本文针对于milvus2.5.15版本的insert流程进行源码概要分析,以后陆续推出针对细节的源码分析
tips
- VChannel = PChannel + Collection ID + Shard Index(Collection 级,逻辑隔离)
- 写流程通过MQ进行解耦,前半段是Proxy执行,后半段在DataNode持久化
- go的chan关键字是异步通知的关键
1、Insert整体导图
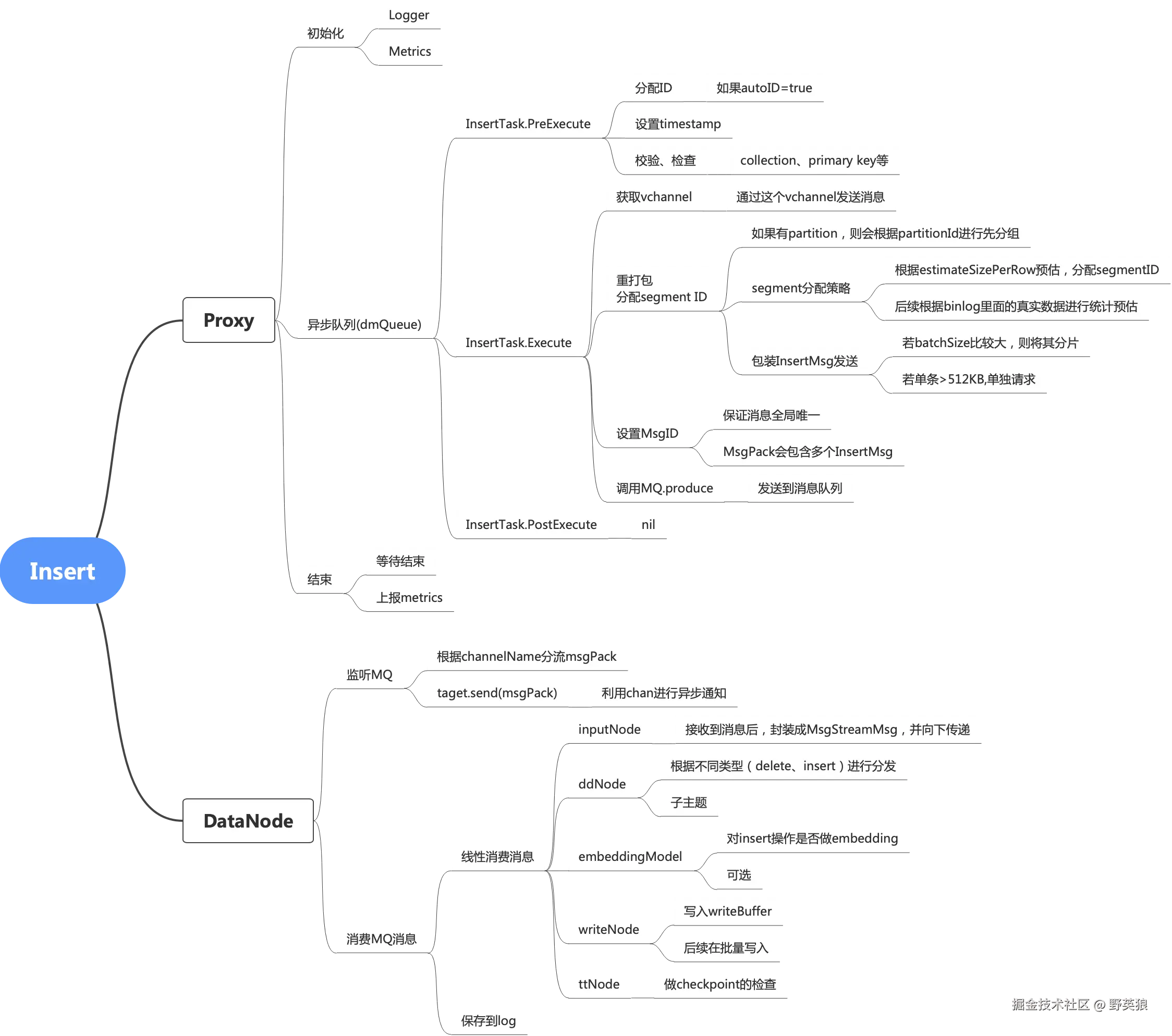
2、源码解析:Proxy
请求的第一步:打到Proxy#Insert
2.1 Proxy#Insert
- 封装成InsertTask;
- 保存进入异步队列
- 等待队列执行完成
- 监控打点、返回结果
scss
func (node *Proxy) Insert(ctx context.Context, request *milvuspb.InsertRequest) (*milvuspb.MutationResult, error) {
......
