Agent、BaseAgent、ReactAgent 分析
请关注微信公众号:阿呆-bot
概述
本文档分析 Spring AI Alibaba Agent Framework 中的核心 Agent 类层次结构,包括 Agent 基类、BaseAgent 抽象类和 ReactAgent 具体实现,重点分析其关键方法、功能职责和类间关系。
入口类说明
Agent - 所有 Agent 的基类
Agent 是所有 Agent 实现的抽象基类,提供了 Agent 的通用能力和 Graph 管理功能。
核心职责:
- 管理 Agent 的名称和描述
- 提供 Graph 的初始化和编译
- 提供统一的调用接口(invoke、stream)
- 支持调度执行
关键代码:
48:128:spring-ai-alibaba-agent-framework/src/main/java/com/alibaba/cloud/ai/graph/agent/Agent.java
public abstract class Agent {
/** The agent's name. Must be a unique identifier within the graph. */
protected String name;
/**
* One line description about the agent's capability. The system can use this for
* decision-making when delegating control to different agents.
*/
protected String description;
protected CompileConfig compileConfig;
protected volatile CompiledGraph compiledGraph;
protected volatile StateGraph graph;
/**
* Protected constructor for initializing all base agent properties.
* @param name the unique name of the agent
* @param description the description of the agent's capability
*/
protected Agent(String name, String description) throws GraphStateException {
this.name = name;
this.description = description;
}
/**
* Default protected constructor for subclasses that need to initialize properties
* differently.
*/
protected Agent() {
// Allow subclasses to initialize properties through other means
}
/**
* Gets the agent's unique name.
* @return the unique name of the agent.
*/
public String name() {
return name;
}
/**
* Gets the one-line description of the agent's capability.
* @return the description of the agent.
*/
public String description() {
return description;
}
public StateGraph getGraph() {
if (this.graph == null) {
try {
this.graph = initGraph();
}
catch (GraphStateException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
return this.graph;
}
public synchronized CompiledGraph getAndCompileGraph() {
if (compiledGraph != null) {
return compiledGraph;
}
StateGraph graph = getGraph();
try {
if (this.compileConfig == null) {
this.compiledGraph = graph.compile();
}
else {
this.compiledGraph = graph.compile(this.compileConfig);
}
} catch (GraphStateException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return this.compiledGraph;
}关键方法:
initGraph():抽象方法,子类实现以创建状态图getAndCompileGraph():获取并编译 Graph(线程安全)invoke():同步调用 Agentstream():流式调用 Agent
BaseAgent - Agent 的抽象扩展
BaseAgent 继承自 Agent,提供了输入输出管理和节点转换能力。
核心职责:
- 管理输入输出 Schema 和类型
- 管理输出键和键策略
- 提供
asNode()方法将 Agent 转换为 Graph 节点
关键代码:
24:107:spring-ai-alibaba-agent-framework/src/main/java/com/alibaba/cloud/ai/graph/agent/BaseAgent.java
public abstract class BaseAgent extends Agent {
protected String inputSchema;
