0 序
- 笔者在项目中使用/运维 InfluxDB 和 OpenGemini 时序数据库已有些年头了,虽然对其数据库源码研究得还不算特别精深,但仍有必要沉淀一二,总结一二了。
此篇主要针对 influxdb v1。如无特殊说明,则默认基于 influxdb v1.7.5 进行源码、原理和架构的分析。
可对标 opengemini v1.2.0(亲测,但不完全兼容)。
- 持续完善中。
1 概述:InfluxDB
InfluxDB
- InfluxDB 是一个用Go语言编写的、开源的、分布式的、(事件、指标)、时间序列(time series database, TSDB)数据库,无需外部依赖;主要处理较高的写入和查询负载,用来存放监控数据。
- 主要用作大量时间戳数据的任何用例的后备存储,例如:DevOps 监控、应用程序指标、Lot传感器数据和实时分析。
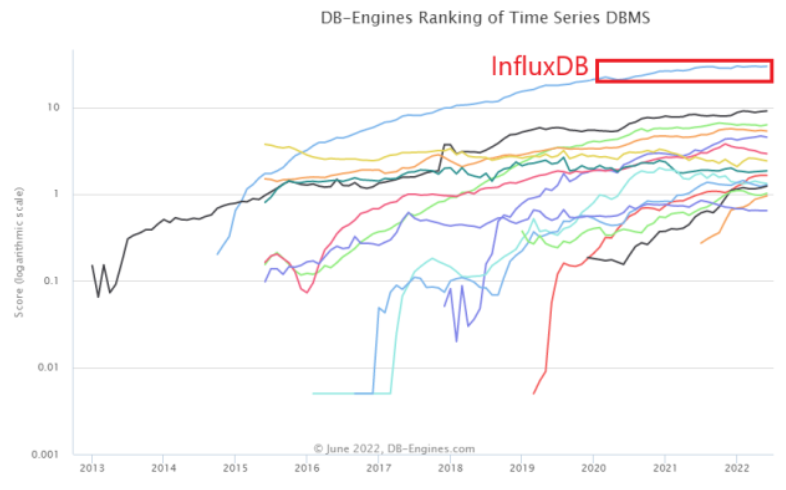
- 客观来看,目前InfluxDB还是事实上的业界标准,其也一直在
DB-Engines时序型数据库排行榜上排名第一。- InfluxDB的母公司是InfluxData,公开信息显示其成立于2013年,其目标是希望解决时间序列数据高性能的存储和查询问题。
发展历程
- 亮点
- 存储引擎: 基于LevelDB => 默认 RocksDB => 放弃难以推进的 Facebook
RocksDB/ BlotDB 引擎 => 自研TSM存储引擎- 自研 TSI 索引
- 自研 函数式语言 Flux
- ...
-
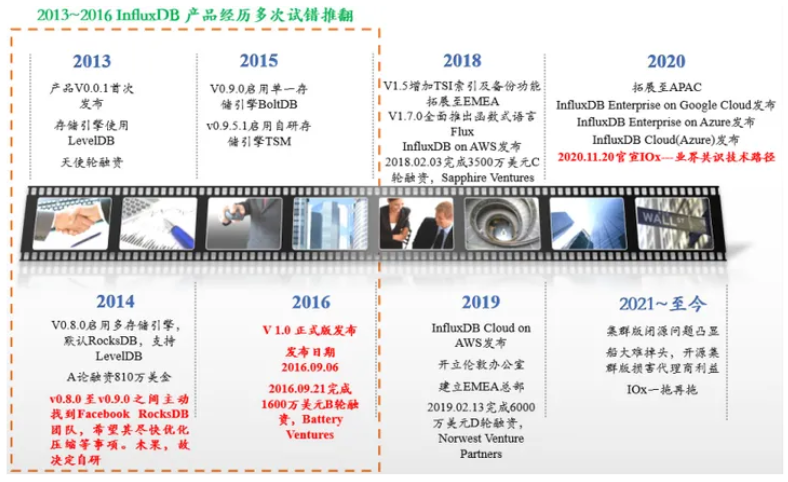
2013年,InfluxDB产品首次发布了V0.0.1版本,客观来讲这更多的还是个非常初级的产品,其存储引擎最开始也是选择了LevelDB,同年其完成了天使轮融资。由于产品的问题,2014年其发布的V0.8.0版本,启用了多存储引擎,默认RocksDB,同时也支持LevelDB。
-
在2014到2015年间(V0.8.0 ~ V0.9.0),InfluxDB曾主动找到Facebook RocksDB团队,希望其尽快优化压缩等事项,但一直未果。所以在2015年,InfluxDB在V0.9.0启用单一存储引擎BoltDB的版本发布后,其V0.9.5.1启用自研存储引擎TSM。直到2016年的09月06日InfluxDB的V 1.0 正式版发布才发布。我们可以看到,作为行业头部时序数据库厂商的InfluxDB在13至16年持续试错,历经3年多,几经周折,最终才找到了自己的方向。也正是在其1.0正式版发布之后,InfluxDB于2016年09月21日完成了1600万美元的B轮融资。
-
时间来到2018年,InfluxDB拓展至EMEA市场,并发布了InfluxDB on AWS,我们可以看到在产品相对稳定后,InfluDB的扩张脚步加快,2018年02月03其也完成3500万美元的C轮融资。2019年其开立了伦敦办公室并建立EMEA总部,资本上完成了6000万美元的D轮融资。2020年InfluxDB拓展至APAC市场,也发布了Azure、Google上的云版本。我们可以看到18年~20年是InfluxDB的高速发展期。但与此同时,其也并非没有隐忧,面对时间线膨胀问题,面对由于自己分布式闭源而造成的用户流失问题等,其目前的版本仍有显著得不足,且有些积重难返。因此2020年11月20日,InfluxDB官宣自己要研发新产品IOx,用以解决其目前产品所存在得问题,但目前经过一年半左右的研发,产品进展不容乐观,一拖再拖。
-
对中国
TSDB数据库厂商的启示。
首先,我觉得大家还是需要客观承认InfluxDB目前是业内的老大,而且其之前在底层存储选型上的多次试错,客观上也帮后来者踩了很多坑,其对于产品的思考是值得我们学习借鉴的。
其次,对于商业开源厂商如何选择商业模式的问题,还需谨慎。因为在Feature-Based模式下,哪些功能开源哪些闭源,对客户流失程度的影响并不好判断那么准确,正如InfluxDB发现问题时,其又因为代理商以及股东等各种利益问题,而造成企业并不好掉头。
最后,我们也应该看到机会,实际上InfluxDB自己也在不停的推翻自己,自己做变革。面对物联网时代时间线膨胀问题,其再一次启程出发要做新产品IOx,而伴随着美国通胀问题的严重,其人员流失等问题也造成了IOx进度不如人意,这正是中国TSDB厂商的机会,在面向时代巨变的今天,大家还是站在同一起跑线上,我们完全可以吸收借鉴他们之前的经验和教训,实现弯道超车。
主要特色
- 专为时间序列数据 量身打造的高性能数据存储。
- TSM引擎提供数据高速读写和压缩等功能。
- 基于时间序列 ,支持
min,max,sum,count,mean,median等系列函数,方便统计
- 简单、高性能的查询/写入 HTTP API。
原生的HTTP支持,内置HTTP API
- 针对时序数据,量身打造类SQL的查询语言,轻松查询聚合数据。
富有强大的SQL语句,轻松查询聚合数据。
-
允许对tag建索引,实现快速有效的查询。
-
数据保留策略(Retention policies)能够有效地使旧数据自动失效。
有效地自动处理掉过期数据。
- 外部依赖少:用
GO语言编写,可以编译一个没有外部依赖项的二进制文件。 - 无结构(无模式):可以是任意数量的列,表字段可自由扩展(普通field)
绝大部分数据库不支持此特性。
- 可拓展的
- 插件支持其他数据摄取协议,例如:Graphite、collected 和 OpenTSDB。
- 连续查询 会自动计算聚合数据 ,从而使频繁查询更加有效。
- 可度量性:你可以实时对大量数据进行计算
- 基于事件:它支持任意的事件数据
- 自带管理界面,方便使用
局限性
- 不支持
UNION,JOIN,HAVING等SQL语法
客户端
Java
依赖坐标
- Maven
xml
<!-- influxdb-java
https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb-java/blob/influxdb-java-2.22/src/main/java/org/influxdb/dto/Point.java#concatenatedFields (可做的写入性能优化: 针对 Double / Float / BigDecimal,取消 format to String 的方式)
{@link com.xxx.sink.MyInfluxDBSinkHistory.invoke }
↘ {@link com.xxx.datasource.InfluxDbConnection.insertBatchAfterHealthCheck }
↘ {@link com.xxx.datasource.InfluxDbConnection.insertBatch(java.util.Collection<org.influxdb.dto.Point>) }
↘ {@link org.influxdb.InfluxDB.write(org.influxdb.dto.BatchPoints) }
↘ {@link org.influxdb.impl.InfluxDBImpl.write(org.influxdb.dto.BatchPoints) }
↘ {@link org.influxdb.dto.BatchPoints.lineProtocol }
↘ {@link org.influxdb.dto.Point.lineProtocol(java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit) }
↘ {@link org.influxdb.dto.Point.concatenatedFields }
-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.influxdb</groupId>
<artifactId>influxdb-java</artifactId>
<version>2.22</version>
</dependency>2 工作原理与架构剖析
核心概念
InfluxDB vs 传统数据库
| InfluxDB | 传统数据库概念 | 区别 |
|---|---|---|
| database | database(数据库) | |
| measurement | table(数据表) | 最明显的区别: 无单独的创建measurement的方法,直接新增一条数据时,若measurement不存在,则直接创建并插入一条数据 |
| point := timestamp + tag + field | record(记录;行,表里面的一行数据) | 在influxDB中,表示: 每个表中,某个时刻,满足某个条件的filed数据(简单来说就是 timestamp + tag + filed)的组成一个point |
Database
- 1个数据库,含多个 保留策略、measurement。
Retention Policy/RP
- Retention Policy(数据保留策略):用以自动处理过期数据的存储策略。
- influxdb 每个新建的数据库都会有一个对应的数据保留策略(retention policy),该策略用来管理数据库中时间过期的数据 ;如果没有指定策略,数据库会有默认的保留策略
autogen。
最初
autogen保留策略的 shargGroupDuration 为默认值7day,duration=0h/永久。
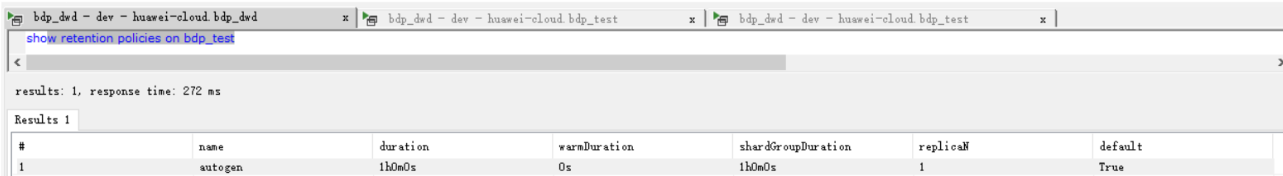
后来
autogen保留策略的 shardGroupDuration 为1h,duration=1h
Measurement (table)
- 1个
Measurement(表) 属于 1个Retention Policy(保留策略)对应的Database(数据库)
Shards : 分片[time + measurement]
shard是influxdb存储引擎TSM的具体实现,负责数据的编码存储、读写服务等。
Shard与TSM文件
shard包含实际的编码和压缩数据,并由磁盘上的TSM(Time Sort Merge)文件表示。
- 将infuxdb中时间序列化的数据按照时间的先后顺序 存入到
shard中,每个shard都负责influxdb中一部分的数据存储工作,并以tsm文件 的表现形式存储在物理磁盘 上;每个存放了数据的shard都属于唯一的、一个shard group(即 多个shard可能存在于单个shard group中)。TSM Tree是专门为influxdb构建的数据存储格式。与现有的
B+ tree或LSM tree实现相比,TSM tree具有更好的压缩和更高的读写吞吐量。
- 每个
shard包含一组特定的series。
给定
shard group中的给定series上的所有Point将存储在磁盘上的相同shard(TSM文件)中。
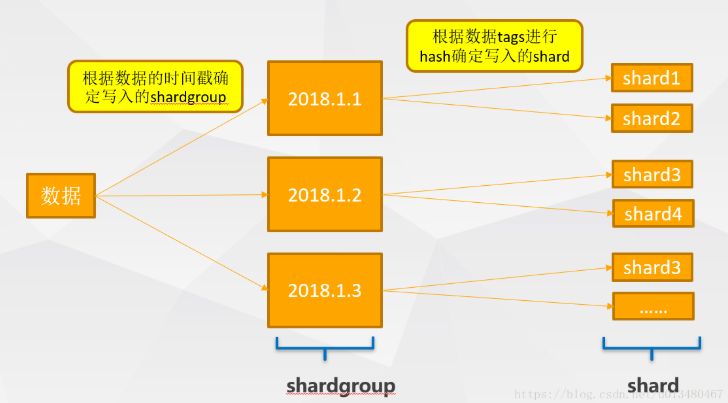
shard主要由4部分组成: Cache、Wal、Tsm file、Compactor。
shard group (分片组)
- 数据存储在
shardGroup的时间跨度。shardGroup是influxdb的一个逻辑存储结构、逻辑容器,其下包含多个shard。
- 每一个shard group都有一个不重叠的时间跨度,数据根据不同的时间跨度存储在不同的shard group中。
-
数据保留策略提供了一个简单高效的方法来清除influxdb数据库中过期数据 ,一旦数据超过过期时间,数据会自动从influxdb中清除,而过期数据清除的时间单位 以"
shard group duration"为单位。 -
shard group负责指定时间跨度的数据存储,这个shard时间跨度(shard duration)就由上文提到的创建RP时指定。如果没有指定,系统将通过RP的数据保留时间来计算。
- 不同
shard group的时间跨度不会重叠。shard group实现了数据按时间分区,这样做的目的是什么?
