在使用 TDesign Vue Next 组件库开发项目时,我们经常会遇到需要深度定制组件样式的情况。最近在开发材质编辑器功能时,就遇到了一个棘手的问题:t-dialog 组件无法通过样式穿透修改内层样式。
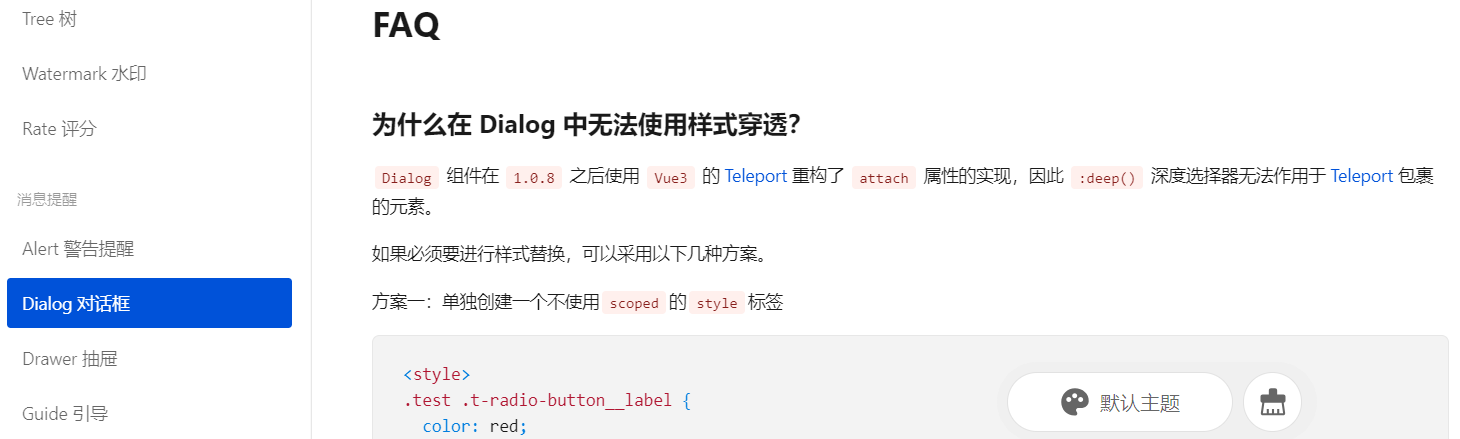
官方链接说明如下:
虽然在该链接中也提到了一些解决方法,但是问题也很多。
本文将分享如何用原生 div 实现一个功能完整的自定义对话框,解决样式定制难题。
问题背景
在材质编辑器项目中,我们需要一个固定尺寸(1024×768px)的对话框,并且要求精确控制内部布局。使用 TDesign 的 t-dialog 组件时,遇到了以下问题:
-
样式穿透失效 :即使使用
:deep()选择器,也无法覆盖 t-dialog 的内层样式 -
padding 不可控:对话框的内边距无法完全移除
-
布局限制:默认的对话框结构限制了自定义布局的灵活性
查看 TDesign 官方文档 后确认,t-dialog 确实不支持样式穿透,官方提供的替代方案也无法满足我们的定制需求。
解决方案:自定义对话框实现
1. 基本结构设计
我们使用两层 div 结构来模拟对话框:
html
<template>
<!-- 遮罩层 -->
<div v-if="dialogVisible" class="custom-dialog-mask">
<!-- 对话框容器 -->
<div ref="dialogRef" class="custom-dialog-container" :style="dialogStyle">
<!-- 对话框头部 -->
<div class="custom-dialog-header" @mousedown="startDrag">
<span class="dialog-title">材质编辑器</span>
<button class="close-btn" @click="handleClose">×</button>
</div>
<!-- 对话框内容 -->
<div class="custom-dialog-body">
<!-- 业务内容 -->
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>2. 遮罩层实现与事件屏蔽
遮罩层的核心作用是屏蔽背景交互 并提供视觉隔离:
html
<style scoped>
.custom-dialog-mask {
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
z-index: 1000;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
pointer-events: auto; /* 关键:确保遮罩层捕获所有事件 */
}
.custom-dialog-container {
position: absolute;
background-color: #1a1a1a;
border: 1px solid #444;
border-radius: 4px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5);
overflow: hidden;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
pointer-events: auto; /* 关键:确保对话框可以接收交互事件 */
}
</style>关键技术点:
-
使用
pointer-events: auto确保事件传递正确 -
遮罩层使用
fixed定位覆盖整个视口 -
半透明背景提供视觉层次感
3. 拖拽功能的完整实现
拖拽功能是自定义对话框的核心特性,需要精细的事件处理:
TypeScript
// 对话框拖拽相关状态
const dialogRef = ref<HTMLElement>()
const isDragging = ref(false)
const dragStartPos = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const dialogStartPos = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const dialogPosition = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
// 对话框样式
const dialogStyle = computed(() => ({
width: '1024px',
height: '768px',
left: `${dialogPosition.value.x}px`,
top: `${dialogPosition.value.y}px`
}))
// 开始拖拽
const startDrag = (e: MouseEvent) => {
if (!dialogRef.value) return
isDragging.value = true
dragStartPos.value = {
x: e.clientX,
y: e.clientY
}
dialogStartPos.value = { ...dialogPosition.value }
document.addEventListener('mousemove', onDrag)
document.addEventListener('mouseup', stopDrag)
e.preventDefault()
e.stopPropagation()
}
// 拖拽中
const onDrag = (e: MouseEvent) => {
if (!isDragging.value) return
const deltaX = e.clientX - dragStartPos.value.x
const deltaY = e.clientY - dragStartPos.value.y
const newX = dialogStartPos.value.x + deltaX
const newY = dialogStartPos.value.y + deltaY
