目录
[1.1 思路](#1.1 思路)
[1.2 代码实现](#1.2 代码实现)
[1.3 简单测试](#1.3 简单测试)
[2.1 思路](#2.1 思路)
[2.2 代码实现](#2.2 代码实现)
[2.3 简单测试](#2.3 简单测试)
[3.1 思路](#3.1 思路)
[3.2 代码实现](#3.2 代码实现)
[3.3 简单测试](#3.3 简单测试)
[4.1 思路](#4.1 思路)
[4.2 代码实现](#4.2 代码实现)
[4.3 简单测试](#4.3 简单测试)
[5.1 思路](#5.1 思路)
[5.2 代码实现](#5.2 代码实现)
[5.3 简单测试](#5.3 简单测试)
本章的完整代码:Logs。
1、实用类的设计
1.1 思路
- 获取系统时间。
- 获取文件所在路径。
- 创建目录。
- 至于文件的创建 ,可以用std::ofstream(输出文件流,不存在就创建)。
1.2 代码实现
- 使用静态成员函数 ,不需要创建对象。
cpp
/*
1. 获取系统时间。
2. 获取文件所在路径。
3. 创建目录。
*/
#ifndef __MY_UTIL_H__
#define __MY_UTIL_H__
#include <string>
#include <ctime>
#include <filesystem> // C++17
namespace LzcLog
{
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
class Util
{
public:
static size_t GetTime(){
return (size_t)time(nullptr);
}
static std::string GetDir(const std::string& file_path){
fs::path dir_path = fs::path(file_path).parent_path(); // 不带末尾分隔符
return dir_path.string() + fs::path::preferred_separator; // 拼接系统默认分隔符
}
static void CreateDir(const std::string& dir_path){
if(fs::exists(dir_path))
return;
fs::create_directories(dir_path);
}
};
}
#endif1.3 简单测试
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Util.hpp"
int main()
{
std::cout << LzcLog::Util::GetTime() << std::endl;
std::string dir = LzcLog::Util::GetDir("./Lzc/xxx/a.txt");
std::cout << dir << std::endl;
LzcLog::Util::CreateDir(dir);
return 0;
}- 输出结果:
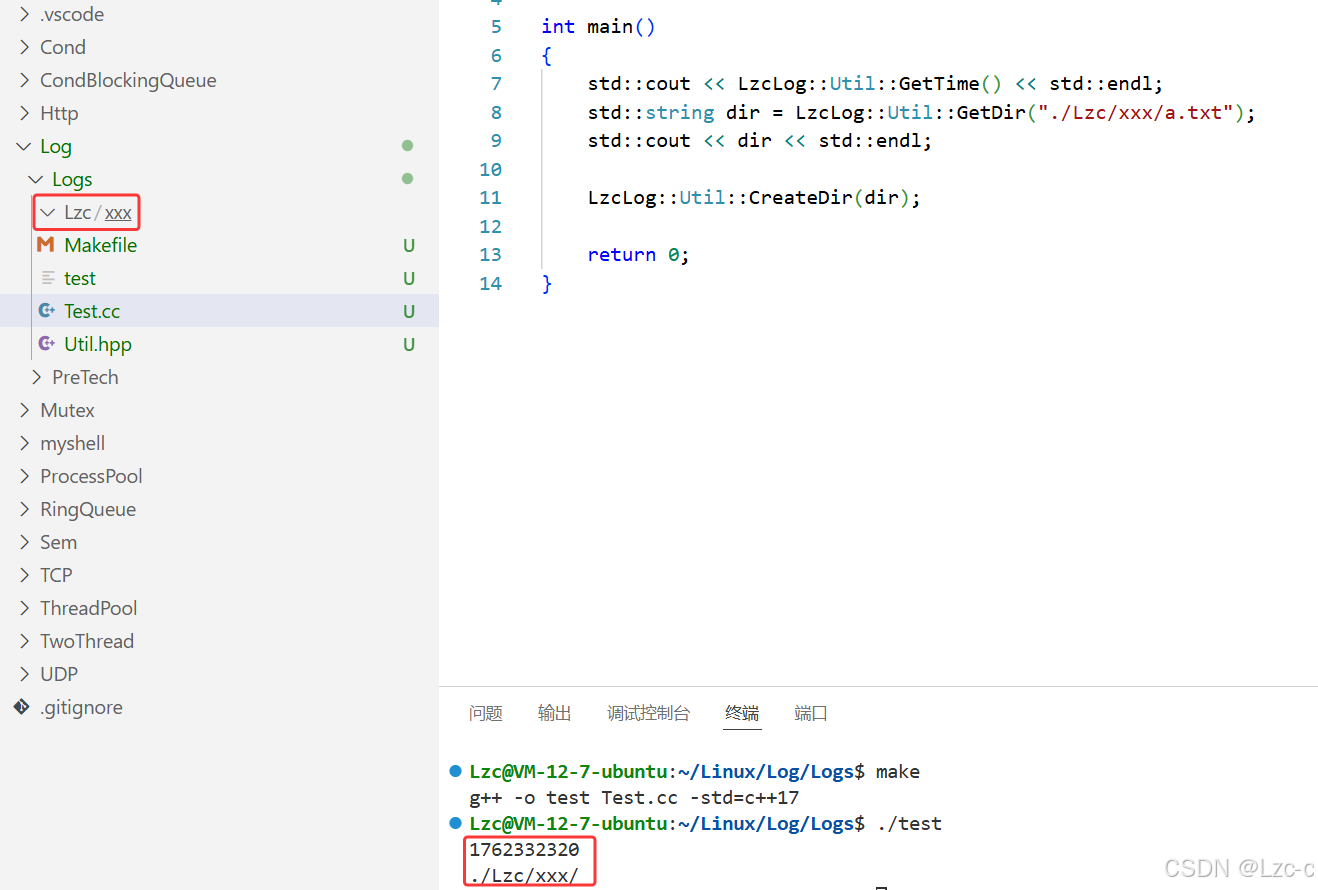
- 时间戳,获取路径,创建目录,没问题。
2、日志等级类的设计
2.1 思路
- 划分日志等级 ,以便于控制日志的输出 (>=设置的等级,才可以输出)。
- DEBUG:调试,调试时的关键信息输出。
- INFO:提示,普通的提示型日志信息。
- WARNING:警告,不影响运行,但是需要注意一下的日志。
- ERROR:错误,程序运行出现错误的日志。
- FATAL:致命,一般是代码异常导致程序无法继续推进运行的日志。
- OFF:关闭。
- 提供等级枚举转字符串 功能。
2.2 代码实现
cpp
/*
1. 划分日志等级,以便于控制日志的输出。
2. 提供等级枚举转字符串功能。
*/
#ifndef __MY_LOG_LEVEL_H__
#define __MY_LOG_LEVEL_H__
#include <string>
namespace LzcLog
{
class LogLevel
{
public:
enum class Value
{
DEBUG = 0,
INFO,
WARNING,
ERROR,
FATAL,
OFF
};
static std::string LogLevelToString(const Value &value)
{
switch (value)
{
case Value::DEBUG:
return "DEBUG";
case Value::INFO:
return "INFO";
case Value::WARNING:
return "WARNING";
case Value::ERROR:
return "ERROR";
case Value::FATAL:
return "FATAL";
case Value::OFF:
return "OFF";
default:
return "UNKNOWN";
}
}
};
}
#endif- 注意 :在类中,