- 一定程度上缓解数据写入热点问题
- 加快数据删除的效率
- 将数据按照时间分割成小的粒度会使得数据过期实现非常简单,InfluxDB中过期数据删除的执行粒度 就是
Shard Group,系统会对每一个Shard Group判断是否过期,而不是一条一条记录判断。

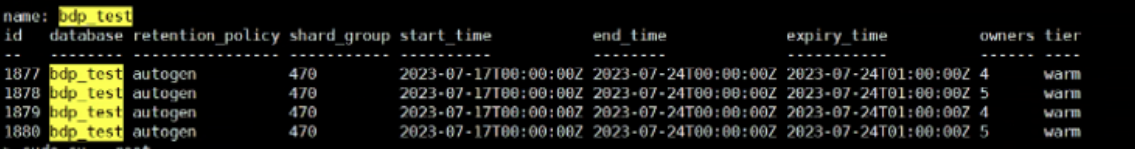
图: 仅保留1个月数据的保留策略,(Retention Policy) Duration != Shard Group Duration
shard磁盘存储统计分析
- 基于华为云 GaussDB for INFLUXDB (基于 OpenGemini)的shard统计:
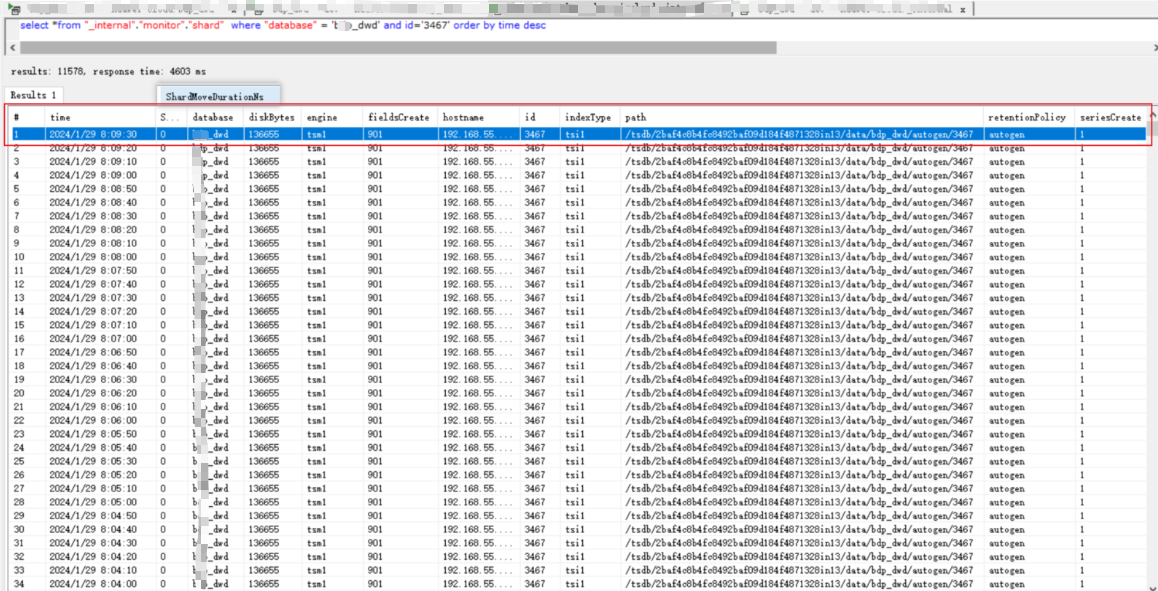
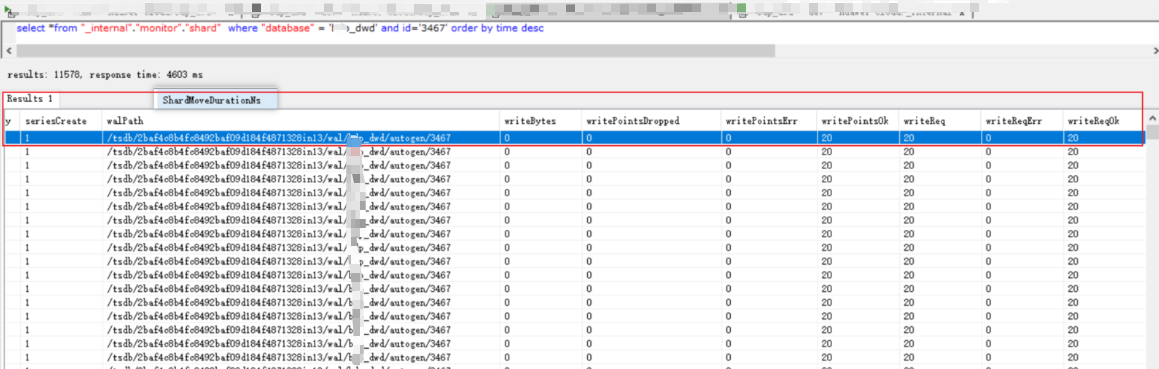
sql
select
*
from "_internal"."monitor"."shard"
where "database" = 'xxx_dwd' and id='3467'
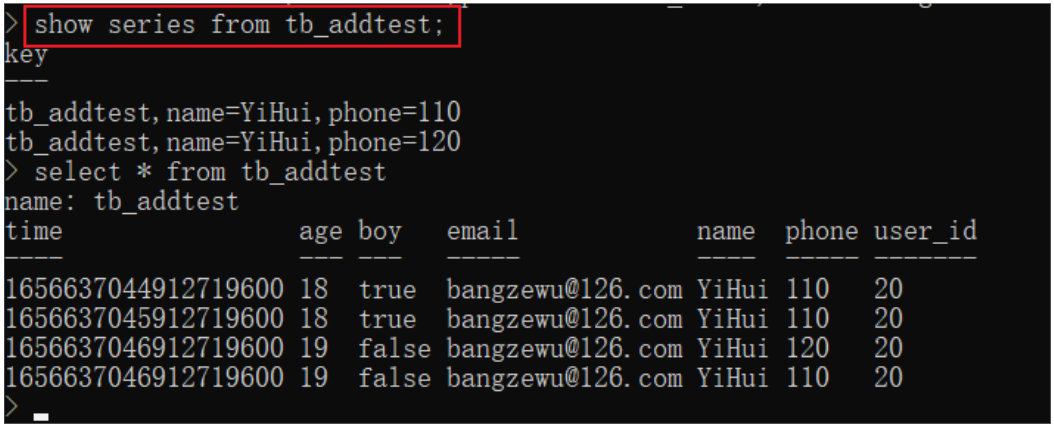
order by time desc Series := tag column sets
-
Series: retentionPolicy(RP)、measurement、tag set(tag key +tag value)的唯一组合。
-
Series的数量 :=
RP*measurement*tagSet -
Series:所有在数据库的数据都是通过图表来展示,而这个series表示这个表里面的数据,可以在图表上画成几条线:通过tags排列组合算出来。
- 一般来讲,监控对象稳定后,
Series基本是固定的。
Influxdb将
Series放在内存 作为索引,加快了数据查询 ,这使得Series的数量不能太大;否则,Influxdb的内存 会被撑爆;默认单个database内Series限制为<100W个。
Point : 记录/record
- Point:时间点数据,数据库中的一行数据。其由 时间戳(time)、标签(tags)、普通字段(field)组成,如下图所示:
| point属性 | 传统数据库概念 |
|---|---|
| time(时间戳,单位:ns) | 每个数据记录时间,自动生成,是数据库的主索引(传统数据库的主键) 每个记录都必然有这个属性,没有显示添加时,默认给一个 |
| field | 各种记录值(没有索引的属性) |
| tags | 各种有索引的属性 |
time/时间列
概念解释
- 每个Point(记录)都必然有这个属性(time),没有显示添加时,默认给一个。
UTC时间
- Influxdb采用UTC存储时间。
UTC时间就是世界标准时间 。UTC 时间戳就是以 1970-01-01T00:00:00 为起点的毫秒数 ,不考虑闰秒。时间戳不分时区,在任意时间点,不同时区的 UTC 时间戳是相同的。
-
时间戳 0 对应的时刻是:Thu Jan 01 1970 08:00:00 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)。
-
时间戳在转换为日期时,会根据本地时区,转换为不同的日期值。
-
1970年之前的日期对应的时间戳为负数,比如 Mon Jan 01 1900 08:00:00 GMT+0805 (中国标准时间) 对应的时间戳为 -2208989143000。
物理学的时间换算
如下概念与物理学概念有关,而INFLUXDB无关:
- 1世纪=100年(year)
- 1年(year)=12月(month)
- 1月(month)=30天(day)=4周(week)
- 1周(week)=7天(day)
- 1天(day)=24小时(hour)
- 1小时(hour)=60分钟(min)
- 1分钟(min)=60秒钟(s, second)
- 1秒钟(s)=1000毫秒(ms, millisecond)
- 1毫秒(ms)=1000微秒(μs, microseconds)
- 1微秒(μs)=1000纳秒(ns, nanosecond)
- 1纳秒(ns)=1000皮秒(ps, picosecond)
时间精度管理
- InfluxDB 作为时间序列数据库,在处理时间数据时,有特殊的机制和规范,在使用时需要注意。
precision[ns,u,ms,s,m,h]
- 在写入和读取 influxdb 中的数据时,时间戳默认单位是纳秒 ,可以通过 precision 参数来指定为其他格式,比如 rfc3339 (YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.nnnnnnnnnZ), h (小时), m (分钟), s (秒), ms (毫秒), u (微妙), ns (纳秒)。
配置时间精度的方式
- 案例**** : CURL写入Point时,通过 precision 指定时间戳单位
使用 curl 来请求写入时,通过 precision 指定时间戳单位:
shell
curl -i -XPOST "http://localhost:8086/write?db=mydb&precision=s" --data-binary 'mymeas,mytag=1 myfield=90 1463683075' 这样,命令后面的时间戳数据 1463683075,会按照秒来解析。
如果不指定precision,默认会按照纳秒来解析,就需要将 1463683075 转换为 1463683075000000000
- 案例 ****: 命令行模式中指定
precision
shell
$ influx -precision ms 这样,所有在该命令窗口中执行的写入和查询语句对应的时间戳单位,都变为毫秒。
- 案例 **:
-execute命令中指定precision
shell
$ influx -execute 'SELECT \* FROM "h2o_feet" LIMIT 3' -database="NOAA_water_database" -precision=rfc3339
name: h2o_feet
--------------
time level description location water_level
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z below 3 feet santa_monica 2.064
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z between 6 and 9 feet coyote_creek 8.12
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z between 6 and 9 feet coyote_creek 8.005 epoch_time、duration
- 在 InfluxDB Select 语句中, epoch 值就是时间戳,只不过 epoch 有更丰富的语义,使用起来更方便灵活。 now() : 本地服务器对应的纳秒时间戳。
Epoch
- epoch 0 (1970-01-01T00:00:00Z)常被用来表示无意义的时间戳,也就是 null。比如,当请求的结果中不包含时间戳时,time 值就会置为 0:
shell
> SELECT MEAN("index") FROM "h2o_quality" GROUP BY location,randtag
name: h2o_quality
tags: location=coyote_creek, randtag=1
time mean
---- ----
1970-01-01T00:00:00Z 50.69033760186263
name: h2o_quality
tags: location=coyote_creek, randtag=2
time mean
---- ----
1970-01-01T00:00:00Z 49.661867544220485
name: h2o_quality
tags: location=coyote_creek, randtag=3
time mean
---- ----
1970-01-01T00:00:00Z 49.360939907550076
name: h2o_quality
tags: location=santa_monica, randtag=1
time mean
---- ----
1970-01-01T00:00:00Z 49.132712456344585 Duration
- 概念解释
duration = integer + duration unit: 用来指定一段时间长度。
duration units = "ns" | "u" | "µ" | "ms" | "s" | "m" | "h" | "d" | "w" .
InfluxDB支持的Duration时间单位
| 单位 | 解释 | 样例值 |
|---|---|---|
| w | 周 | 4w |
| d | 天/日 | 7d |
| h | 小时 | 7200h |
| m | 分钟 | 60m |
| s | 秒 | 1439856720s |
| ms | 毫秒 | 1726799024823ms |
| u/µ | 微秒 | 1726799024823000u |
| ns | 纳秒 | 1531992939634316937ns 1439856720000000000 (默认单位:纳秒) |
- 使用场景
场景1:Retention Policy
在 InfluxDB 中,配置数据库的 Retention Policy 中会用到 duration,比如:
sql
-- Create a retention policy.
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "10m.events" ON "somedb" DURATION 60m **REPLICATION 2
-- Create a retention policy and set it as the DEFAULT.
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "10m.events" ON "somedb" DURATION 60m REPLICATION 2 DEFAULT
-- Create a retention policy and specify the shard group duration.
CREATE RETENTION POLICY "10m.events" ON "somedb" DURATION 60m REPLICATION 2 SHARD DURATION 30m场景2:Select语句
在 select 语句中也会用到 duration:
sql
SELECT mean("value") FROM "cpu" GROUP BY region, time(1d) fill(0) tz('America/Chicago')
SELECT MEAN(value) FROM cpu GROUP BY time(10m)
SELECT "water_level" FROM "h2o_feet" WHERE "location" = 'santa_monica' WHERE time > 24043524m - 6m epoch_time
epoch time就是 UTC 时间戳,默认单位为纳秒,可以通过 epoch_time 值后面跟 duration unit 来指定 precision。
epoch_time 支持基本的算术运算,比如 + 或 -,特别需要注意的是,influxQL 要求运算符与 epoch_time 之间要有空格。
time format 为 rfc3339:
sql
> SELECT "water_level" FROM "h2o_feet" WHERE "location" = 'santa_monica' AND time >= '2015-08-18T00:00:00.000000000Z' AND time <= '2015-08-18T00:12:00Z'
name: h2o_feet
time water_level
---- -----------
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 2.064
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z 2.116
2015-08-18T00:12:00Z 2.028 - 没有指定 duration unit时,默认为纳秒:
sql
> SELECT "water_level" FROM "h2o_feet" WHERE "location" = 'santa_monica' AND time >= 1439856000000000000 AND time <= 1439856720000000000
name: h2o_feet
time water_level
---- -----------
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 2.064
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z 2.116
2015-08-18T00:12:00Z 2.028 通过添加 duration uni t 来指定 precision 为秒:
sql
> SELECT "water_level" FROM "h2o_feet" WHERE "location" = 'santa_monica' AND time >= 1439856000s AND time <= 1439856720s
name: h2o_feet
time water_level
---- -----------
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 2.064
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z 2.116
2015-08-18T00:12:00Z 2.028 对 epoch_time 进行简单的运算:
sql
> SELECT "water_level" FROM "h2o_feet" WHERE time > 24043524m - 6m
name: h2o_feet
time water_level
---- -----------
2015-09-18T21:24:00Z 5.013
2015-09-18T21:30:00Z 5.01 使用
now()函数来指定相对时间:
sql
> SELECT "water_level" FROM "h2o_feet" WHERE time > now() - 1h 参考文献
tag(标签)
- tag(标签): kv结构,在database中,
tag + measurement一起构建索引,参与索引创建。
因此,适合作为查询的过滤条件
- tag的数据量不要太多,最好能有典型的辨别性(和mysql的建立索引的原则差不多)
- tag value只能为
String类型 tags是可选 的,在measurement中不设置 tag也是可以的,但是强烈建议你用上它,因为tag是有索引的,tags相当于SQL中的有索引的列。
field (普通字段/列)
- field,存储数据: kv结构
数据类型
-
支持的数据类型 共计4种: long(integer), String, boolean, float
-
在influxdb中,字段必须存在。
注意,字段是没有索引 的。如果使用字段作为查询条件 ,会扫描符合查询条件的所有字段值,性能不及tag。类比一下,fields相当于SQL中没有索引的列。
类型转换
-
SELECT子句支持使用语法**::**指定field的类型和基本的类型转换操作。 -
语法
sql
SELECT _clause <field_key>**::<type>** FROM_clause 语法描述
type可以是float ,integer ,string 或boolean。在大多数情况下,如果field_key 没有存储指定type 的数据,那么TSDB For InfluxDB®将不会返回任何数据。
请参见 转换 获得更多相关信息。
- 示例
sql
> SELECT "water_level"::float FROM "h2o_feet" LIMIT 4
name: h2o_feet
--------------
time water_level
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 8.12
2015-08-18T00:00:00Z 2.064
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z 8.005
2015-08-18T00:06:00Z 2.116该查询返回field key water_level为浮点型的数据。
- 类型转换
语法::允许用户在查询中执行基本的类型转换。目前,Aliyun TSDB For InfluxDB(2.0.3)®仅支持field value做如下转换:
| Integer/Long --> float/Double |
|---|
| Float/Double --> integer/Long |
其他的转换情况,只能在查询后通过程序进行转换了。
例如:将浮点型的field value转换成字符串(不支持该功能)
sql
> SELECT "water_level"::string FROM "h2o_feet" LIMIT 4因为不支持将浮点型的field value转换成字符串,所以该查询不返回任何数据。
特色函数
- influxdb函数分为聚合函数 ,选择函数 ,转换函数 ,预测函数等。
除了与普通数据库一样提供了基本操作函数外,还提供了一些特色函数以方便数据统计计算,下面会一一介绍其中一些常用的特色函数。
- 聚合函数:FILL(), INTEGRAL(),SPREAD(), STDDEV(),MEAN(), MEDIAN()等。
- 选择函数: SAMPLE(), PERCENTILE(), FIRST(), LAST(), TOP(), BOTTOM()等。
- 转换函数: DERIVATIVE(), DIFFERENCE()等。
- 预测函数:HOLT_WINTERS()。
关系辨析: (Retention Policy) Duration != Shard Group Duration , 数据删除场景
- 分片组的数据保留单位时长,最小为1h(retention policy duration must be at least 1h0m0s)。
- 如果设置为0,数据永久保存(官方默认 RP ),否则过期清理。
- InfluxDB没有提供直接删除 和更新数据 的接口,数据只能通过
RP进行删除
- 此举还可加快数据按时间维度查找的效率
- 实现了将数据按照时间分区 的特性。将时序数据按照时间分区是时序数据库一个非常重要的特性,基本上所有时序数据查询操作都会带有时间的过滤条件,比如查询最近一小时或最近一天,数据分区可以有效根据时间维度选择部分目标分区,淘汰部分分区.
