策略模式(Strategy Pattern)是一种行为设计模式,它允许你定义一系列算法,并将每个算法封装起来,使它们可以相互替换。下面介绍策略模式在 TypeScript 中的实现。
策略模式基本概念
策略模式包含三个主要部分:
- Context(上下文):维护一个策略对象的引用
- Strategy(策略接口):定义所有支持的算法的公共接口
- ConcreteStrategy(具体策略):实现策略接口的具体算法
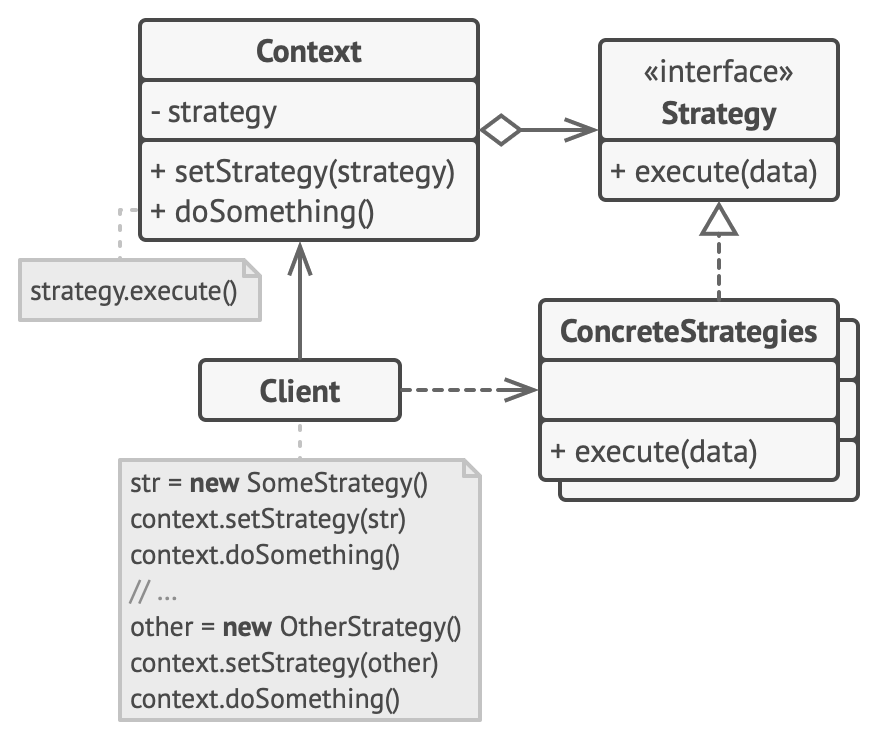
基础实现
1. 定义策略接口
typescript
// 策略接口
interface PaymentStrategy {
pay(amount: number): void;
}2. 实现具体策略类
typescript
// 信用卡支付策略
class CreditCardPayment implements PaymentStrategy {
private cardNumber: string;
private name: string;
constructor(cardNumber: string, name: string) {
this.cardNumber = cardNumber;
this.name = name;
}
pay(amount: number): void {
console.log(`使用信用卡支付 $${amount}`);
console.log(`卡号: ${this.cardNumber}, 持卡人: ${this.name}`);
}
}
// PayPal支付策略
class PayPalPayment implements PaymentStrategy {
private email: string;
constructor(email: string) {
this.email = email;
}
pay(amount: number): void {
console.log(`使用PayPal支付 $${amount}`);
console.log(`邮箱: ${this.email}`);
}
}
// 加密货币支付策略
class CryptoPayment implements PaymentStrategy {
private walletAddress: string;
constructor(walletAddress: string) {
this.walletAddress = walletAddress;
}
pay(amount: number): void {
console.log(`使用加密货币支付 $${amount}`);
console.log(`钱包地址: ${this.walletAddress}`);
}
}3. 创建上下文类
typescript
// 支付上下文
class PaymentContext {
private strategy: PaymentStrategy;
constructor(strategy: PaymentStrategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 设置支付策略
setStrategy(strategy: PaymentStrategy): void {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 执行支付
executePayment(amount: number): void {
this.strategy.pay(amount);
}
}4. 使用示例
typescript
// 使用示例
const paymentContext = new PaymentContext(new CreditCardPayment("1234-5678-9012", "张三"));
// 使用信用卡支付
paymentContext.executePayment(100);
// 切换到PayPal支付
paymentContext.setStrategy(new PayPalPayment("zhang@example.com"));
paymentContext.executePayment(200);
// 切换到加密货币支付
paymentContext.setStrategy(new CryptoPayment("1A1zP1eP5QGefi2DMPTfTL5SLmv7DivfNa"));
paymentContext.executePayment(300);更复杂的示例:排序策略
typescript
// 排序策略接口
interface SortStrategy<T> {
sort(items: T[]): T[];
}
// 冒泡排序策略
class BubbleSort<T> implements SortStrategy<T> {
sort(items: T[]): T[] {
console.log("使用冒泡排序");
const arr = [...items];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
[arr[j], arr[j + 1]] = [arr[j + 1], arr[j]];
}
}
}
return arr;
}
}
// 快速排序策略
