目录
[5、Styled Component](#5、Styled Component)
[列表:ScrollView + map()、SetionList、FlatList、VirtualList、FlashList](#列表:ScrollView + map()、SetionList、FlatList、VirtualList、FlashList)
[FlashList 主要特性:](#FlashList 主要特性:)
TextInput、Switch、ActivityIndicator
[React Native Reanimated(推荐)](#React Native Reanimated(推荐))
继ReactNative基础总结(https://blog.csdn.net/qq_50909707/article/details/127788413)后,再次梳理出此文章。
一、路由
参考官方文档:https://docs.expo.dev/tutorial/add-navigation/
1、基于文件的路由框架
官网文档描述:
Expo路由器基础知识
Expo Router 是一个基于文件的路由框架,适用于 React Native 和 Web 应用。它管理屏幕间的导航,并在多个平台上使用相同的组件。要开始使用,我们需要了解以下约定:
- 应用目录:一个特殊的目录,仅包含路由及其布局。添加到此目录的任何文件都会成为我们原生应用中的一个屏幕,同时也会作为网页显示。
- 根布局:app/_layout.tsx文件。它定义了共享的 UI 元素,例如标题栏和标签栏,以便它们在不同的路由之间保持一致。
- 文件名约定:索引 文件名(例如index.tsx)与其父目录匹配,不添加路径段。例如,app目录中的index.tsx文件与 route匹配。
/ - 路由文件默认导出 React 组件。它可以采用 .router 、
.js.js.jsx、.ts.js 或.tsx.js 扩展名。 - Android、iOS 和网页版共享统一的导航结构。
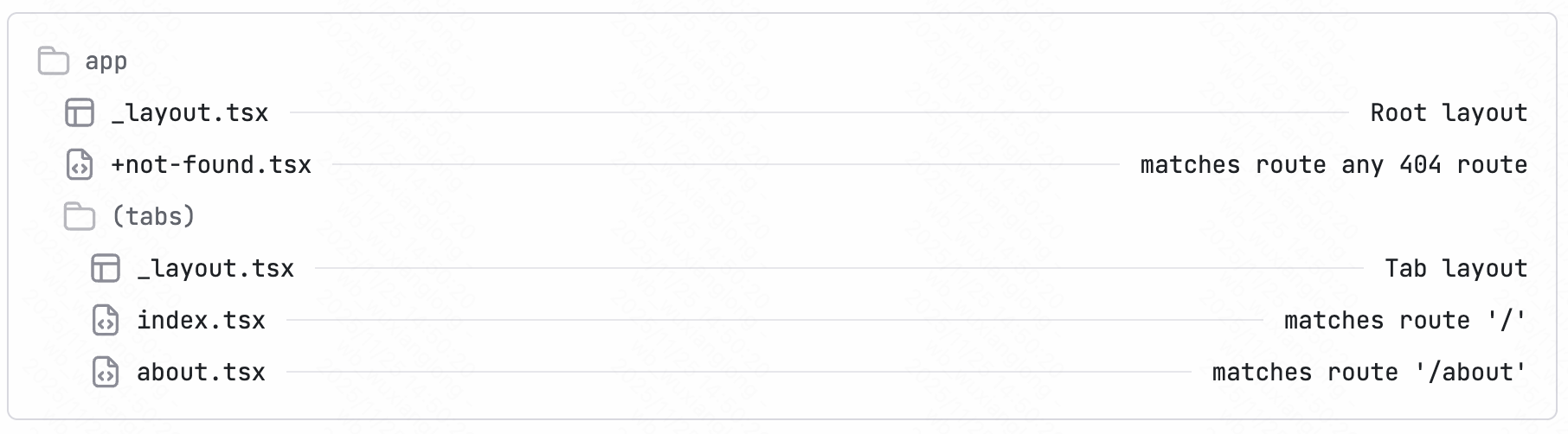
个人描述:
简单得说,expo将路由通过文件夹进行管理,路由文件都存放在app文件夹下,如图:
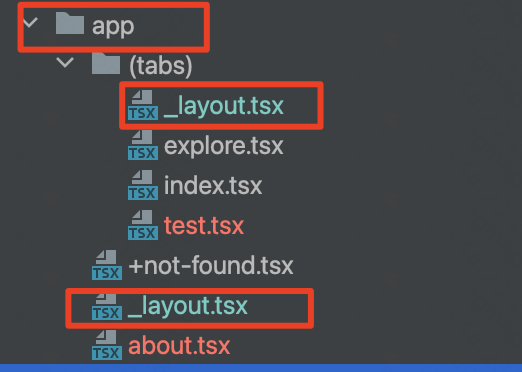
通过app文件夹作为基准进行路由,如:
"/app/index" 对应 "/" 这个根路径pathname;"/app/(tabs)/index"对应"/(tabs)"这个tabs目录的index根页面;"/app/about"对应"/about"路径;"/app/(tabs)/explore"对应"/(tabs)/expore"路径,以此类推。
我们可以通过expo提供的路由标签或api来进行调用pathname进行路由跳转。
类似于Web框架Nextjs框架里的路由文件夹管理。
2、路由配置
在app文件夹下创建的组件会被expo自动生成对应路由,如:app/test02.tsx文件会生成/test02的路由。
对应路由页面样式和相关参数的配置可以通过以下来实现,需要注意的是,对应路由即使不在_layout文件里配置也会生效,只是在_layout页面可以整体配置对应页面的参数和样式,如:
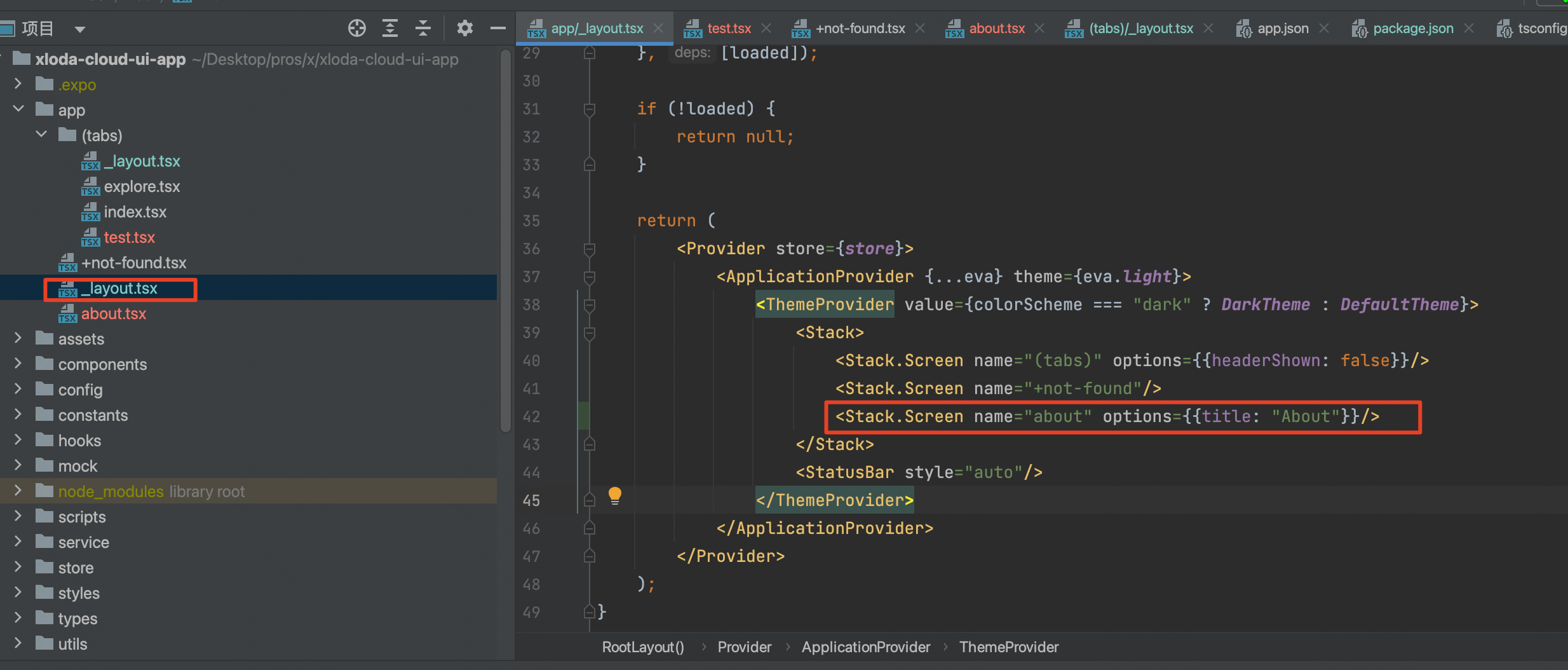
Stack栈代表着一个路由,name属性与对应层级的文件名称对应,如:about.tsx对应name="about"。
特别地,tab页通过配置Tab.Screen标签的name来进行配置,名称也是对应关系,如图:
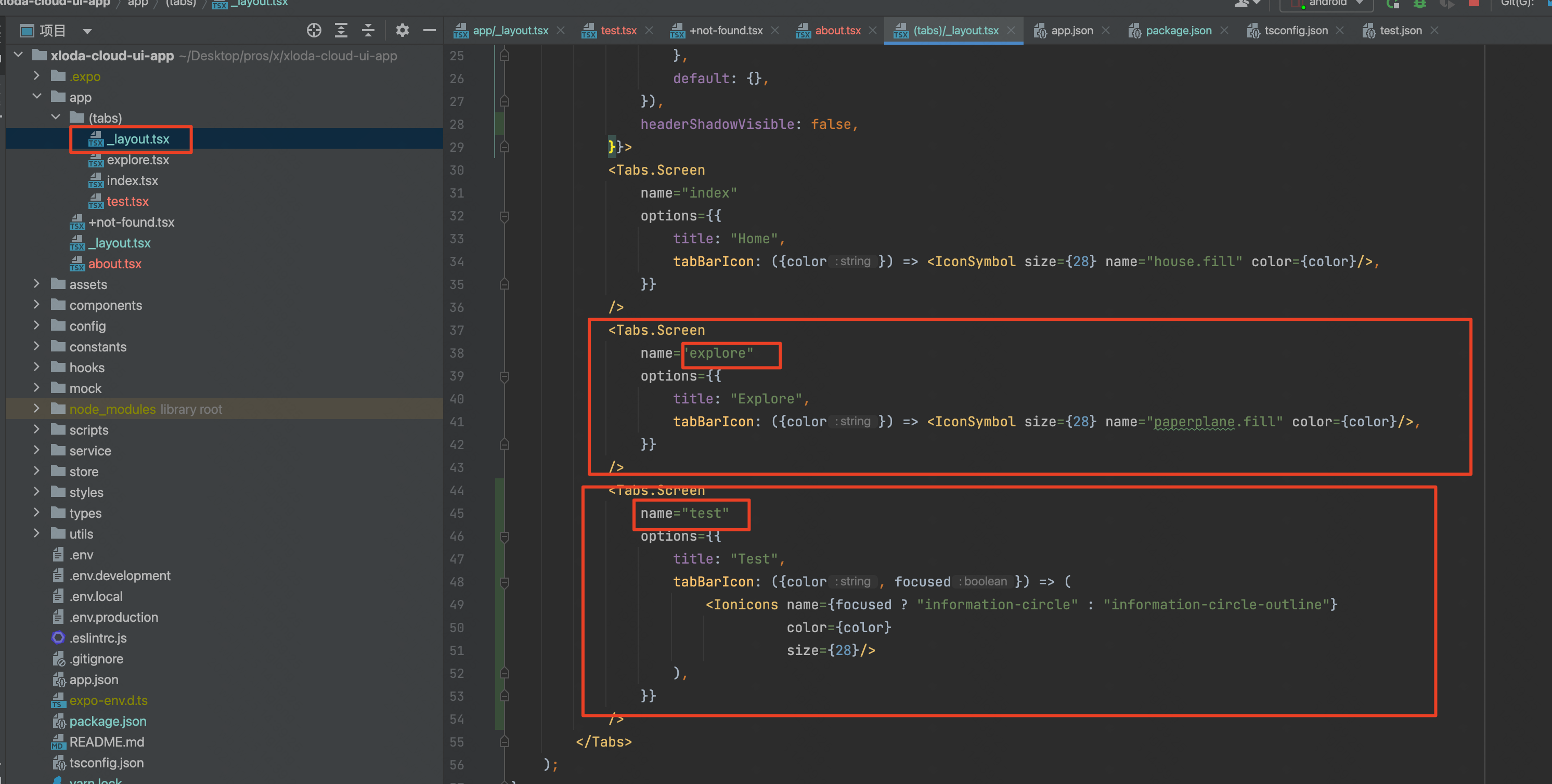
通过配置类似标签来实现路由注册。
3、_layout文件
这个文件是公共样式和路由配置的核心文件,如全局的公共组件可以在/app/_layout.tsx中进行配置,tab页的公共样式组件可以在/app/(tabs)/_layout.tsx文件中配置。
如:
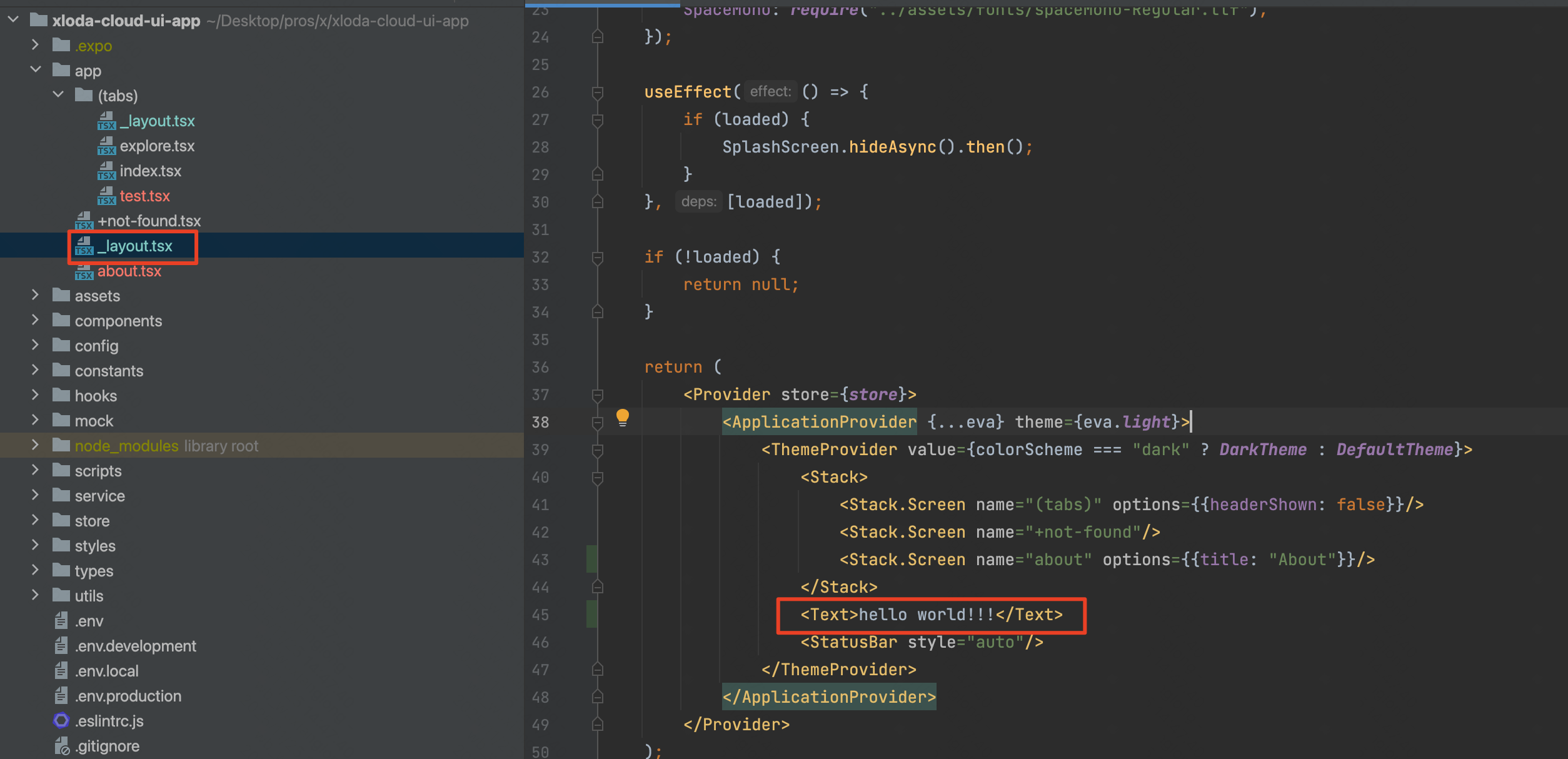
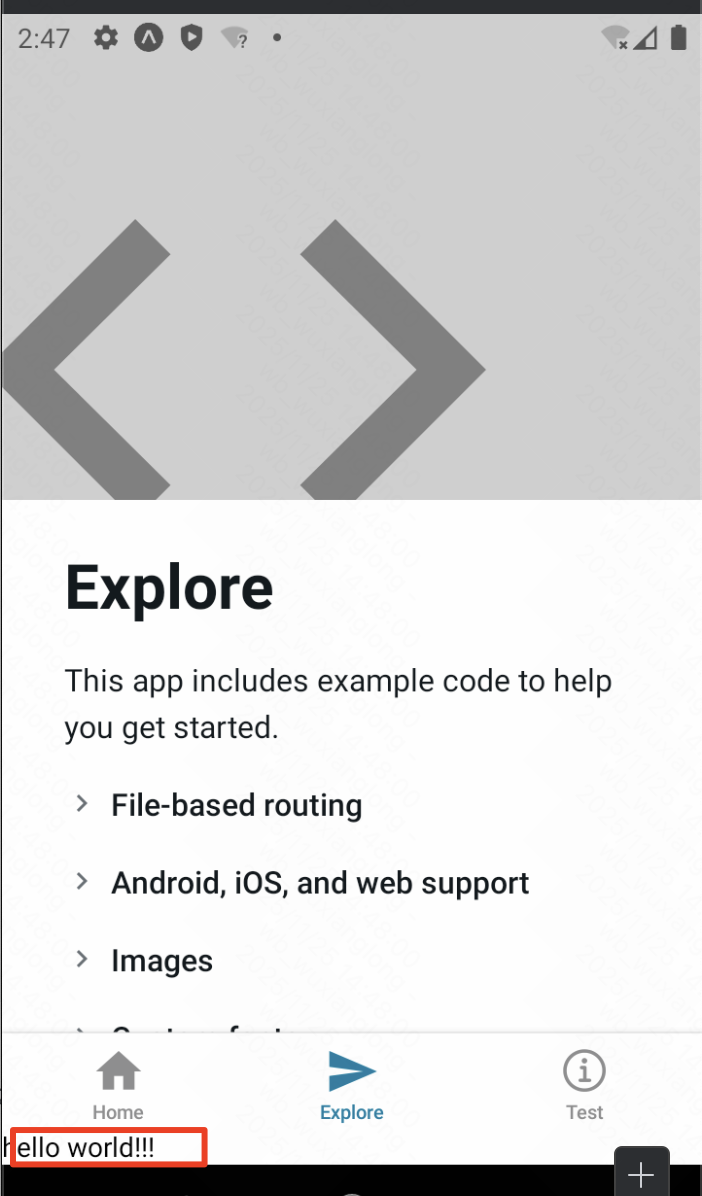
layout会层层递进生效!
另外,tab页的layout可以在Tabs标签上配置属性以实现tab栏的样式自定义风格,
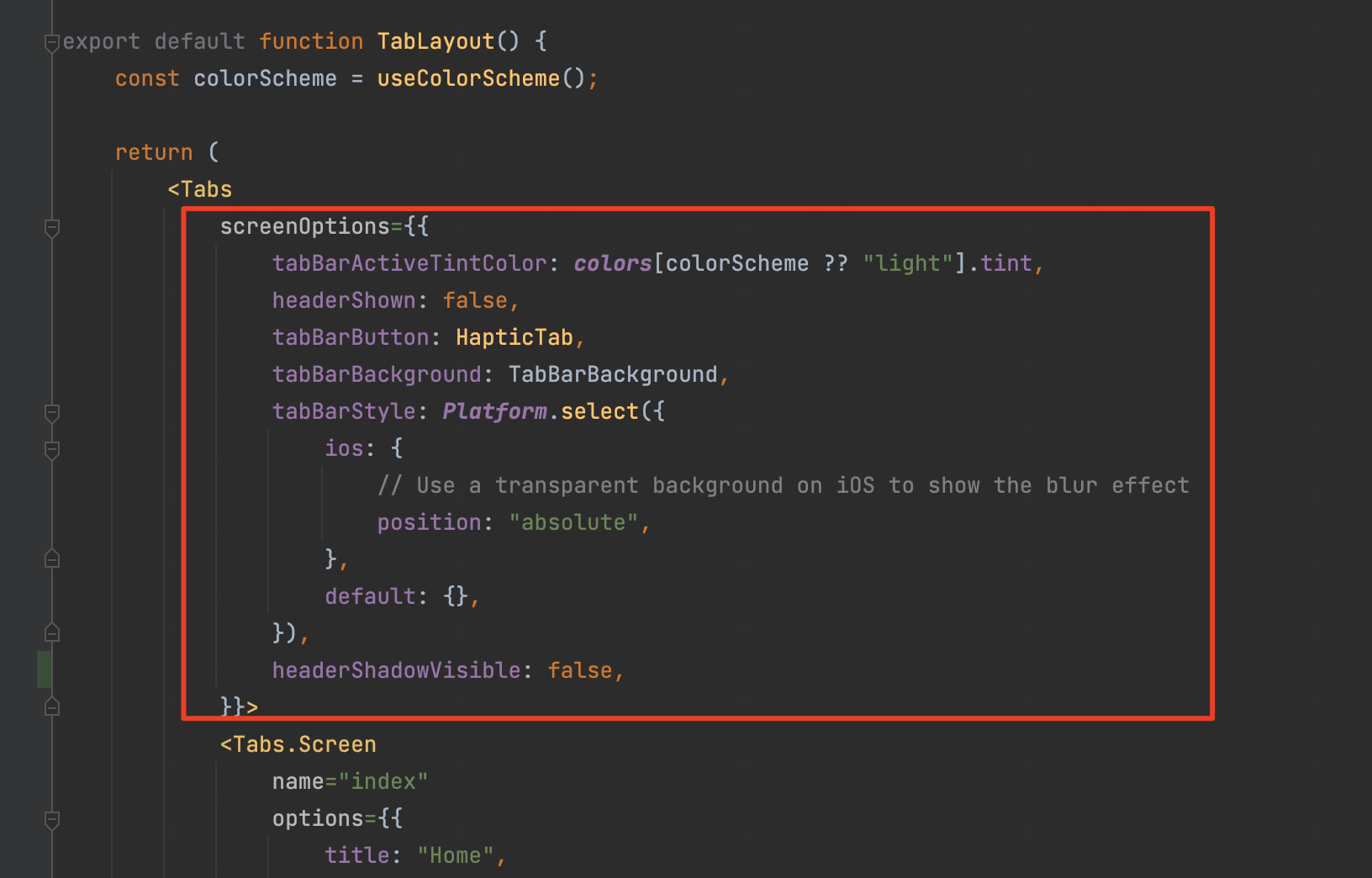
参考文档:https://docs.expo.dev/tutorial/add-navigation/
二、样式
1、StyleSheet
在reactNative里不能直接使用css等样式管理了,我们需要使用StyleSheet来进行样式设置。
通过StyleSheet.create的静态方法进行设置。标签的style属性可以传入单个对象,也可以是一个样式对象数组,具体参考案例代码。
案例:
javascript
import {View, Text, StyleSheet} from "react-native";
export default function Home() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Text style={styles.text}>标题</Text>
<Text style={[styles.text, styles.child]}>内容</Text>
<Text style={{color: "red"}}>直接设置</Text>
<Text style={[styles.text, styles.child, {color: "yellow"}]}>混合使用</Text>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
padding: 15,
margin: 10,
},
text: {
fontSize: 18,
color: "blue",
},
child: {
marginTop: 5,
}
});2、注意事项
值得注意的是,在ReactNative中样式默认是不会被子标签继承的。
(1)一般情况,默认不继承:
javascript
<View style={{fontSize: 20, color: 'red'}}>
<Text>这个文本不会继承字体大小和颜色</Text>
</View>效果:
上面的 Text 组件不会自动继承 fontSize 和 color。
特殊情况,文本样式继承:
只有文本相关的样式在 Text 组件内部会部分继承:
javascript
<Text style={{fontSize: 20, color: 'red', fontWeight: 'bold'}}>
父文本
<Text>子文本会继承字体样式</Text>
</Text>效果:
(2) ReactNative默认是flex布局,与web布局的flex有些差别,ReactNative默认的flex-direction是column,而网页中默认的flex布局是row。

(3)样式不加像素单位, 即:不能加px,vh,vw等,但可以是百分比。
(4) StyleSheet不支持类似CSS那样的伪类选择器(Styled-Component可以实现这点)。
3、StyleSheet.create和直接传对象的区别
在 React Native 中,使用 StyleSheet.create 和直接使用对象字面量在功能上都能工作,但它们有一些重要的区别:
(1)关键区别
-
StyleSheet.create会将样式序列化并发送到原生端,提升渲染性能 -
直接使用对象每次渲染都会创建新的对象,可能影响性能
(2)验证和错误提示
StyleSheet.create 会在开发时进行样式验证:
javascript
// 这会给出警告
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
invalidProp: 'value', // 无效属性会警告
},
});
// 直接对象不会验证
const styles = {
container: {
flex: 1,
invalidProp: 'value', // 无警告
},
};(3)引用方式
