一.插件化的基本介绍
插件化apk并不安装,它是使用在宿主app的组件去加载插件的资源上,它有以下几个好处:
1.解决安装包太大;
2.方法655535;
3.动态使用;
插件化的基本实现:
1.占位式 (采用占坑和标准的方式去加载插件)
2.Hook式
1.合并插件和宿主的dex和res
2.新建loadedApk通过动态选择插件和宿主的loaderApk的方式
二.占位式(插装式)插件化
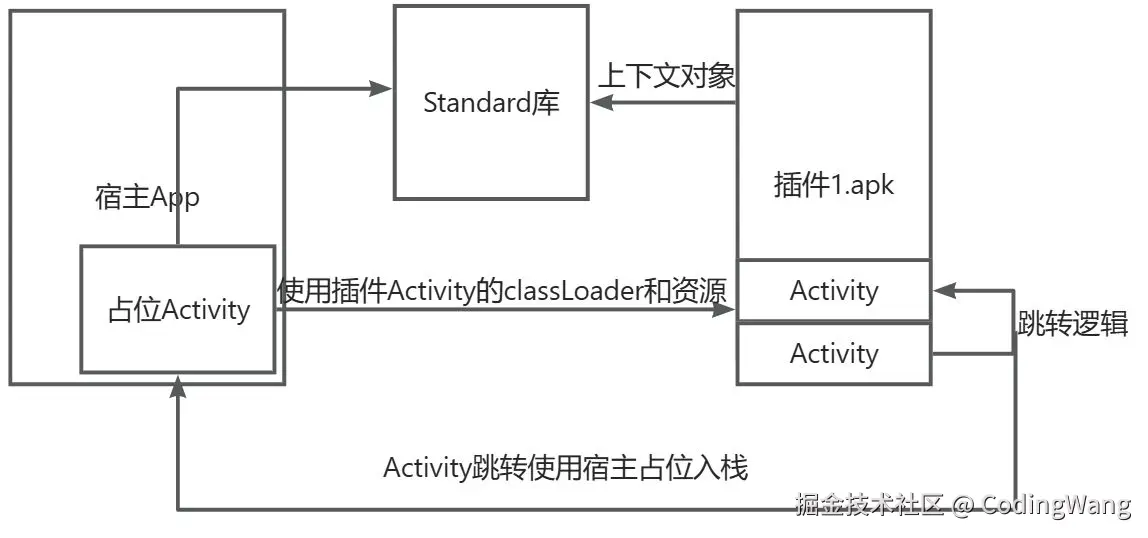
1.占位式Activity
1.插件APK没有安装,没有上下文环境,需要用代理的Activity(占位或叫插装)来加载插件Activity的资源
2.插件Activity的跳转需要依赖宿主的占位Activity来完成入栈出栈的效果。
kotlin
//插件代理(占位)Activity
class ProxyActivity : Activity() {
//占位的Activity 使用plugin Apk的资源文件
override fun getResources(): Resources {
return PluginManager.getInstance(this).resources
}
//占位Activity 使用Plugin的class 文件
override fun getClassLoader(): ClassLoader {
return PluginManager.getInstance(this).dexClassLoader
}
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
val clzName=intent.getStringExtra("clzName")
val clz :Class<*> = classLoader.loadClass(clzName)
val constructor = clz.getConstructor() //获取PluginActivity 构造方法
val activity: ActivityInterface =
constructor.newInstance() as ActivityInterface //强转成ActivityInterface
//注入当前Activity
activity.insertAppContext(this)
activity.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
}