protected Type inputType;
protected String outputSchema;
protected Class<?> outputType;
/** The output key for the agent's result */
protected String outputKey;
protected KeyStrategy outputKeyStrategy;
protected boolean includeContents;
protected boolean returnReasoningContents;
public BaseAgent(String name, String description, boolean includeContents, boolean returnReasoningContents, String outputKey,
KeyStrategy outputKeyStrategy) throws GraphStateException {
super(name, description);
this.includeContents = includeContents;
this.returnReasoningContents = returnReasoningContents;
this.outputKey = outputKey;
this.outputKeyStrategy = outputKeyStrategy;
}
public abstract Node asNode(boolean includeContents, boolean returnReasoningContents, String outputKeyToParent);
public boolean isIncludeContents() {
return includeContents;
}
public String getOutputKey() {
return outputKey;
}
public void setOutputKey(String outputKey) {
this.outputKey = outputKey;
}
public KeyStrategy getOutputKeyStrategy() {
return outputKeyStrategy;
}
public void setOutputKeyStrategy(KeyStrategy outputKeyStrategy) {
this.outputKeyStrategy = outputKeyStrategy;
}
String getInputSchema() {
return inputSchema;
}
void setInputSchema(String inputSchema) {
this.inputSchema = inputSchema;
}
Type getInputType() {
return inputType;
}
void setInputType(Type inputType) {
this.inputType = inputType;
}
String getOutputSchema() {
return outputSchema;
}
void setOutputSchema(String outputSchema) {
this.outputSchema = outputSchema;
}
void setIncludeContents(boolean includeContents) {
this.includeContents = includeContents;
}
public boolean isReturnReasoningContents() {
return returnReasoningContents;
}
public void setReturnReasoningContents(boolean returnReasoningContents) {
this.returnReasoningContents = returnReasoningContents;
}
}关键方法:
asNode():抽象方法,将 Agent 转换为 Graph 节点,用于嵌套 Agent
ReactAgent - ReAct 模式实现
ReactAgent 是 BaseAgent 的具体实现,实现了经典的 ReAct(Reasoning + Acting)模式。
核心职责:
- 实现 ReAct 循环:推理 → 行动 → 观察
- 管理 LLM 节点和工具节点
- 支持 Hook 和 Interceptor 扩展
- 控制最大迭代次数
关键代码:
79:126:spring-ai-alibaba-agent-framework/src/main/java/com/alibaba/cloud/ai/graph/agent/ReactAgent.java
public class ReactAgent extends BaseAgent {
private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_ITERATIONS = 10;
private final AgentLlmNode llmNode;
private final AgentToolNode toolNode;
private CompiledGraph compiledGraph;
private List<Hook> hooks;
private List<ModelInterceptor> modelInterceptors;
private List<ToolInterceptor> toolInterceptors;
private int maxIterations;
private int iterations = 0;
private String instruction;
private Function<OverAllState, Boolean> shouldContinueFunc;