关系辨析: Shard = Cache + Wal + Tsm file + Compactor
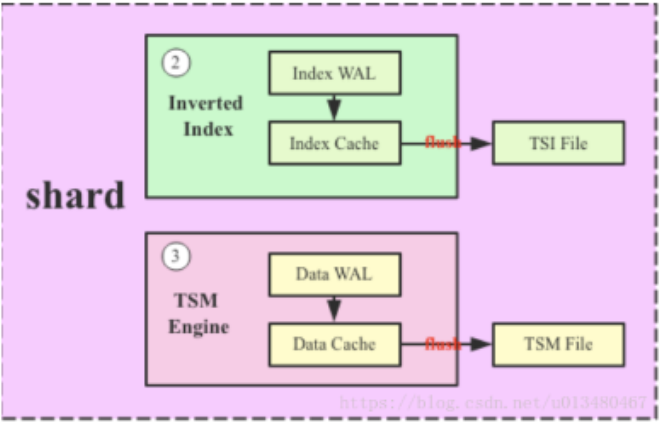
shard主要由4部分组成: Cache、Wal、Tsm file、Compactor。
关系辨析:retention policy(保留策略)、shard(分片)、shard group(分片组)
- retention policy duration must be greater than the shard duration
- 译文:在一个retention policy (
RP)中,如果指定保留时间(duration )为24小时,每个shard duration 为1小时,即每个shard的时间跨度为1个小时,那么总共有24个时间跨度为1小时的shard,在触发数据的 RP 后,删除最早的时间跨度的shard。则: shard group 中对应的就会存在24个shard,每次到达过期时间,就会删除最早的shard,并生成一个新的shard。
- 解释:数据保留策略 提供了一个简单高效 的方法用来清除InfluxDB数据库中的过期数据,一旦
shard数据超过过期时间,数据会自动从InfluxDB中清除,而过期数据清除的时间单位以shard group的duration为单位。
关系辨析: shard vs. measurement
在 InfluxDB 中,shard 和 measurement 是两个重要的概念。
Shard是 InfluxDB 中用于存储数据的最小单元。
每个 shard 都是一个独立的文件,存储一个时间范围内的时序数据。InfluxDB 会根据数据的写入时间自动将数据分配到不同的 shard 中。
Measurement是 InfluxDB 中用于组织数据的概念,类比关系型数据库中的【表】。
它可以理解为一个指标或事件的类型。
例如,CPU 使用率、内存使用率、网络流量等都是不同的 measurement。
- 数量关系
- 一个 shard 可以存储多个 measurement 的数据。
- 一个 measurement 的数据可以分散存储在多个 shard 中。
- 具体来说,InfluxDB 是根据以下规则将**Point(时间点数据)**分配到 shard 中的:
- 根据数据的写入时间。InfluxDB 会根据数据的写入时间戳将数据分配到不同的 shard 中。每个 shard 存储一个时间范围内的时序数据。
- 根据数据所属的 measurement。InfluxDB 会根据数据的 measurement 将数据分配到不同的 shard 中。这样可以确保相同 measurement 的数据都存储在同一个 shard 中,以便于查询。
- Shard 和 measurement 的作用
- Shard 可以提高 InfluxDB 的存储性能和 scalability。通过将数据分散存储在多个 shard 中,InfluxDB 可以并行处理数据写入和查询请求,从而提高性能。
- Measurement 可以帮助用户更好地组织和管理数据。通过将数据按 measurement 分类,用户可以更轻松地找到所需的数据。
- 一些有关 InfluxDB 中 shard 和 measurement 的最佳实践:
- 尽量使用不同的
measurement来存储不同的指标或事件类型。这样可以提高数据的组织性和可管理性。- 对于写入量较大的 measurement ,可以考虑使用更大的
shard size。这样可以减少 shard 的数量,提高查询性能。- 定期清理过期的 shard。这样可以释放存储空间,提高 InfluxDB 的性能。
关系辨析: shard vs. shard group
-
将InfluxDB中时间序列化的数据按照时间的先后顺序存入到shard中,每个shard中都负责InfluxDB中一部分的数据存储工作,并以tsm文件的表现形式存储在物理磁盘上,每个存放了数据的shard都属于一个shard group。
-
shard group可以理解为存放shard的容器 ,所有的shard在逻辑上都属于这个shard group,每个shard group中的shard都有一个对应的时间跨度 和过期时间 ,每一个shard group都有一个默认的时间跨度,叫做shard group duration。
架构设计
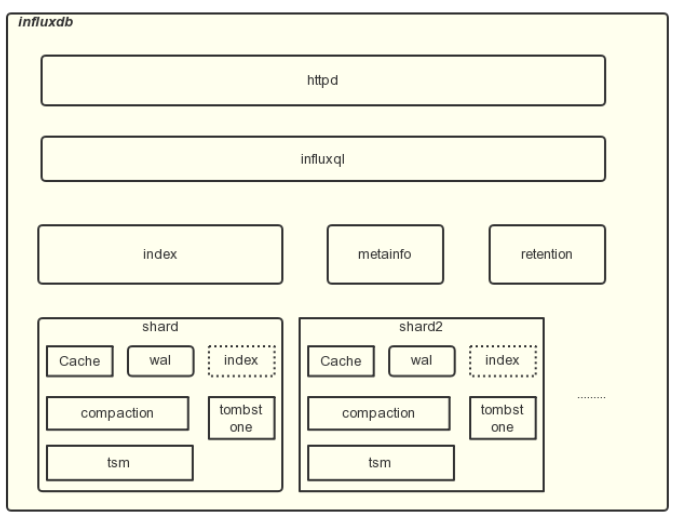
-
httpd:influxdb内部所有的api请求均通过httpd接口对外提供服务。 -
influxql:influxdb内部实现了一个sql parser 模块,在数据读取写入过程中会对输入的sql进行解析。 -
metainfo:metainfo记录了influxdb所有的元信息,并且dump到某一个file中,元信息包括database name, retention policy, shard groups, user等。 -
index:tags的索引信息 -
retention:自动清理过期数据功能。 -
tsdb:influxdb中最核心的模块:存储引擎层
influxdb引擎层的思路基本类似于
lsm tree,influxdb将其称之为tsm tree, lsm tree的介绍文章非常的多,这里不详细进行描述。
shard
- influxdb将数据按照时间分区存储 ,每个分区称之为
shard, 每个shard有各自的存储引擎存储数据,且相互独立。作者在官方文档注明这么做的原因是为了快速删除过期数据,拆分为shard后删除数据只需要直接清理shard所有的数据文件即可。
- 删除过期数据是时序数据库一个比较重要的的特性,如性能数据只保持最近一个月或者几个月的数据的需求。
架构设计和数据布局
每个 InfluxDB 用例都是独一无二的,您的 schema 也反映了这种独特性。通常,为查询设计的架构可以简化查询并提高查询性能。我们为大多数用例推荐以下设计指南:
数据存储位置(标签或字段)
-
您的查询应指导您在 标签(Tag) 中存储哪些数据,以及在 字段(Field) 中存储哪些数据
-
将常用的查询和分组(group() 或 GROUP BY)元数据存储在标签中。
-
如果每个数据点包含不同的值,则将数据存储在字段中。
-
将数值存储为字段(标签值 仅支持字符串值)。
避免过多的序列
- InfluxDB 为以下数据元素建立索引以加速读取
- measurement(测量)
- 标签
- 标签值 已建立索引,而 字段值 未建立索引。
这意味着按标签 查询比按字段 查询性能更高。但是,当创建过多的索引时,写入和读取都可能开始减慢。
- 每个唯一的索引数据元素集 形成一个序列键。
- 标签(Tag) 包含高度可变的信息,如唯一 ID、哈希和随机字符串,会导致大量的【序列(series)】,也称为**【高 序列基数】**。
- 高序列基数 是许多数据库工作负载中高内存使用率的主要驱动因素。
因此,为了减少内存消耗,请考虑将高基数值存储在字段值中,而不是标签或字段键中。
使用推荐的命名约定
- 在命名标签和字段键时,请使用以下约定
- 避免在标签和字段键中使用保留关键字
- 避免相同的标签和字段名称
- 避免在 measurement(测量)和键中编码数据
- 避免在一个标签中包含多个信息
避免在标签和字段键中使用保留关键字
并非必需,但避免在标签和字段键中使用保留关键字可以简化编写查询的过程,因为您不必将键括在双引号中。请参阅 InfluxQL 和 Flux 关键字 以避免使用。
此外,如果标签或字段键包含[A-z,_]以外的字符,则必须在 InfluxQL 中将其括在双引号中,或在 Flux 中使用 方括号表示法。
避免标签和字段使用相同的名称
- 避免对标签和字段键使用相同的名称。这通常会导致查询数据时出现意外行为。
如果您不小心为标签和字段添加了相同的名称,请参阅 常见问题解答,了解有关如何可预测地查询数据以及如何解决此问题的信息。
避免在 measurement(测量)和键中编码数据
-
将数据存储在 标签值 或 字段值 中,而不是 标签键、字段键 或 measurement(测量) 中。如果您将架构设计为将数据存储在标签和字段值中,则您的查询将更易于编写且效率更高。
-
此外,通过不在写入数据时创建 measurement(测量)和键,您将保持较低的基数。要了解有关高序列基数对性能的影响的更多信息,请参阅 如何查找和减少高序列基数。
比较架构
- 比较以下以行协议表示的有效架构。
- 推荐 :以下架构将元数据 存储在单独的
crop、plot和region标签中。temp字段包含可变的数值数据。
shell
Good Measurements schema - Data encoded in tags (recommended)
-------------
weather_sensor,crop=blueberries,plot=1,region=north temp=50.1 1472515200000000000
weather_sensor,crop=blueberries,plot=2,region=midwest temp=49.8 1472515200000000000
- 不推荐:以下架构将多个属性(crop、plot 和 region)连接(blueberries.plot-1.north)在 measurement(测量)中,类似于 Graphite 指标。
shell
Bad Measurements schema - Data encoded in the measurement (not recommended)
-------------
blueberries.plot-1.north temp=50.1 1472515200000000000
blueberries.plot-2.midwest temp=49.8 1472515200000000000
- 不推荐:以下架构将多个属性(crop、plot 和 region)连接(blueberries.plot-1.north)在字段键中。
shell
Bad Keys schema - Data encoded in field keys (not recommended)
-------------
weather_sensor blueberries.plot-1.north.temp=50.1 1472515200000000000
weather_sensor blueberries.plot-2.midwest.temp=49.8 1472515200000000000比较查询
- 比较 良好 Measurement(测量) 和 不良 Measurement(测量) 架构的以下查询。
Flux 查询计算 north 区域中蓝莓的平均 temp
- 易于查询:良好 Measurement(测量) 数据很容易按 region 标签值进行过滤,如以下示例所示。
shell
// Query *Good Measurements*, data stored in separate tag values (recommended)
from(bucket: "<database>/<retention_policy>")
|> range(start:2016-08-30T00:00:00Z)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "weather_sensor" and r.region == "north" and r._field == "temp")
|> mean()
- 难以查询:不良 Measurement(测量) 需要使用正则表达式从 measurement(测量)中提取 plot 和 region,如以下示例所示。
shell
// Query *Bad Measurements*, data encoded in the measurement (not recommended)
from(bucket: "<database>/<retention_policy>")
|> range(start:2016-08-30T00:00:00Z)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement =~ /\.north$/ and r._field == "temp")
|> mean()- **复杂的 measurement(测量)**使某些查询变得不可能。
例如,使用 不良 Measurement(测量) 架构无法计算两个地块的平均温度。
InfluxQL 示例查询架构
txt
# Query *Bad Measurements*, data encoded in the measurement (not recommended)
> SELECT mean("temp") FROM /\.north$/
# Query *Good Measurements*, data stored in separate tag values (recommended)
> SELECT mean("temp") FROM "weather_sensor" WHERE "region" = 'north'避免在一个标签中放入多个信息
- 将包含多个信息的单个标签拆分为单独的标签,可以简化您的查询,并通过减少对正则表达式的需求来提高性能。
考虑以下以行协议表示的架构。
示例行协议架构
txt
Schema 1 - Multiple data encoded in a single tag
-------------
weather_sensor,crop=blueberries,location=plot-1.north temp=50.1 1472515200000000000
weather_sensor,crop=blueberries,location=plot-2.midwest temp=49.8 1472515200000000000架构 1 数据将多个单独的参数(plot 和 region)编码为一个长标签值 (plot-1.north)。将其与以下以行协议表示的架构进行比较。
txt
Schema 2 - Data encoded in multiple tags
-------------
weather_sensor,crop=blueberries,plot=1,region=north temp=50.1 1472515200000000000
weather_sensor,crop=blueberries,plot=2,region=midwest temp=49.8 1472515200000000000- 使用 Flux 或 InfluxQL 计算 north 区域中蓝莓的平均 temp。架构 2 更可取,因为使用多个标签,您不需要正则表达式。
Flux 示例查询架构
txt
// Schema 1 - Query for multiple data encoded in a single tag
from(bucket:"<database>/<retention_policy>")
|> range(start:2016-08-30T00:00:00Z)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "weather_sensor" and r.location =~ /\.north$/ and r._field == "temp")
|> mean()
// Schema 2 - Query for data encoded in multiple tags
from(bucket:"<database>/<retention_policy>")
|> range(start:2016-08-30T00:00:00Z)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "weather_sensor" and r.region == "north" and r._field == "temp")
|> mean()InfluxQL 示例查询架构
txt
# Schema 1 - Query for multiple data encoded in a single tag
> SELECT mean("temp") FROM "weather_sensor" WHERE location =~ /\.north$/
# Schema 2 - Query for data encoded in multiple tags
> SELECT mean("temp") FROM "weather_sensor" WHERE region = 'north'分片组持续时间管理
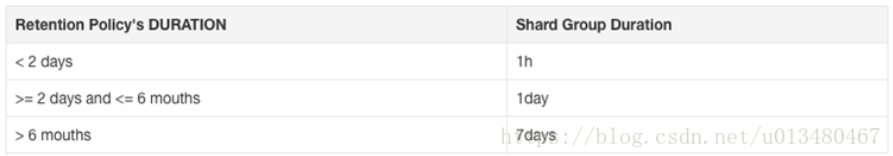
分片组持续时间概述
- InfluxDB 将数据存储在**分片组(shard group)**中。
- 分片组 按 保留策略 (RP) 组织,并存储时间戳落在称为 分片持续时间 的特定时间间隔内的数据。
- 如果未提供分片组持续时间,则分片组持续时间由创建 RP 时的 RP 持续时间 确定。默认值为:
| RP 持续时间 | 分片组持续时间 |
|---|---|
| < 2 天 | 1 小时 |
| >= 2 天且 <= 6 个月 | 1 天 |
| > 6 个月 | 7 天 |
- 分片组持续时间 也可以为每个 RP 配置。要配置分片组持续时间,请参阅 保留策略管理。
分片组持续时间权衡
- 确定最佳分片组持续时间需要在以下两者之间找到平衡
- 较长分片带来的更好的整体性能
- 较短分片提供的灵活性
长分片组持续时间
- 较长的分片组持续时间使 InfluxDB 可以在同一逻辑位置存储更多数据。这减少了数据重复,提高了压缩效率,并在某些情况下提高了查询速度。
短分片组持续时间
- 较短的分片组持续时间允许系统更有效地删除数据和记录增量备份。当 InfluxDB 执行 RP 时,它会删除整个分片组,而不是单个数据点,即使这些点比 RP 持续时间更旧。只有当分片组的持续时间结束时间早于 RP 持续时间时,才会删除分片组。
例如,如果您的 RP 持续时间为一天,则 InfluxDB 将每小时删除一小时的数据,并且始终有 25 个分片组。一天中的每小时一个,以及一个部分过期的额外分片组,但在整个分片组早于 24 小时之前不会删除。
注意: 要考虑的特殊用例:按时间过滤架构数据(例如标签、序列、measurement(测量))。例如,如果您想在一个小时的时间间隔内过滤架构数据,则必须将分片组持续时间设置为 1 小时。有关更多信息,请参阅 按时间过滤架构数据。
分片组持续时间建议
- 默认分片组持续时间适用于大多数情况。但是,高吞吐量或长时间运行的实例将受益于使用较长的分片组持续时间。以下是一些较长分片组持续时间的建议
| RP 持续时间 | 分片组持续时间 |
|---|---|
| <= 1 天 | 6 小时 |
| > 1 天且 <= 7 天 | 1 天 |
| > 7 天且 <= 3 个月 | 7 天 |
| > 3 个月 | 30 天 |
| 无限 | 52 周或更长 |
注意: 请注意,
INF(无限)不是 有效的分片组持续时间。在数据覆盖数十年且永远不会删除的极端情况下,像 1040w(20 年)这样的长分片组持续时间是完全有效的。
- 设置分片组持续时间之前要考虑的其他因素
用于回填的分片组持续时间
- 批量插入过去大时间范围内的历史数据将立即触发创建大量分片。
并发访问 和写入数百 或数千个分片的开销可能会迅速导致【性能下降】和【内存耗尽】。
- 在写入历史数据时,我们强烈建议临时设置较长的分片组持续时间,以便创建较少的分片。
通常,52 周的分片组持续时间非常适合回填。
2 工程源码编译
3 进程启动流程
4 配置加载流程
5 HTTP 数据写入流程
InfluxDB的数据写入流程的主要/关键步骤:
step1 客户端: 数据准备
- 客户端将数据格式化为InfluxDB支持的格式,如 Line Protocol 或 Point 对象。
- 数据需包含测量名称(measurement)、标签(tag)、字段(field)和时间戳(timestamp)。例如:
sql
measurement,tag_key=tag_value field_key=field_value timestamp或通过API构造
Point对象:
sql
var point = PointData.Measurement("temperature")
.Tag("location", "workshop1")
.Field("value", 25.6)
.Timestamp(DateTime.UtcNow, WritePrecision.Ns);step2 客户端/服务端: 连接与认证
- 客户端: 通过
HTTP/UDP等协议连接到InfluxDB服务器,并提供认证信息(如Token),建立写入会话。 - 服务端:
http请求是由httpd服务处理的,httpd服务的源码目录是services/httpd, 通过 Golang 原生的包net/http实现。- 在
cmd/influxd/run/server.go在NewServer()函数中对 httpd 服务进行配置,并在 cmd/influxd/run/server.go 中的 Open 函数中调用 s.appendHTTPService(s.config.HTTPD) 加载和配置 httpd 服务,然后调用 service.Open() 启动 httpd 服务。Handler.serverWrite()函数中:
- 调用 r.URL.Query().Get("db")获取写请求中指定的目标数据库的名称,然后调用 h.MetaClient.Database(database) 判断该数据库是否存在,如果该数据库不存在,报错返回。
- 如果开启了认证功能,则调用 h.WriteAuthrizer.AuthorizeWrite(user.ID(), database) 进行认证。
- 调用 models.ParsePointsWithPrecision(buf.bytes(), time.Now().UTC(), r.URL.Query().Get("precision")) 解析写请求 HTTP 报体中的时序数据记录。
- 调用 r.URL.Query().Get("consistency") 获取写请求中指定的写一致性级别。
- 最后调用 h.PointsWrite.WriterPoints(database, r.URL.Query().Get("rp") , consistency, user, points) 执行时序数据记录的写入操作。(详情参见 step3 及之后步骤)
step3 服务端: Shard路由
InfluxDB根据数据的时间范围和标签信息,将数据路由到对应的Shard。
Shard是数据存储的基本单元,负责处理特定时间范围和数据分区的写入请求。
step4 服务端: 写入 WAL 文件
- 数据首先被追加写入