javascript
// StyleSheet.create - 推荐
<View style={styles.container} />
// 直接对象
<View style={styles.container} /> // 看起来一样,但内部处理不同
// 内联对象 - 不推荐(每次渲染都创建新对象)
<View style={{ flex: 1, backgroundColor: '#fff' }} />(4)动态样式处理
对于动态样式,推荐结合使用:
javascript
const MyComponent = ({ isActive }) => {
return (
<View style={[
styles.container,
isActive && styles.active, // 条件样式
{ marginTop: 10 } // 动态值
]}>
<Text>内容</Text>
</View>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
padding: 16,
backgroundColor: '#f0f0f0',
},
active: {
backgroundColor: '#007AFF',
},
});普通场景推荐使用StyleSheet.create
4、样式管理
由于ReactNative的样式都是通过js对象来赋值的,我们可以通过js或ts文件来存储对应的样式,再通过引入样式文件的形式赋值给对应的style属性。
对于容器包裹的命名格式可以进行规范:如下:
javascript
// 通过命名约定来模拟嵌套
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
padding: 20,
},
'container__header': {
fontSize: 24,
fontWeight: 'bold',
},
'container__content': {
marginTop: 10,
},
'container__content__text': {
fontSize: 16,
color: '#666',
},
});对于大型项目或样式需要动态渲染的项目,可考虑使用Styled-Components进行管理。
javascript
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
const Container = styled.View`
flex: 1;
padding: 20px;
.header {
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.content {
margin-top: 10px;
.text {
font-size: 16px;
color: #666;
}
}
`;
// 使用
<Container>
<Text className="header">标题</Text>
<View className="content">
<Text className="text">内容</Text>
</View>
</Container>
5、Styled Component
官方文档:https://styled-components.com/docs
(1)安装依赖
yarn add styled-components(2)简单案例
javascript
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
// 创建样式化的 View 组件
const Container = styled.View`
flex: 1;
background-color: #f5f5f5;
padding: 20px;
`;
// 创建样式化的 Text 组件
const Title = styled.Text`
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
color: yellow;
margin-bottom: 10px;
`;
// 创建样式化的 Button 组件
const Button = styled.TouchableOpacity`
background-color: #007bff;
padding: 12px 24px;
border-radius: 8px;
align-items: center;
`;
const ButtonText = styled.Text`
color: white;
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: 600;
`;
// 使用示例
export default function Home() {
return (
<Container>
<Title>欢迎使用 Styled Components</Title>
<Button onPress={() => console.log('按钮点击')}>
<ButtonText>点击我</ButtonText>
</Button>
</Container>
);
}效果:
styled.ReactNative里的核心组件名表示选择类别,再赋予样式,类似于web开发中的css的样式设置。
(3)支持所有核心组件
javascript
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
// 所有 React Native 核心组件都支持
const StyledView = styled.View`
/* 样式 */
`;
const StyledText = styled.Text`
/* 样式 */
`;
const StyledImage = styled.Image`
/* 样式 */
`;
const StyledScrollView = styled.ScrollView`
/* 样式 */
`;
const StyledFlatList = styled.FlatList`
/* 样式 */
`;
const StyledTextInput = styled.TextInput`
/* 样式 */
`;
const StyledTouchableOpacity = styled.TouchableOpacity`
/* 样式 */
`;
const StyledTouchableHighlight = styled.TouchableHighlight`
/* 样式 */
`;(4)高级功能-props动态样式
javascript
import styled from "styled-components/native";
import {Text} from "react-native";
// 根据 props 动态改变样式
const DynamicButton = styled.TouchableOpacity`
background-color: ${(props: any) =>
props?.primary ? "#007bff" :
props?.secondary ? "#6c757d" :
props?.success ? "#28a745" :
"#e9ecef"
};
padding: ${(props: any) => props?.large ? "16px 32px" : "12px 24px"};
border-radius: ${(props: any) => props?.round ? "50px" : "8px"};
opacity: ${(props: any) => props?.disabled ? 0.6 : 1};
`;
// 使用示例
export default function Home() {
return (
<>
<DynamicButton primary>
<Text>主要按钮</Text>
</DynamicButton>
<DynamicButton secondary large>
<Text>大号次要按钮</Text>
</DynamicButton>
<DynamicButton success round disabled>