public ReactAgent(AgentLlmNode llmNode, AgentToolNode toolNode, CompileConfig compileConfig, Builder builder) throws GraphStateException {
super(builder.name, builder.description, builder.includeContents, builder.returnReasoningContents, builder.outputKey, builder.outputKeyStrategy);
this.instruction = builder.instruction;
this.llmNode = llmNode;
this.toolNode = toolNode;
this.compileConfig = compileConfig;
this.shouldContinueFunc = builder.shouldContinueFunc;
this.hooks = builder.hooks;
this.modelInterceptors = builder.modelInterceptors;
this.toolInterceptors = builder.toolInterceptors;
this.includeContents = builder.includeContents;
this.inputSchema = builder.inputSchema;
this.inputType = builder.inputType;
this.outputSchema = builder.outputSchema;
this.outputType = builder.outputType;
this.maxIterations = builder.maxIterations <= 0 ? DEFAULT_MAX_ITERATIONS : builder.maxIterations;
// Set interceptors to nodes
if (this.modelInterceptors != null && !this.modelInterceptors.isEmpty()) {
this.llmNode.setModelInterceptors(this.modelInterceptors);
}
if (this.toolInterceptors != null && !this.toolInterceptors.isEmpty()) {
this.toolNode.setToolInterceptors(this.toolInterceptors);
}
}Graph 初始化:
195:255:spring-ai-alibaba-agent-framework/src/main/java/com/alibaba/cloud/ai/graph/agent/ReactAgent.java
@Override
protected StateGraph initGraph() throws GraphStateException {
KeyStrategyFactory keyStrategyFactory = buildMessagesKeyStrategyFactory();
if (hooks == null) {
hooks = new ArrayList<>();
}
// Validate hook uniqueness
Set<String> hookNames = new HashSet<>();
for (Hook hook : hooks) {
if (!hookNames.add(hook.getName())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Duplicate hook instances found");
}
}
// Create graph
StateGraph graph = new StateGraph(name, keyStrategyFactory);
graph.addNode("model", node_async(this.llmNode));
graph.addNode("tool", node_async(this.toolNode));
// some hooks may need tools so they can do some initialization/cleanup on start/end of agent loop
setupToolsForHooks(hooks, toolNode);
// Add hook nodes
for (Hook hook : hooks) {
if (hook instanceof AgentHook agentHook) {
graph.addNode(hook.getName() + ".before", agentHook::beforeAgent);
graph.addNode(hook.getName() + ".after", agentHook::afterAgent);
} else if (hook instanceof ModelHook modelHook) {
graph.addNode(hook.getName() + ".beforeModel", modelHook::beforeModel);
if (modelHook instanceof HumanInTheLoopHook humanInTheLoopHook) {
graph.addNode(hook.getName() + ".afterModel", humanInTheLoopHook);
} else {
graph.addNode(hook.getName() + ".afterModel", modelHook::afterModel);
}
}