WAL(Write-Ahead Log)文件,用于保证数据的持久性和故障恢复。
WAL记录了所有写入操作,即使系统崩溃,也能通过WAL恢复未持久化的数据。
step5 服务端: 缓存写入
- 数据同时写入内存缓存(如Data Cache或Inverted Index Cache)。
缓存用于提高写入性能,减少磁盘I/O操作。
step6 服务端: 持久化到磁盘
- 当缓存 达到一定大小或时间阈值时,数据从缓存Flush到磁盘,形成
TSM(Time-Structured Merge Tree)文件。
TSM文件是InfluxDB存储时序数据的底层文件格式,采用列式存储和压缩技术,优化数据读取和查询性能。
step7 服务端: 构建索引
- 数据写入过程中,Inverted Index引擎会构建倒排索引,用于支持多维查询。
索引记录了标签与数据点的映射关系,加速基于标签的过滤和查询操作。
step8 服务端: 返回写入结果
-
InfluxDB完成数据写入后,向客户端返回写入成功或失败的响应。
-
客户端: 可根据响应判断数据是否成功写入。
章节总结 & 注意事项
InfluxDB 3.x版本引入了存算分离架构 ,数据持久化到对象存储(如S3、本地磁盘)或内存中。- 批量写入数据 时,建议使用批量API(如 WritePoints )提高写入效率。
- 数据写入性能 受
Shard配置、缓存大小 、WAL设置等因素影响,需根据业务需求进行调优。
consistency: 写入的一致性级别
-
consistency参数,由client在request中传入,标识了shard有N个replica的情况下,如何确定shard是否写入成功。
-
如果client没有传入consistency参数,server端默认ConsistencyLevelOne,即只要一个replica写入OK,就返回client成功。
-
consistency参数:
- all: 所有的replica都写入成功则返回成功;
- quorum: 大多数的replica写入成功,则返回成功;
- one: 任何一个replica写入成功,则返回成功;
- any: 任何一个replica写入成功,或者被写入Hinted-Handoff缓存,则返回成功;
- 案例:以3节点,2replica为例:
| Level | required |
|---|---|
| all | 2 |
| quorum | 2 |
| one | 1 |
| any | 1 |
go
// cluster/points_writer.go
func (w *PointsWriter) writeToShard(shard *meta.ShardInfo, database, retentionPolicy string,
consistency models.ConsistencyLevel, points []models.Point) error {
// The required number of writes to achieve the requested consistency level
required := len(shard.Owners)
switch consistency {
case models.ConsistencyLevelAny, models.ConsistencyLevelOne:
required = 1
case models.ConsistencyLevelQuorum:
required = required/2 + 1
}
......
}推荐文献
6 HTTP 数据查询流程
Z 最佳实践-附件
附件: JDBC操作封装 | MyInfluxDbConnection
java
package com.xxx.datasource;
import com.xxx.datasource.entity.DataSource;
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDB;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDBException;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDBFactory;
import org.influxdb.dto.BatchPoints;
import org.influxdb.dto.Point;
import org.influxdb.dto.Pong;
import org.influxdb.dto.Query;
import org.influxdb.dto.QueryResult;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import javax.annotation.Nullable;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class InfluxDbConnection {
private final static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(InfluxDbConnection.class);
//数据库名
private String database;
//用户名
private String username;
//密码
private String password;
//连接地址
private String url;
//数据存贮策略
private String retentionPolicy;
private int actions;
private int flushDuration;
//连接instance
private InfluxDB influxDB;
//对 influxDb 连接,最近一次健康检测的时间
private Long latestHealthCheckTime = -1L;
private Boolean latestHealthCheckResult = true;//初始化状态: 健康
public InfluxDbConnection(String database, String username, String password, String url, String retentionPolicy,int actions, int flushDuration) {
this.database = database;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.url = url;
this.retentionPolicy= retentionPolicy;
this.actions = actions;
this.flushDuration = flushDuration;
createConnection(actions, flushDuration);
}
public InfluxDbConnection(String database, String username, String password, String url, String retentionPolicy) {
this(database, username, password, url, retentionPolicy, DataSource.ACTIONS_DEFAULT, DataSource.FLUSH_DURATION_DEFAULT );
}
public InfluxDbConnection(DataSource dataSource) {
this(
dataSource.getDatabase(), dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword(), dataSource.getUrl()
, dataSource.getRetentionPolicy() , dataSource.getActions() , dataSource.getFlushDuration()
);
}
// private void createConnection(){
// influxDB = InfluxDBFactory.connect(url, username, password);
// influxDB.setRetentionPolicy(retentionPolicy);
// influxDB.enableBatch(10000,1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// }
/**
* 创建连接
* @param actions 批量写入的 point 个数
* @param flushDuration 最晚刷新时间 (单位: 时间)
*/
public static InfluxDB createConnection(
String url, String username,String password
, String database, String retentionPolicy
, int actions, int flushDuration
){
InfluxDB influxDB = null;
//influxDB = InfluxDBFactory.connect(url, username, password);
OkHttpClient.Builder httpClient = new OkHttpClient.Builder();
//httpClient.connectTimeout(100, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
// .readTimeout(100, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
// .writeTimeout(100, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
influxDB = InfluxDBFactory.connect(url, username, password, httpClient);
influxDB.setDatabase(database);
influxDB.setRetentionPolicy(retentionPolicy);
influxDB.setConsistency( InfluxDB.ConsistencyLevel.ONE );
influxDB.setLogLevel(InfluxDB.LogLevel.BASIC);
influxDB.enableBatch(actions,flushDuration, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return influxDB;
}
private void createConnection(int actions, int flushDuration){
if(this.influxDB == null){
this.influxDB = createConnection(url, username, password, database, retentionPolicy, this.actions, this.flushDuration );
this.health( -1, 1, false );//创建完成后对其进行健康检测
}
}
private void createConnection(){
createConnection(this.actions, this.flushDuration);
}
//重建连接
private InfluxDB recreateConnection(){
if( this.influxDB != null ){
this.influxDB.close();//先尝试关闭原来的连接
this.influxDB = null; //置空
}
this.influxDB = createConnection(url, username, password, database, retentionPolicy, this.actions, this.flushDuration );
return influxDB;
}
/**
* 向数据库写数据
* @reference-doc
* [1] https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb-java/blob/influxdb-java-2.22/src/main/java/org/influxdb/impl/InfluxDBImpl.java
* [2] https://www.influxdata.com/blog/influxdb-java-client-performance-and-functionality-improvements/
* @note
* 1. [不支持-批量写] write(final String records) 方法 : 未利用到 InfluxDBImpl#enableBatch 的批量写特性
* 2. [支持-批量写] write(final Point point) 方法 : 能利用到 InfluxDBImpl#enableBatch 的批量写特性(可能会延后执行) [此处使用的方式]
* 3. [支持-批量写] write(BatchPoints batchPoints) 方法: 未利用 InfluxDBImpl#enableBatch 的批量写特性,而是由用户每次请求所控制,其每次请求的 points 即该批量写的所有数据 (请求时即执行)
* BatchPoints.Builder builder = BatchPoints.database(database);
* builder.points(points);
* BatchPoints batchPoints = builder.build();
* influxDB.write(batchPoints);
* 本方式,详情参见该方法: {@link #insertBatch(Collection) }
*/
public void insert(Point point) {
this.influxDB.write(point);
}
public void insertBatch(Point point) {
this.influxDB.write(point);
}
/**
* 批量写入
* @note
* Point.Builder pointBuilder = Point.measurement( measurement );
* Point point = pointBuilder.build();
* Point[] points = new Point[]{ point };
* @param points
*/
public void insertBatch(Point[] points){
insertBatch( Arrays.asList(points) );
}
public void insertBatch(Collection<Point> points){
InfluxDB influxDB = this.influxDB.enableGzip();
BatchPoints.Builder builder = BatchPoints.database(database);//BatchPoints.database(this.database);//静态方法,将对全局产生影响
builder.points(points);
BatchPoints batchPoints = builder.build();
influxDB.write(batchPoints);
}
//以行协议格式批量写入
public void insertBatchAsLineProtocol(List<String> points){
InfluxDB influxDBConnection = influxDB.enableGzip();
influxDBConnection.write(points);
}
/**
* 在健康检测后批量写入 point 数据
* @note
* @param points
* @param healthCheckMaxRetryCount
* @param throwExceptionWhenWriteFail 写失败时的是否抛异常
* @param errorMessageWhenWriteFailTemplate 写失败时的异常日志信息模板 (允许为 null)
* @param errorMessageWhenWriteFailArgs 写失败时的异常日志信息参数 (允许为 null)
* @return 是否写入成功(true:成功, false:失败)
*/
public Boolean insertBatchAfterHealthCheck(
Collection<Point> points
, Integer healthCheckIntervalMs
, int healthCheckMaxRetryCount
, Boolean throwExceptionWhenWriteFail
, @Nullable String errorMessageWhenWriteFailTemplate
, @Nullable Object ... errorMessageWhenWriteFailArgs
){
Boolean health = this.health( healthCheckIntervalMs, healthCheckMaxRetryCount, true);//健康检测,最大重试 healthCheckMaxRetryCount 次,如果最终仍检测失败将上抛异常
String errorMessage = null;
try {
this.insertBatch(points);
} catch (InfluxDBException exception){
//eg : org.influxdb.InfluxDBException$PointsBeyondRetentionPolicyException: partial write: points beyond retention policy dropped=1
String errorMessageWhenWriteFail = (errorMessageWhenWriteFailTemplate !=null) ? ( String.format( errorMessageWhenWriteFailTemplate, errorMessageWhenWriteFailArgs ) ): null;
errorMessage = (errorMessageWhenWriteFail != null? errorMessageWhenWriteFail + " " : "") + String.format(
"Fail to write the points(size:%d) to influxdb when batch insert! health:%b, exception.isRetryWorth: %b, exception.message : %s"
, points == null ? "null" : points.size(), health, exception.isRetryWorth(), exception.getMessage()
);
log.error( errorMessage + ", exception:" , exception.getMessage() );
if(throwExceptionWhenWriteFail) {
throw new RuntimeException( errorMessage, exception );
}
}
return errorMessage == null ? true : false;
}
/**
* 在健康检测后批量写入 point 数据,且写失败时将重试
* @param maxRetryCount 最大重试次数
* @param retryIntervalMs 重试的间隔时间(单位:毫秒)
* @return
*/
public Boolean insertBatchAfterHealthCheckWithRetry(
Integer maxRetryCount, Integer retryIntervalMs
, Collection<Point> points
, Integer healthCheckIntervalMs
, int healthCheckMaxRetryCount
, Boolean throwExceptionWhenWriteFail
, @Nullable String errorMessageWhenWriteFailTemplate
, @Nullable Object ... errorMessageWhenWriteFailArgs
) throws InterruptedException {
Boolean executeResult = false;//执行是否完成及成功
Exception latestException = null;
String latestErrorMessage = null;//最近一次健康检查的异常日志
Integer retryCount = 0; //调用次数的计数器
while( (!executeResult) && retryCount < maxRetryCount) {//循环尝试
//尝试执行1次
try {
executeResult = this.insertBatchAfterHealthCheck(points, healthCheckIntervalMs, healthCheckMaxRetryCount, throwExceptionWhenWriteFail, errorMessageWhenWriteFailTemplate, errorMessageWhenWriteFailArgs);
} catch (Exception exception) {
latestErrorMessage = String.format(
"Batch write fail!exception.message:%s, retryCount:%d, maxRetryCount:%d, connectionInfo:%s",
exception.getMessage(), retryCount, maxRetryCount, toString()
);
latestException = exception;
log.error( latestErrorMessage + ", exception :", exception );
//判断是否继续重试?