<Text>圆形成功按钮</Text>
</DynamicButton>
</>
);
}效果:
这里可以通过配置组件动态参数来实现样式配置。
(5)高级功能-继承样式
javascript
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
// 基础按钮样式
const BaseButton = styled.TouchableOpacity`
padding: 12px 24px;
border-radius: 8px;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
`;
// 继承基础按钮样式
const PrimaryButton = styled(BaseButton)`
background-color: #007bff;
`;
const DangerButton = styled(BaseButton)`
background-color: #dc3545;
`;
const OutlineButton = styled(BaseButton)`
background-color: transparent;
border: 2px solid #007bff;
`;(6)高级功能-主题theme
javascript
// 1. 创建主题
import styled, {ThemeProvider} from "styled-components/native";
const theme = {
colors: {
primary: "#007bff",
secondary: "#6c757d",
success: "#28a745",
danger: "#dc3545",
warning: "#ffc107",
info: "#17a2b8",
light: "#f8f9fa",
dark: "#343a40",
background: "#f5f5f5",
text: "#212529",
white: "#ffffff",
},
fonts: {
regular: "System",
bold: "System",
light: "System",
},
spacing: {
xs: 4,
sm: 8,
md: 16,
lg: 24,
xl: 32,
},
borderRadius: {
sm: 4,
md: 8,
lg: 16,
round: 50,
}
};
// 2. 在 App 中提供主题
export default function App() {
return (
<ThemeProvider theme={theme}>
<ThemedButton>
<ThemedText>Theme!!!!</ThemedText>
</ThemedButton>
</ThemeProvider>
);
}
// 3. 在组件中使用主题
const ThemedButton = styled.TouchableOpacity`
background-color: ${props => props.theme.colors.primary};
padding: ${props => props.theme.spacing.md}px ${props => props.theme.spacing.lg}px;
border-radius: ${props => props.theme.borderRadius.md}px;
`;
const ThemedText = styled.Text`
color: ${props => props.theme.colors.text};
font-family: ${props => props.theme.fonts.regular};
`;效果:
(7)高级功能-使用CSS辅助函数
javascript
import styled, { css } from 'styled-components/native';
// 定义可重用的样式块
const shadowStyle = css`
shadow-color: #000;
shadow-offset: 0px 2px;
shadow-opacity: 0.25;
shadow-radius: 3.84px;
elevation: 5;
`;
const flexCenter = css`
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
`;
// 在组件中使用
const Card = styled.View`
background-color: white;
border-radius: 12px;
padding: 16px;
${shadowStyle}
${props => props.centered && flexCenter}
`;这就类似于sass、less中的样式继承。
(8)高级功能-媒体查询media(响应式)
javascript
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
// 定义断点
const breakpoints = {
small: 576,
medium: 768,
large: 992,
xlarge: 1200,
};
// 创建媒体查询辅助函数
const media = Object.keys(breakpoints).reduce((acc, label) => {
acc[label] = (...args) => css`
@media (min-width: ${breakpoints[label]}px) {
${css(...args)}
}
`;
return acc;
}, {});
// 使用媒体查询
const ResponsiveContainer = styled.View`
flex: 1;
padding: 16px;
${media.small`
padding: 20px;
`}
${media.medium`
padding: 24px;
`}
${media.large`
padding: 32px;
`}
`;类似于web开发中样式在不同尺寸中的响应式控制。
(9)性能优化
1、优先选用性能最好的StyleSheet,其次需要功能高度自定义化可以使用Styled-Component;
2、样组件的位置。
javascript
// 1. 避免在 render 中创建新的样式组件
// ❌ 错误做法(每次渲染都创建新组件)
function BadExample({ color }) {
const BadStyledText = styled.Text`
color: ${color};
`;
return <BadStyledText>文本</BadStyledText>;
}
// ✅ 正确做法(组件在外部定义)
const GoodStyledText = styled.Text`
color: ${props => props.color};
`;
function GoodExample({ color }) {
return <GoodStyledText color={color}>文本</GoodStyledText>;
}
// 2. 使用 useTheme hook(避免 props drilling)
import { useTheme } from 'styled-components/native';
function ThemedComponent() {
const theme = useTheme();
return (
<View style={{ backgroundColor: theme.colors.background }}>
<Text style={{ color: theme.colors.text }}>使用主题</Text>
</View>
);
}(10)使用ts泛型
javascript
import styled from 'styled-components/native';
// 定义 Props 接口
interface ButtonProps {
primary?: boolean;