else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unsupported hook type: " + hook.getClass().getName());
}
}
// Categorize hooks by position
List<Hook> beforeAgentHooks = filterHooksByPosition(hooks, HookPosition.BEFORE_AGENT);
List<Hook> afterAgentHooks = filterHooksByPosition(hooks, HookPosition.AFTER_AGENT);
List<Hook> beforeModelHooks = filterHooksByPosition(hooks, HookPosition.BEFORE_MODEL);
List<Hook> afterModelHooks = filterHooksByPosition(hooks, HookPosition.AFTER_MODEL);
// Determine node flow
String entryNode = determineEntryNode(beforeAgentHooks, beforeModelHooks);
String loopEntryNode = determineLoopEntryNode(beforeModelHooks);
String loopExitNode = determineLoopExitNode(afterModelHooks);
String exitNode = determineExitNode(afterAgentHooks);
// Set up edges
graph.addEdge(START, entryNode);
setupHookEdges(graph, beforeAgentHooks, afterAgentHooks, beforeModelHooks, afterModelHooks,
entryNode, loopEntryNode, loopExitNode, exitNode, true, this);
return graph;
}关键类关系
以下 PlantUML 类图展示了 Agent 类层次结构:
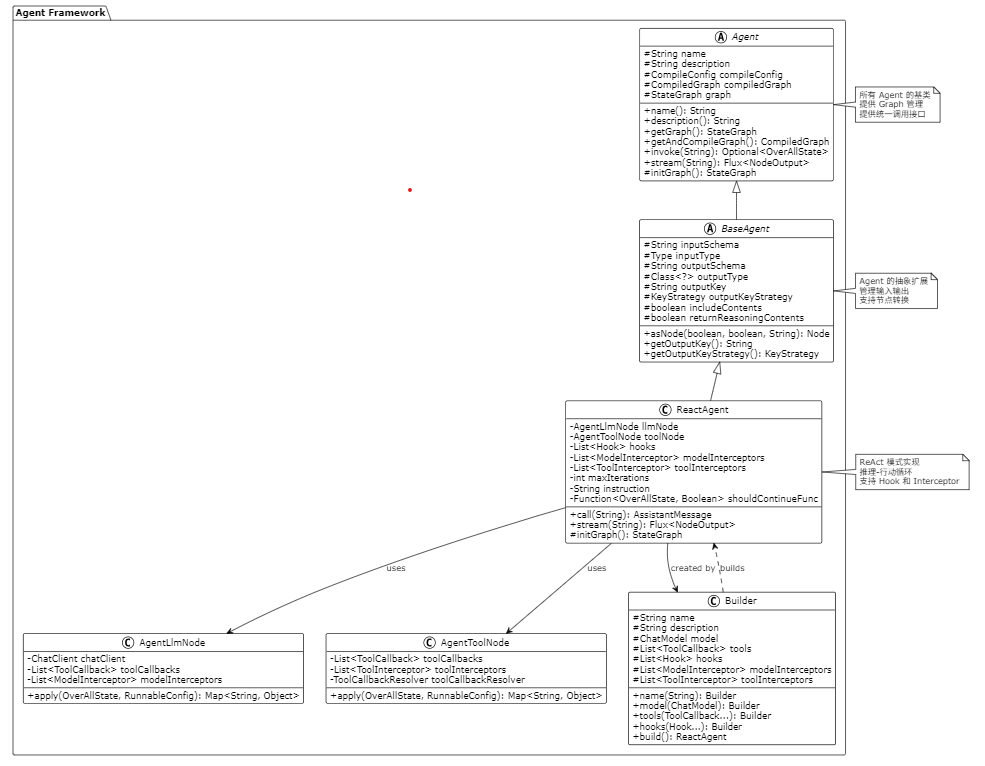
关键流程
以下 PlantUML 时序图展示了 ReactAgent 的执行流程:
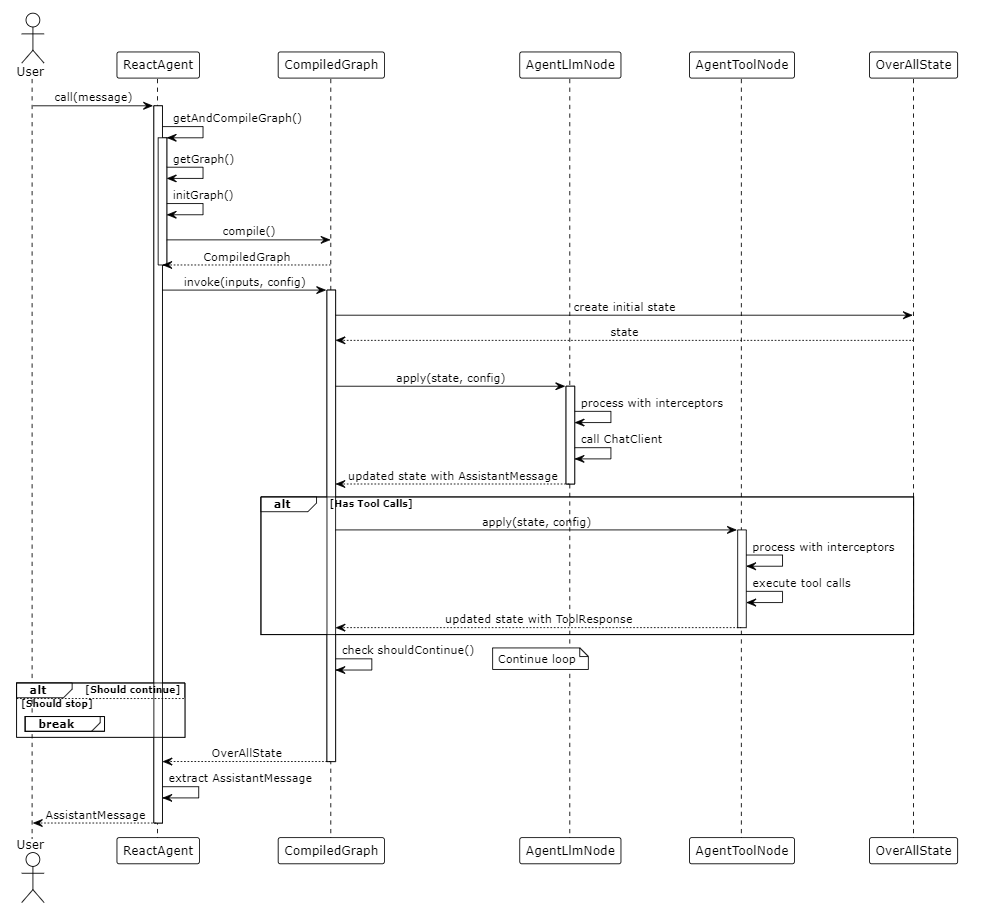
实现关键点说明
1. 模板方法模式
Agent 使用模板方法模式:
initGraph()是抽象方法,子类实现具体的图构建逻辑getAndCompileGraph()是模板方法,定义了 Graph 的获取和编译流程
2. Builder 模式
ReactAgent 使用 Builder 模式构建:
Builder类提供流畅的 API- 支持链式调用配置各种参数
- 在
build()时创建ReactAgent实例
3. ReAct 循环实现
ReactAgent 通过 Graph 实现 ReAct 循环:
- model 节点:LLM 推理,决定下一步行动
- tool 节点:执行工具调用
- 条件边:根据 LLM 输出决定是否继续循环
4. Hook 集成机制
Hook 被集成到 Graph 中:
AgentHook:在 Agent 执行前后插入节点ModelHook:在模型调用前后插入节点- 通过
HookPosition控制执行时机
5. Interceptor 链式调用
Interceptor 通过链式调用实现:
ModelInterceptor:拦截模型调用请求和响应ToolInterceptor:拦截工具调用请求和响应- 支持请求修改和响应处理
6. 状态管理
使用 OverAllState 管理状态:
messages键存储对话历史input键存储用户输入- 支持键策略控制状态更新方式
总结说明
核心设计理念
- 分层抽象:Agent → BaseAgent → ReactAgent 三层设计,职责清晰
- ReAct 模式:通过 Graph 实现推理-行动循环
- 可扩展性:通过 Hook 和 Interceptor 机制支持扩展
- 状态驱动:基于状态图的状态驱动执行
关键优势
- 灵活性:支持多种调用方式(同步、异步、流式)
- 可扩展性:Hook 和 Interceptor 机制支持功能扩展
- 可组合性 :通过
asNode()方法支持 Agent 嵌套 - 类型安全:支持输入输出 Schema 和类型定义
使用场景
- 单 Agent 应用:直接使用 ReactAgent 构建单 Agent 应用
- 多 Agent 编排 :通过
asNode()方法将 ReactAgent 转换为节点,用于 FlowAgent 编排 - 嵌套 Agent:支持 Agent 嵌套,实现复杂的 Agent 层次结构
关键方法说明
Agent 基类方法
initGraph():抽象方法,子类必须实现,用于创建状态图getAndCompileGraph():获取并编译 Graph,使用双重检查锁定确保线程安全invoke():同步调用 Agent,返回Optional<OverAllState>stream():流式调用 Agent,返回Flux<NodeOutput>
BaseAgent 方法
asNode():抽象方法,将 Agent 转换为 Graph 节点,用于嵌套场景getOutputKey():获取输出键,用于从状态中提取结果getOutputKeyStrategy():获取输出键策略,控制状态更新方式
ReactAgent 方法
call():同步调用,返回AssistantMessageinitGraph():创建 ReAct 循环的状态图setupToolsForHooks():为 Hook 注入工具filterHooksByPosition():根据位置过滤 Hook
Agent Framework 通过这种层次化的设计,实现了灵活、可扩展的 Agent 开发框架,为构建智能应用提供了坚实的基础。