if( exception.getMessage().contains("point time is expired")) {// Point 是过期数据时,不予重试,直接上抛异常 | Caused by: org.influxdb.InfluxDBException: partial write: point time is expired, compared with rp duration dropped=3
throw new RuntimeException(latestErrorMessage, latestException);
} else {//继续重试
//Q: 线程休眠的逻辑放在此处是否合理? A: 认为此处是合理的,因为该方法被设计为在健康检测后批量写入 point 数据,且写失败时将等待一段时间后再重试。因此,此处的线程休眠是合理的。
Thread.sleep( retryIntervalMs );//线程休眠, //Thread.sleep( {入参的的时间单位毫秒级} );
}
}
retryCount++;
}
if( (!executeResult) && (retryCount >= maxRetryCount) ){
throw new RuntimeException(latestErrorMessage, latestException);
}
return executeResult;
}
public QueryResult query(String measurement){
return influxDB.query(new Query("SELECT * FROM " + measurement, database));
}
public QueryResult queryResult(String sql){
return influxDB.query(new Query(sql, database,true));
}
public void close(){
if(this.influxDB != null){
influxDB.close();
}
}
/**
* 健康检测
* @return
*/
public boolean health(InfluxDB influxDB){
Pong ping = influxDB.ping();
this.latestHealthCheckTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.latestHealthCheckResult = ping.isGood();
return this.latestHealthCheckResult;
}
public boolean health(){
return health(influxDB);
}
/**
* 健康检测
* @note 若检测失败,最大重试 maxRetryCount 次,如果最终仍检测失败将上抛异常
* @param healthCheckIntervalMs 健康检查的间隔时间(单位: ms,毫秒)
* if healthCheckIntervalMs == -1: 不考虑健康间隔时间,每次请求本方法时,必须立即进行健康检测
* else healthCheckIntervalMs != -1 : 考虑健康检测时间,但如果本次请求本方法时尚未达到健康检测触发条件时,将直接返回最近1次的健康检测结果。
* @param maxRetryCount 最大重试次数
* @return 健康检测结果
*/
public Boolean health(Integer healthCheckIntervalMs, Integer maxRetryCount, Boolean throwExceptionWhenNotHealth){
InfluxDB influxDB = this.influxDB;
Boolean healthCheckResult = false;//检测结果是否为健康
if( healthCheckIntervalMs.equals( -1 )){//禁用 healthCheckIntervalMs 特性
Integer retryCount = 0; //连接检测的计数器
String latestErrorMessage = null;//最近一次健康检查的异常日志
while( (!healthCheckResult) && retryCount < maxRetryCount) {//循环尝试
//判断连接是否断开,是则新建连接
try {
healthCheckResult = this.health(influxDB);
if ( !healthCheckResult ) {
influxDB = recreateConnection();//新建连接
this.influxDB = influxDB; //更新当前 this.influxDB 屬性
}
} catch (Exception exception) {
latestErrorMessage = String.format(
"Health check fail!exception.message:%s, retryCount:%d, maxRetryCount:%d, connectionInfo:%s",
exception.getMessage(), retryCount, maxRetryCount, toString()
);
log.error( latestErrorMessage + ", exception :", exception );
if(throwExceptionWhenNotHealth) {
}
}
retryCount++;
}
if( (!healthCheckResult) && throwExceptionWhenNotHealth ){
throw new RuntimeException( "latestErrorMessage:" + latestErrorMessage );
}
} else {//启用 healthCheckIntervalMs 特性
Long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if( currentTime >= ( this.latestHealthCheckTime + healthCheckIntervalMs) ) {//达到健康检测的触发条件
healthCheckResult = this.health( -1, maxRetryCount, throwExceptionWhenNotHealth);//立即进行健康检测
} else {
healthCheckResult = this.latestHealthCheckResult;//直接返回上一次的健康检查结果
}
}
return healthCheckResult;
}
public Boolean health(Integer maxRetryCount){
return health(-1, 3, true);
}
public Pong ping(){
Pong ping = influxDB.ping();
return ping;
}
public InfluxDB getInfluxDB() {
return influxDB;
}
public Long getLatestHealthCheckTime() {
return latestHealthCheckTime;
}
public Boolean getLatestHealthCheckResult() {
return latestHealthCheckResult;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "InfluxDbConnection{" +
"database='" + database + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password=[" + (password==null?"null" : password.length()) + "]" +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", retentionPolicy='" + retentionPolicy + '\'' +
", actions=" + actions +
", flushDuration=" + flushDuration +
", influxDB=" + influxDB +
", latestHealthCheckResult=" + latestHealthCheckResult +
", latestHealthCheckTime=" + latestHealthCheckTime +
'}';
}
}附件: influxdb-java | Point#concatenatedFields
- 数据写入性能优化: 重写
influxdb-java:2.22的{@link org.influxdb.dto.Point#concatenatedFields }方法,针对 数值型字段,取消原 format to string 的方式 (NUMBER_FORMATTER.get().format(value));
java
package org.influxdb.dto;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.math.RoundingMode;
import java.text.NumberFormat;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.Locale;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.influxdb.BuilderException;
import org.influxdb.annotation.Column;
import org.influxdb.annotation.Measurement;
import org.influxdb.annotation.TimeColumn;
import org.influxdb.impl.Preconditions;
/**
* @description 重写: org/influxdb/dto/Point.java#concatenatedFields
*/
/**
* Representation of a InfluxDB database Point.
*
* @author stefan.majer [at] gmail.com
*
*/
public class Point {
private String measurement;
private Map<String, String> tags;
private Number time;
private TimeUnit precision = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS;
private Map<String, Object> fields;
private static final int MAX_FRACTION_DIGITS = 340;
private static final ThreadLocal<NumberFormat> NUMBER_FORMATTER =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> {
NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getInstance(Locale.ENGLISH);
numberFormat.setMaximumFractionDigits(MAX_FRACTION_DIGITS);
numberFormat.setGroupingUsed(false);
numberFormat.setMinimumFractionDigits(1);
return numberFormat;
});
private static final int DEFAULT_STRING_BUILDER_SIZE = 1024;
private static final ThreadLocal<StringBuilder> CACHED_STRINGBUILDERS =
ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new StringBuilder(DEFAULT_STRING_BUILDER_SIZE));
Point() {
}
/**
* Create a new Point Build build to create a new Point in a fluent manner.
*
* @param measurement
* the name of the measurement.
* @return the Builder to be able to add further Builder calls.
*/
public static Builder measurement(final String measurement) {
return new Builder(measurement);
}
/**
* Create a new Point Build build to create a new Point in a fluent manner from a POJO.
*
* @param clazz Class of the POJO
* @return the Builder instance
*/
public static Builder measurementByPOJO(final Class<?> clazz) {
Objects.requireNonNull(clazz, "clazz");
throwExceptionIfMissingAnnotation(clazz, Measurement.class);
String measurementName = findMeasurementName(clazz);
return new Builder(measurementName);
}
private static void throwExceptionIfMissingAnnotation(final Class<?> clazz,
final Class<? extends Annotation> expectedClass) {
if (!clazz.isAnnotationPresent(expectedClass)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Class " + clazz.getName() + " is not annotated with @"
+ Measurement.class.getSimpleName());
}
}
/**
* Builder for a new Point.
*
* @author stefan.majer [at] gmail.com
*
*/
public static final class Builder {
private static final BigInteger NANOSECONDS_PER_SECOND = BigInteger.valueOf(1000000000L);
private final String measurement;
private final Map<String, String> tags = new TreeMap<>();
private Number time;
private TimeUnit precision;
private final Map<String, Object> fields = new TreeMap<>();
/**
* @param measurement
*/
Builder(final String measurement) {
this.measurement = measurement;
}
/**
* Add a tag to this point.
*
* @param tagName
* the tag name
* @param value
* the tag value
* @return the Builder instance.
*/
public Builder tag(final String tagName, final String value) {
Objects.requireNonNull(tagName, "tagName");
Objects.requireNonNull(value, "value");
if (!tagName.isEmpty() && !value.isEmpty()) {
tags.put(tagName, value);
}
return this;
}
/**
* Add a Map of tags to add to this point.
*
* @param tagsToAdd
* the Map of tags to add
* @return the Builder instance.
*/
public Builder tag(final Map<String, String> tagsToAdd) {
for (Entry<String, String> tag : tagsToAdd.entrySet()) {
tag(tag.getKey(), tag.getValue());
}
return this;
}
/**
* Add a field to this point.
*
* @param field
* the field name
* @param value
* the value of this field
* @return the Builder instance.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("checkstyle:finalparameters")
@Deprecated
public Builder field(final String field, Object value) {
if (value instanceof Number) {
if (value instanceof Byte) {
value = ((Byte) value).doubleValue();
} else if (value instanceof Short) {
value = ((Short) value).doubleValue();
} else if (value instanceof Integer) {
value = ((Integer) value).doubleValue();
} else if (value instanceof Long) {
value = ((Long) value).doubleValue();
} else if (value instanceof BigInteger) {
value = ((BigInteger) value).doubleValue();
}
}
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final boolean value) {
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final long value) {
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final double value) {
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final int value) {
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final float value) {
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final short value) {
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final Number value) {
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
public Builder addField(final String field, final String value) {
Objects.requireNonNull(value, "value");
fields.put(field, value);
return this;
}
/**
* Add a Map of fields to this point.
*
* @param fieldsToAdd
* the fields to add
* @return the Builder instance.
*/
public Builder fields(final Map<String, Object> fieldsToAdd) {
this.fields.putAll(fieldsToAdd);
return this;
}
/**
* Add a time to this point.
*
* @param timeToSet the time for this point
* @param precisionToSet the TimeUnit
* @return the Builder instance.
*/
public Builder time(final Number timeToSet, final TimeUnit precisionToSet) {
Objects.requireNonNull(timeToSet, "timeToSet");
Objects.requireNonNull(precisionToSet, "precisionToSet");
this.time = timeToSet;
this.precision = precisionToSet;
return this;
}
/**
* Add a time to this point as long.
* only kept for binary compatibility with previous releases.
*
* @param timeToSet the time for this point as long
* @param precisionToSet the TimeUnit
* @return the Builder instance.
*/
public Builder time(final long timeToSet, final TimeUnit precisionToSet) {
return time((Number) timeToSet, precisionToSet);
}
/**
* Add a time to this point as Long.
* only kept for binary compatibility with previous releases.
*
* @param timeToSet the time for this point as Long
* @param precisionToSet the TimeUnit
* @return the Builder instance.
*/
public Builder time(final Long timeToSet, final TimeUnit precisionToSet) {
return time((Number) timeToSet, precisionToSet);
}
/**
* Does this builder contain any fields?
*
* @return true, if the builder contains any fields, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean hasFields() {
return !fields.isEmpty();
}
/**
* Adds field map from object by reflection using {@link org.influxdb.annotation.Column}
* annotation.
*
* @param pojo POJO Object with annotation {@link org.influxdb.annotation.Column} on fields
* @return the Builder instance
*/
public Builder addFieldsFromPOJO(final Object pojo) {
Class<? extends Object> clazz = pojo.getClass();
while (clazz != null) {
for (Field field : clazz.getDeclaredFields()) {
Column column = field.getAnnotation(Column.class);
if (column == null) {
continue;
}
field.setAccessible(true);
String fieldName = column.name();
addFieldByAttribute(pojo, field, column, fieldName);
}
clazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
}
if (this.fields.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Class " + pojo.getClass().getName()
+ " has no @" + Column.class.getSimpleName() + " annotation");
}
return this;
}
private void addFieldByAttribute(final Object pojo, final Field field, final Column column,
final String fieldName) {
try {
Object fieldValue = field.get(pojo);
TimeColumn tc = field.getAnnotation(TimeColumn.class);
if (tc != null && Instant.class.isAssignableFrom(field.getType())) {
Optional.ofNullable((Instant) fieldValue).ifPresent(instant -> {
TimeUnit timeUnit = tc.timeUnit();
if (timeUnit == TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS || timeUnit == TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS) {
this.time = BigInteger.valueOf(instant.getEpochSecond())
.multiply(NANOSECONDS_PER_SECOND)
.add(BigInteger.valueOf(instant.getNano()))
.divide(BigInteger.valueOf(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.convert(1, timeUnit)));
} else {
this.time = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(instant.toEpochMilli(), timeUnit);
this.precision = timeUnit;
}
this.precision = timeUnit;
});
return;
}
if (column.tag()) {
if (fieldValue != null) {
this.tags.put(fieldName, (String) fieldValue);
}
} else {
if (fieldValue != null) {
this.fields.put(fieldName, fieldValue);
}
}
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | IllegalAccessException e) {
// Can not happen since we use metadata got from the object
throw new BuilderException(
"Field " + fieldName + " could not found on class " + pojo.getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
/**
* Create a new Point.
*
* @return the newly created Point.
*/
public Point build() {
Preconditions.checkNonEmptyString(this.measurement, "measurement");
Preconditions.checkPositiveNumber(this.fields.size(), "fields size");
Point point = new Point();
point.setFields(this.fields);
point.setMeasurement(this.measurement);
if (this.time != null) {
point.setTime(this.time);
point.setPrecision(this.precision);
}
point.setTags(this.tags);
return point;
}
}
/**
* @param measurement
* the measurement to set
*/
void setMeasurement(final String measurement) {
this.measurement = measurement;
}
/**
* @param time
* the time to set
*/
void setTime(final Number time) {
this.time = time;
}
/**
* @param tags
* the tags to set
*/
void setTags(final Map<String, String> tags) {
this.tags = tags;
}
/**
* @return the tags
*/
Map<String, String> getTags() {
return this.tags;
}
/**
* @param precision
* the precision to set
*/
void setPrecision(final TimeUnit precision) {
this.precision = precision;
}
/**
* @return the fields
*/
Map<String, Object> getFields() {
return this.fields;
}
/**
* @param fields
* the fields to set
*/
void setFields(final Map<String, Object> fields) {
this.fields = fields;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
Point point = (Point) o;
return Objects.equals(measurement, point.measurement)
&& Objects.equals(tags, point.tags)
&& Objects.equals(time, point.time)
&& precision == point.precision
&& Objects.equals(fields, point.fields);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(measurement, tags, time, precision, fields);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("Point [name=");
builder.append(this.measurement);
if (this.time != null) {
builder.append(", time=");
builder.append(this.time);
}
builder.append(", tags=");
builder.append(this.tags);
if (this.precision != null) {
builder.append(", precision=");
builder.append(this.precision);
}
builder.append(", fields=");
builder.append(this.fields);
builder.append("]");
return builder.toString();
}
/**
* Calculate the lineprotocol entry for a single Point.
* <p>
* NaN and infinity values are silently dropped as they are unsupported:
* https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb/issues/4089
*
* @see <a href="https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v1.7/write_protocols/line_protocol_reference/">
* InfluxDB line protocol reference</a>
*
* @return the String without newLine, empty when there are no fields to write
*/
public String lineProtocol() {
return lineProtocol(null);
}
/**
* Calculate the lineprotocol entry for a single point, using a specific {@link TimeUnit} for the timestamp.