override fun startActivity(intent: Intent) {
//接受插件Activity传过来的参数,再用自己去跳转。
val clz=intent.getStringExtra("clzName")
println("pluginPath ProxyActivity startActivity :${clz}")
val proxyIntent=Intent(this,ProxyActivity::class.java)
proxyIntent.putExtra("clzName",clz)
super.startActivity(proxyIntent)
}
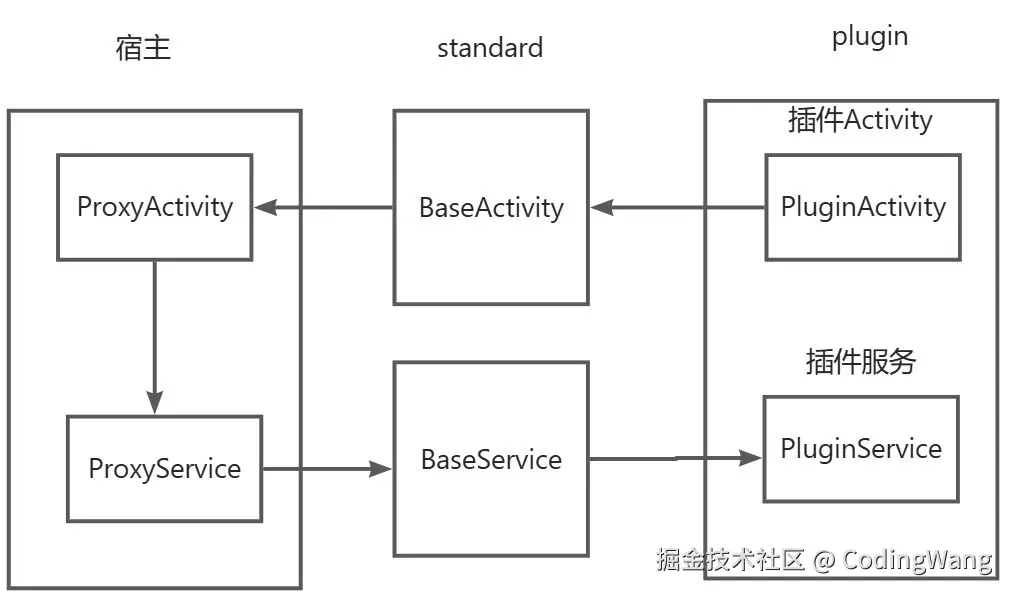
}2.占位式Service
1.使用占位的Activity去启动占位的Service
2.通过占位的service去执行PluginService中的start方法
3.占位式广播
流程参考占位的Service。
4.静态广播的注册(Hook方式)
静态广播的注册时机:
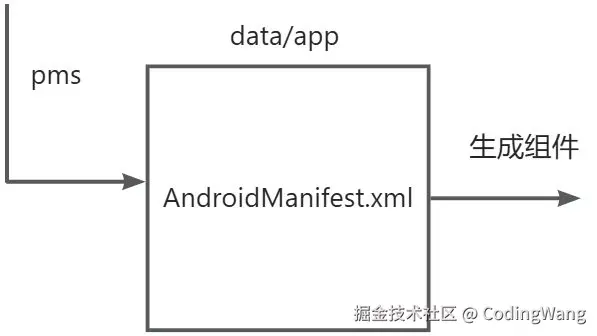
设备启动时,app会重新安装,并且解析androidManifest.xml中的组件,然后自动注册;
app安装的时候,会在data/app中放置目录,并且在data/data/pkgName创建所属目录,然后再data/dalvik-cache中创建虚拟器加载指令的目录。所以我们需要关心的是app安装后的扫描的data/app中的目录,系统会解析这个apk下的AndroidManifest.xml的组件,
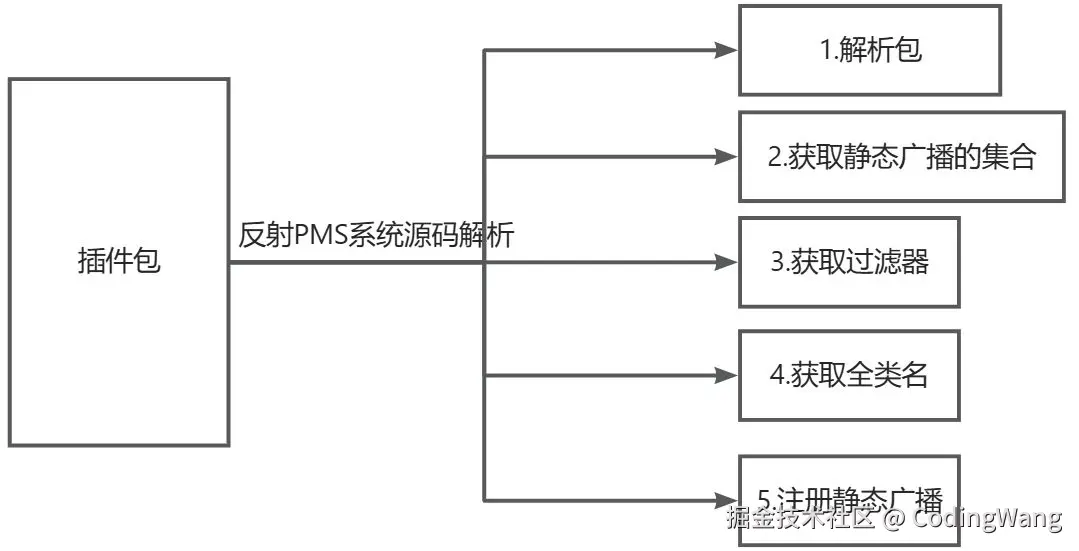
我们看下android11的解析源码:
scala
//1.PackageParser中加载apk的方法
public Package parsePackage(File packageFile, int flags) throws PackageParserException {
return parsePackage(packageFile, flags, false /* useCaches */);
}
//2.存放Receiver列表
public final static class Package implements Parcelable {
...
public final ArrayList<Activity> receivers = new ArrayList<Activity>(0);
...