size?: 'small' | 'medium' | 'large';
disabled?: boolean;
}
// 使用泛型定义样式组件
const StyledButton = styled.TouchableOpacity<ButtonProps>`
background-color: ${props => props.primary ? '#007bff' : '#6c757d'};
padding: ${props => {
switch (props.size) {
case 'small': return '8px 16px';
case 'large': return '16px 32px';
default: return '12px 24px';
}
}};
opacity: ${props => props.disabled ? 0.6 : 1};
`;6、transform属性(补充)
在js中书写transform属性和web端书写有些差别,需要书写为如下格式:
javascript
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
transform: [
{ translateX: 100 },
{ rotate: '45deg' }
] as ViewStyle['transform']
},
})加入类型判断以编码ts报红。
此外,还可以结合动画一起实现过渡效果,详情见下面的动画部分总结。
javascript
import { Animated } from 'react-native';
// ✅ 推荐:使用原生驱动
Animated.timing(animatedValue, {
toValue: 1,
duration: 300,
useNativeDriver: true, // 启用原生驱动
}).start();
// 在样式中使用
<Animated.View style={{
transform: [
{ translateX: animatedValue.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 1],
outputRange: [0, 100]
})}
]
}} />三、基础组件
1、概览
核心组件和原生组件
参考:https://reactnative.dev/docs/intro-react-native-components
ReactNative中的核心组件经过编译会对应生成app中的原生组件,示例如图:
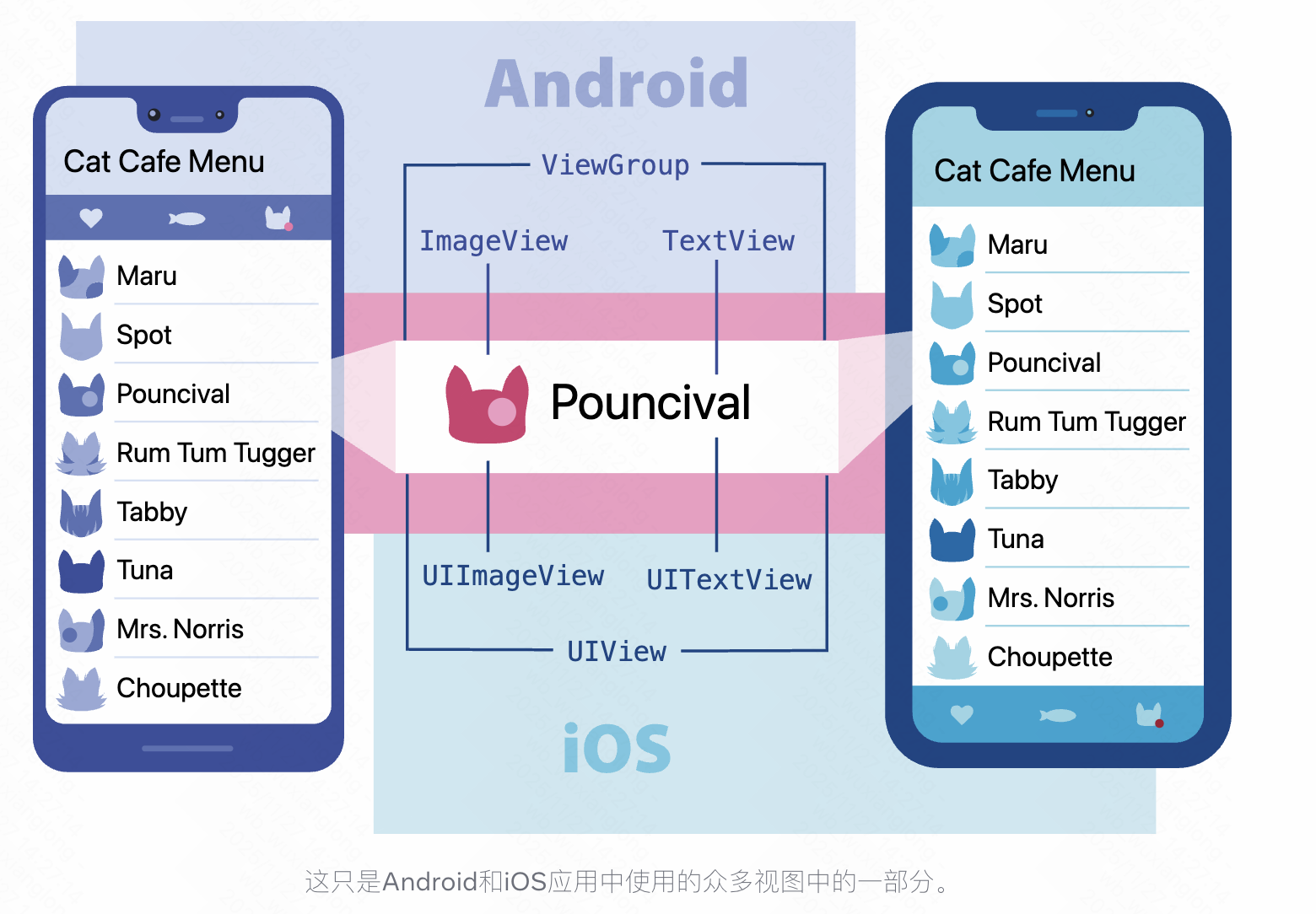
reactNative的核心组件列表:
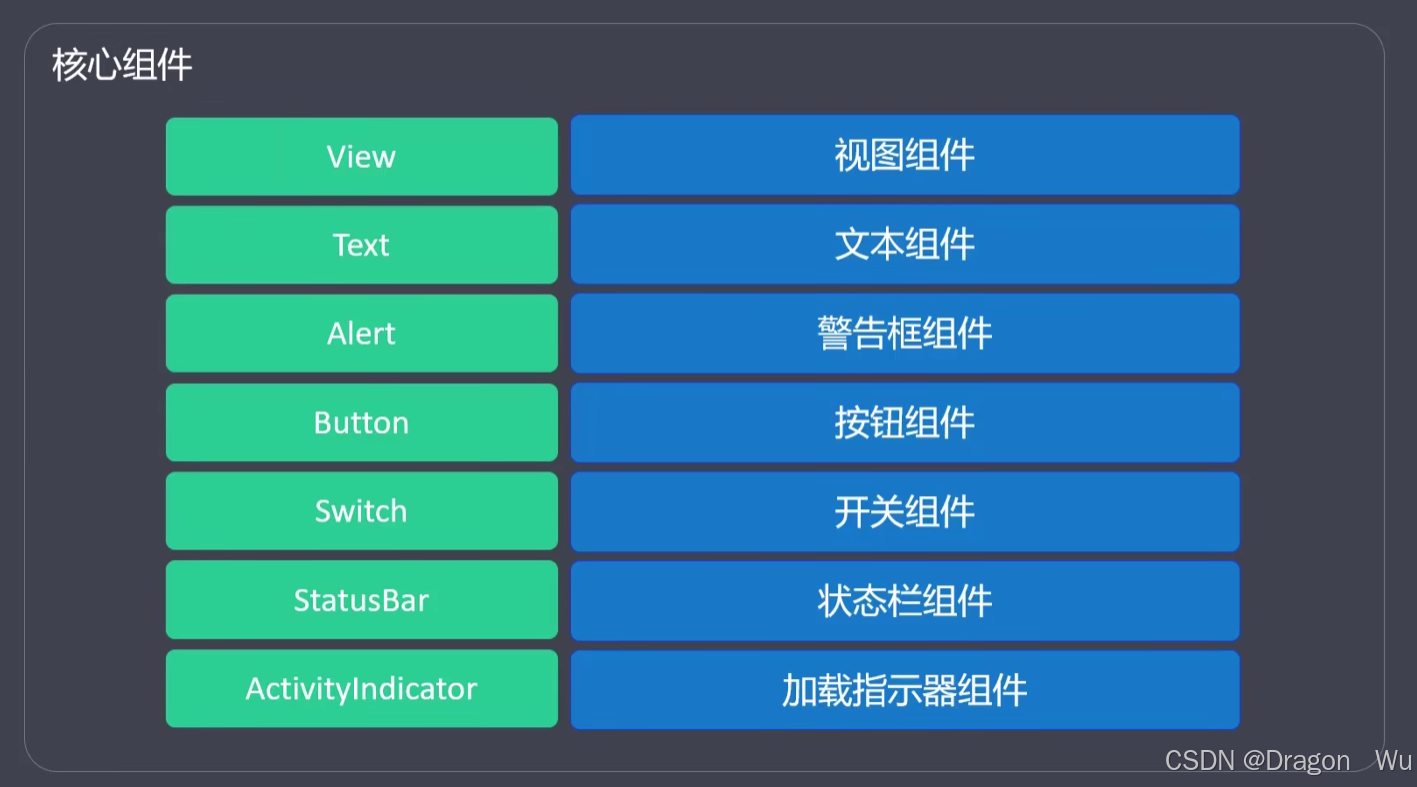

可直接从ReactNative中引入的就是核心组件。
常用组件
以下是一些常用的组件举例。第三方组件需要先下载对应依赖才能使用,可以考虑expo go框架提供的对应组件依赖。后面会介绍expo提供的一些常用组件。
|-------------------|---------------------------------------------|
| 组件名 | 作用 |
| StatusBar | 可以用于修改手机顶部状态栏的显示,hidden=true时隐藏状态栏 |
| Siwtch | 用于控件状态 |
| ActivityIndicator | 加载时的圆形加载条 |
| Touchable | 点击时有样式改变效果,类似于按钮 |
| ScrollView | 可滚动的视图,View是不能滚动的,但这个可以。可设置水平滚动或垂直滚动。可作为导航栏 |
| SafeAreaView | 可以保证视图存于合理的视图区域,可避免某些手机刘海屏对视图的遮挡 |
| SetionList | 可以进行分组的列表 |
| FlatList | 支持水平布局的列表 |
2、核心组件的使用
View、Text、ScrollView
View对应视图,类似web开发中的div标签,同为块级元素,元素独占一行;Text对应文字,类似web开发中的p标签,但不完全像p标签,内嵌时不会换行。Text默认会换行,Text内嵌Text时内部的Text标签不会换行,可以理解为在Text里面时类似于span标签,具体效果见案例。
注意:View标签不能直接写入文字,需内嵌Text标签使用。文字都需使用Text标签包裹。
这两个标签在小程序开发中也有类似的设置,可以对比参考。
代码示例:
javascript
import {View, Text, StyleSheet} from "react-native";
export default function Home() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<View>
<Text>
在Text标签内写文字01
<Text>
在Text标签内写文字02
</Text>
</Text>
<Text>
在Text标签内写文字03
</Text>
</View>
<View>
<Text>
在Text标签内写文字04
</Text>
</View>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
}
})效果:可以看到嵌套的Text标签没有换行,兄弟Text标签间出现了换行。

案例二:ScrollView与View
javascript
import {View, StyleSheet, Text, ScrollView} from "react-native";
export default function Home() {
return (
<ScrollView style={styles.container}>
<View style={styles.content}>
<View>
<Text>bottom</Text>
</View>
</View>
</ScrollView>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {},
content: {
width: "100%",
height: 2000,
justifyContent: "flex-end"
}
});效果: 使用ScrollView在页面超出显示区时才能滑动到底部,若将这里的ScrollView的container换成View组件就不能滑动了。
使用ScrollView在页面超出显示区时才能滑动到底部,若将这里的ScrollView的container换成View组件就不能滑动了。
ScrollView与View对比
简单来说:
-
View:是一个静态的、固定大小的矩形区域,用于显示内容(如文字、图片)和响应用户交互。它本身无法处理超出其边界的内容。 -
ScrollView:是一个动态的、可滚动的容器,它内部有一个"视口",可以通过滑动来查看比这个"视口"更大的内容。
为了更好地理解,我们可以用一个比喻:
-
View就像一张 固定大小的相片。- 你只能看到相框内的内容。如果照片本身比相框大,那么超出的部分你就看不到了(被裁剪了)。
-
ScrollView就像一部 智能手机 的屏幕。- 屏幕本身大小是固定的,但你可以在上面查看一张非常长的网页或一张高分辨率的全景照片。通过手指滑动,你可以让屏幕这个"视口"在整张网页或照片上移动,从而浏览全部内容。手机屏幕就是
ScrollView的frame,而整个网页或照片就是它的contentSize。
- 屏幕本身大小是固定的,但你可以在上面查看一张非常长的网页或一张高分辨率的全景照片。通过手指滑动,你可以让屏幕这个"视口"在整张网页或照片上移动,从而浏览全部内容。手机屏幕就是
Alert、Button
在reactNative中也可以直接使用alert函数类似于web开发中的效果,但某些设备可能不识别这个函数无法显示。只能用于简单消息的特定设备测试用。
javascript
alert("hello")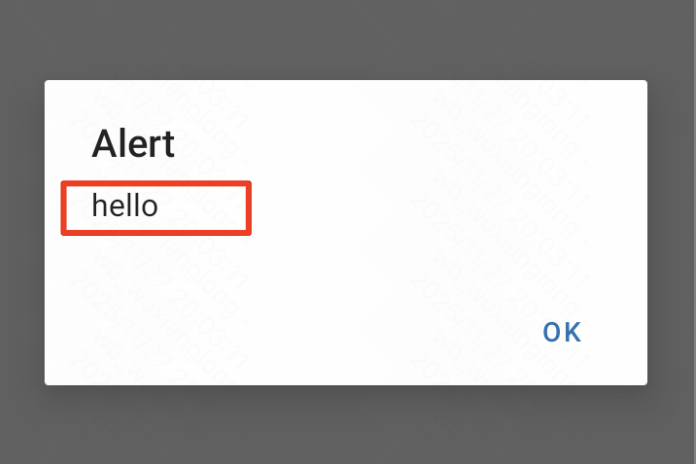
此时,我们需要用到Alert.alert这个api来实现相应的效果。