- static关键字的作用是修饰 "需要占用内存的成员 "(成员变量 / 成员函数),无需创建对象, 通过 类名::成员 访问。
- 类型成员 (如嵌套的 enum/struct/using),不占用任何内存 ,无需创建对象, 通过 类名::类型名 访问(无需 static)。如:std::string::npos。
2.3 简单测试
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "LogLevel.hpp"
int main()
{
std::cout << LzcLog::LogLevel::LogLevelToString(LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::DEBUG) << std::endl;
std::cout << LzcLog::LogLevel::LogLevelToString(LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::INFO) << std::endl;
std::cout << LzcLog::LogLevel::LogLevelToString(LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::WARNING) << std::endl;
std::cout << LzcLog::LogLevel::LogLevelToString(LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::ERROR) << std::endl;
std::cout << LzcLog::LogLevel::LogLevelToString(LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::FATAL) << std::endl;
std::cout << LzcLog::LogLevel::LogLevelToString(LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::OFF) << std::endl;
return 0;
}- 输出结果:

- 日志等级的输出,没问题。
3、日志消息类的设计
3.1 思路
-
目的:中间存储 日志输出所需 的各项要素。
-
时间:描述本条日志的输出时间。
-
线程ID:描述本条日志是哪个线程输出的。
-
日志等级:描述本条日志的等级。
-
日志器名称 :日志器是 "可定制的工具",不同的人(或模块)可以拿着自己定制的 "工具" 写日志,各自方便、互不影响。
-
日志文件名:描述本条日志在哪个源码文件中输出的。
-
日志行号:描述本条日志在源码文件的哪一行输出的。
-
日志数据 :本条日志的有效载荷数据。
-
3.2 代码实现
- 因为外部需要访问日志消息的要素 ,所以直接使用struct,外部能够直接访问。
cpp
/*
中间存储 日志输出所需的各项要素。
1. 时间:描述本条日志的输出时间。
2. 线程ID:描述本条日志是哪个线程输出的。
3. 日志等级:描述本条日志的等级。
4. 日志器名称:
5. 日志文件名:描述本条日志在哪个源码文件中输出的。
6. 日志行号:描述本条日志在源码文件的哪一行输出的。
7. 日志数据:本条日志的有效载荷数据。
*/
#ifndef __MY_LOG_MESSAGE_H__
#define __MY_LOG_MESSAGE_H__
#include "Util.hpp"
#include "LogLevel.hpp"
#include <thread>
namespace LzcLog
{
struct LogMessage
{
size_t _ctime;
std::thread::id _tid;
LogLevel::Value _value;
std::string _logger;
std::string _file_name;
size_t _line_num;
std::string _payload;
LogMessage(const LogLevel::Value& value,
const std::string& logger,
const std::string& file_name,
size_t line_num,
const std::string& payload)
:_ctime(Util::GetTime())
,_tid(std::this_thread::get_id())
,_value(value)
,_logger(logger)
,_file_name(file_name)
,_line_num(line_num)
,_payload(payload)
{}
};
}
#endif3.3 简单测试
- 简单测试,只能编译一下,看有没有问题。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "LogMessage.hpp"
int main()