}
//3.receiver具体的表示
public final static class Activity extends Component<ActivityIntentInfo> implements Parcelable {
}
public static abstract class Component<II extends IntentInfo> {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public final ArrayList<II> intents; //IntentFilter
}
//5.全类名的获取
//ActivityInfo 持有了manifest的全类名,我们需要反射这个方法
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static final ActivityInfo generateActivityInfo(Activity a, int flags,
PackageUserState state, int userId) {
ActivityInfo ai = new ActivityInfo(a.info);
return ai;
}示例代码:
ini
public void pareApk() {
try {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() + File.separator + "plugin.apk");
Class mParser = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageParser");
Object object = mParser.newInstance(); //1.获取packageParser对象
/**
* public Package parsePackage(File packageFile, int flags) throws PackageParserException {
*/
Method method = mParser.getMethod("parsePackage", File.class, int.class);
Object objectPackage = method.invoke(object, file, PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES); //2.获取到解析的包
//3获取manifest中的receiver清单文件的list
Field field = objectPackage.getClass().getDeclaredField("receivers");
ArrayList arrayList = (ArrayList) field.get(objectPackage);
Class filterClz = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageParser$Component");
Field intentField = filterClz.getField("intents");
for (Object receiver : arrayList) {
//获取intent-filter
ArrayList<IntentFilter> intents = (ArrayList) intentField.get(receiver);
//我们还有一个任务,就是要拿到android:name=".StaticReceiver"
// activityInfo.name; == android:name=".StaticReceiver"
//分析源码如何拿到ActivityInfo
Class mPackageUserState = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageUserState");
Class mUserHandle = Class.forName("android.os.UserHandle");
int userId = (int) mUserHandle.getMethod("getCallingUserId").invoke(null);
/**
*执行此方法,就能拿到ActivityInfo
* public static final ActivityInfo generateActivityInfo(ActivityInfo ai, int flags,
* PackageUserState state, int userId)
*
*/
Method generateActivityInfoMethod = mParser.getMethod("generateActivityInfo", receiver.getClass(),
int.class, mPackageUserState, int.class);
//执行此方法,拿到ActivityInfo
ActivityInfo mActivityInfo = (ActivityInfo) generateActivityInfoMethod.invoke(null, receiver,
0,
mPackageUserState.newInstance(),
userId);
String receiverClassName = mActivityInfo.name; //com.seven.pluginapp.StaticReceiver
System.out.println("pareApk--->>" + receiverClassName);
Class mStaticReceiverClass = getDexClassLoader().loadClass(receiverClassName);
System.out.println("pareApk1--->>" + receiverClassName);
BroadcastReceiver broadcastReceiver = (BroadcastReceiver) mStaticReceiverClass.newInstance();
for (IntentFilter intentFilter : intents) {
//注册广播
context.registerReceiver(broadcastReceiver, intentFilter);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}三.Hook式插件化
hook可以帮助我们改变系统的某些功能,动态的添加一些功能。
1.Hook初体验
当我们点击按钮时,会去设置监听事件,我们拦截系统view设置的监听事件,为其加盐后再执行后续操作,就实现了简单的钩子操作。
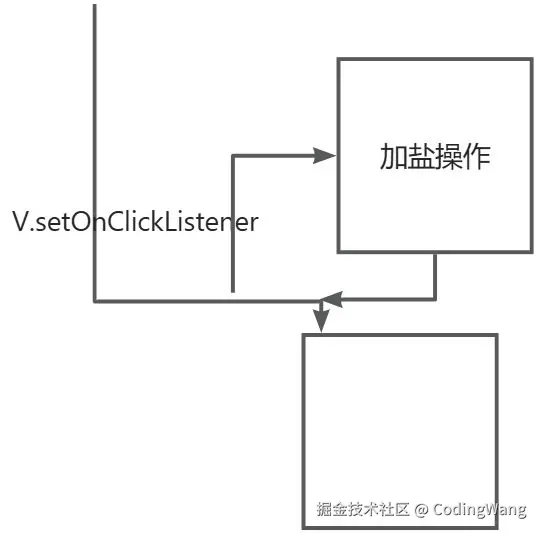
代码示例:我们通过实例化一个OnClickListener动态代理对象,并且通过反射修改源码的ListenerInfo中的OnClickListener为我们动态代理的对象,这样就可以加盐了。
kotlin
/**
* 动态代理+加反射来hook操作
* 替换view的OnClickListener 加入自己的操作
*/
fun hookButton(view: Button) {
//替换Button中的listener 下面是view的设置监听的源码 我们需要用自己的方法设置
// public void setOnClickListener(@Nullable OnClickListener l) {
// if (!isClickable()) {
// setClickable(true);
// }
// getListenerInfo().mOnClickListener = l;
// }
val listenerInfoClz = Class.forName("android.view.View$ListenerInfo")
// ListenerInfo getListenerInfo() {
// if (mListenerInfo != null) {
// return mListenerInfo;
// }
// mListenerInfo = new ListenerInfo();
// return mListenerInfo;
// }
val listenerInfoObjectMethod = View::class.java.getDeclaredMethod("getListenerInfo")
listenerInfoObjectMethod.isAccessible=true
val listenerInfoObject = listenerInfoObjectMethod.invoke(view) //需要ListenerInfo对象
var listenerInfo: Field =listenerInfoClz.getField("mOnClickListener") //获取默认的属性
val onClickListener= listenerInfo.get(listenerInfoObject) //需要得到ClickListener对象 也是被代理的对象
//view.OnClickListener的动态代理
val proxyOnClickListener = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
classLoader, arrayOf(OnClickListener::class.java)
) { proxy, method, args ->
//加入自己的逻辑
view.text = "hook it before click !"
