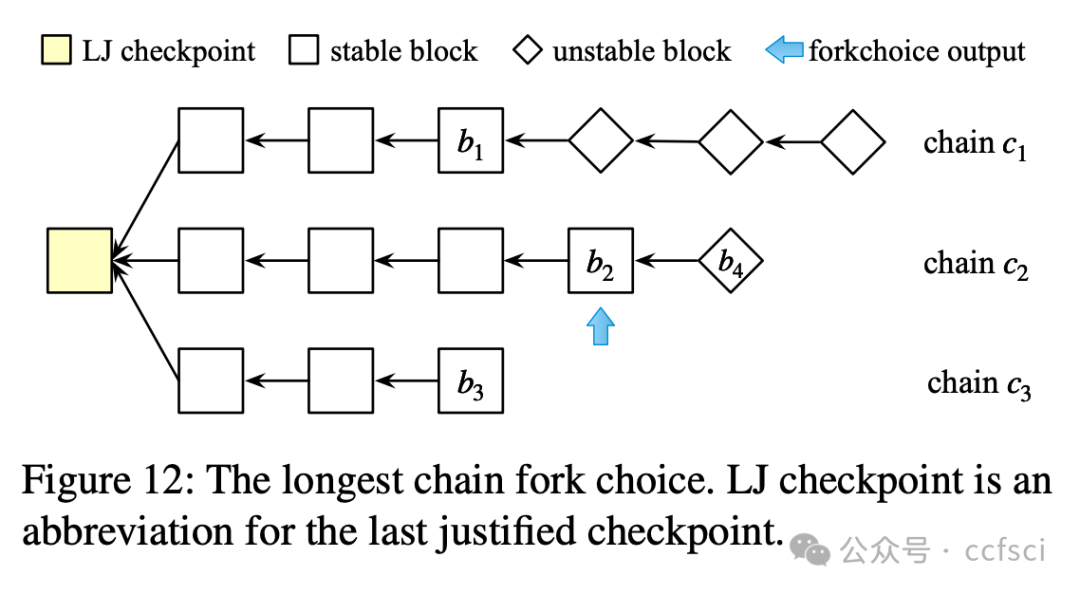
Ethereum transitioned from Proof-of-Work consensus to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus in September 2022. While this upgrade brings significant improvements (e.g., lower energy costs and higher throughput), it also introduces new vulnerabilities. One notable example is the so-called malicious reorganization attack. Malicious reorganization denotes an attack in which the Byzantine faulty validators intentionally manipulate the canonical chain so the blocks by honest validators are discarded. By doing so, the faulty validators can gain benefits such as higher rewards, lower chain quality, or even posing a liveness threat to the system.
In this work, we show that the majority of the known attacks on Ethereum PoS are some form of reorganization attacks. In practice, most of these attacks can be launched even if the network is synchronous (there exists a known upper bound for message transmission and processing). Different from existing studies that mitigate the attacks in an ad-hoc way, we take a systematic approach and provide an elegant yet efficient solution to reorganization attacks. Our solution is provably secure such that no reorganization attacks can be launched in a synchronous network. In a partially synchronous network, our approach achieves the conventional safety and liveness properties of the consensus protocol. Our evaluation results show that our solution is resilient to five types of reorganization attacks and also highly efficient.
以太坊于 2022 年 9 月从工作量证明 (PoW) 共识过渡到权益证明 (PoS) 共识。此次升级虽然带来了显著的改进(例如,更低的能源成本和更高的吞吐量),但也带来了新的漏洞。一个显著的例子就是所谓的恶意重组攻击。恶意重组是指拜占庭式故障验证者故意操纵规范链,导致诚实验证者生成的区块被丢弃的攻击。通过这样做,故障验证者可以获得诸如更高的奖励、更低的链质量,甚至对系统构成活性威胁等好处。
本文表明,大多数已知的针对以太坊 PoS 的攻击都属于某种形式的重组攻击。实际上,即使网络是同步的(存在已知的消息传输和处理上限),大多数此类攻击也可以发起。与现有以临时方式缓解攻击的研究不同,我们采用系统性方法,并提供了一种优雅而高效的重组攻击解决方案。我们的解决方案已被证明是安全的,在同步网络中不会发起任何重组攻击。在部分同步网络中,我们的方法实现了共识协议的常规安全性和活性特性。我们的评估结果表明,我们的解决方案能够抵御五种类型的重组攻击,并且非常高效。
Pdf下载链接:
https://www.usenix.org/system/files/usenixsecurity25-zhang-mingfei.pdf