* <p>
* NaN and infinity values are silently dropped as they are unsupported:
* https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb/issues/4089
*
* @see <a href="https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v1.7/write_protocols/line_protocol_reference/">
* InfluxDB line protocol reference</a>
*
* @param precision the time precision unit for this point
* @return the String without newLine, empty when there are no fields to write
*/
public String lineProtocol(final TimeUnit precision) {
// setLength(0) is used for reusing cached StringBuilder instance per thread
// it reduces GC activity and performs better then new StringBuilder()
StringBuilder sb = CACHED_STRINGBUILDERS.get();
sb.setLength(0);
escapeKey(sb, measurement);
concatenatedTags(sb);
int writtenFields = concatenatedFields(sb);
if (writtenFields == 0) {
return "";
}
formatedTime(sb, precision);
return sb.toString();
}
private void concatenatedTags(final StringBuilder sb) {
for (Entry<String, String> tag : this.tags.entrySet()) {
sb.append(',');
escapeKey(sb, tag.getKey());
sb.append('=');
escapeKey(sb, tag.getValue());
}
sb.append(' ');
}
/**
* 构建 fields 字段
* @description
* 1. 数据写入性能优化: 重写 {@link org.influxdb.dto.Point#concatenatedFields }方法,针对 数值型字段,取消原 format to string 的方式 (`NUMBER_FORMATTER.get().format(value)`);
* @param sb
* @return
*/
private int concatenatedFields(final StringBuilder sb) {
int fieldCount = 0;
for (Entry<String, Object> field : this.fields.entrySet()) {
Object value = field.getValue();
if (value == null || isNotFinite(value)) {
continue;
}
escapeKey(sb, field.getKey());
sb.append('=');
if (value instanceof Number) {
if (value instanceof Double || value instanceof Float || value instanceof BigDecimal) {
sb.append(value);
//sb.append(NUMBER_FORMATTER.get().format(value));
} else {
sb.append(value).append('i');
}
} else if (value instanceof String) {
String stringValue = (String) value;
sb.append('"');
escapeField(sb, stringValue);
sb.append('"');
} else {
sb.append(value);
}
sb.append(',');
fieldCount++;
}
// efficiently chop off the trailing comma
int lengthMinusOne = sb.length() - 1;
if (sb.charAt(lengthMinusOne) == ',') {
sb.setLength(lengthMinusOne);
}
return fieldCount;
}
static void escapeKey(final StringBuilder sb, final String key) {
for (int i = 0; i < key.length(); i++) {
switch (key.charAt(i)) {
case ' ':
case ',':
case '=':
sb.append('\\');
default:
sb.append(key.charAt(i));
}
}
}
static void escapeField(final StringBuilder sb, final String field) {
for (int i = 0; i < field.length(); i++) {
switch (field.charAt(i)) {
case '\\':
case '\"':
sb.append('\\');
default:
sb.append(field.charAt(i));
}
}
}
private static boolean isNotFinite(final Object value) {
return value instanceof Double && !Double.isFinite((Double) value)
|| value instanceof Float && !Float.isFinite((Float) value);
}
private void formatedTime(final StringBuilder sb, final TimeUnit precision) {
if (this.time == null) {
return;
}
TimeUnit converterPrecision = precision;
if (converterPrecision == null) {
converterPrecision = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS;
}
if (this.time instanceof BigInteger) {
BigInteger time = (BigInteger) this.time;
long conversionFactor = converterPrecision.convert(1, this.precision);
if (conversionFactor >= 1) {
time = time.multiply(BigInteger.valueOf(conversionFactor));
} else {
conversionFactor = this.precision.convert(1, converterPrecision);
time = time.divide(BigInteger.valueOf(conversionFactor));
}
sb.append(" ").append(time);
} else if (this.time instanceof BigDecimal) {
BigDecimal time = (BigDecimal) this.time;
long conversionFactor = converterPrecision.convert(1, this.precision);
if (conversionFactor >= 1) {
time = time.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(conversionFactor));
} else {
conversionFactor = this.precision.convert(1, converterPrecision);
time = time.divide(BigDecimal.valueOf(conversionFactor), RoundingMode.HALF_UP);
}
sb.append(" ").append(time.toBigInteger());
} else {
sb.append(" ").append(converterPrecision.convert(this.time.longValue(), this.precision));
}
}
private static String findMeasurementName(final Class<?> clazz) {
return clazz.getAnnotation(Measurement.class).name();
}
}附件: influxdb-java | BatchProcessor
- 修改了
influxdb-java:2.22的下列方法,添加批量写的耗时观测日志:
write()
==== 该方法被如下调用:put(final AbstractBatchEntry): 核心场景1BatchProcessor#constructor(...)#flushRunnable: 核心场景2flush()flushAndShutdown()
java
package org.influxdb.impl;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDB;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDB.ConsistencyLevel;
import org.influxdb.dto.BatchPoints;
import org.influxdb.dto.Point;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* A BatchProcessor can be attached to a InfluxDB Instance to collect single point writes and
* aggregates them to BatchPoints to get a better write performance.
*
* @author stefan.majer [at] gmail.com
* @note
* 1. 修改了下列方法,添加批量写的耗时日志:
* write()
* ==== 该方法被如下调用
* put(final AbstractBatchEntry) : 核心场景1
* BatchProcessor#constructor(...)#flushRunnable : 核心场景2
* flush()
* flushAndShutdown()
*/
@Slf4j
public final class BatchProcessor {
private static final Logger LOG = Logger.getLogger(BatchProcessor.class.getName());
protected final BlockingQueue<AbstractBatchEntry> queue;
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler;
private final BiConsumer<Iterable<Point>, Throwable> exceptionHandler;
final InfluxDB influxDB;
final int actions;
private final TimeUnit flushIntervalUnit;
private final int flushInterval;
private final ConsistencyLevel consistencyLevel;
private final int jitterInterval;
private final TimeUnit precision;
private final BatchWriter batchWriter;
private boolean dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion;
Consumer<Point> droppedActionHandler;
Supplier<Double> randomSupplier;
/**
* The Builder to create a BatchProcessor instance.
*/
public static final class Builder {
private final InfluxDB influxDB;
private ThreadFactory threadFactory = Executors.defaultThreadFactory();
private int actions;
private TimeUnit flushIntervalUnit;
private int flushInterval;
private int jitterInterval;
// this is a default value if the InfluxDb.enableBatch(BatchOptions) IS NOT used
// the reason is backward compatibility
private int bufferLimit = 0;
private TimeUnit precision;
private BiConsumer<Iterable<Point>, Throwable> exceptionHandler = (entries, throwable) -> { };
private ConsistencyLevel consistencyLevel;
private boolean dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion;
private Consumer<Point> droppedActionsHandler;
/**
* @param threadFactory
* is optional.
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder threadFactory(final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
return this;
}
/**
* @param influxDB
* is mandatory.
*/
public Builder(final InfluxDB influxDB) {
this.influxDB = influxDB;
}
/**
* The number of actions after which a batchwrite must be performed.
*
* @param maxActions
* number of Points written after which a write must happen.
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder actions(final int maxActions) {
this.actions = maxActions;
return this;
}
/**
* The interval at which at least should issued a write.
*
* @param interval
* the interval
* @param unit
* the TimeUnit of the interval
*
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder interval(final int interval, final TimeUnit unit) {
this.flushInterval = interval;
this.flushIntervalUnit = unit;
return this;
}
/**
* The interval at which at least should issued a write.
*
* @param flushInterval
* the flush interval
* @param jitterInterval
* the flush jitter interval
* @param unit
* the TimeUnit of the interval
*
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder interval(final int flushInterval, final int jitterInterval, final TimeUnit unit) {
this.flushInterval = flushInterval;
this.jitterInterval = jitterInterval;
this.flushIntervalUnit = unit;
return this;
}
/**
* A buffer for failed writes so that the writes will be retried later on. When the buffer is full and
* new points are written, oldest entries in the buffer are lost.
*
* @param bufferLimit maximum number of points stored in the buffer
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder bufferLimit(final int bufferLimit) {
this.bufferLimit = bufferLimit;
return this;
}
/**
* A callback to be used when an error occurs during a batchwrite.
*
* @param handler
* the handler
*
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder exceptionHandler(final BiConsumer<Iterable<Point>, Throwable> handler) {
this.exceptionHandler = handler;
return this;
}
/**
* To define the behaviour when the action queue exhausts. If unspecified, will default to false which means that
* the {@link InfluxDB#write(Point)} will be blocked till the space in the queue is created.
* true means that the newer actions being written to the queue will dropped and
* {@link BatchProcessor#droppedActionHandler} will be called.
*
* @param dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion
* the dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion
*
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion(final boolean dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion) {
this.dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion = dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion;
return this;
}
/**
* A callback to be used when an actions are dropped on action queue exhaustion.
*
* @param handler
* the handler
*
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder droppedActionHandler(final Consumer<Point> handler) {
this.droppedActionsHandler = handler;
return this;
}
/**
* Consistency level for batch write.
*
* @param consistencyLevel
* the consistencyLevel
*
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder consistencyLevel(final ConsistencyLevel consistencyLevel) {
this.consistencyLevel = consistencyLevel;
return this;
}
/**
* Set the time precision to use for the batch.
*
* @param precision
* the precision
*
* @return this Builder to use it fluent
*/
public Builder precision(final TimeUnit precision) {
this.precision = precision;
return this;
}
/**
* Create the BatchProcessor.
*
* @return the BatchProcessor instance.
*/
public BatchProcessor build() {
Objects.requireNonNull(this.influxDB, "influxDB");
Preconditions.checkPositiveNumber(this.actions, "actions");
Preconditions.checkPositiveNumber(this.flushInterval, "flushInterval");
Preconditions.checkNotNegativeNumber(jitterInterval, "jitterInterval");
Preconditions.checkNotNegativeNumber(bufferLimit, "bufferLimit");
Objects.requireNonNull(this.flushIntervalUnit, "flushIntervalUnit");
Objects.requireNonNull(this.threadFactory, "threadFactory");
Objects.requireNonNull(this.exceptionHandler, "exceptionHandler");
BatchWriter batchWriter;
if (this.bufferLimit > this.actions) {
batchWriter = new RetryCapableBatchWriter(this.influxDB, this.exceptionHandler, this.bufferLimit, this.actions);
} else {
batchWriter = new OneShotBatchWriter(this.influxDB);
}
return new BatchProcessor(this.influxDB, batchWriter, this.threadFactory, this.actions, this.flushIntervalUnit,
this.flushInterval, this.jitterInterval, exceptionHandler, this.consistencyLevel,
this.precision, this.dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion, this.droppedActionsHandler);
}
}
abstract static class AbstractBatchEntry {
private final Point point;
public AbstractBatchEntry(final Point point) {
this.point = point;
}
public Point getPoint() {
return this.point;
}
}
static class HttpBatchEntry extends AbstractBatchEntry {
private final String db;
private final String rp;
public HttpBatchEntry(final Point point, final String db, final String rp) {
super(point);
this.db = db;
this.rp = rp;
}
public String getDb() {
return this.db;
}
public String getRp() {
return this.rp;
}
}
static class UdpBatchEntry extends AbstractBatchEntry {
private final int udpPort;
public UdpBatchEntry(final Point point, final int udpPort) {
super(point);
this.udpPort = udpPort;
}
public int getUdpPort() {
return this.udpPort;
}
}
/**
* Static method to create the Builder for this BatchProcessor.
*
* @param influxDB
* the influxdb database handle.
* @return the Builder to create the BatchProcessor.
*/
public static Builder builder(final InfluxDB influxDB) {
return new Builder(influxDB);
}
BatchProcessor(final InfluxDB influxDB, final BatchWriter batchWriter, final ThreadFactory threadFactory,
final int actions, final TimeUnit flushIntervalUnit, final int flushInterval, final int jitterInterval,
final BiConsumer<Iterable<Point>, Throwable> exceptionHandler,
final ConsistencyLevel consistencyLevel, final TimeUnit precision,
final boolean dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion, final Consumer<Point> droppedActionHandler) {
super();
this.influxDB = influxDB;
this.batchWriter = batchWriter;
this.actions = actions;
this.flushIntervalUnit = flushIntervalUnit;
this.flushInterval = flushInterval;
this.jitterInterval = jitterInterval;
this.scheduler = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor(threadFactory);
this.exceptionHandler = exceptionHandler;
this.consistencyLevel = consistencyLevel;
this.precision = precision;
this.dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion = dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion;
this.droppedActionHandler = droppedActionHandler;
if (actions > 1 && actions < Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
this.queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(actions);
} else {
this.queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
}
this.randomSupplier = Math::random;
Runnable flushRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// write doesn't throw any exceptions
write();
int jitterInterval = (int) (randomSupplier.get() * BatchProcessor.this.jitterInterval);
BatchProcessor.this.scheduler.schedule(this,
BatchProcessor.this.flushInterval + jitterInterval, BatchProcessor.this.flushIntervalUnit);
}
};
// Flush at specified Rate
this.scheduler.schedule(flushRunnable,
this.flushInterval + (int) (randomSupplier.get() * BatchProcessor.this.jitterInterval),
this.flushIntervalUnit);
}
private static Long logBatchWriteTimeConsumingInterval = 5*60*1000*1000L;//单位:ns
private AtomicLong latestLogBatchWriteTimeConsumingTimestamp = new AtomicLong(logBatchWriteTimeConsumingInterval);//增加1个记录上一次打印日志的时间戳变量
void write() {
Long startTime = System.nanoTime();//1纳秒=0.00000 0001秒
List<Point> currentBatch = null;
try {
if (this.queue.isEmpty()) {
BatchProcessor.this.batchWriter.write(Collections.emptyList());
return;
}
//for batch on HTTP.
Map<String, BatchPoints> batchKeyToBatchPoints = new HashMap<>();
//for batch on UDP.
Map<Integer, List<String>> udpPortToBatchPoints = new HashMap<>();
List<AbstractBatchEntry> batchEntries = new ArrayList<>(this.queue.size());
this.queue.drainTo(batchEntries);
currentBatch = new ArrayList<>(batchEntries.size());
for (AbstractBatchEntry batchEntry : batchEntries) {
Point point = batchEntry.getPoint();
currentBatch.add(point);
if (batchEntry instanceof HttpBatchEntry) {
HttpBatchEntry httpBatchEntry = HttpBatchEntry.class.cast(batchEntry);
String dbName = httpBatchEntry.getDb();
String rp = httpBatchEntry.getRp();
String batchKey = dbName + "_" + rp;
if (!batchKeyToBatchPoints.containsKey(batchKey)) {
BatchPoints batchPoints = BatchPoints.database(dbName)
.retentionPolicy(rp).consistency(getConsistencyLevel())
.precision(getPrecision()).build();
batchKeyToBatchPoints.put(batchKey, batchPoints);
}
batchKeyToBatchPoints.get(batchKey).point(point);
} else if (batchEntry instanceof UdpBatchEntry) {
UdpBatchEntry udpBatchEntry = UdpBatchEntry.class.cast(batchEntry);
int udpPort = udpBatchEntry.getUdpPort();
if (!udpPortToBatchPoints.containsKey(udpPort)) {
List<String> batchPoints = new ArrayList<String>();
udpPortToBatchPoints.put(udpPort, batchPoints);
}
udpPortToBatchPoints.get(udpPort).add(point.lineProtocol());
}
}
BatchProcessor.this.batchWriter.write(batchKeyToBatchPoints.values());
for (Entry<Integer, List<String>> entry : udpPortToBatchPoints.entrySet()) {
for (String lineprotocolStr : entry.getValue()) {
BatchProcessor.this.influxDB.write(entry.getKey(), lineprotocolStr);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// any exception wouldn't stop the scheduler
exceptionHandler.accept(currentBatch, t);
LOG.log(Level.SEVERE, "Batch could not be sent. Data will be lost", t);
}
Long endTime = System.nanoTime();
if( (endTime - latestLogBatchWriteTimeConsumingTimestamp.get() ) >= logBatchWriteTimeConsumingInterval ){
Long timDiffNs = (endTime-startTime);
log.info("Success to batch write points to tsdb by `BatchProcessor#write`!time-consuming:{}ns={}ms, actions:{}, queue.size:{}", timDiffNs, timDiffNs/1000000L, actions, queue.size());
latestLogBatchWriteTimeConsumingTimestamp.set( endTime );
}
}
/**
* Put a single BatchEntry to the cache for later processing.
*
* @param batchEntry
* the batchEntry to write to the cache.