println("proxy do it-->>>> $args" )
println("method:$method")
method.invoke(onClickListener,view)//反射被代理对象的执行onClick方法
}
//换成动态代理的对象 当收到点击事件回调onClick事件时,会先执行代理对象的方法
listenerInfo.set(listenerInfoObject,proxyOnClickListener)
}2.Hook实现Activity注入
我们启动Activity时需要再Manifest中注册,如果不注册会报错,我们使用Hook技术绕过Manifest的检查,并且再实例化时Hook实例化需要跳转的Activity,从而实现Activity的启动。
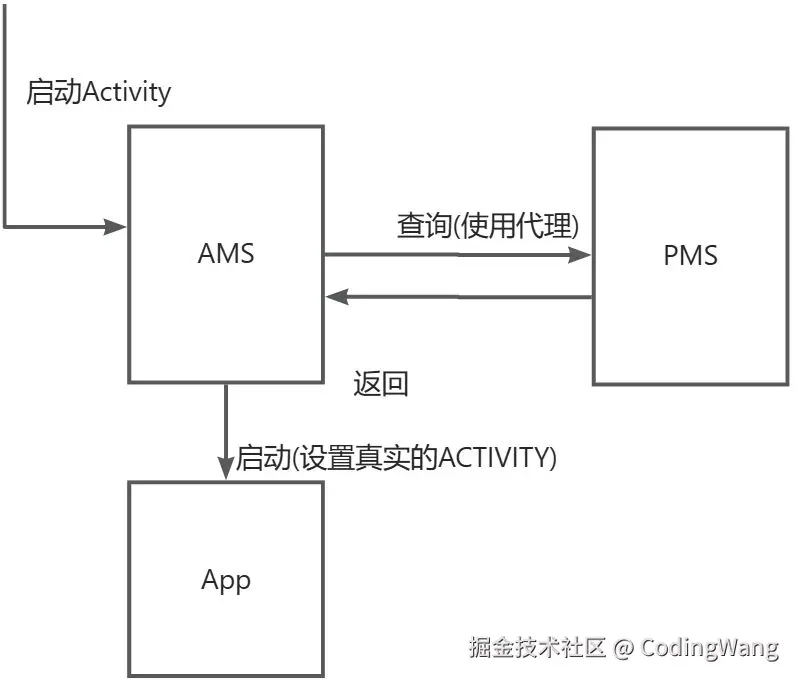
代码示例:
ini
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
try {
hookAms();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
hookSystemHandler();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 绕过清单检测
* @throws Exception
*/
public void hookAms() throws Exception {
//动态代理
Class mIActivityManagerClass = Class. forName("android.app.IActivityManager");
Class mActivityManagerNativeClass2 = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityManagerNative");
Object mIActivityManager = mActivityManagerNativeClass2.getMethod( "getDefault").invoke( null);
Object mIActivityManagerProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(
getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{mIActivityManagerClass},//要监听的接口
new AmsInvocationHandler(mIActivityManager));
Class mActivityManagerNativeClass = Class. forName("android.app.ActivityManagerNative");
Field gDefaultField = mActivityManagerNativeClass.getDeclaredField( "gDefault");
gDefaultField.setAccessible(true);//
Object gDefault = gDefaultField. get(null);
//替换点
Class mSingletonClass = Class. forName("android.util.Singleton");
//获取此字段 mInstance
Field mInstanceField = mSingletonClass. getDeclaredField( "mInstance");
mInstanceField.setAccessible(true);//让虚拟机不要检测权限修饰符
//替换
mInstanceField.set(gDefault,mIActivityManagerProxy);//替换是需要gDefault
}
/**
* 2.实例化自己的Activity
* @throws Exception
*/
public void hookSystemHandler() throws Exception {
Field mCallbackFiled = Handler.class.getDeclaredField("mCallback");
mCallbackFiled.setAccessible(true);//
Class mActivityThreadClass = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
Object mActivityThread = mActivityThreadClass.getMethod("currentActivityThread").invoke(null);
Field mHField = mActivityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("mH");
mHField.setAccessible(true);
//获取真正对象
Handler mH = (Handler) mHField.get(mActivityThread);
mCallbackFiled.set(mH, new ProxyHandlerCallback());//替换增加我们自己的实现代码
}
private class ProxyHandlerCallback implements Handler.Callback {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
Log.i("HookApp", "handleMessage: " + msg.what);
if (msg.what == 100) {
Log.i("HookApp", "---->: " + msg.obj.getClass());
try {
Object obj = msg.obj;
//我们要获取之前Hook携带过来的 Proxy
Field intentField = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField("intent");
intentField.setAccessible(true);
//获取intent对象,才能取出携带过来的I action Intent
Intent intent = (Intent) intentField.get(obj);
// actionIntent == TestActivityIntent
Intent actionIntent = intent.getParcelableExtra("oldIntent");
if (actionIntent != null) {
intent.setClass(HookApp.this, HookActivity.class);
intentField.set(obj, actionIntent);//把ProxyActivity 换成 HookActivity
Log.i("HookApp", "---->: SET--->>> " );
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
}
class AmsInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object iActivityManagerObject;
public AmsInvocationHandler(Object iActivityManagerObject) {
this.iActivityManagerObject = iActivityManagerObject;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Log.d("HookApp", "AmsInvocationHandler invoke--->>>>>>" + method.getName());
if ("startActivity".contains(method.getName())) {
Intent intent = null;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
Object arg = args[i];
if (arg instanceof Intent) {
intent = (Intent) args[i]; // 原意图,过不了安检
index = i;
break;
}
}
Log.d("HookApp", "start ProxyActivity--->>>>>>"+index); //使用代理的绕过安检