it := &insertTask{}
......
// 入异步队列(那quque的类型一共有几种呢?)
if err := node.sched.dmQueue.Enqueue(enqueuedTask); err != nil {
log.Warn("Failed to enqueue insert task: " + err.Error())
.......
}
log.Debug("Detail of insert request in Proxy")
// 等待异步任务结束
if err := it.WaitToFinish(); err != nil {
log.Warn("Failed to execute insert task in task scheduler: " + err.Error())
metrics.ProxyFunctionCall.WithLabelValues(strconv.FormatInt(paramtable.GetNodeID(), 10), method,
metrics.FailLabel, request.GetDbName(), request.GetCollectionName()).Inc()
return constructFailedResponse(err), nil
}
......
// 上报监控打点; insert的耗时、qps等
metrics.ProxyInsertVectors.
WithLabelValues(nodeID, dbName, collectionName).
Add(float64(successCnt))
metrics.ProxyMutationLatency.
WithLabelValues(nodeID, metrics.InsertLabel, dbName, collectionName).
Observe(float64(tr.ElapseSpan().Milliseconds()))
metrics.ProxyCollectionMutationLatency.
WithLabelValues(nodeID, metrics.InsertLabel, collectionName).
Observe(float64(tr.ElapseSpan().Milliseconds()))
return it.result, nil
}主要流程定义在taskScheduler#processTask(和search的核心流程一致) 核心的功能在InsertTask#PreExecute、Execute、PostExecute;
2.1.1 疑问:dmQueue的异步轮训在哪里启动呢?
答案是在task_Scheduler.go#Start的方法;(具体如何启动的源码:且待下文分析)
Loop一共有4种类型
- difinitionLoop: 对Database、Collection、Alias、ResourceGroup这些资源的操作;
- controlLoop: 只有Flush操作
- manipulationLoop: 主要是insert、update、delete三种类型
- queryLoop: 是query、search类型
scss
func (sched *taskScheduler) Start() error {
sched.wg.Add(1)
go sched.definitionLoop()
sched.wg.Add(1)
go sched.controlLoop()
sched.wg.Add(1)
go sched.manipulationLoop()
sched.wg.Add(1)
go sched.queryLoop()
return nil
}2.2 InsertTask#PreExecute
主要做数据校验
- collectionId是否存在、insertSize是否大于阈值,动态字段的校验
- 申请全局唯一rowId
- 提取partitionKey
- NaN、长度、容量验证
go
func (it *insertTask) PreExecute(ctx context.Context) error {
// 数据校验,比如:collection是否存在,insert的batch条数是否过多
.....
// 申请全局唯一的ID
rowNums := uint32(it.insertMsg.NRows())
// set insertTask.rowIDs
var rowIDBegin UniqueID
var rowIDEnd UniqueID
tr := timerecord.NewTimeRecorder("applyPK")
rowIDBegin, rowIDEnd, _ = it.idAllocator.Alloc(rowNums)
metrics.ProxyApplyPrimaryKeyLatency.WithLabelValues(strconv.FormatInt(paramtable.GetNodeID(), 10)).Observe(float64(tr.ElapseSpan().Milliseconds()))
it.insertMsg.RowIDs = make([]UniqueID, rowNums)
for i := rowIDBegin; i < rowIDEnd; i++ {
offset := i - rowIDBegin
it.insertMsg.RowIDs[offset] = i
}
// 设置插入时间
// set insertTask.timeStamps
rowNum := it.insertMsg.NRows()
it.insertMsg.Timestamps = make([]uint64, rowNum)
for index := range it.insertMsg.Timestamps {
it.insertMsg.Timestamps[index] = it.insertMsg.BeginTimestamp
}
.....