{
LzcLog::LogMessage log_message(LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::INFO, "root", "main.cc", 9, "xxx");
return 0;
}- 输出结果:
- 编译没问题。
4、日志输出格式化类的设计
4.1 思路
-
目的:自定义 日志信息的格式。
-
Formatter中,std::string _pattern成员 :保存日志输出的格式化字符串 。如:[%d{%H:%M%S}][%t][%p][%c][%f:%l]%T%m%n
- 格式化的字符 如下:
- %d 日期。会有格式化子项如:%d{%H:%:M:%S},子项用"{ }"。只有'{',没有匹配的'}',就跳过'{'。
- %t 线程id。
- %p 日志等级。
- %c 日志器名称。
- %f 文件名。
- %l 行号。
- %T缩进。
- %m 日志消息。
- %n 换行。
- %xyz,不存在的格式化字符 ,打印空。
- 只有%% ,才是% ;单个% ,无效,打印空。
- 其他普通字符 ,直接输出。
- 格式化的字符 如下:
-
Formatter中,std::vector<FormatChar::ptr>_format_chars成员 :用于按序保存 格式化字符串中,格式化字符对应的对象 (如:%d对应的对象,%t对应的对象)。格式化字符可能有子项(如:%d{%H:%M%S},%d有子项%H:%M:%S),要将这个子项传给其构造函数。
-
因为要将不同的格式化字符对象放在一个std::vector中 ,所以抽象一个基类,std::vector存放基类指针 ;再来个多态 ,方便std::vector 中的格式化字符对象 都使用同一个函数 ,将其日志消息的要素,存放到消息字符串中。
-
解析格式化字符串的思路:
*cpp// [%d{%H:%M%S}][%t][%p][%c][%f:%l]%T%m%n /* 解析格式化字符串的思路。 存储临时的字符串 1. 收集连续的普通字符, 2. 不为空,就插入,再清空 3. 遍历到末尾,就退出循环 4. pos指向%,如果%后面没有字符,认为是无效的的%,直接break 5. 判断%后面的字符类型 if是% 插入%,跳过 % + %(两个字符) else // 是格式化字符 { 6. 判断后面是否有子项 if有子项,即有'{' if找到对应的'}' 跳过'}' 保存sub_format else // 没有对应的'}',即没有子项 跳过'{', else // 没有子项 跳过 % + key(两个字符) 插入key,sub_format // sub_format为空,会使用默认格式 } */
4.2 代码实现
cpp
/*
自定义 格式化日志信息。(可以自定义,以哪种格式,输出日志消息)
1. Formatter中,pattern成员:保存日志输出的"格式字符串"。
如:[%d{%H:%M%S}][%t][%p][%c][%c][%f:%l]%T%m%n
%d 日期。会有格式化子项如:%d{%H:%:M:%S}
%t 线程id。
%p 日志等级。
%c 日志器名称。
%f 文件名。
%l 行号。
%T 缩进。
%m 日志消息。
%n 换行。
%xyz,不存在的格式化字符,打印空。
只有%%,才是%,单个%,无效,打印空。
其他普通字符,直接输出。
2. Formatter中,std::vector<FormatItem::ptr> items成员:
用于"按序"保存格式化字符串中,格式化字符对应的对象(如:%d对应的对象,%t对应的对象)。
格式化字符可能有子项((如:%d{%H:%M%S},%d有子项%H:%M:%S)),
要将这个子项传给其构造函数。
3. 因为要将不同的格式化字符对象放在一个std::vector中,所以抽象一个基类,std::vector存放基类指针;
再来个多态,方便vector中的元素都使用同一个函数,将其日志消息的要素,存放到消息字符串中。
*/
#ifndef __MY_LOG_FORMATTER_H__
#define __MY_LOG_FORMATTER_H__
#include "LogMessage.hpp"
#include "LogLevel.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
namespace LzcLog
{
class FormatChar
{
public:
using ptr = std::shared_ptr<FormatChar>; // 为什么是shared_ptr?因为后面要拷贝到vector中
virtual ~FormatChar() = default;
virtual void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) = 0;
};
class TimeFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