Intent proxyIntent = new Intent(HookApp.this, ProxyActivity.class);
proxyIntent.putExtra("oldIntent", intent);
args[index] = proxyIntent;
}
return method.invoke(iActivityManagerObject, args);
}
}3.Hook实现插件和宿主dex的合并
1.流程示意图
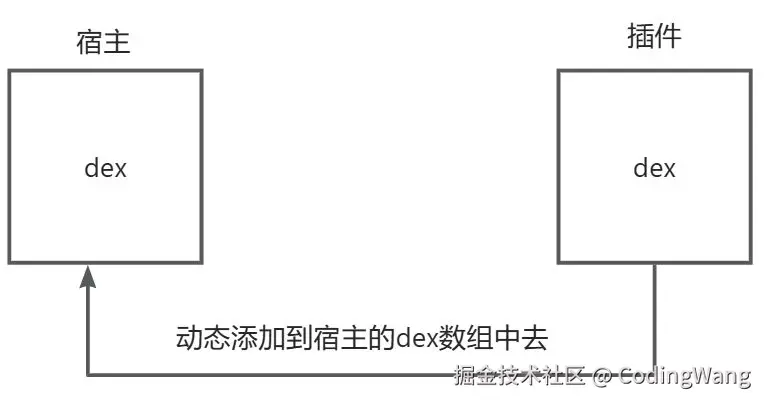
2.dexLoader初始化
BootClassLoader为java的类加载器;
PathClassLoader为android的dex加载器,它的内部设置的parent(并非父类设置的是BootClassLoader)。
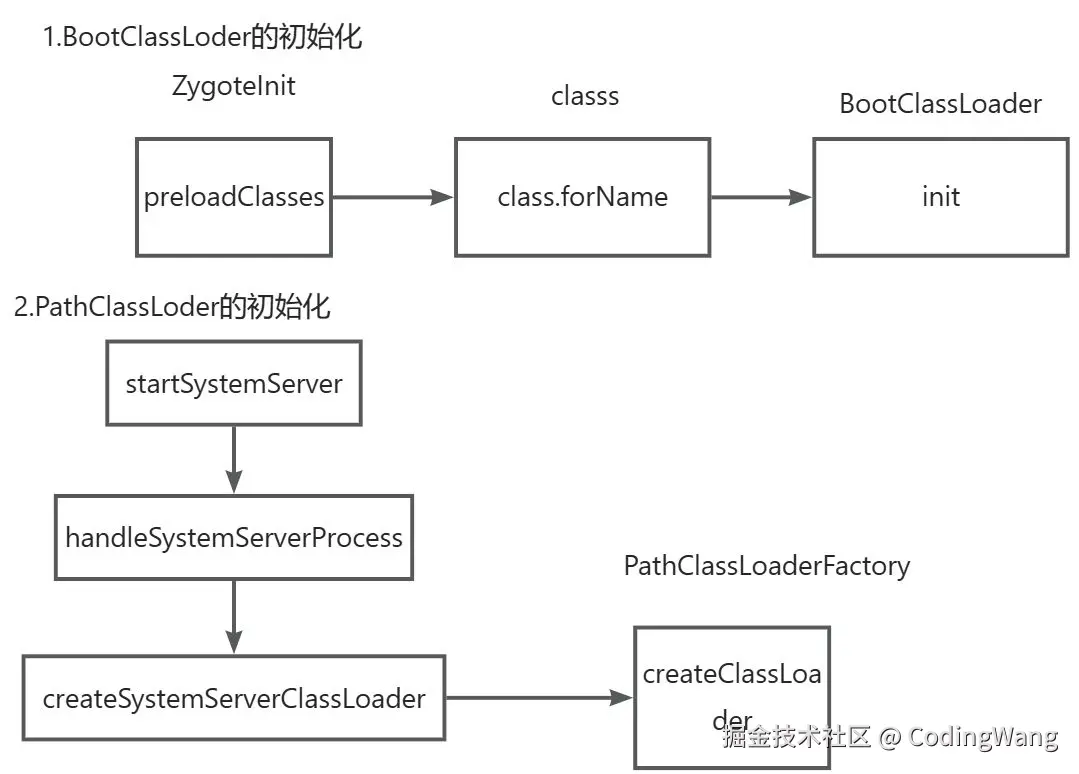
3.loadClass流程
BathDexClassLoader是PathClassLoader的父类
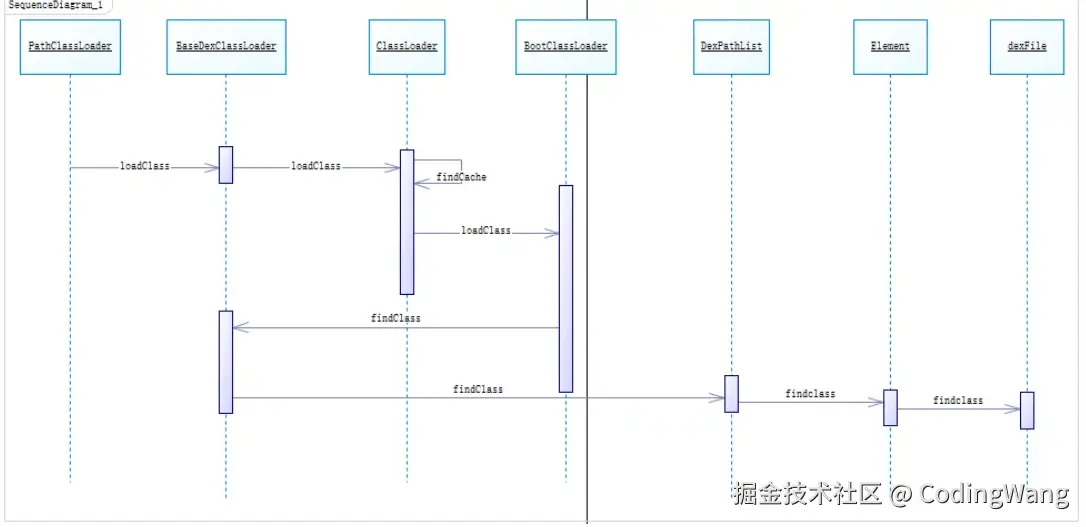
代码示例:hook点为将插件的dex插入的BaseDexClassLoader中的dexPathList中去。
ini
public class HookDexApp extends Application {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
try {
mergePluginDex();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
mergePluginLayout();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public Resources getResources() {
Log.d("PluginDexManager", "getResources---->>>>:"+resources );
// return resources == null ? super.getResources() : resources;
return PluginDexManager.getInstance(this).getResource();
}
@Override
public AssetManager getAssets() {
Log.d("PluginDexManager", "getAssets---->>>>:"+assetManager );
// return assetManager == null ? super.getAssets() : assetManager;
return PluginDexManager.getInstance(this).getAssetManager();
}
private String pluginPath() {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory() + File.separator + "pluginCompose.apk");
System.out.println("composePluginDex:" + file.getPath());
Log.d("PluginDexManager", "pluginPath---->>>>:" + file.getPath());
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("composePluginDex 插件不存在");
return null;
}
return file.getAbsolutePath();
}
/**
* 1.找到宿主的dexElements
* 2.找到插件的dexElements
* 3.合并插件的dexElements到宿主中去
*/
public void mergePluginDex() throws Exception {
String path = pluginPath();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(path)) {
return;
}
//1.获取宿主的dexElements
PathClassLoader pathClassLoader = (PathClassLoader) getClassLoader();//获取的就是pathClassLoader
Class<?> baseDexClassLoader = Class.forName("dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader");
Field pathListField = baseDexClassLoader.getDeclaredField("pathList");//pathList的属性
pathListField.setAccessible(true);
Object mDexPathList = pathListField.get(pathClassLoader);//获取patList
Field dexelementField = mDexPathList.getClass().getDeclaredField("dexElements"); //获取它的dexElements
dexelementField.setAccessible(true);
Object dexElements = dexelementField.get(mDexPathList);
//2.获取插件的dexElements
DexClassLoader dexClzLoaderPlugin = new DexClassLoader(path,
getDir("plugin", Context.MODE_PRIVATE).getAbsolutePath(), null,
getClassLoader());
Class<?> baseDexClassLoaderPlugin = Class.forName("dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader");
Field pathListFieldPlugin = baseDexClassLoaderPlugin.getDeclaredField("pathList");
pathListFieldPlugin.setAccessible(true);
Object objPathListPlugin = pathListFieldPlugin.get(dexClzLoaderPlugin);//获取patList
Field dexElementPluginField = objPathListPlugin.getClass().getDeclaredField("dexElements"); //DexPathList中的获取它的dexElements
dexElementPluginField.setAccessible(true);
Object dexElementsPlugin = dexElementPluginField.get(objPathListPlugin);
//3.合并
//根据类型创建数组
int mainLen = Array.getLength(dexElements);
int pluginLen = Array.getLength(dexElementsPlugin);
int mergeLen = mainLen + pluginLen;
Object newElements = Array.newInstance(dexElements.getClass().getComponentType(),
mergeLen);
for (int i = 0; i < mergeLen; i++) {
if (i<mainLen) {
//合并数组
Array.set(newElements, i, Array.get(dexElements, i));
} else {
//合并插件
Array.set(newElements, i, Array.get(dexElementsPlugin, i - mainLen));
}
}
Log.d("PluginDexManager", "pluginLen---->>>>:" + pluginLen+",mainLen:"+mainLen);
Field dexelementField2 = mDexPathList.getClass().getDeclaredField("dexElements"); //获取它的dexElements
dexelementField2.setAccessible(true);