案例代码:在reactNative中点击事件是onPress而不是web中的onClick。
javascript
import {View, Button, StyleSheet, Alert} from "react-native";
export default function Home() {
const simpleAlert = () => {
// 基本用法
Alert.alert("标题", "消息内容");
}
const alertWithButton = () => {
// 带按钮的 Alert
Alert.alert(
"确认删除",
"您确定要删除这个项目吗?",
[
{
text: "取消",
style: "cancel",
},
{
text: "删除",
onPress: () => console.log("删除操作"),
style: "destructive",
},
]
);
}
const alertWithThreeButton = () => {
// 三个按钮
Alert.alert(
"更新提示",
"有新版本可用",
[
{
text: "稍后提醒",
onPress: () => console.log("稍后提醒"),
style: undefined
},
{
text: "忽略",
onPress: () => console.log("忽略"),
style: "cancel",
},
{
text: "立即更新",
onPress: () => console.log("立即更新"),
style: "default"
},
]
);
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Button title={"基本用法"}
color={"red"}
onPress={simpleAlert}/>
<Button title={"两个按钮"}
color={"green"}
onPress={alertWithButton}/>
<Button title={"三个按钮"} onPress={alertWithThreeButton}/>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
padding: 15,
margin: 10,
}
});效果: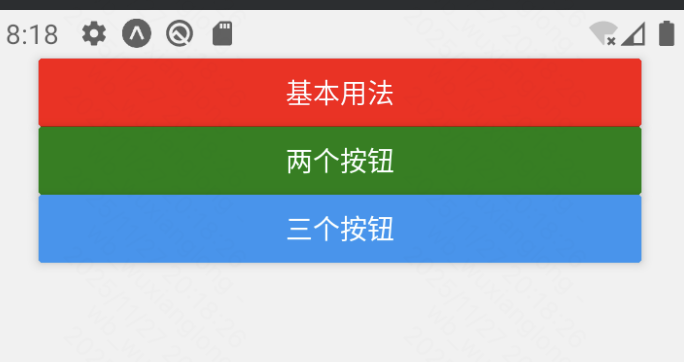
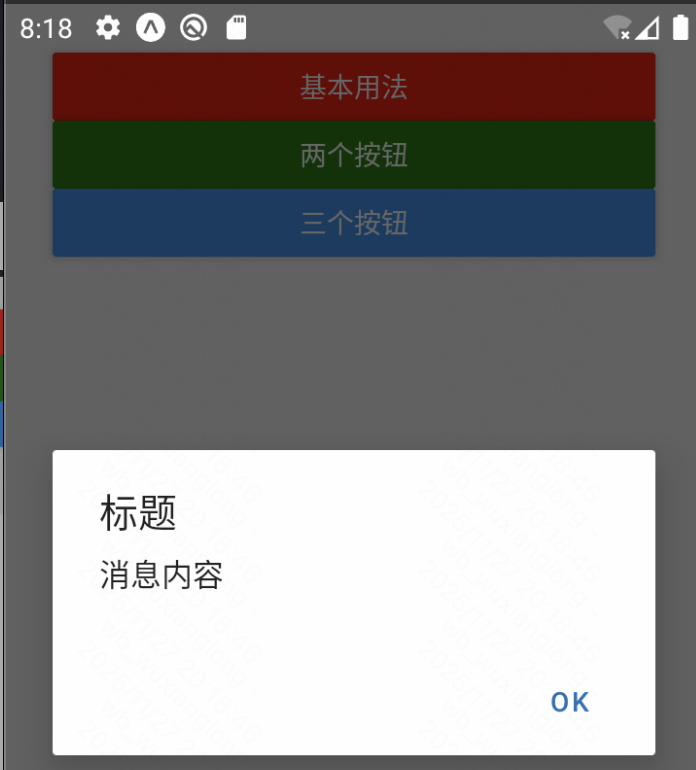


Alert可以设置title,message和button属性,其中button属性又有对应的四个按钮样式设置。
参考:https://reactnative.dev/docs/alert
组件中的Button和web中的不同在于,文字需要设置到title属性中,可以通过设置color来修改按钮颜色。
参考:https://reactnative.dev/docs/button
Touchable、Pressable
两个都是热区组件,用于实现类似Button的点击触发事件的效果。
|---------|----------------|-----------------------------|
| 对比项 | Touchable | Pressable |
| API设计 | 每个变种有特定的行为 | 统一的 API,通过配置实现不同效果 |
| 状态管理 | 内置视觉反馈(如透明度变化) | 需要手动处理按压状态 |
| 功能丰富度 | \ | Pressable 提供更细粒度的控制 |
| 性能 | 较老的实现,可能存在性能问题 | 更优化的性能,更好的内存管理 |
| 平台特性 | \ | Pressable 支持 Android Ripple |
Pressable 提供了更好的性能、更灵活的 API 和更好的类型支持,是 React Native 触摸交互的未来方向。(推荐使用Pressable)
Touchable案例(了解即可):
javascript
import {View, Text, TouchableHighlight, TouchableOpacity, TouchableWithoutFeedback, StyleSheet} from "react-native";
export default function Home() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<TouchableHighlight onPress={() => console.log("触碰高亮显示")}>
<Text>触碰高亮</Text>
</TouchableHighlight>
<TouchableOpacity onPress={() => console.log("触碰透明度变化")}>
<Text>触碰透明度变化</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
<TouchableWithoutFeedback onPress={() => console.log("触碰无响应")}>
<Text>触碰无响应</Text>
</TouchableWithoutFeedback>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
}
})Pressable:
参考:https://reactnative.dev/docs/next/pressable
触发事件:
在被包裹的元素上Pressable:
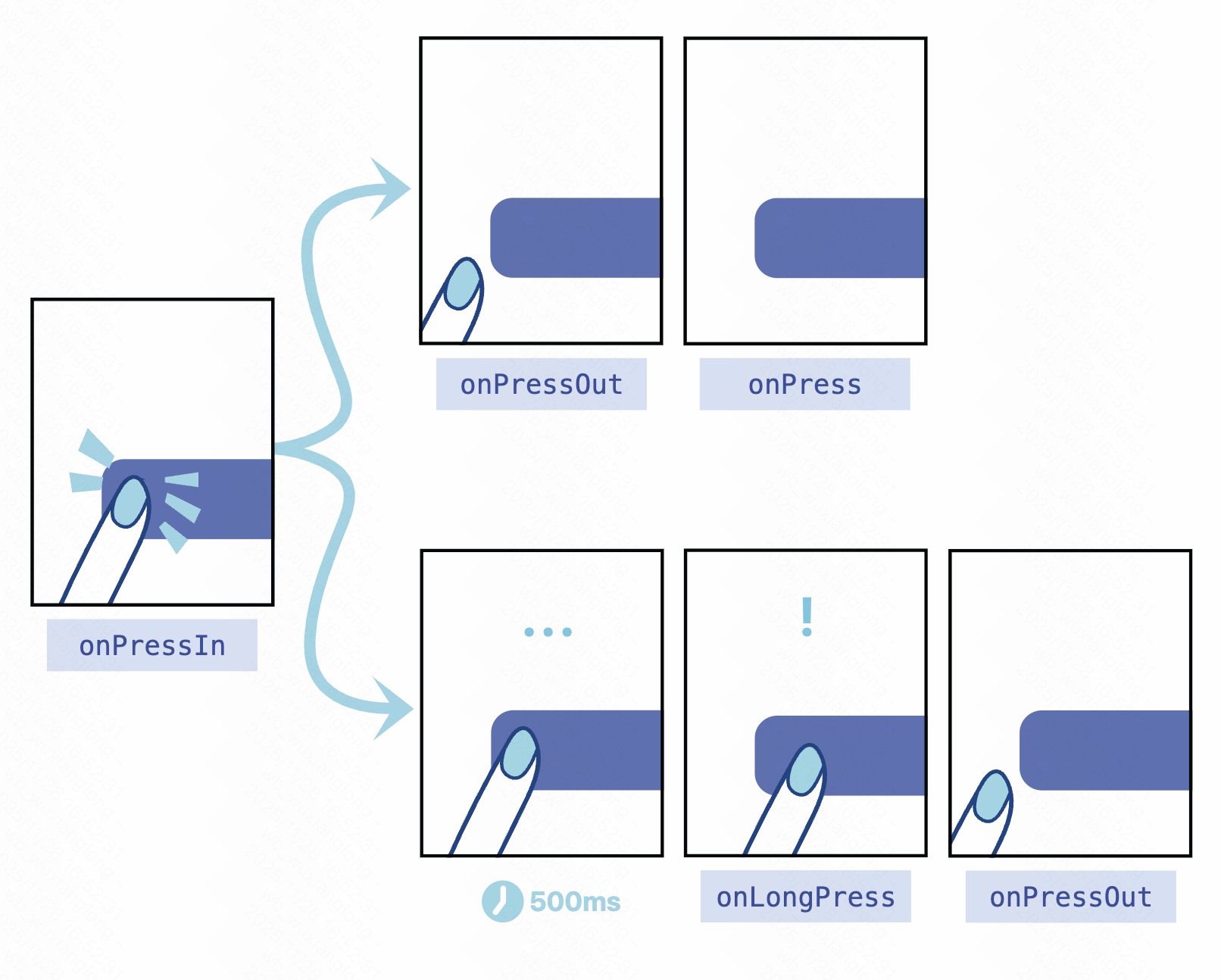
- onPressIn当按下按钮时调用。
- onPressOut当按压手势被取消激活时调用。
按下按钮后onPressIn,将会出现以下两种情况之一:
- 这个人会移开手指,onPressOut然后扣动扳机onPress。
- 如果用户手指停留时间超过 500 毫秒才移开,onLongPress则会触发事件。(onPressOut即使用户移开手指,事件仍然会触发。)
案例:
javascript
import {View, Text, StyleSheet, Pressable, StyleProp, ViewStyle} from "react-native";
import {useState} from "react";
export default function Home() {
const [pressed, setPressed] = useState(false)
const pressStyle = {
opacity: pressed ? 0.5 : 1,
transform: [{scale: pressed ? 0.95 : 2}]
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
{/* Pressable 的状态处理 */}
<Pressable
style={pressStyle as StyleProp<ViewStyle>}
onPress={() => setPressed(true)}
>
<Text>Press me</Text>
</Pressable>
{/* android_ripple只在android上有效果,在ios上需使用上面状态改变来实现过渡效果 */}
<Pressable
android_ripple={{
color: "rgba(0,0,0,0.2)",
borderless: false
}}
>
<Text>Android Ripple Effect</Text>
</Pressable>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
}
})Image、ImagePicker
首先是ReactNative提供的Image组件:
参考: https://reactnative.dev/docs/next/images
加载图片的三种方式:1)本地路径;2)图片的URI地址;3)图片的Base64字符串。
这里为什么推荐使用expo-image的Image标签?