TimeFormatChar(const std::string &sub_format = "%H:%M:%S")
: _sub_format(sub_format)
{
if(_sub_format.empty()) _sub_format = "%H:%M:%S";
}
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
time_t time = message._ctime;
struct tm t;
localtime_r(&time, &t);
char s[128] = {0};
// 子格式可能无效,strftime返回0时输出空
if (strftime(s, sizeof(s) - 1, _sub_format.c_str(), &t) > 0)
{
os << s;
}
}
private:
std::string _sub_format;
};
class ThreadIdFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << message._tid;
}
};
class LogLevelFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << LogLevel::LogLevelToString(message._value);
}
};
class LoggerFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << message._logger;
}
};
class FileNameFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << message._file_name;
}
};
class LineNumFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << message._line_num;
}
};
class TabFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << " "; // "\t"会因为前面字符的长度,跳的距离不一样
}
};
class PayloadFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
// os << message._payload;
os.write(message._payload.data(), message._payload.size()); // 强制按size输出
}
};
class NewLineFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << std::endl; // 使用'\n'不兼容
}
};
class OtherFormatChar : public FormatChar
{
public:
OtherFormatChar(const std::string &str = "")
: _str(str)
{
}
void Format(std::ostream &os, const LogMessage &message) override
{
os << _str;
}
private:
std::string _str;
};
class LogFormatter
{
public:
LogFormatter(const std::string &pattern = "[%d{%H:%M:%S}][%t][%p][%c][%f:%l]%T%m%n")
: _pattern(pattern)
{
ParsePattern(); // 重新解析默认格式
}
std::string format(const LogMessage &message)
{
std::stringstream ss;
for (auto &format_char : _format_chars)
format_char->Format(ss, message);
return ss.str();
}
private:
FormatChar::ptr CreateFormatChar(char key, const std::string &sub_format = "")
{
switch (key) {
case 'd': return std::make_shared<TimeFormatChar>(sub_format);
case 't': return std::make_shared<ThreadIdFormatChar>();
case 'p': return std::make_shared<LogLevelFormatChar>();
case 'c': return std::make_shared<LoggerFormatChar>();
case 'f': return std::make_shared<FileNameFormatChar>();