//设置到宿主中去
dexelementField2.set(mDexPathList, newElements);
Log.d("PluginDexManager", "set---->>>>newElements: success" );
}
private Resources resources;
private AssetManager assetManager;
/**
* @throws Exception
*/
public void mergePluginLayout() throws Exception {
String pluginPath = pluginPath();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(pluginPath)) {
return;
}
assetManager=AssetManager.class.newInstance();
//执行此 public final int addAssetPath(String path)方法,才能把插件的路径添加进去
Method method = assetManager.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("addAssetPath", String.class);//类类型
method.setAccessible(true);
method.invoke(assetManager, pluginPath);
Resources r = getResources();//到的是宿主的配置信息
//实例化此方法 final StringBlock[] ensureStringBlocks()
Method ensureStringBlocksMethod = assetManager.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("ensureStringBlocks");
ensureStringBlocksMethod.setAccessible(true);
ensureStringBlocksMethod.invoke(assetManager);//执行了ensureStringBlocksstring.xmlcolor.xml anim.xml被
//特殊:专门加载插件资源
resources = new Resources(assetManager, r.getDisplayMetrics(), r.getConfiguration());
}插件中使用宿主的application的asset和resource
kotlin
open class BaseActivity:AppCompatActivity() {
//使用宿主合并的的asset
override fun getAssets(): AssetManager {
if ((application!=null&&application.assets!=null)) {
return application.assets
}
return super.getAssets()
}
//使用宿主合并的的resource
override fun getResources(): Resources {
if ((application!=null&&application.resources!=null)) {
return application.resources
}
return super.getResources()
}
}四.LoadedApk方式实现插件化
ActivityThread启动Activity流程解析
csharp
case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY: {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "activityStart");
//Activity的跳转记录
final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord) msg.obj;
//获取LoadedApk
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
r.activityInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo);
handleLaunchActivity(r, null, "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY");
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
}
//从缓存中取,没有则新建一个
private LoadedApk getPackageInfo(ApplicationInfo aInfo, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo,
ClassLoader baseLoader, boolean securityViolation, boolean includeCode,
boolean registerPackage) {
final boolean differentUser = (UserHandle.myUserId() != UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.uid));
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
WeakReference<LoadedApk> ref;
if (differentUser) {
// Caching not supported across users
ref = null;
} else if (includeCode) {
ref = mPackages.get(aInfo.packageName);
} else {
ref = mResourcePackages.get(aInfo.packageName);
}
LoadedApk packageInfo = ref != null ? ref.get() : null;
if (packageInfo == null || (packageInfo.mResources != null
&& !packageInfo.mResources.getAssets().isUpToDate())) {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, (includeCode ? "Loading code package "
: "Loading resource-only package ") + aInfo.packageName
+ " (in " + (mBoundApplication != null
? mBoundApplication.processName : null)
+ ")");
packageInfo =
new LoadedApk(this, aInfo, compatInfo, baseLoader,
securityViolation, includeCode &&
(aInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_HAS_CODE) != 0, registerPackage);
if (mSystemThread && "android".equals(aInfo.packageName)) {
packageInfo.installSystemApplicationInfo(aInfo,
getSystemContext().mPackageInfo.getClassLoader());
}
if (differentUser) {
// Caching not supported across users
} else if (includeCode) {
mPackages.put(aInfo.packageName,
new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo));
} else {
mResourcePackages.put(aInfo.packageName,
new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo));
}
}
return packageInfo;
}