*/
void put(final AbstractBatchEntry batchEntry) {
try {
if (this.dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion) {
if (!this.queue.offer(batchEntry)) {
this.droppedActionHandler.accept(batchEntry.getPoint());
return;
}
} else {
this.queue.put(batchEntry);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
if (this.queue.size() >= this.actions) {
this.scheduler.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
write();
}
});
}
}
/**
* Flush the current open writes to influxdb and end stop the reaper thread. This should only be
* called if no batch processing is needed anymore.
*
*/
void flushAndShutdown() {
this.write();
this.scheduler.shutdown();
this.batchWriter.close();
}
/**
* Flush the current open writes to InfluxDB. This will block until all pending points are written.
*/
void flush() {
this.write();
}
public ConsistencyLevel getConsistencyLevel() {
return consistencyLevel;
}
public TimeUnit getPrecision() {
return precision;
}
BatchWriter getBatchWriter() {
return batchWriter;
}
public boolean isDropActionsOnQueueExhaustion() {
return dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion;
}
public Consumer<Point> getDroppedActionHandler() {
return droppedActionHandler;
}
}附件: influxdb-java | InfluxDBImpl#ping()
- 重写
influxdb-java:2.22的InfluxDBImpl#ping()方法的逻辑,以兼容OpenGemini(v1.2.0)
java
package org.influxdb.impl;
import com.squareup.moshi.JsonAdapter;
import com.squareup.moshi.Moshi;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import okhttp3.*;
import okhttp3.logging.HttpLoggingInterceptor;
import okhttp3.logging.HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level;
import okio.BufferedSource;
import org.influxdb.BatchOptions;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDB;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDBException;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDBIOException;
import org.influxdb.dto.*;
import org.influxdb.impl.*;
import org.influxdb.impl.BatchProcessor.HttpBatchEntry;
import org.influxdb.impl.BatchProcessor.UdpBatchEntry;
import org.influxdb.msgpack.MessagePackConverterFactory;
import org.influxdb.msgpack.MessagePackTraverser;
import retrofit2.Call;
import retrofit2.Callback;
import retrofit2.Converter.Factory;
import retrofit2.Response;
import retrofit2.Retrofit;
import retrofit2.converter.moshi.MoshiConverterFactory;
import java.io.EOFException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadFactory;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
import java.util.function.Consumer;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* Implementation of a InluxDB API.
* @note
* 重写 {InfluxDBImpl#ping() } 方法的逻辑,以兼容 OpenGemini
* @author
* stefan.majer [at] gmail.com
* johnny zen
* @reference-doc
* [1] https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb-java/tree/influxdb-java-2.22/src/main/java/org/influxdb
* [2] https://github.com/influxdata/influxdb-java/blob/influxdb-java-2.22/src/main/java/org/influxdb/impl/InfluxDBImpl.java
*/
@Slf4j
public class InfluxDBImpl implements InfluxDB {
private static final String APPLICATION_MSGPACK = "application/x-msgpack";
static final MediaType MEDIA_TYPE_STRING = MediaType.parse("text/plain");
private static final String SHOW_DATABASE_COMMAND_ENCODED = Query.encode("SHOW DATABASES");
/**
* This static constant holds the http logging log level expected in DEBUG mode
* It is set by System property {@code org.influxdb.InfluxDB.logLevel}.
*
* @see InfluxDB#LOG_LEVEL_PROPERTY
*/
private static final LogLevel LOG_LEVEL = LogLevel.parseLogLevel(System.getProperty(LOG_LEVEL_PROPERTY));
private final String hostName;
private String version;
private final Retrofit retrofit;
private final OkHttpClient client;
private final InfluxDBService influxDBService;
private BatchProcessor batchProcessor;
private final AtomicBoolean batchEnabled = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private final LongAdder writeCount = new LongAdder();
private final LongAdder unBatchedCount = new LongAdder();
private final LongAdder batchedCount = new LongAdder();
private volatile DatagramSocket datagramSocket;
private final HttpLoggingInterceptor loggingInterceptor;
private final GzipRequestInterceptor gzipRequestInterceptor;
private LogLevel logLevel = LogLevel.NONE;
private String database;
private String retentionPolicy = "autogen";
private ConsistencyLevel consistency = ConsistencyLevel.ONE;
private final boolean messagePack;
private Boolean messagePackSupport;
private final ChunkProccesor chunkProccesor;
/**
* Constructs a new {@code InfluxDBImpl}.
*
* @param url
* The InfluxDB server API URL
* @param username
* The InfluxDB user name
* @param password
* The InfluxDB user password
* @param okHttpBuilder
* The OkHttp Client Builder
* @param responseFormat
* The {@code ResponseFormat} to use for response from InfluxDB
* server
*/
public InfluxDBImpl(final String url, final String username, final String password,
final OkHttpClient.Builder okHttpBuilder, final ResponseFormat responseFormat) {
this(url, username, password, okHttpBuilder, new Retrofit.Builder(), responseFormat);
}
/**
* Constructs a new {@code InfluxDBImpl}.
*
* @param url
* The InfluxDB server API URL
* @param username
* The InfluxDB user name
* @param password
* The InfluxDB user password
* @param okHttpBuilder
* The OkHttp Client Builder
* @param retrofitBuilder
* The Retrofit Builder
* @param responseFormat
* The {@code ResponseFormat} to use for response from InfluxDB
* server
*/
public InfluxDBImpl(final String url, final String username, final String password,
final OkHttpClient.Builder okHttpBuilder, final Retrofit.Builder retrofitBuilder,
final ResponseFormat responseFormat) {
this.messagePack = ResponseFormat.MSGPACK.equals(responseFormat);
this.hostName = parseHost(url);
this.loggingInterceptor = new HttpLoggingInterceptor();
setLogLevel(LOG_LEVEL);
this.gzipRequestInterceptor = new GzipRequestInterceptor();
OkHttpClient.Builder clonedOkHttpBuilder = okHttpBuilder.build().newBuilder()
.addInterceptor(loggingInterceptor)
.addInterceptor(gzipRequestInterceptor);
if (username != null && password != null) {
clonedOkHttpBuilder.addInterceptor(new BasicAuthInterceptor(username, password));
}
Factory converterFactory = null;
switch (responseFormat) {
case MSGPACK:
clonedOkHttpBuilder.addInterceptor(chain -> {
Request request = chain.request().newBuilder().addHeader("Accept", APPLICATION_MSGPACK).build();
return chain.proceed(request);
});
converterFactory = MessagePackConverterFactory.create();
chunkProccesor = new MessagePackChunkProccesor();
break;
case JSON:
default:
converterFactory = MoshiConverterFactory.create();
Moshi moshi = new Moshi.Builder().build();
JsonAdapter<QueryResult> adapter = moshi.adapter(QueryResult.class);
chunkProccesor = new JSONChunkProccesor(adapter);
break;
}
this.client = clonedOkHttpBuilder.build();
Retrofit.Builder clonedRetrofitBuilder = retrofitBuilder.baseUrl(url).build().newBuilder();
this.retrofit = clonedRetrofitBuilder.client(this.client)
.addConverterFactory(converterFactory).build();
this.influxDBService = this.retrofit.create(InfluxDBService.class);
}
public InfluxDBImpl(final String url, final String username, final String password,
final OkHttpClient.Builder client) {
this(url, username, password, client, ResponseFormat.JSON);
}
InfluxDBImpl(final String url, final String username, final String password, final OkHttpClient.Builder client,
final InfluxDBService influxDBService, final JsonAdapter<QueryResult> adapter) {
super();
this.messagePack = false;
this.hostName = parseHost(url);
this.loggingInterceptor = new HttpLoggingInterceptor();
setLogLevel(LOG_LEVEL);
this.gzipRequestInterceptor = new GzipRequestInterceptor();
OkHttpClient.Builder clonedBuilder = client.build().newBuilder()
.addInterceptor(loggingInterceptor)
.addInterceptor(gzipRequestInterceptor)
.addInterceptor(new BasicAuthInterceptor(username, password));
this.client = clonedBuilder.build();
this.retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder().baseUrl(url)
.client(this.client)
.addConverterFactory(MoshiConverterFactory.create()).build();
this.influxDBService = influxDBService;
chunkProccesor = new JSONChunkProccesor(adapter);
}
public InfluxDBImpl(final String url, final String username, final String password, final OkHttpClient.Builder client,
final String database, final String retentionPolicy, final ConsistencyLevel consistency) {
this(url, username, password, client);
setConsistency(consistency);
setDatabase(database);
setRetentionPolicy(retentionPolicy);
}
private String parseHost(final String url) {
String hostName;
try {
URI uri = new URI(url);
hostName = uri.getHost();
} catch (URISyntaxException e1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to parse url: " + url, e1);
}
if (hostName == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to parse url: " + url);
}
try {
InetAddress.getByName(hostName);
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
throw new InfluxDBIOException(e);
}
return hostName;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB setLogLevel(final LogLevel logLevel) {
switch (logLevel) {
case NONE:
this.loggingInterceptor.setLevel(Level.NONE);
break;
case BASIC:
this.loggingInterceptor.setLevel(Level.BASIC);
break;
case HEADERS:
this.loggingInterceptor.setLevel(Level.HEADERS);
break;
case FULL:
this.loggingInterceptor.setLevel(Level.BODY);
break;
default:
break;
}
this.logLevel = logLevel;
return this;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public InfluxDB enableGzip() {
this.gzipRequestInterceptor.enable();
return this;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public InfluxDB disableGzip() {
this.gzipRequestInterceptor.disable();
return this;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean isGzipEnabled() {
return this.gzipRequestInterceptor.isEnabled();
}
@Override
public InfluxDB enableBatch() {
enableBatch(BatchOptions.DEFAULTS);
return this;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB enableBatch(final BatchOptions batchOptions) {
if (this.batchEnabled.get()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BatchProcessing is already enabled.");
}
this.batchProcessor = BatchProcessor
.builder(this)
.actions(batchOptions.getActions())
.exceptionHandler(batchOptions.getExceptionHandler())
.interval(batchOptions.getFlushDuration(), batchOptions.getJitterDuration(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
.threadFactory(batchOptions.getThreadFactory())
.bufferLimit(batchOptions.getBufferLimit())
.consistencyLevel(batchOptions.getConsistency())
.precision(batchOptions.getPrecision())
.dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion(batchOptions.isDropActionsOnQueueExhaustion())
.droppedActionHandler(batchOptions.getDroppedActionHandler())
.build();
this.batchEnabled.set(true);
return this;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB enableBatch(final int actions, final int flushDuration,
final TimeUnit flushDurationTimeUnit) {
enableBatch(actions, flushDuration, flushDurationTimeUnit, Executors.defaultThreadFactory());
return this;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB enableBatch(final int actions, final int flushDuration,
final TimeUnit flushDurationTimeUnit, final ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
enableBatch(actions, flushDuration, flushDurationTimeUnit, threadFactory, (points, throwable) -> { });
return this;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB enableBatch(final int actions, final int flushDuration, final TimeUnit flushDurationTimeUnit,
final ThreadFactory threadFactory,
final BiConsumer<Iterable<Point>, Throwable> exceptionHandler,
final ConsistencyLevel consistency) {
enableBatch(actions, flushDuration, flushDurationTimeUnit, threadFactory, exceptionHandler)
.setConsistency(consistency);
return this;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB enableBatch(final int actions, final int flushDuration, final TimeUnit flushDurationTimeUnit,
final ThreadFactory threadFactory,
final BiConsumer<Iterable<Point>, Throwable> exceptionHandler) {
enableBatch(actions, flushDuration, 0, flushDurationTimeUnit, threadFactory, exceptionHandler, false, null);
return this;
}
private InfluxDB enableBatch(final int actions, final int flushDuration, final int jitterDuration,
final TimeUnit durationTimeUnit, final ThreadFactory threadFactory,
final BiConsumer<Iterable<Point>, Throwable> exceptionHandler,
final boolean dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion, final Consumer<Point> droppedActionHandler) {
if (this.batchEnabled.get()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BatchProcessing is already enabled.");
}
this.batchProcessor = BatchProcessor
.builder(this)
.actions(actions)
.exceptionHandler(exceptionHandler)
.interval(flushDuration, jitterDuration, durationTimeUnit)
.threadFactory(threadFactory)
.consistencyLevel(consistency)
.dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion(dropActionsOnQueueExhaustion)
.droppedActionHandler(droppedActionHandler)
.build();
this.batchEnabled.set(true);
return this;
}
@Override
public void disableBatch() {
this.batchEnabled.set(false);
if (this.batchProcessor != null) {
this.batchProcessor.flushAndShutdown();
}
}
@Override
public boolean isBatchEnabled() {
return this.batchEnabled.get();
}
// @demo Gemini
// curl -v -XGET http://xx.yy.zz.kk:8086/ping
// Note: Unnecessary use of -X or --request, GET is already inferred.
// * Trying xx.yy.zz.kk...
// * TCP_NODELAY set
//* Connected to xx.yy.zz.kk (xx.yy.zz.kk) port 8086 (#0)
// > GET /ping HTTP/1.1
// > Host: xx.yy.zz.kk:8086
// > User-Agent: curl/7.55.1
// > Accept: */*
//>
//< HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
//< Content-Type: application/json
//< Request-Id: 50754f89-56f8-11ef-818b-fa163e301ea5
//< X-Geminidb-Build: OSS
//< X-Geminidb-Version: v1.2.0
//< X-Request-Id: 50754f89-56f8-11ef-818b-fa163e301ea5
//< Date: Sat, 10 Aug 2024 09:09:57 GMT
//<
//* Connection #0 to host xx.yy.zz.kk left intact
// @demo Influxdb
//> curl -v -XGET http://xx.yy.zz.mm:8635/ping
//Note: Unnecessary use of -X or --request, GET is already inferred.
// * Trying xx.yy.zz.mm...