case 'l': return std::make_shared<LineNumFormatChar>();
case 'T': return std::make_shared<TabFormatChar>();
case 'm': return std::make_shared<PayloadFormatChar>();
case 'n': return std::make_shared<NewLineFormatChar>();
default: return std::make_shared<OtherFormatChar>(""); // 无效key,输出空
}
}
// 核心:解析格式化字符串_pattern
void ParsePattern()
{
// [%d{%H:%M%S}][%t][%p][%c][%f:%l]%T%m%n
/*
解析格式化字符串的思路。
存储临时的字符串
1. 收集连续的普通字符,
2. 不为空,就插入,再清空
3. 遍历到末尾,就退出循环
4. pos指向%,如果%后面没有字符,认为是无效的的%,直接break
5. 判断%后面的字符类型
if是%
插入%,跳过 % + %(两个字符)
else // 是格式化字符
{
6. 判断后面是否有子项
if有子项,即有'{'
if找到对应的'}'
跳过'}'
保存sub_format
else // 没有对应的'}',即没有子项
跳过'{',
else // 没有子项
跳过 % + key(两个字符)
插入key,sub_format // sub_format为空,会使用默认格式
}
*/
size_t pos = 0;
const size_t n = _pattern.size();
std::string tmp_str;
while(pos < n)
{
// 1. 收集连续的普通字符
while(pos < n && _pattern[pos] != '%')
{
tmp_str += _pattern[pos];
++pos;
}
// 2. tmp_str不为空,就插入,并清空
if(!tmp_str.empty())
{
_format_chars.push_back(std::make_shared<OtherFormatChar>(tmp_str));
tmp_str.clear();
}
// 3. 遍历到末尾,就退出循环
if(pos >= n)
break;
// 4. pos指向%,如果%后面没有字符,认为是无效的的%,直接break
if(pos + 1 == n)
break;
// 5. pos指向%,判断%后面的字符类型
if(_pattern[pos+1] == '%')
{
_format_chars.push_back(std::make_shared<OtherFormatChar>("%"));
pos += 2;
}
else // 是格式化字符
{
// 6. 判断后面是否有子项
char key = _pattern[pos+1]; // 格式化字符
std::string sub_format;
size_t start = pos + 2;
if(start < n && _pattern[start] == '{') // 有子项,start指向'{'
{
size_t end = _pattern.find("}", start+1);
if(end != std::string::npos) // 找到'}'
{
pos = end + 1;
sub_format = _pattern.substr(start+1, end-start-1);
}
else // 没有配对的'}',即没有子项
{
pos = start + 1; // 跳过'{'
}
}
else // 没有子项
{
pos += 2; // 跳过 % + key(2个字符)
}
_format_chars.push_back(CreateFormatChar(key, sub_format)); // 如果sub_format为空,会用默认的格式
}
}
}
std::string _pattern;
std::vector<FormatChar::ptr> _format_chars;
};
}
#endif4.3 简单测试
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "LogFormatter.hpp"
int main()
{
// 构造测试日志消息(自定义字段)
LzcLog::LogMessage test_msg(
LzcLog::LogLevel::Value::INFO, // %p 日志等级:INFO
"user_login_logger", // %c 日志器名称
__FILE__, // %f 文件名
__LINE__, // %l 行号
"用户张三登录成功, IP: 192.168.1.100" // 日志内容
);
std::cout << "===== 测试1: 默认格式 =====" << std::endl;