}通过流程分析,我们可以通过新建一个LoadedApk然后注入到ActivityThread的缓存中去,并且我们可以在此之前通过包名的控制当前使用的LoadedApk来决定运行时使用的LoadedApk,示例代码如下:
ini
private class ProxyHandlerCallback implements Handler.Callback {
private Handler mH;
public ProxyHandlerCallback(Handler mH) {
this.mH = mH;
}
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
Log.i("HookApp", "handleMessage: " + msg.what);
if (msg.what == 100) {
Log.i("HookApp", "---->: " + msg.obj.getClass());
try {
Object obj = msg.obj;
//我们要获取之前Hook携带过来的 Proxy
Field intentField = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField("intent");
intentField.setAccessible(true);
//获取intent对象,才能取出携带过来的I action Intent
Intent intent = (Intent) intentField.get(obj);
// actionIntent == TestActivityIntent
Intent actionIntent = intent.getParcelableExtra("oldIntent");
if (actionIntent != null) {
/***
*我们在以下代码中,对插件和宿主进行区分
*/
Field activityInfoField = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField("activityInfo");
activityInfoField.setAccessible(true);//授权
ActivityInfo activityInfo = (ActivityInfo) activityInfoField.get(obj);
//什么时候加载插件的?
if (actionIntent.getPackage() == null) {//证明是插件
System.out.println("start plugin --->>>>");
activityInfo.applicationInfo.packageName = actionIntent.getComponent().getPackageName();
System.out.println("start plugin --->>>>" + actionIntent.getComponent().getPackageName());
hookGetPackageInfo();
} else {//宿主
System.out.println("start home --->>>>");
activityInfo.applicationInfo.packageName = actionIntent.getPackage();
}
//实例化自己的真实的
intentField.set(obj, actionIntent);//把ProxyActivity 换成真正的
Log.i("HookApp", "---->: SET--->>> ");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
mH.handleMessage(msg);
// 让系统继续正常往下执行
// return false; // 系统就会往下执行
return true; // 系统不会往下执行
}
}
/**
* 自己创造一个LoadedApk.ClassLoader 添加到 mPackages,此LoadedApk 专门用来加载插件里面的 class
*/
private void customLoadedApkAction() throws Exception {
File pluginDirFile = getDir("plugin", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
File file = new File( pluginDirFile.getAbsoluteFile() + File.separator + "pluginLoaded.apk");
if (!file.exists()) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("插件包不存在..." + file.getAbsolutePath());
}
String pulginPath = file.getAbsolutePath();
// mPackages 添加 自定义的LoadedApk
// final ArrayMap<String, WeakReference<LoadedApk>> mPackages 添加自定义LoadedApk
Class mActivityThreadClass = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
// 执行此方法 public static ActivityThread currentActivityThread() 拿到 ActivityThread对象
Object mActivityThread = mActivityThreadClass.getMethod("currentActivityThread").invoke(null);
Field mPackagesField = mActivityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("mPackages");
mPackagesField.setAccessible(true);
// 拿到mPackages对象
Object mPackagesObj = mPackagesField.get(mActivityThread);
Map mPackages = (Map) mPackagesObj;
// 如何自定义一个 LoadedApk,系统是如何创造LoadedApk的,我们就怎么去创造LoadedApk
// 执行此 public final LoadedApk getPackageInfoNoCheck(ApplicationInfo ai, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo)
Class mCompatibilityInfoClass = Class.forName("android.content.res.CompatibilityInfo");
Field defaultField = mCompatibilityInfoClass.getDeclaredField("DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO");
defaultField.setAccessible(true);
Object defaultObj = defaultField.get(null);
/**
* ApplicationInfo 如何获取, APK解析源码分析
*/
ApplicationInfo applicationInfo = getApplicationInfoAction();
Method mLoadedApkMethod = mActivityThreadClass.getMethod("getPackageInfoNoCheck", ApplicationInfo.class, mCompatibilityInfoClass); // 类类型
// 执行 才能拿到 LoedApk 对象
Object mLoadedApk = mLoadedApkMethod.invoke(mActivityThread, applicationInfo, defaultObj);
// 自定义加载器 加载插件
// String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory, String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent
File fileDir = getDir("pulginPathDir", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