由于原生Image标签只在IOS端支持svg图片,在Andriod端上不支持svg,我们需要借助第三方库来解决这个问题。
案例代码:
javascript
import {View, StyleSheet, Image} from "react-native";
const img = require("@/assets/images/react-logo.png");
export default function Home() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Image style={styles.img} source={img}/>
<Image style={styles.img} source={require("@/assets/images/react-logo.png")}/>
<Image style={styles.img} source={{uri: "https://reactnative.dev/img/tiny_logo.png"}}/>
<Image style={styles.img}
source={{
uri: "data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAADMAAAAzCAYAAAA6oTAqAAAAEXRFWHRTb2Z0d2FyZQBwbmdjcnVzaEB1SfMAAABQSURBVGje7dSxCQBACARB+2/ab8BEeQNhFi6WSYzYLYudDQYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgZmcvDqYGBgmhivGQYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgbmQw+P/eMrC5UTVAAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==",
}}
/>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
},
img: {
height: 50,
width: 50
}
})效果:
Expo提供的Image组件:
参考: https://docs.expo.dev/versions/latest/sdk/image/
对应实现上面效果的案例:
javascript
import {View, StyleSheet} from "react-native";
import { Image } from 'expo-image';
const img = require("@/assets/images/react-logo.png");
export default function Home() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Image style={styles.img} source={img}/>
<Image style={styles.img} source={require("@/assets/images/react-logo.png")}/>
<Image style={styles.img} source={{uri: "https://reactnative.dev/img/tiny_logo.png"}}/>
<Image style={styles.img}
source={{
uri: "data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAADMAAAAzCAYAAAA6oTAqAAAAEXRFWHRTb2Z0d2FyZQBwbmdjcnVzaEB1SfMAAABQSURBVGje7dSxCQBACARB+2/ab8BEeQNhFi6WSYzYLYudDQYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgZmcvDqYGBgmhivGQYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgYGBgbmQw+P/eMrC5UTVAAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==",
}}
/>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
},
img: {
height: 50,
width: 50
}
})对比ReactNative提供的Image组件和Expo提供的Image组件:
ReactNative提供的:
-
React Native核心组件
-
基础图片显示功能
-
需要手动处理缓存、性能优化
-
对WebP等格式支持有限
Expo提供的:
增强功能:
-
更好的性能:内置内存管理、磁盘缓存
-
更多格式:原生支持WebP、AVIF等
-
高级功能:
-
模糊占位符(blurhash)
-
平滑的图片过渡动画
-
图片预加载
-
更好的错误处理
-
| 特性 | React Native Image | Expo Image |
|---|---|---|
| 缓存控制 | 手动实现 | 自动管理 |
| 图片格式支持 | 基础格式 | WebP, AVIF等 |
| 加载效果 | 有限 | 模糊占位、过渡动画 |
| 性能优化 | 需要自行优化 | 内置优化 |
| 包大小 | 较小 | 稍大 |
| 依赖关系 | 无额外依赖 | 需要Expo环境 |
对比下来显示,Expo项目最好使用Expo提供的Image组件。总之,兼容性好选expo go 的image就对了!
ImagePicker
参考:
javascript
import {View, StyleSheet, Pressable, Text} from "react-native";
import {Image} from "expo-image";
import * as ImagePicker from "expo-image-picker";
import {useState} from "react";
export default function Home() {
const [img, setImg] = useState<string | undefined>()
const pickImageAsync = async () => {
let result = await ImagePicker.launchImageLibraryAsync({
mediaTypes: ["images"],
allowsEditing: true,
quality: 1,
});
if (!result.canceled) {
setImg(result.assets[0].uri);
} else {
alert("You did not select any image.");
}
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Image style={styles.img} source={{uri: img}}/>
<Pressable onPress={pickImageAsync}>
<Text>上传图片</Text>
</Pressable>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
},
img: {
height: 50,
width: 50
}
})效果:点击按钮上传手机图片并显示。

列表:ScrollView + map()、SetionList、FlatList、VirtualList、FlashList
测试数据的代码:
javascript
interface DataType {
name: string,
age: number,
isMale: boolean,
}
const arr: DataType[] = [
{
name: "Jack",
age: 20,
isMale: true
},
{
name: "Mark",
age: 21,
isMale: true
},
{
name: "Alice",
age: 18,
isMale: false
},
{
name: "Jack233",
age: 20,
isMale: true
},
{
name: "Mark233",
age: 21,
isMale: true
},
{
name: "Alice233",
age: 18,
isMale: false
},
{
name: "Jack9527",
age: 20,
isMale: true
},
{
name: "Mark9527",
age: 21,
isMale: true
},
{
name: "Alice9527",
age: 18,
isMale: false
},
]使用ScrollView+map完成遍历:
javascript
export default function Home() {
return (
<ScrollView style={styles.container}>
<View>
{
arr.map((item: DataType, index: number) => (
<View style={styles.item} key={"map-" + index}>
<Text>{item.name}</Text>
<Text>{item.age}岁</Text>
<Text>{item.isMale ? "男" : "女"}</Text>
</View>
))
}
</View>
</ScrollView>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {},
item: {
marginVertical: 10,
backgroundColor: "gray"
}
})效果:
使用SectionList完成分组遍历:
注意,SectionList、FlatList不能用ScrollView作为父容器包裹,因为SectionList已自带来ScrollView属性。
javascript
export default function Home() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<SectionList
sections={[
{
title: "group01",
data: arr
},
{
title: "group02",
data: arr
},
{
title: "group03",
data: arr
}]}
keyExtractor={(item: DataType, index: number) => item.name + index}
renderSectionHeader={({section}) => (
<Text style={styles.header}>{section.title}</Text>
)}
renderItem={({item}) => (
<View style={styles.item}>
<Text>{item.name}</Text>
<Text>{item.age}岁</Text>
<Text>{item.isMale ? "男" : "女"}</Text>
</View>
)}/>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {},
item: {
marginVertical: 10,
backgroundColor: "gray"
},
header: {
color: "blue",
fontSize: 20,
fontWeight: 600
}
})效果: 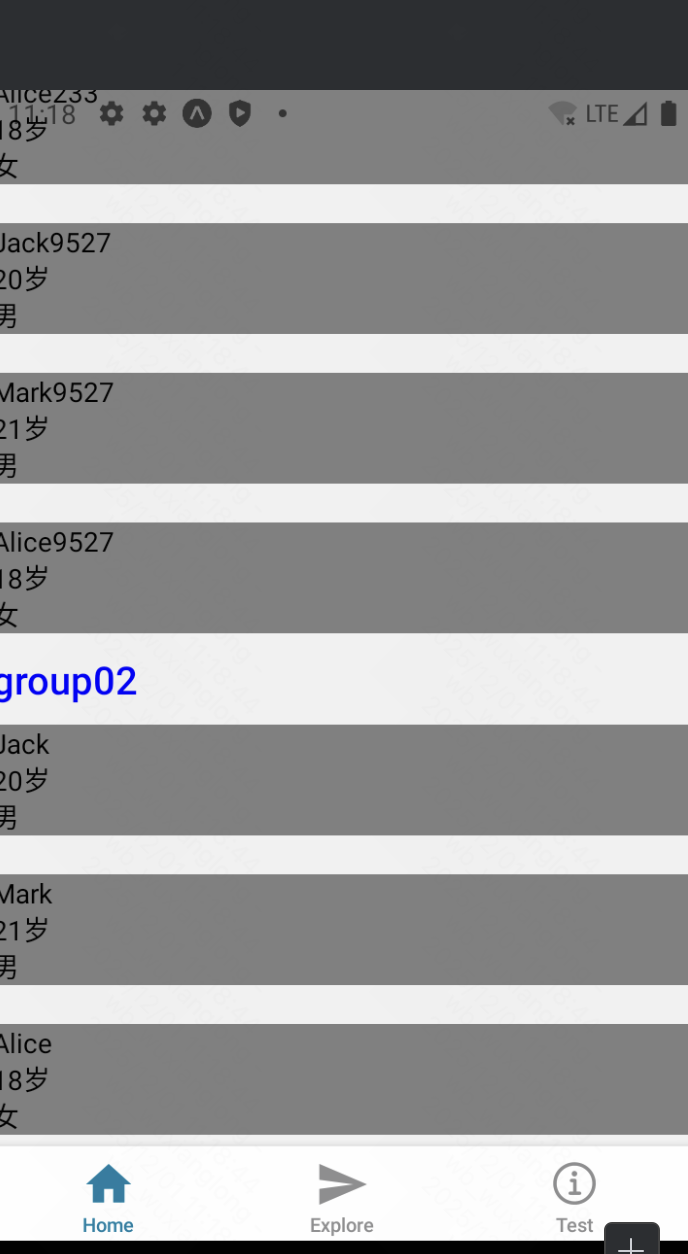
分组显示成功,sectionList有4个关键属性需要配置,
sections: 对应分组的数据;
keyExtractor: 对应item项的key;
renderSectionHeader: 渲染分组title的组件
renderItem: 渲染分组item项的组件,类似于map中item项渲染。
参考:https://reactnative.dev/docs/sectionlist
使用FlatList案例(最常用的列表,推荐使用):
javascript
export default function Home() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<FlatList
data={arr}
keyExtractor={(item: DataType, index: number) => item.name + index}
renderItem={({item}) => (
<View style={styles.item}>
<Text>{item.name}</Text>
<Text>{item.age}岁</Text>
<Text>{item.isMale ? "男" : "女"}</Text>
</View>
)}/>
</View>
);
}3个关键属性:
data: 对应列表;
keyExtractor: 对应item项的key;
renderItem: 渲染分组item项的组件,类似于map中item项渲染。
参考:https://reactnative.dev/docs/flatlist
VirtualizedList(一般不用再去调这个底层实现):
参考:https://reactnative.cn/docs/virtualizedlist
FlatList和SectionList的底层实现。FlatList 和 SectionList 使用起来更方便,同时也有相对更详细的文档。一般来说,仅当想获得比 FlatList 更高的灵活性(比如说在使用 immutable data 而不是 普通数组)的时候,你才应该考虑使用 VirtualizedList。
Vritualization 通过维护一个有限的渲染窗口(其中包含可见的元素),并将渲染窗口之外的元素全部用合适的定长空白空间代替的方式,极大的改善了内存消耗以及在有大量数据情况下的使用性能。这个渲染窗口能响应滚动行为。当一个元素离可视区太远时,它就有一个较低优先级;否则就获得一个较高的优先级。渲染窗口通过这种方式逐步渲染其中的元素(在进行了任何交互之后),以尽量减少出现空白区域的可能性。
使用FlashList遍历超大列表:
参考:https://shopify.github.io/flash-list/#install
https://docs.expo.dev/versions/latest/sdk/flash-list/
此为第三方组件,使用需先安装:
javascript
npx expo install @shopify/flash-listFlashList 由 Shopify 开发,针对大规模数据列表进行了极致优化。它不仅保留了 FlatList 的 API 设计,还提升了渲染速度,适用于超大数据集的高性能渲染。
FlashList 主要特性:
- 优化渲染,速度提升 10 倍
- 流畅滚动,内存占用更低
- API 兼容