LzcLog::LogFormatter default_formatter; // 默认格式: [%d{%H:%M:%S}][%t][%p][%c][%f:%l]%T%m%n
std::cout << default_formatter.format(test_msg);
std::cout << "===== 测试2: 自定义格式(简化版) =====" << std::endl;
LzcLog::LogFormatter custom_formatter("[%d{%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S}][%p] %m %% 完成\n"); // 包含%%转义
std::cout << custom_formatter.format(test_msg);
std::cout << "===== 测试3: 边界场景(无效key+未闭合子项) =====" << std::endl;
LzcLog::LogFormatter edge_formatter("[%d{YYYY-MM-DD][%x][%t]%T%m\n"); // %x是无效key,%d子项无闭合(故意写漏})
std::cout << edge_formatter.format(test_msg);
return 0;
}- 输出结果:

- 测试1和2,没问题;测试3,跳过了'{',不存在的格式化字符,打印空,没问题。
5、日志落地类的设计
5.1 思路
- 目的 :将格式化完成的日志消息字符串 ,输出到指定位置 。
- 标准输出。
- 指定文件。
- 滚动文件 (文件按时间 /大小进行滚动)。下面,以文件的大小进行滚动。
- 使用简单工厂模式(工厂外套一层模板,自动生成),支持扩展输出到不同的位置。
5.2 代码实现
cpp
/*
1. 抽象输出
Log(const std::string& message) = 0;
2. 标准输出
std::cout.write(message.data(), message.size());
3. 指定文件
构造时,先创建目录,再ofs.open(file_path),先创建,再打开。
log里面 写入失败,std::cout << "日志写入文件失败" << std::endl;
4. 滚动文件BySize
构造时,创建目录,再创建并打开文件。文件名称 = basename + 创建的时间。
log里面,如果 超出了指定的大小,就关闭文件并清空当前的大小,再打开新文件。
5. 简单工厂模板
*/
#ifndef __MY_LOG_SINK_H__
#define __MY_LOG_SINK_H__
#include "Util.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
namespace LzcLog
{
class LogSink
{
public:
using ptr = std::shared_ptr<LogSink>;
virtual ~LogSink() = default;
virtual void Log(const std::string &message) = 0;
};
class StdoutSink : public LogSink
{
public:
void Log(const std::string &message) override
{
std::cout.write(message.data(), message.size());
std::cout.flush(); // 修复:强制刷新,不丢日志
}
};
class FileSink : public LogSink
{
public:
FileSink(const std::string &file_path)
{
Util::CreateDir(Util::GetDir(file_path));
_ofs.open(file_path, std::ios::binary | std::ios::app);
if (!_ofs.is_open())
{
// 运行时错误提示(Release模式有效)
std::cerr << "打开日志文件失败!路径:" << file_path << std::endl;
abort();
}
}
void Log(const std::string &message) override
{
_ofs.write(message.data(), message.size());
_ofs.flush(); // 修复:强制刷新,不丢日志
// 用 fail() 判断写入失败(更精准)
if (_ofs.fail())
{
std::cerr << "日志写入文件失败!" << std::endl;
_ofs.clear(); // 清除错误状态
}
}
private:
std::ofstream _ofs;
};
class RollBySizeSink : public LogSink
{
public:
// base_path,如:"./xxx/roll_by_size-"