// 自定义 加载插件的 ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = new PluginClassLoader(pulginPath,fileDir.getAbsolutePath(), null, getClassLoader());
Field mClassLoaderField = mLoadedApk.getClass().getDeclaredField("mClassLoader");
mClassLoaderField.setAccessible(true);
mClassLoaderField.set(mLoadedApk, classLoader); // 替换 LoadedApk 里面的 ClassLoader
// 添加自定义的 LoadedApk 专门加载 插件里面的 class
// 最终的目标 mPackages.put(插件的包名,插件的LoadedApk);
WeakReference weakReference = new WeakReference(mLoadedApk); // 放入 自定义的LoadedApk --》 插件的
mPackages.put(applicationInfo.packageName, weakReference); // 增加了我们自己的LoadedApk
}
/**
* 获取 ApplicationInfo 为插件服务的
* @return
* @throws
*/
private ApplicationInfo getApplicationInfoAction() throws Exception {
// 执行此public static ApplicationInfo generateApplicationInfo方法,拿到ApplicationInfo
Class mPackageParserClass = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageParser");
Object mPackageParser = mPackageParserClass.newInstance();
// generateApplicationInfo方法的类类型
Class $PackageClass = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageParser$Package");
Class mPackageUserStateClass = Class.forName("android.content.pm.PackageUserState");
Method mApplicationInfoMethod = mPackageParserClass.getMethod("generateApplicationInfo",$PackageClass,
int.class, mPackageUserStateClass);
File dirFile = getDir("plugin", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
File file = new File(dirFile.getAbsoluteFile() + File.separator + "pluginLoaded.apk");
String pulginPath = file.getAbsolutePath();
// 执行此public Package parsePackage(File packageFile, int flags)方法,拿到 Package
// 获得执行方法的对象
Method mPackageMethod = mPackageParserClass.getMethod("parsePackage", File.class, int.class);
Object mPackage = mPackageMethod.invoke(mPackageParser, file, PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES);
// 参数 Package p, int flags, PackageUserState state
ApplicationInfo applicationInfo = (ApplicationInfo)
mApplicationInfoMethod.invoke(mPackageParser, mPackage, 0, mPackageUserStateClass.newInstance());
// 获得的 ApplicationInfo 就是插件的 ApplicationInfo
// 我们这里获取的 ApplicationInfo
// applicationInfo.publicSourceDir = 插件的路径;
// applicationInfo.sourceDir = 插件的路径;
applicationInfo.publicSourceDir = pulginPath;
applicationInfo.sourceDir = pulginPath;
return applicationInfo;
}
/**
* 自定义classLoader去加载插件
*/
static class PluginClassLoader extends DexClassLoader {
/**
* @param dexPath
* @param optimizedDirectory
* @param librarySearchPath
* @param parent
*/
public PluginClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory, String librarySearchPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, optimizedDirectory, librarySearchPath, parent);
}
}
// Hook 拦截此 getPackageInfo 做自己的逻辑
private void hookGetPackageInfo() {
try {
// sPackageManager 替换 我们自己的动态代理
Class mActivityThreadClass = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
Field sCurrentActivityThreadField = mActivityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("sCurrentActivityThread");
sCurrentActivityThreadField.setAccessible(true);
Field sPackageManagerField = mActivityThreadClass.getDeclaredField("sPackageManager");
sPackageManagerField.setAccessible(true);
final Object packageManager = sPackageManagerField.get(null);
/**
* 动态代理
*/
Class mIPackageManagerClass = Class.forName("android.content.pm.IPackageManager");
Object mIPackageManagerProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{mIPackageManagerClass}, // 要监听的接口
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if ("getPackageInfo".equals(method.getName())) {
// 如何才能绕过 PMS, 欺骗系统
// pi != null
return new PackageInfo(); // 成功绕过 PMS检测
}
// 让系统正常继续执行下去
return method.invoke(packageManager, args);
}
});
// 替换 狸猫换太子 换成我们自己的 动态代理
sPackageManagerField.set(null, mIPackageManagerProxy);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}