FlatList,迁移成本低
案例:
javascript
import React from "react";
import { View, Text, StatusBar } from "react-native";
import { FlashList } from "@shopify/flash-list";
const DATA = [
{
title: "First Item",
},
{
title: "Second Item",
},
];
const MyList = () => {
return (
<FlashList
data={DATA}
renderItem={({ item }) => <Text>{item.title}</Text>}
/>
);
};选择指南
📊 决策流程图
数据量少 (< 50项) → ScrollView
↓
数据量大 → 需要分组? → 是 → SectionList
↓
否 → 性能要求极高? → 是 → FlashList
↓
否 → FlatList(默认选择)🎯 详细选择标准
| 组件 | 数据量 | 性能 | 功能 | 复杂度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ScrollView | < 50项 | 差(无虚拟化) | 基础 | 简单 |
| FlatList | 任意 | 优秀 | 丰富 | 中等 |
| SectionList | 任意 | 优秀 | 分组+丰富 | 较高 |
| FlashList | 超大 | 极佳 | 丰富 | 中等 |
💡 实用建议
-
默认选择 FlatList - 适用于80%的场景
-
数据分组用 SectionList - 通讯录、分类商品
-
短列表用 ScrollView - 设置页面、简单表单
-
性能瓶颈用 FlashList - 社交媒体feed、大型数据集
TextInput、Switch、ActivityIndicator
参考:https://reactnative.dev/docs/textinput
https://reactnative.dev/docs/switch
https://reactnative.dev/docs/activityindicator
javascript
import {View, StyleSheet, ActivityIndicator, TextInput, Switch} from "react-native";
import {useState} from "react";
export default function Home() {
const [value, setValue] = useState("")
const [loading, setLoading] = useState(true)
const onChangeTxt = (e: string) => {
console.log(e)
setValue(e)
}
const onChangeSwitch = (e: boolean) => {
console.log(e)
setLoading(prev => !prev)
}
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<TextInput
style={styles.input}
onChangeText={onChangeTxt}
value={value}
placeholder={"请输入"}
/>
<Switch
trackColor={{false: "red", true: "green"}} // 设置滑槽颜色
thumbColor={"blue"} // 设置圆点颜色
value={loading}
onValueChange={onChangeSwitch}
/>
<ActivityIndicator
color="purple"
animating={loading}
size="large"/>
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
},
input: {
borderWidth: 1,
borderColor: "black",
width: 200,
height: 50
}
})效果: 
Modal模态框
参考: https://reactnative.dev/docs/modal
可以考虑直接使用UI库,样式更佳。
javascript
import React, {useState} from 'react';
import {Alert, Modal, StyleSheet, Text, Pressable, View} from 'react-native';
import {SafeAreaView, SafeAreaProvider} from 'react-native-safe-area-context';
const App = () => {
const [modalVisible, setModalVisible] = useState(false);
return (
<SafeAreaProvider>
<SafeAreaView style={styles.centeredView}>
<Modal
animationType="slide"
transparent={true}
visible={modalVisible}
onRequestClose={() => {
Alert.alert('Modal has been closed.');
setModalVisible(!modalVisible);
}}>
<View style={styles.centeredView}>
<View style={styles.modalView}>
<Text style={styles.modalText}>Hello World!</Text>
<Pressable
style={[styles.button, styles.buttonClose]}
onPress={() => setModalVisible(!modalVisible)}>
<Text style={styles.textStyle}>Hide Modal</Text>
</Pressable>
</View>
</View>
</Modal>
<Pressable
style={[styles.button, styles.buttonOpen]}
onPress={() => setModalVisible(true)}>
<Text style={styles.textStyle}>Show Modal</Text>
</Pressable>
</SafeAreaView>
</SafeAreaProvider>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
centeredView: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
modalView: {
margin: 20,
backgroundColor: 'white',
borderRadius: 20,
padding: 35,
alignItems: 'center',
shadowColor: '#000',
shadowOffset: {
width: 0,
height: 2,
},
shadowOpacity: 0.25,
shadowRadius: 4,
elevation: 5,
},
button: {
borderRadius: 20,
padding: 10,
elevation: 2,
},
buttonOpen: {
backgroundColor: '#F194FF',
},
buttonClose: {
backgroundColor: '#2196F3',
},
textStyle: {
color: 'white',
fontWeight: 'bold',
textAlign: 'center',
},
modalText: {
marginBottom: 15,
textAlign: 'center',
},
});
export default App;效果: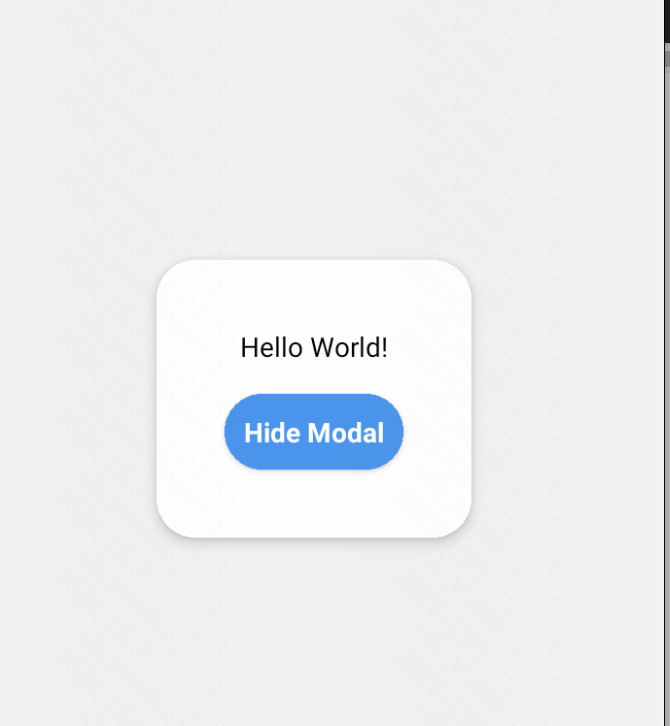
3、全局组件配置
(1)状态栏
由于这里使用了expo框架,我们直接使用expo提供的StatusBar来进行演示。一般在_layout里全局共享一个StatusBar即可。
参考:https://docs.expo.dev/versions/latest/sdk/status-bar/#api
https://docs.expo.dev/develop/user-interface/system-bars/
javascript
import {View} from "react-native";
import {StatusBar} from "expo-status-bar";
export default function Home() {
return (
<View>
<StatusBar
style={"auto"} // 默认值为auto。例如:如果您的应用处于深色模式,则样式将为"light"。
hidden={false} // 是否隐藏状态栏
animated={true} // 如果状态栏属性更改之间的过渡需要动画效果
/>
</View>
);
}效果:
(2)安全区域
某些设备上线显示可能是刘海屏,普通的显示页面可能被遮挡
参考:https://docs.expo.dev/versions/latest/sdk/safe-area-context/
如图: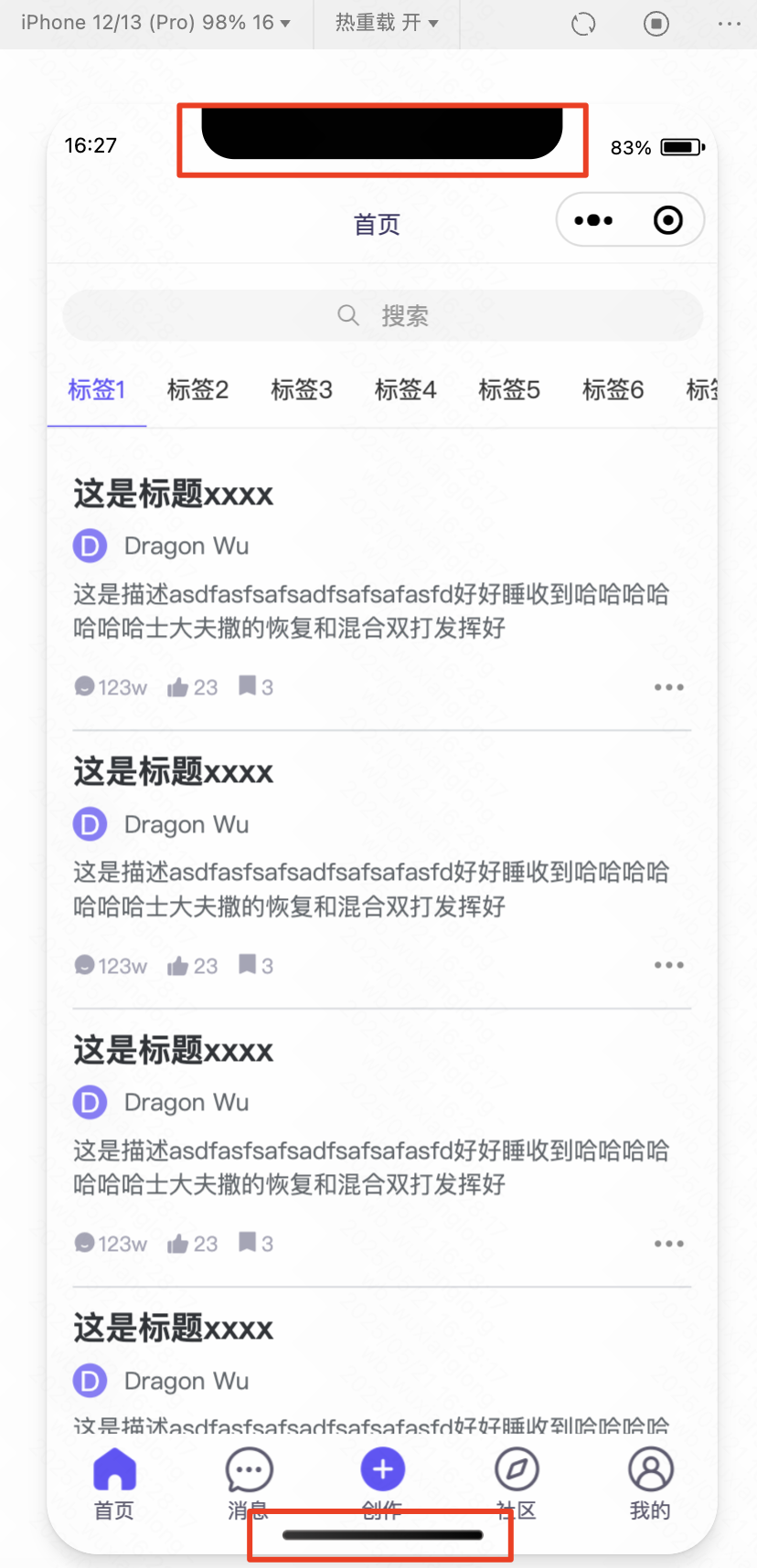 ,使用安全区域后可以使区域不被遮挡。
,使用安全区域后可以使区域不被遮挡。
在expo框架中,有以下api可以进行使用:
javascript
import {
SafeAreaView,
SafeAreaProvider,
SafeAreaInsetsContext,
useSafeAreaInsets,
} from 'react-native-safe-area-context';SafeAreaView:
如果你在视图上设置了自己的内边距,它将添加到安全区域的内边距中。
javascript
import { SafeAreaView } from 'react-native-safe-area-context';
function SomeComponent() {
return (
<SafeAreaView>
<View />
</SafeAreaView>
);
}useSafeAreaInsets():
使用挂钩可以直接接触到安全区域的嵌件。这是一种更高级的使用方式,其性能可能不如SafeAreaView旋转设备。
javascript
import { useSafeAreaInsets } from 'react-native-safe-area-context';
function HookComponent() {
const insets = useSafeAreaInsets();
return <View style={{ paddingTop: insets.top }} />;
}context:
要使用安全区域上下文,需要SafeAreaProvider在应用程序根组件中添加。
javascript
import { SafeAreaProvider } from 'react-native-safe-area-context';
function App() {
return <SafeAreaProvider>...</SafeAreaProvider>;
}然后,可以使用useSafeAreaInsets()hook 和消费者 API 来访问插入数据:
优化:
如果可以,请使用它SafeAreaView。它是原生实现的,因此旋转设备时,异步桥接不会产生延迟。(推荐使用SafeAreaView)
(3)启动动画
参考:https://docs.expo.dev/develop/user-interface/splash-screen-and-app-icon/#splash-screen
配置app.json里的插件即可:值得注意的是,该效果要导出再安装后才能看到效果,测试环境不能直接看到效果。
javascript
"plugins": [
"expo-router",
[
"expo-splash-screen",
{
"image": "./assets/images/splash-icon.png",
"imageWidth": 200,
"resizeMode": "contain",
"backgroundColor": "#ffffff"
}
]
],不过,这样设置只能设置启动的图片,并不能设置加载效果或炫酷的动画效果。若需要设置进入时的加载过渡效果页面,可以考虑中全局_layout中设置loading状态。
(4)应用图标
参考:https://docs.expo.dev/develop/user-interface/splash-screen-and-app-icon/#app-icon
配置app.json的icon属性:
javascript
{
"icon": "./assets/images/icon.png"
}4、动画
原生Animated
app端不能像web端一样通过css端transition等实现过渡动画效果,对此,app端的解决方案是使用Animated。
参考:https://reactnative.cn/docs/next/animated
Animated库旨在使动画变得流畅,强大并易于构建和维护。Animated侧重于输入和输出之间的声明性关系,以及两者之间的可配置变换,此外还提供了简单的 start/stop方法来控制基于时间的动画执行。
创建动画最基本的工作流程是先创建一个 Animated.Value ,将它连接到动画组件的一个或多个样式属性,然后使用Animated.timing()通过动画效果展示数据的变化:
注:不要直接修改动画值!你可以用useRef Hook来返回一个可修改的 ref 引用。ref 对象的
current属性在初始化时被赋予给定的动画值,且在组件的生命周期内保存不被销毁。
组件必须经过特殊的处理才能用于动画。
React Native中有四个组件是可以直接使用动画的,分别是Animated.View、Animated.Text、Animated.ScrollView、Animated.Image。
创建动画步骤:
1)创建初始值:Animated.Value() 单个值 、Animated.ValueXY() 向量值 ;
2)将初始值绑定在动画组件上:
一般将其绑定到某个样式属性上,例如opacity、translate等;
3)通过动画类型API,一帧一帧地更改初始值。
Animated提供了三种动画类型。每种动画类型都提供了特定的函数曲线,用于控制动画值从初始值变化到最终值的变化过程:
- Animated.decay()以指定的初始速度开始变化,然后变化速度越来越慢直至停下。
- Animated.spring()提供了一个基础的弹簧物理模型.