// 回填field对应的field ID
// set field ID to insert field data
err = fillFieldPropertiesBySchema(it.insertMsg.GetFieldsData(), schema.CollectionSchema)
if err != nil {
log.Info("set fieldID to fieldData failed",
zap.Error(err))
return err
}
......
// 验证partitionKeyId
return nil
}2.3 InsertTask#Execute
- 预估数据大小,给数据分配指定segmentId;若insert data数据量比较大,分批、给不同的data数据指定不同的segmentId;(如果msg超过512k,还会进行msg进行拆分,防止某个消息body体过大)
- 把数据发送到指定的Topic
scss
func (it *insertTask) Execute(ctx context.Context) error {
......
// assign segmentID for insert data and repack data by segmentID
var msgPack *msgstream.MsgPack
if it.partitionKeys == nil {
// 见下文
msgPack, err = repackInsertData(it.TraceCtx(), channelNames, it.insertMsg, it.result, it.idAllocator, it.segIDAssigner)
} else {
msgPack, err = repackInsertDataWithPartitionKey(it.TraceCtx(), channelNames, it.partitionKeys, it.insertMsg, it.result, it.idAllocator, it.segIDAssigner)
}
......
log.Debug("assign segmentID for insert data success",
zap.Duration("assign segmentID duration", assignSegmentIDDur))
// 把消息发送到消息队列
err = stream.Produce(ctx, msgPack)
......
}2.3.1 msg_pack#repackInsertDataByPartition
根据partition重新打包;
- 分配segmentId
- 封装msg,如果单个msg大小大于阈值,就会封装下一个msg,最后这些msg都会打包发到消息队列;
go
func repackInsertDataByPartition(ctx context.Context,
partitionName string,
rowOffsets []int,
channelName string,
insertMsg *msgstream.InsertMsg,
segIDAssigner *segIDAssigner,
) ([]msgstream.TsMsg, error) {
res := make([]msgstream.TsMsg, 0)
maxTs := Timestamp(0)
for _, offset := range rowOffsets {
ts := insertMsg.Timestamps[offset]
if maxTs < ts {
maxTs = ts
}
}
partitionID, err := globalMetaCache.GetPartitionID(ctx, insertMsg.GetDbName(), insertMsg.CollectionName, partitionName)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
beforeAssign := time.Now()
assignedSegmentInfos, err := segIDAssigner.GetSegmentID(insertMsg.CollectionID, partitionID, channelName, uint32(len(rowOffsets)), maxTs)
......
startPos := 0
for segmentID, count := range assignedSegmentInfos {
subRowOffsets := rowOffsets[startPos : startPos+int(count)]
msgs, err := genInsertMsgsByPartition(ctx, segmentID, partitionID, partitionName, subRowOffsets, channelName, insertMsg)
if err != nil {
log.Ctx(ctx).Warn("repack insert data to insert msgs failed",
zap.String("collectionName", insertMsg.CollectionName),
zap.Int64("partitionID", partitionID),
zap.Error(err))
return nil, err
}
res = append(res, msgs...)
startPos += int(count)
}
return res, nil
}2.4 InsertTask#PostExecute
无实现
3、DataNode
3.1 Dispatcher#work 轮询监听
- 轮询监听到MQ获取的消息
- 过滤掉已经消费的旧消息
- 将MQ消息分发到vchannel
go
func (d *Dispatcher) work() {
log := log.With(zap.String("pchannel", d.pchannel), zap.Int64("id", d.ID()))
log.Info("begin to work")
defer d.wg.Done()
for {
select {
case <-d.done:
log.Info("stop working")
return
// 从MQ中获取MsgPack
case pack := <-d.stream.Chan():
if pack == nil || len(pack.EndPositions) != 1 {
log.Error("consumed invalid msgPack", zap.Any("pack", pack))
continue
}
d.curTs.Store(pack.EndPositions[0].GetTimestamp())
targetPacks := d.groupingMsgs(pack)
for vchannel, p := range targetPacks {
var err error
t, _ := d.targets.Get(vchannel)
isReplicateChannel := strings.Contains(vchannel, paramtable.Get().CommonCfg.ReplicateMsgChannel.GetValue())
// The dispatcher seeks from the oldest target,
// so for each target, msg before the target position must be filtered out.