class QuickSort<T> implements SortStrategy<T> {
sort(items: T[]): T[] {
console.log("使用快速排序");
if (items.length <= 1) return items;
const pivot = items[0];
const left = [];
const right = [];
for (let i = 1; i < items.length; i++) {
if (items[i] < pivot) {
left.push(items[i]);
} else {
right.push(items[i]);
}
}
return [...this.sort(left), pivot, ...this.sort(right)];
}
}
// 排序上下文
class Sorter<T> {
private strategy: SortStrategy<T>;
constructor(strategy: SortStrategy<T>) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
setStrategy(strategy: SortStrategy<T>): void {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
sort(items: T[]): T[] {
return this.strategy.sort(items);
}
}
// 使用示例
const numbers = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90];
const sorter = new Sorter<number>(new BubbleSort<number>());
console.log("排序前:", numbers);
console.log("排序后:", sorter.sort(numbers));
// 切换排序策略
sorter.setStrategy(new QuickSort<number>());
console.log("使用快速排序:", sorter.sort(numbers));使用函数式编程的实现
TypeScript 也支持函数式风格的策略模式:
typescript
// 策略类型定义
type DiscountStrategy = (amount: number) => number;
// 具体策略函数
const noDiscount: DiscountStrategy = (amount: number) => amount;
const percentageDiscount = (percentage: number): DiscountStrategy =>
(amount: number) => amount * (1 - percentage / 100);
const fixedDiscount = (discount: number): DiscountStrategy =>
(amount: number) => Math.max(0, amount - discount);
// 上下文
class ShoppingCart {
private items: number[] = [];
private discountStrategy: DiscountStrategy = noDiscount;
addItem(price: number): void {
this.items.push(price);
}
setDiscountStrategy(strategy: DiscountStrategy): void {
this.discountStrategy = strategy;
}
getTotal(): number {
const subtotal = this.items.reduce((sum, price) => sum + price, 0);
return this.discountStrategy(subtotal);
}
}
// 使用示例
const cart = new ShoppingCart();
cart.addItem(100);
cart.addItem(50);
cart.addItem(30);
console.log("原价:", cart.getTotal()); // 180
cart.setDiscountStrategy(percentageDiscount(10)); // 9折
console.log("9折后:", cart.getTotal()); // 162
cart.setDiscountStrategy(fixedDiscount(50)); // 减50
console.log("减50后:", cart.getTotal()); // 130策略模式的优点
- 开闭原则:可以引入新策略而不修改现有代码
- 消除条件语句:避免大量的 if-else 或 switch-case 语句
- 算法复用:可以在不同的上下文中复用策略
- 测试友好:每个策略都可以独立测试
适用场景
- 一个系统需要在多种算法中选择一种时
- 有多个条件语句来选择不同的行为时
- 需要动态切换算法时
- 希望将算法的使用与实现分离时
策略模式是非常实用的设计模式,特别适合处理需要灵活切换行为的场景。