刷新(F5/Ctrl+R)的完整流程:
1. 传统刷新 vs 前端路由
// 传统刷新(会经过服务器):
window.location.reload() // 向服务器请求当前URL
window.location.href = '/home' // 向服务器请求 /home 页面
// 前端路由(不经过服务器):
this.$router.push('/home') // 前端路由跳转,不请求服务器2. 刷新的详细过程
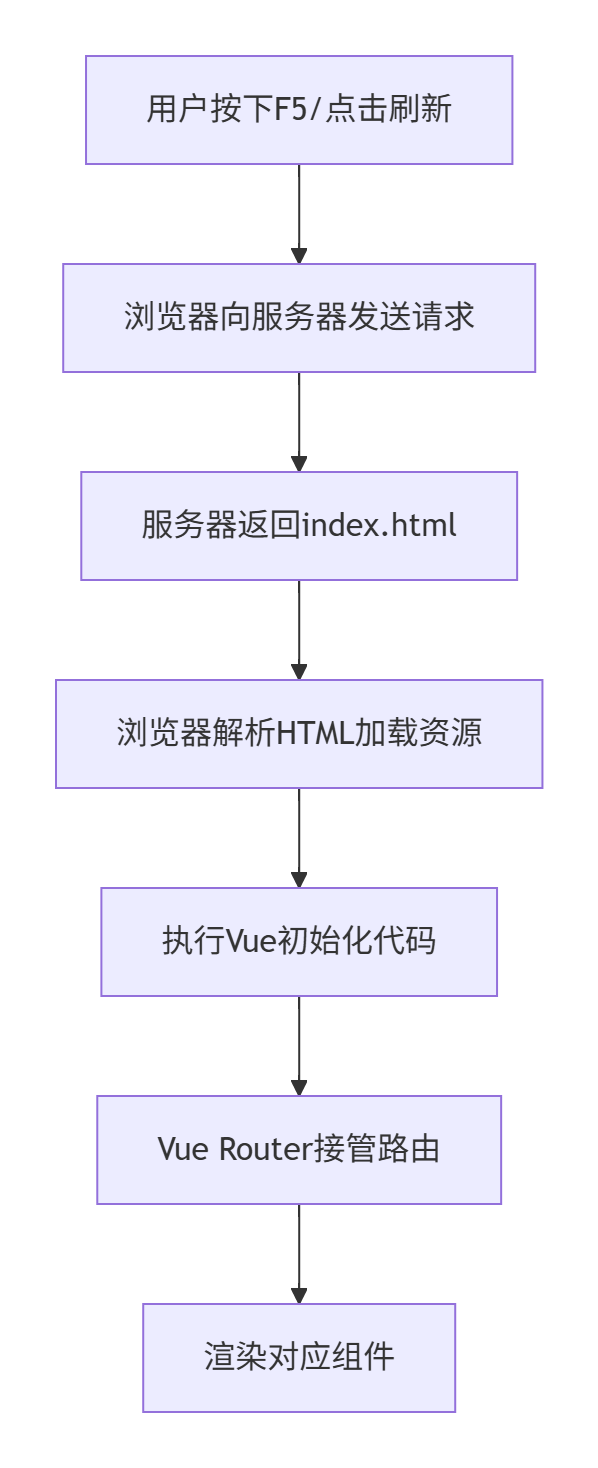
// 1. 用户点击刷新按钮(F5/Ctrl+R)
// 2. 浏览器向服务器发送当前URL的HTTP请求
// 3. 服务器返回 index.html 文件
// 4. 浏览器解析HTML,加载CSS、JS等资源
// 5. 执行 main.js 中的Vue初始化代码:
// main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
new Vue({
router, // 路由接管URL
store, // 状态恢复
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app') // 挂载到 #app 元素
// 6. Vue Router开始工作,根据当前URL匹配路由
// 7. 渲染对应的组件3. 路由模式的影响
// router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
mode: 'history', // 模式不同,刷新行为也不同
routes: [...]
})hash 模式(默认)
URL示例:http://example.com/#/home
刷新时:服务器只收到 http://example.com/
#后面的部分由前端处理history 模式(需要服务器配置)
URL示例:http://example.com/home
刷新时:服务器会收到 http://example.com/home
需要服务器配置,对404的URL也返回index.html4. 刷新导致的状态丢失
// 刷新会导致:
// 1. Vue实例重新创建
// 2. Vuex状态重置
// 3. 组件生命周期重新开始
// 4. 内存中的数据清空
// 解决方案:状态持久化
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-persistedstate'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
user: null,
cart: []
},
plugins: [
// 自动保存到 localStorage
createPersistedState({
key: 'my-app',
storage: window.localStorage
})
]
})5. 服务端配置示例
# nginx 配置(history模式必需)
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html;
# 处理前端路由的404问题
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
}
}
// Node.js Express 配置
const express = require('express')
const path = require('path')
const app = express()
// 静态文件
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'dist')))
// 所有路由都返回 index.html
app.get('*', (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'dist', 'index.html'))
})
app.listen(3000)6. 刷新时的数据恢复
<template>
<div>
<h1>{{ pageTitle }}</h1>
<!-- 刷新后数据会重新加载 -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
pageTitle: ''
}
},
async mounted() {
// 每次刷新都会执行
await this.loadData()
},
methods: {
async loadData() {
// 1. 从API获取数据
const response = await fetch('/api/data')
this.pageTitle = response.data.title
// 2. 或从sessionStorage恢复
const saved = sessionStorage.getItem('pageData')
if (saved) {
this.pageTitle = JSON.parse(saved).title
}
}
},
// 生命周期钩子执行顺序
beforeCreate() { console.log('beforeCreate - 刷新后执行') },
created() { console.log('created - 刷新后执行') },
beforeMount() { console.log('beforeMount - 刷新后执行') },
mounted() { console.log('mounted - 刷新后执行') }
}
</script>总结对比
| 操作 | 是否请求服务器 | Vue是否重新初始化 | 状态是否保持 |
|---|---|---|---|
$router.push() |
❌ 否 | ❌ 否 | ✅ 是 |
| 浏览器刷新 | ✅ 是 | ✅ 是 | ❌ 否 |
window.location.href |
✅ 是 | ✅ 是 | ❌ 否 |
| 前进/后退按钮 | ❌ 否 | ❌ 否 | ✅ 是 |
关键点:
-
刷新 = 全新页面加载 = 服务器请求 + Vue重新初始化
-
前端路由跳转 = 组件切换 = 不请求服务器
-
要避免刷新丢失状态,需要持久化存储(localStorage、Vuex持久化插件等)