RollBySizeSink(const std::string &base_path, size_t max_size)
: _base_path(base_path),
_max_size(max_size), _cur_size(0)
{
Util::CreateDir(Util::GetDir(_base_path));
OpenFile();
}
void Log(const std::string &message) override
{
if (_cur_size >= _max_size)
{
_ofs.close();
OpenFile();
_cur_size = 0;
}
_ofs.write(message.data(), message.size());
_ofs.flush(); // 修复:强制刷新,不丢日志
if (_ofs.fail())
{
std::cerr << "滚动日志写入失败!" << std::endl;
_ofs.clear();
_cur_size = 0; // 重置大小,避免一直触发滚动
}
_cur_size += message.size();
}
private:
void OpenFile()
{
std::string file_path = _base_path + CreationTime();
_ofs.open(file_path, std::ios::binary | std::ios::app);
if (!_ofs.is_open())
{
// 运行时错误提示(Release模式有效),包含错误码
std::cerr << "打开日志文件失败!路径:" << file_path << std::endl;
abort();
}
}
std::string CreationTime()
{
time_t time = Util::GetTime();
struct tm t;
localtime_r(&time, &t);
std::string file_name;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << t.tm_year + 1900
<< (t.tm_mon + 1 < 10 ? "0" : "") << (t.tm_mon + 1) // 补0,文件名更规范
<< (t.tm_mday < 10 ? "0" : "") << t.tm_mday
<< (t.tm_hour < 10 ? "0" : "") << t.tm_hour
<< (t.tm_min < 10 ? "0" : "") << t.tm_min
<< (t.tm_sec < 10 ? "0" : "") << t.tm_sec
<< ".log";
return ss.str();
}
std::string _base_path;
std::ofstream _ofs;
const size_t _max_size;
size_t _cur_size;
};
class SinkFactory
{
public:
template<typename SinkType, typename ...Args>
static LogSink::ptr CreateSink(Args&& ...args)
{
return std::make_shared<SinkType>(std::forward<Args>(args)...);
}
};
}
#endif5.3 简单测试
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "LogSink.hpp"
#include <unistd.h>
int main()
{
// 1. 测试 标准输出(直接看终端)
auto stdout_sink = LzcLog::SinkFactory::CreateSink<LzcLog::StdoutSink>();
stdout_sink->Log("标准输出测试成功!\n");
// 2. 测试 指定文件写入(看 ./logs/test.log)
auto file_sink = LzcLog::SinkFactory::CreateSink<LzcLog::FileSink>("./test.log");
file_sink->Log("文件写入测试成功!");
// 3. 测试 按大小滚动(阈值200字节,写2条100字节日志,触发滚动)
auto roll_sink = LzcLog::SinkFactory::CreateSink<LzcLog::RollBySizeSink>("./xxx/roll_by_size-", 99);
std::string log = "滚动测试日志:" + std::string(80, 'a') + "\n"; // 约100字节
roll_sink->Log(log);
sleep(1);
roll_sink->Log(log); // 第2条触发滚动
return 0;
}- 输出结果:
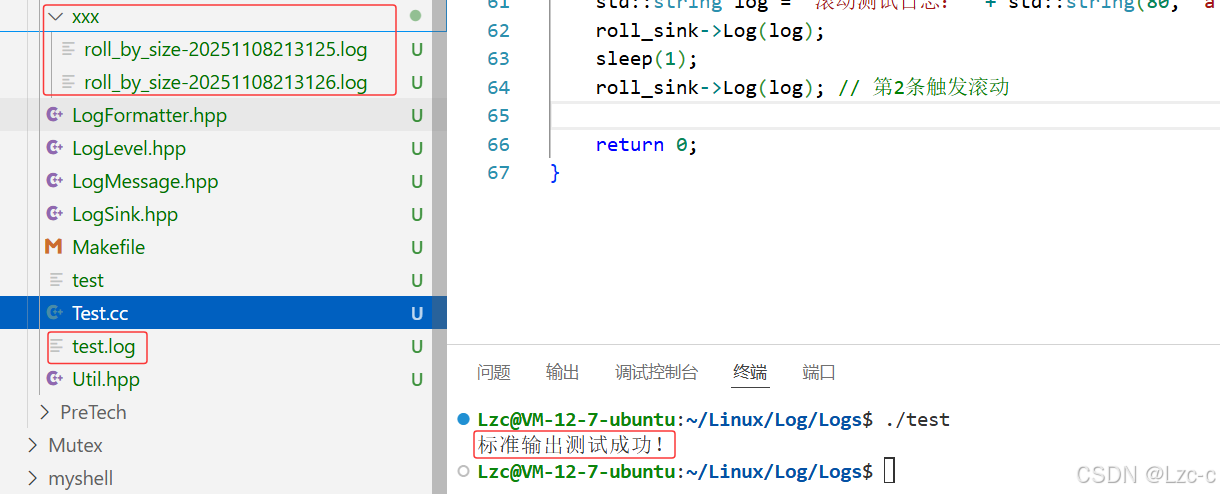
- 文件的创建和消息的输出,没问题。