// * TCP_NODELAY set
//* Connected to xx.yy.zz.mm (xx.yy.zz.mm) port 8635 (#0)
// > GET /ping HTTP/1.1
// > Host: xx.yy.zz.mm:8635
// > User-Agent: curl/7.55.1
// > Accept: */*
//>
//< HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
//< Content-Type: application/json
//< Request-Id: 736a0d01-56f8-11ef-a859-fa163e42c8ae
//< X-Influxdb-Build: OSS
//< X-Influxdb-Version: 1.7.4
//< X-Request-Id: 736a0d01-56f8-11ef-a859-fa163e42c8ae
//< Date: Sat, 10 Aug 2024 09:10:55 GMT
//<
//* Connection #0 to host xx.yy.zz.mm left intact
/**
* ping
* @note Gemini & InfluxDB
* 核心用途: 健康检测
*
* 为兼容 OpenGemini (Gemini Http Response[X-Geminidb-Version] 中使用的 Header 与 InfluxDB [X-Influxdb-Version] 的完全不同,无法识别出 version 字段,
* 1. 重写了 {@link InfluxDBImpl#ping() }
* 2. 故感兴趣的可以了解下 ping.isGood()(isGood方法本质上是判断 version == "unknown" ) 作为健康监测的判断逻辑
* @reference-doc
* [1] {@link InfluxDBImpl#ping() }
* [2] {@link InfluxDBImpl#InfluxDBImpl(String, String, String, OkHttpClient.Builder, Retrofit.Builder, ResponseFormat) }
* @return
*/
@Override
public Pong ping() {
final long started = System.currentTimeMillis();
Call<ResponseBody> call = this.influxDBService.ping();
try {
Response<ResponseBody> response = call.execute();
Headers headers = response.headers();
String version = "unknown";
for (String name : headers.toMultimap().keySet()) {
//if (null != name && ( "X-Influxdb-Version".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
if (null != name && ( "X-Influxdb-Version".equalsIgnoreCase(name) || "X-Geminidb-Version".equalsIgnoreCase(name))) {
//version = headers.get(name);
version = name + ":" + headers.get(name);
break;
}
}
Pong pong = new Pong();
pong.setVersion(version);
pong.setResponseTime(System.currentTimeMillis() - started);
return pong;
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InfluxDBIOException(e);
}
}
@Override
public String version() {
if (version == null) {
this.version = ping().getVersion();
}
return this.version;
}
@Override
public void write(final Point point) {
write(database, retentionPolicy, point);
}
@Override
public void write(final String records) {
write(database, retentionPolicy, consistency, records);
}
@Override
public void write(final List<String> records) {
write(database, retentionPolicy, consistency, records);
}
@Override
public void write(final String database, final String retentionPolicy, final Point point) {
if (this.batchEnabled.get()) {
HttpBatchEntry batchEntry = new HttpBatchEntry(point, database, retentionPolicy);
this.batchProcessor.put(batchEntry);
} else {
BatchPoints batchPoints = BatchPoints.database(database)
.retentionPolicy(retentionPolicy).build();
batchPoints.point(point);
this.write(batchPoints);
this.unBatchedCount.increment();
}
this.writeCount.increment();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void write(final int udpPort, final Point point) {
if (this.batchEnabled.get()) {
UdpBatchEntry batchEntry = new UdpBatchEntry(point, udpPort);
this.batchProcessor.put(batchEntry);
} else {
this.write(udpPort, point.lineProtocol());
this.unBatchedCount.increment();
}
this.writeCount.increment();
}
@Override
public void write(final BatchPoints batchPoints) {
this.batchedCount.add(batchPoints.getPoints().size());
//Long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
String lineProtocolStr = batchPoints.lineProtocol();
RequestBody lineProtocol = RequestBody.create(MEDIA_TYPE_STRING, lineProtocolStr);
//Long timeConsuming = System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
//log.info("batchPoints to lineProtocol | time-consuming: {}ms, lineProtocol.length:{}", timeConsuming, lineProtocolStr.length() );
String db = batchPoints.getDatabase();
if (db == null) {
db = this.database;
}
execute(this.influxDBService.writePoints(
db,
batchPoints.getRetentionPolicy(),
TimeUtil.toTimePrecision(batchPoints.getPrecision()),
batchPoints.getConsistency().value(),
lineProtocol
)
);
}
@Override
public void writeWithRetry(final BatchPoints batchPoints) {
if (isBatchEnabled()) {
batchProcessor.getBatchWriter().write(Collections.singleton(batchPoints));
} else {
write(batchPoints);
}
}
@Override
public void write(final String database, final String retentionPolicy, final ConsistencyLevel consistency,
final TimeUnit precision, final String records) {
RequestBody requestBody = RequestBody.create(MEDIA_TYPE_STRING, records);
execute(
this.influxDBService.writePoints(
database,
retentionPolicy,
TimeUtil.toTimePrecision(precision),
consistency.value(),
requestBody
)
);
}
@Override
public void write(final String database, final String retentionPolicy, final ConsistencyLevel consistency,
final String records) {
write(database, retentionPolicy, consistency, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS, records);
}
@Override
public void write(final String database, final String retentionPolicy, final ConsistencyLevel consistency,
final List<String> records) {
write(database, retentionPolicy, consistency, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS, records);
}
@Override
public void write(final String database, final String retentionPolicy, final ConsistencyLevel consistency,
final TimeUnit precision, final List<String> records) {
write(database, retentionPolicy, consistency, precision, String.join("\n", records));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void write(final int udpPort, final String records) {
initialDatagramSocket();
byte[] bytes = records.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
try {
datagramSocket.send(new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, new InetSocketAddress(hostName, udpPort)));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InfluxDBIOException(e);
}
}
private void initialDatagramSocket() {
if (datagramSocket == null) {
synchronized (InfluxDBImpl.class) {
if (datagramSocket == null) {
try {
datagramSocket = new DatagramSocket();
} catch (SocketException e) {
throw new InfluxDBIOException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void write(final int udpPort, final List<String> records) {
write(udpPort, String.join("\n", records));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public QueryResult query(final Query query) {
return executeQuery(callQuery(query));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void query(final Query query, final Consumer<QueryResult> onSuccess, final Consumer<Throwable> onFailure) {
final Call<QueryResult> call = callQuery(query);
call.enqueue(new Callback<QueryResult>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(final Call<QueryResult> call, final Response<QueryResult> response) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
onSuccess.accept(response.body());
} else {
Throwable t = null;
String errorBody = null;
try {
if (response.errorBody() != null) {
errorBody = response.errorBody().string();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
t = e;
}
if (t != null) {
onFailure.accept(new InfluxDBException(response.message(), t));
} else if (errorBody != null) {
onFailure.accept(new InfluxDBException(response.message() + " - " + errorBody));
} else {
onFailure.accept(new InfluxDBException(response.message()));
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(final Call<QueryResult> call, final Throwable throwable) {
onFailure.accept(throwable);
}
});
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void query(final Query query, final int chunkSize, final Consumer<QueryResult> onNext) {
query(query, chunkSize, onNext, () -> { });
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void query(final Query query, final int chunkSize, final BiConsumer<Cancellable, QueryResult> onNext) {
query(query, chunkSize, onNext, () -> { });
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void query(final Query query, final int chunkSize, final Consumer<QueryResult> onNext,
final Runnable onComplete) {
query(query, chunkSize, (cancellable, queryResult) -> onNext.accept(queryResult), onComplete);
}
@Override
public void query(final Query query, final int chunkSize, final BiConsumer<Cancellable, QueryResult> onNext,
final Runnable onComplete) {
query(query, chunkSize, onNext, onComplete, null);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void query(final Query query, final int chunkSize, final BiConsumer<Cancellable, QueryResult> onNext,
final Runnable onComplete, final Consumer<Throwable> onFailure) {
Call<ResponseBody> call;
if (query instanceof BoundParameterQuery) {
BoundParameterQuery boundParameterQuery = (BoundParameterQuery) query;
call = this.influxDBService.query(getDatabase(query), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded(), chunkSize,
boundParameterQuery.getParameterJsonWithUrlEncoded());
} else {
if (query.requiresPost()) {
call = this.influxDBService.query(getDatabase(query), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded(), chunkSize, null);
} else {
call = this.influxDBService.query(getDatabase(query), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded(), chunkSize);
}
}
call.enqueue(new Callback<ResponseBody>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(final Call<ResponseBody> call, final Response<ResponseBody> response) {
Cancellable cancellable = new Cancellable() {
@Override
public void cancel() {
call.cancel();
}
@Override
public boolean isCanceled() {
return call.isCanceled();
}
};
try {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
ResponseBody chunkedBody = response.body();
chunkProccesor.process(chunkedBody, cancellable, onNext, onComplete);
} else {
// REVIEW: must be handled consistently with IOException.
ResponseBody errorBody = response.errorBody();
if (errorBody != null) {
InfluxDBException influxDBException = new InfluxDBException(errorBody.string());
if (onFailure == null) {
throw influxDBException;
} else {
onFailure.accept(influxDBException);
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
QueryResult queryResult = new QueryResult();
queryResult.setError(e.toString());
onNext.accept(cancellable, queryResult);
//passing null onFailure consumer is here for backward compatibility
//where the empty queryResult containing error is propagating into onNext consumer
if (onFailure != null) {
onFailure.accept(e);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
call.cancel();
if (onFailure != null) {
onFailure.accept(e);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(final Call<ResponseBody> call, final Throwable t) {
if (onFailure == null) {
throw new InfluxDBException(t);
} else {
onFailure.accept(t);
}
}
});
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public QueryResult query(final Query query, final TimeUnit timeUnit) {
Call<QueryResult> call;
if (query instanceof BoundParameterQuery) {
BoundParameterQuery boundParameterQuery = (BoundParameterQuery) query;
call = this.influxDBService.query(getDatabase(query),
TimeUtil.toTimePrecision(timeUnit), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded(),
boundParameterQuery.getParameterJsonWithUrlEncoded());
} else {
if (query.requiresPost()) {
call = this.influxDBService.query(getDatabase(query),
TimeUtil.toTimePrecision(timeUnit), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded(), null);
} else {
call = this.influxDBService.query(getDatabase(query),
TimeUtil.toTimePrecision(timeUnit), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded());
}
}
return executeQuery(call);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void createDatabase(final String name) {
Preconditions.checkNonEmptyString(name, "name");
String createDatabaseQueryString = String.format("CREATE DATABASE \"%s\"", name);
executeQuery(this.influxDBService.postQuery(Query.encode(createDatabaseQueryString)));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void deleteDatabase(final String name) {
executeQuery(this.influxDBService.postQuery(Query.encode("DROP DATABASE \"" + name + "\"")));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public List<String> describeDatabases() {
QueryResult result = executeQuery(this.influxDBService.postQuery(SHOW_DATABASE_COMMAND_ENCODED));
// {"results":[{"series":[{"name":"databases","columns":["name"],"values":[["mydb"]]}]}]}
// Series [name=databases, columns=[name], values=[[mydb], [unittest_1433605300968]]]
List<List<Object>> databaseNames = result.getResults().get(0).getSeries().get(0).getValues();
List<String> databases = new ArrayList<>();
if (databaseNames != null) {
for (List<Object> database : databaseNames) {
databases.add(database.get(0).toString());
}
}
return databases;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public boolean databaseExists(final String name) {
List<String> databases = this.describeDatabases();
for (String databaseName : databases) {
if (databaseName.trim().equals(name)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* Calls the influxDBService for the query.
*/
private Call<QueryResult> callQuery(final Query query) {
Call<QueryResult> call;
if (query instanceof BoundParameterQuery) {
BoundParameterQuery boundParameterQuery = (BoundParameterQuery) query;
call = this.influxDBService.postQuery(getDatabase(query), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded(),
boundParameterQuery.getParameterJsonWithUrlEncoded());
} else {
if (query.requiresPost()) {
call = this.influxDBService.postQuery(getDatabase(query), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded());
} else {
call = this.influxDBService.query(getDatabase(query), query.getCommandWithUrlEncoded());
}
}
return call;
}
static class ErrorMessage {
public String error;
}
private boolean checkMessagePackSupport() {
Matcher matcher = Pattern.compile("(\\d+\\.*)+").matcher(version());
if (!matcher.find()) {
return false;
}
String s = matcher.group();
String[] versionNumbers = s.split("\\.");
final int major = Integer.parseInt(versionNumbers[0]);
final int minor = Integer.parseInt(versionNumbers[1]);
final int fromMinor = 4;
return (major >= 2) || ((major == 1) && (minor >= fromMinor));
}
private QueryResult executeQuery(final Call<QueryResult> call) {
if (messagePack) {
if (messagePackSupport == null) {
messagePackSupport = checkMessagePackSupport();
}
if (!messagePackSupport) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
"MessagePack format is only supported from InfluxDB version 1.4 and later");
}
}
return execute(call);
}
private <T> T execute(final Call<T> call) {
try {
Response<T> response = call.execute();
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
return response.body();
}
try (ResponseBody errorBody = response.errorBody()) {
if (messagePack) {
throw InfluxDBException.buildExceptionForErrorState(errorBody.byteStream());
} else {
throw InfluxDBException.buildExceptionForErrorState(errorBody.string());
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InfluxDBIOException(e);
}
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void flush() {
if (!batchEnabled.get()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("BatchProcessing is not enabled.");
}
batchProcessor.flush();
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void close() {
try {
this.disableBatch();
} finally {
if (datagramSocket != null && !datagramSocket.isClosed()) {
datagramSocket.close();
}
}
this.client.dispatcher().executorService().shutdown();
this.client.connectionPool().evictAll();
}
@Override
public InfluxDB setConsistency(final ConsistencyLevel consistency) {
this.consistency = consistency;
return this;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB setDatabase(final String database) {
this.database = database;
return this;
}
@Override
public InfluxDB setRetentionPolicy(final String retentionPolicy) {
this.retentionPolicy = retentionPolicy;
return this;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void createRetentionPolicy(final String rpName, final String database, final String duration,
final String shardDuration, final int replicationFactor, final boolean isDefault) {
Preconditions.checkNonEmptyString(rpName, "retentionPolicyName");
Preconditions.checkNonEmptyString(database, "database");
Preconditions.checkNonEmptyString(duration, "retentionDuration");
Preconditions.checkDuration(duration, "retentionDuration");
if (shardDuration != null && !shardDuration.isEmpty()) {
Preconditions.checkDuration(shardDuration, "shardDuration");
}
Preconditions.checkPositiveNumber(replicationFactor, "replicationFactor");
StringBuilder queryBuilder = new StringBuilder("CREATE RETENTION POLICY \"");
queryBuilder.append(rpName)
.append("\" ON \"")
.append(database)
.append("\" DURATION ")
.append(duration)
.append(" REPLICATION ")
.append(replicationFactor);
if (shardDuration != null && !shardDuration.isEmpty()) {
queryBuilder.append(" SHARD DURATION ");
queryBuilder.append(shardDuration);
}
if (isDefault) {
queryBuilder.append(" DEFAULT");
}
executeQuery(this.influxDBService.postQuery(Query.encode(queryBuilder.toString())));
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void createRetentionPolicy(final String rpName, final String database, final String duration,
final int replicationFactor, final boolean isDefault) {
createRetentionPolicy(rpName, database, duration, null, replicationFactor, isDefault);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void createRetentionPolicy(final String rpName, final String database, final String duration,
final String shardDuration, final int replicationFactor) {
createRetentionPolicy(rpName, database, duration, null, replicationFactor, false);
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @param rpName the name of the retentionPolicy
* @param database the name of the database
*/
@Override
public void dropRetentionPolicy(final String rpName, final String database) {
Preconditions.checkNonEmptyString(rpName, "retentionPolicyName");
Preconditions.checkNonEmptyString(database, "database");
StringBuilder queryBuilder = new StringBuilder("DROP RETENTION POLICY \"");
queryBuilder.append(rpName)
.append("\" ON \"")
.append(database)
.append("\"");
executeQuery(this.influxDBService.postQuery(Query.encode(queryBuilder.toString())));
}
private String getDatabase(final Query query) {
String db = query.getDatabase();
if (db == null) {
return this.database;
}
return db;
}
private interface ChunkProccesor {
void process(ResponseBody chunkedBody, Cancellable cancellable,
BiConsumer<Cancellable, QueryResult> consumer, Runnable onComplete) throws IOException;
}
private class MessagePackChunkProccesor implements ChunkProccesor {
@Override
public void process(final ResponseBody chunkedBody, final Cancellable cancellable,
final BiConsumer<Cancellable, QueryResult> consumer, final Runnable onComplete)
throws IOException {
MessagePackTraverser traverser = new MessagePackTraverser();
try (InputStream is = chunkedBody.byteStream()) {
for (Iterator<QueryResult> it = traverser.traverse(is).iterator(); it.hasNext() && !cancellable.isCanceled();) {
QueryResult result = it.next();
consumer.accept(cancellable, result);
}
}
if (!cancellable.isCanceled()) {
onComplete.run();
}
}
}
private class JSONChunkProccesor implements ChunkProccesor {
private JsonAdapter<QueryResult> adapter;
public JSONChunkProccesor(final JsonAdapter<QueryResult> adapter) {
this.adapter = adapter;
}
@Override
public void process(final ResponseBody chunkedBody, final Cancellable cancellable,
final BiConsumer<Cancellable, QueryResult> consumer, final Runnable onComplete)
throws IOException {
try {
BufferedSource source = chunkedBody.source();
while (!cancellable.isCanceled()) {
QueryResult result = adapter.fromJson(source);
if (result != null) {
consumer.accept(cancellable, result);
}
}
} catch (EOFException e) {
QueryResult queryResult = new QueryResult();
queryResult.setError("DONE");
consumer.accept(cancellable, queryResult);
if (!cancellable.isCanceled()) {
onComplete.run();
}
} finally {
chunkedBody.close();
}
}
}
}Y 推荐文献
- Influxdb