if p.EndTs <= t.pos.GetTimestamp() && !isReplicateChannel {
......
continue
}
// 准备消费
err = t.send(p)
......
}
if !d.pullbackDone && pack.EndPositions[0].GetTimestamp() >= d.pullbackEndTs {
d.pullbackDoneNotifier.Finish(struct{}{})
log.Info("dispatcher pullback done",
zap.Uint64("pullbackEndTs", d.pullbackEndTs),
zap.Time("pullbackTime", tsoutil.PhysicalTime(d.pullbackEndTs)),
)
d.pullbackDone = true
}
}
}
}3.2 nodeCtxManager#workNodeStart
- 不要循环,通过chan获取异步消息,
- 然后将消息传递到后续的nodes
go
func (nodeCtxManager *nodeCtxManager) workNodeStart() {
defer nodeCtxManager.closeWg.Done()
for {
select {
case <-nodeCtxManager.closeCh:
return
// handles node work spinning
// 1. collectMessage from upstream or just produce Msg from InputNode
// 2. invoke node.Operate
// 3. deliver the Operate result to downstream nodes
default:
inputNode := nodeCtxManager.inputNodeCtx
curNode := inputNode
for curNode != nil {
// inputs from inputsMessages for Operate
var input, output []Msg
if curNode != inputNode {
// inputNode.input not from nodeCtx.inputChannel
input = <-curNode.inputChannel
}
// the input message decides whether the operate method is executed
n := curNode.node
curNode.blockMutex.RLock()
if !n.IsValidInMsg(input) {
curNode.blockMutex.RUnlock()
curNode = inputNode
continue
}
if nodeCtxManager.lastAccessTime != nil {
nodeCtxManager.lastAccessTime.Store(time.Now())
}
output = n.Operate(input)
curNode.blockMutex.RUnlock()
// the output decide whether the node should be closed.
if isCloseMsg(output) {
nodeCtxManager.closeOnce.Do(func() {
close(nodeCtxManager.closeCh)
})
if curNode.inputChannel != nil {
close(curNode.inputChannel)
}
}
// deliver to all following flow graph node.
if curNode.downstream != nil {
curNode.downstream.inputChannel <- output
}
if enableTtChecker && curNode.checker != nil {
curNode.checker.Check()
}
curNode = curNode.downstream
}
}
}
}InputNode#Operate:解析消息
且听下文分解
ddNode:根据类型分类
且听下文分解
embeddingNode:是否使用embeddiing
且听下文分解
writeNode:执行写操作
且听下文分解
ttNode:更新checkpoint
且听下文分解
4、其他疑问点
4.1 PChannel和VChannel、Collection的区别是什么?
- PChannel:可以理解成一个消息通道的Topic
- VChannel:是Milvus的逻辑分片通道, 一个Shard 对应一个VChannel VChannel的命名规则:%s_%sv%d : %pchannel_%collectionIDv%shardId ;比如: dml_0_144121v2 : 表示vchannel是dml_0,collectionID是144121, shardId是2
- Collection:Milvus的集合结构, 一个Collection有多个Shard,所以Collection:VChannel = 1:n
- Segment是Milvus存储单元,Collection中包含多个Segment;
5、学习感悟
- 思想是共通的,这里面的Proxy模块的dmQueue的异步串行队列、Dispatcher.dispatch监听,以及获取监听消息后的Nodes链的串行执行,是否和Netty中的workQueue、EventLoop.run、ChannelPipeline的逻辑执行链路一样呢?
- 语言只是载体,思想才是精髓;