// 限制对话框在可视区域内
const maxX = window.innerWidth - 1024
const maxY = window.innerHeight - 768
dialogPosition.value = {
x: Math.max(0, Math.min(newX, maxX)),
y: Math.max(0, Math.min(newY, maxY))
}
e.preventDefault()
e.stopPropagation()
}
// 停止拖拽
const stopDrag = (e?: MouseEvent) => {
isDragging.value = false
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', onDrag)
document.removeEventListener('mouseup', stopDrag)
if (e) {
e.preventDefault()
e.stopPropagation()
}
}
// 对话框居中
const centerDialog = () => {
if (dialogRef.value) {
const dialogWidth = 1024
const dialogHeight = 768
const windowWidth = window.innerWidth
const windowHeight = window.innerHeight
dialogPosition.value = {
x: (windowWidth - dialogWidth) / 2,
y: (windowHeight - dialogHeight) / 2
}
}
}拖拽实现的关键要点:
-
精确的位置计算:
-
记录拖拽开始时的鼠标位置和对话框位置
-
使用差值计算新位置,避免位置跳跃
-
-
边界限制:
-
计算可视区域边界,防止对话框被拖出屏幕
-
使用
Math.max(0, Math.min(newX, maxX))进行边界约束
-
-
事件管理:
-
在
mousedown时添加全局事件监听 -
在
mouseup时及时移除事件监听,防止内存泄漏 -
使用
stopPropagation()防止事件冒泡干扰
-
-
视觉反馈:
-
头部区域设置
cursor: move提示可拖拽 -
拖拽时改为
cursor: grabbing提供操作反馈
-
4. 完整的样式实现
css
<style scoped>
/* 对话框头部 */
.custom-dialog-header {
height: 40px;
background-color: #2d2d2d;
border-bottom: 1px solid #444;
color: #e0e0e0;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: space-between;
padding: 0 12px;
cursor: move;
user-select: none;
flex-shrink: 0;
}
.dialog-title {
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
}
.close-btn {
background: none;
border: none;
color: #e0e0e0;
font-size: 20px;
width: 24px;
height: 24px;
border-radius: 2px;
cursor: pointer;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
transition: background-color 0.2s;
}
.close-btn:hover {
background-color: #444;
}
/* 对话框内容 */
.custom-dialog-body {
flex: 1;
overflow: hidden;
}
/* 拖拽时的样式反馈 */
.custom-dialog-header:active {
cursor: grabbing;
}
</style>优势与收获
相比 t-dialog 的优势
-
完全的样式控制:不再受限于组件库的样式结构
-
精准的尺寸控制:可以精确控制对话框和内部布局的尺寸
-
灵活的事件处理:可以自定义各种交互行为
-
更好的性能:减少不必要的样式计算和组件层次
实现过程中的经验总结
-
事件处理要精细:拖拽功能需要仔细处理事件的生命周期
-
边界检查很重要:确保对话框不会移出可视区域
-
用户体验要考虑:提供视觉反馈,如拖拽光标变化
-
代码组织要清晰:将拖拽逻辑封装成可复用的函数
完整代码示例
以下是整合后的完整组件代码:
html
<template>
<div v-if="dialogVisible" class="custom-dialog-mask">
<div
ref="dialogRef"
class="custom-dialog-container"
:style="dialogStyle"
>
<div class="custom-dialog-header" @mousedown="startDrag">
<span class="dialog-title">材质编辑器</span>
<button class="close-btn" @click="handleClose">×</button>
</div>
<div class="custom-dialog-body">
<!-- 具体的业务内容 -->
<slot></slot>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { ref, computed, onMounted, onUnmounted, nextTick, watch } from 'vue'
interface Props {
visible: boolean
width?: string
height?: string