- Animated.timing()使用easing 函数让数值随时间动起来。(类似ease-in-out)
案例:
javascript
import {StyleSheet, View, Animated, Alert, Pressable, Text} from "react-native";
import {useRef} from "react";
export default function Home() {
// 1、创建ref初始值
const refCurrent = useRef(new Animated.Value(0)).current
const spin = refCurrent.interpolate({
inputRange: [0, 1],
outputRange: ["0deg", "360deg"]
});
const go = () => {
Animated.timing(refCurrent, { // 2、选择淡入淡出过渡的函数
toValue: 45, // 改变到哪个值
duration: 2000, // 过渡时间,毫秒
useNativeDriver: true, // 启用原生方式渲染动画(执行效率更高)
}).start(() => {
Alert.alert(
"value已改变,过渡完毕!"
)
})
}
const back = () => {
Animated.spring(refCurrent, {
toValue: 0, // 目标值
friction: 5, // 摩擦力,控制反弹
tension: 40, // 张力,控制速度
useNativeDriver: true, // 使用原生驱动提高性能
}).start()
}
return (<View style={styles.container}>
<Animated.View style={[
styles.card,
{
transform: [{rotate: spin}] as any
}
]}>
<Text>旋转效果</Text>
</Animated.View>
<Animated.View style={{
backgroundColor: "gray",
width: 200,
height: 200,
marginTop: 20,
opacity: refCurrent
}}>
<Animated.Text style={{
// 3、 绑定动态值到样式上
color: refCurrent === 1 ? "yellow" : "red"
}}>
动画效果
</Animated.Text>
</Animated.View>
<View>
<Pressable onPress={go}>
<Text>逐渐改变</Text>
</Pressable>
<Pressable onPress={back}>
<Text>弹走</Text>
</Pressable>
</View>
</View>)
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center",
},
card: {
width: 100,
height: 100,
backgroundColor: "blue",
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
}
})效果:点击会实现过渡动画效果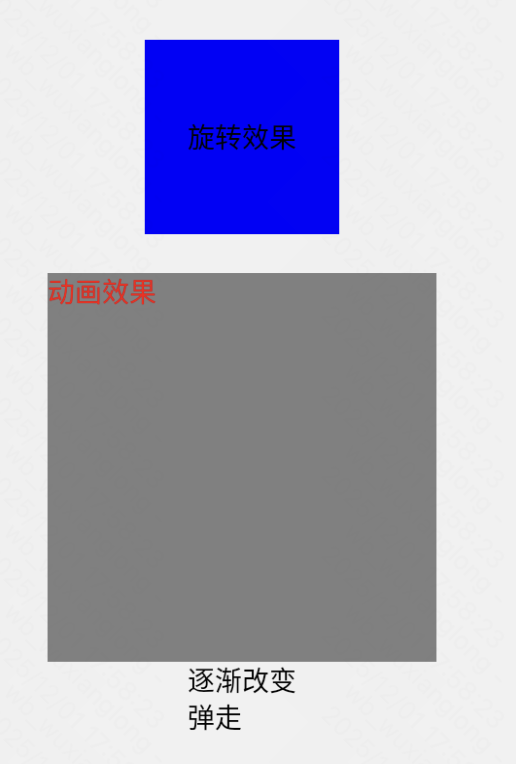
这里有用到这个方法:
interpolate()函数允许输入范围映射到不同的输出范围。默认情况下,它将推断超出给定范围的曲线,但也可以限制输出值。它默认使用线性插值,但也支持缓动功能。
React Native Reanimated(推荐)
Reanimated 2+ 提供更强大的性能,支持手势驱动的动画。
一个提供 API 的库,可以大大简化创建流畅、强大且易于维护的动画的过程。
参考:
https://docs.expo.dev/versions/latest/sdk/reanimated/
https://docs.swmansion.com/react-native-reanimated/docs/fundamentals/your-first-animation
动画过渡效果参考:
https://docs.swmansion.com/react-native-reanimated/docs/fundamentals/customizing-animation
案例:
javascript
import Animated, {useSharedValue, withSpring} from "react-native-reanimated";
import {Button, View} from "react-native";
export default function App() {
// 1、创建共享值
const width = useSharedValue(100);
const handlePress = () => {
// 2、使用过渡函数包裹值的变更
width.value = withSpring(width.value + 50);
};
return (
<View style={{flex: 1, alignItems: "center", justifyContent: "center"}}>
<Animated.View
style={{
// 3、传入值
width,
height: 100,
backgroundColor: "violet",
marginBottom: 20
}}
/>
<Button onPress={handlePress} title="Click me"/>
</View>
);
}效果: 点击出现过渡变长。
点击出现过渡变长。
这种方法明显更好管理样式,且简单方便调用,更多过渡效果参考官方文档。
4、第三方常用组件
(1)WebView
参考:https://docs.expo.dev/versions/latest/sdk/webview/
安装依赖:
npx expo install react-native-webview案例:
javascript
import {WebView} from "react-native-webview";
import Constants from "expo-constants";
import {StyleSheet} from "react-native";
export default function App() {
return (
<WebView
style={styles.container}
source={{uri: "https//example.com"}}
/>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
marginTop: Constants.statusBarHeight,
},
});效果:
网页被嵌入了app中,对于一些混合型应用,在不追求底层性能的情况下非常推荐使用。
(2)截图功能
参考:https://docs.expo.dev/versions/latest/sdk/captureRef/
使用方法:
1)安装依赖:
javascript
npx expo install react-native-view-shot2)引入,并包裹需要截图的Dom对象
javascript
import ViewShot from "react-native-view-shot";
<ViewShot ref={viewShotRef} style={styles.container}>
<Target/>
</ViewShot>- 绑定对应ViewShot的ref对象
javascript
const viewShotRef = useRef<ViewShot | null>(null)4)调用ref对象的capture方法进行截图
javascript
const uri = await viewShotRef.current?.capture?.();案例:
javascript
import {Button, StyleSheet, Text, View} from "react-native";
import {Image} from "expo-image";
import ViewShot from "react-native-view-shot";
import {useRef, useState} from "react";
const placeHolder = require("@/assets/images/test.png");
export default function App() {
const viewShotRef = useRef<ViewShot | null>(null)
const [img, setImg] = useState<string | undefined>()
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const save = async () => {
try {
const uri = await viewShotRef.current?.capture?.();
if (uri) {
setImg(await uri)
setCount(prev => prev + 1)
}
console.log("图片URI:", uri);
// 可以保存到相册或分享
} catch (error) {
console.error("截图失败:", error);
}
}
return (
<ViewShot ref={viewShotRef} style={styles.container}>
<Image style={styles.img} source={img ? {uri: img} : placeHolder}/>
<View style={styles.cover}>
<Text style={styles.text}>这是count: {count}!!!</Text>
</View>
<Button title={"保存"} onPress={save}/>
</ViewShot>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: "center",
alignItems: "center",
},
img: {
width: 200,
height: 200,
borderRadius: 8,
marginBottom: 10
},
cover: {
position: "absolute",
},
text: {
textAlign: "center",
color: "white",
fontSize: 32
}
});效果: 点击截图以后就会保存图片并重新渲染截图。
点击截图以后就会保存图片并重新渲染截图。
(3)手势
expo集成:react-native-gesture-handler - Expo文档
官方文档:Installation | React Native Gesture Handler
使用手势可以结合动画实现联动效果,详情见官方文档。
首先安装依赖:
javascript
npx expo install react-native-gesture-handler案例代码,测试其中的Tap敲击手势,当组件被敲击时触发相应逻辑:
javascript
import {TouchableOpacity, Text, StyleSheet} from "react-native";
import {Gesture, GestureDetector, GestureHandlerRootView} from "react-native-gesture-handler";
// 使用示例
export default function Home() {
const gesture = Gesture.Tap()
.onBegin(() => {
console.log("tap begin")
})
.onEnd(() => {
console.log("tap end")
})
return (
<GestureHandlerRootView style={styles.container}>
<GestureDetector gesture={gesture}>
<TouchableOpacity style={styles.button}>
<Text style={styles.text}>按钮</Text>
</TouchableOpacity>
</GestureDetector>
</GestureHandlerRootView>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
},
button: {
backgroundColor: "blue"
},
text: {
color: "white"
}
})注意:在使用GestureDetector前,需要用GestureHandlerRootView包裹需要使用手势的页面结点。
5、小图标
(1)Expo项目自带的
更多expo自带的iconfont查询:@expo/vector-icons@15.0.3
javascript
import { View, StyleSheet } from 'react-native';
import Ionicons from '@expo/vector-icons/Ionicons';
export default function App() {
return (
<View style={styles.container}>
<Ionicons name="checkmark-circle" size={32} color="green" />
</View>
);
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
});(2)自定义阿里Iconfont
阿里云下载.ttf文件的步骤这里不再复述。
配置app.json
javascript
{
"expo": {
"extra": {
"iconFont": {
"family": "iconfont",
"file": "./assets/fonts/iconfont.ttf"
}
}
}
}创建IconFont组件
案例代码如下:
javascript
import React from 'react';
import { Text, StyleSheet } from 'react-native';
import { useFonts } from 'expo-font';
// 从 iconfont.css 中提取的 Unicode 编码
const iconMap = {
'test': '\ue62f',
// 添加更多图标...
};
const IconFont = ({ name, size = 24, color = '#000', style, ...props }) => {
const [fontsLoaded] = useFonts({
'iconfont': require('../assets/icons/iconfont.ttf'),
});
if (!fontsLoaded) {
return null;
}
return (
<Text
style={[
styles.icon,
{ fontFamily: 'iconfont', fontSize: size, color },
style,
]}
{...props}
>
{iconMap[name] || '\ue62f'}
</Text>
);
};
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
icon: {
fontFamily: 'iconfont',
},
});
export default IconFont;调用组件案例:
javascript
import {View, StyleSheet} from "react-native";
import IconFont from "@/components/IconFont";
// 使用示例
export default function Home() {
return (<View style={styles.container}>
<IconFont name="test" size={30} color="#34C759"/>
</View>)
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
container: {
flex: 1,
alignItems: "center",
justifyContent: "center"
}
})效果:
注意:这里的unicode编码是css文件里对应的,需要使用/u前缀,如:\ue62f
6、精选UI库
推荐:ReactNative Paper
官方文档:入门指南 |React Native Paper
(1)安装依赖
expo项目一般安装第一个就行了
javascript
yarn add react-native-paper如果使用 Expo 的特定版本,可能需要安装额外依赖
javascript
yarn add react-native-safe-area-context
yarn add react-native-vector-icons(2)包裹入口文件
javascript
import * as React from 'react';
import { PaperProvider } from 'react-native-paper';
import App from './src/App';
export default function Main() {
return (
<PaperProvider>
<App />
</PaperProvider>
);
}(3)也可配置主题
javascript
import * as React from 'react';
import {
MD3LightTheme as DefaultTheme,
PaperProvider,
} from 'react-native-paper';
import App from './src/App';
const theme = {
...DefaultTheme,
// Specify custom property
myOwnProperty: true,
// Specify custom property in nested object
colors: {
...DefaultTheme.colors,
myOwnColor: '#BADA55',
},
};
export default function Main() {
return (
<PaperProvider theme={theme}>
<App />
</PaperProvider>
);
}(4)测试集成效果
javascript
import * as React from 'react';
import { Appbar } from 'react-native-paper';
import { Platform } from 'react-native';
const MORE_ICON = Platform.OS === 'ios' ? 'dots-horizontal' : 'dots-vertical';
const MyComponent = () => (
<Appbar.Header>
<Appbar.Header>
<Appbar.BackAction onPress={() => {}} />
</Appbar.Header>
</Appbar.Header>
);
export default MyComponent;效果:
集成成功!
总结到此,后续补充!