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
width: '1024px',
height: '768px'
})
const emit = defineEmits<{
(e: 'update:visible', value: boolean): void
(e: 'close'): void
}>()
// 状态管理
const dialogVisible = ref(props.visible)
// 拖拽相关状态
const dialogRef = ref<HTMLElement>()
const isDragging = ref(false)
const dragStartPos = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const dialogStartPos = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
const dialogPosition = ref({ x: 0, y: 0 })
// 对话框样式
const dialogStyle = computed(() => ({
width: props.width,
height: props.height,
left: `${dialogPosition.value.x}px`,
top: `${dialogPosition.value.y}px`
}))
// 监听 visible 变化
watch(() => props.visible, (newVal) => {
dialogVisible.value = newVal
if (newVal) {
nextTick(() => {
centerDialog()
})
}
})
// 居中对话框
const centerDialog = () => {
if (dialogRef.value) {
const dialogWidth = parseInt(props.width)
const dialogHeight = parseInt(props.height)
const windowWidth = window.innerWidth
const windowHeight = window.innerHeight
dialogPosition.value = {
x: (windowWidth - dialogWidth) / 2,
y: (windowHeight - dialogHeight) / 2
}
}
}
// 拖拽功能
const startDrag = (e: MouseEvent) => {
if (!dialogRef.value) return
isDragging.value = true
dragStartPos.value = { x: e.clientX, y: e.clientY }
dialogStartPos.value = { ...dialogPosition.value }
document.addEventListener('mousemove', onDrag)
document.addEventListener('mouseup', stopDrag)
e.preventDefault()
e.stopPropagation()
}
const onDrag = (e: MouseEvent) => {
if (!isDragging.value) return
const deltaX = e.clientX - dragStartPos.value.x
const deltaY = e.clientY - dragStartPos.value.y
const newX = dialogStartPos.value.x + deltaX
const newY = dialogStartPos.value.y + deltaY
const maxX = window.innerWidth - parseInt(props.width)
const maxY = window.innerHeight - parseInt(props.height)
dialogPosition.value = {
x: Math.max(0, Math.min(newX, maxX)),
y: Math.max(0, Math.min(newY, maxY))
}
e.preventDefault()
e.stopPropagation()
}
const stopDrag = () => {
isDragging.value = false
document.removeEventListener('mousemove', onDrag)
document.removeEventListener('mouseup', stopDrag)
}
// 关闭对话框
const handleClose = () => {
dialogVisible.value = false
emit('update:visible', false)
emit('close')
}
// 生命周期
onMounted(() => {
if (dialogVisible.value) {
centerDialog()
}
window.addEventListener('resize', centerDialog)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
stopDrag()
window.removeEventListener('resize', centerDialog)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
/* 样式同上文 */
</style>结语
通过这个自定义对话框的实现,我们不仅解决了 TDesign t-dialog 的样式限制问题,还获得了更大的灵活性和控制力。这种方案特别适合需要高度定制化的复杂对话框场景。
当然,这种实现方式也需要更多的代码和维护成本,在简单场景下可能还是使用组件库提供的对话框更合适。但在需要深度定制的场景中,掌握这种自定义实现方法将会是很有价值的技能。