目录

一、递归乘法

只需要在递归调用的时候求一下最小值,以最小值为基准,就可以解决题目故意设的超时值。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int multiply(int A, int B) {
int max = Math.max(A,B);
int min = Math.min(A,B);
if(min == 1) return max;
return max + multiply(min - 1 ,max);
}
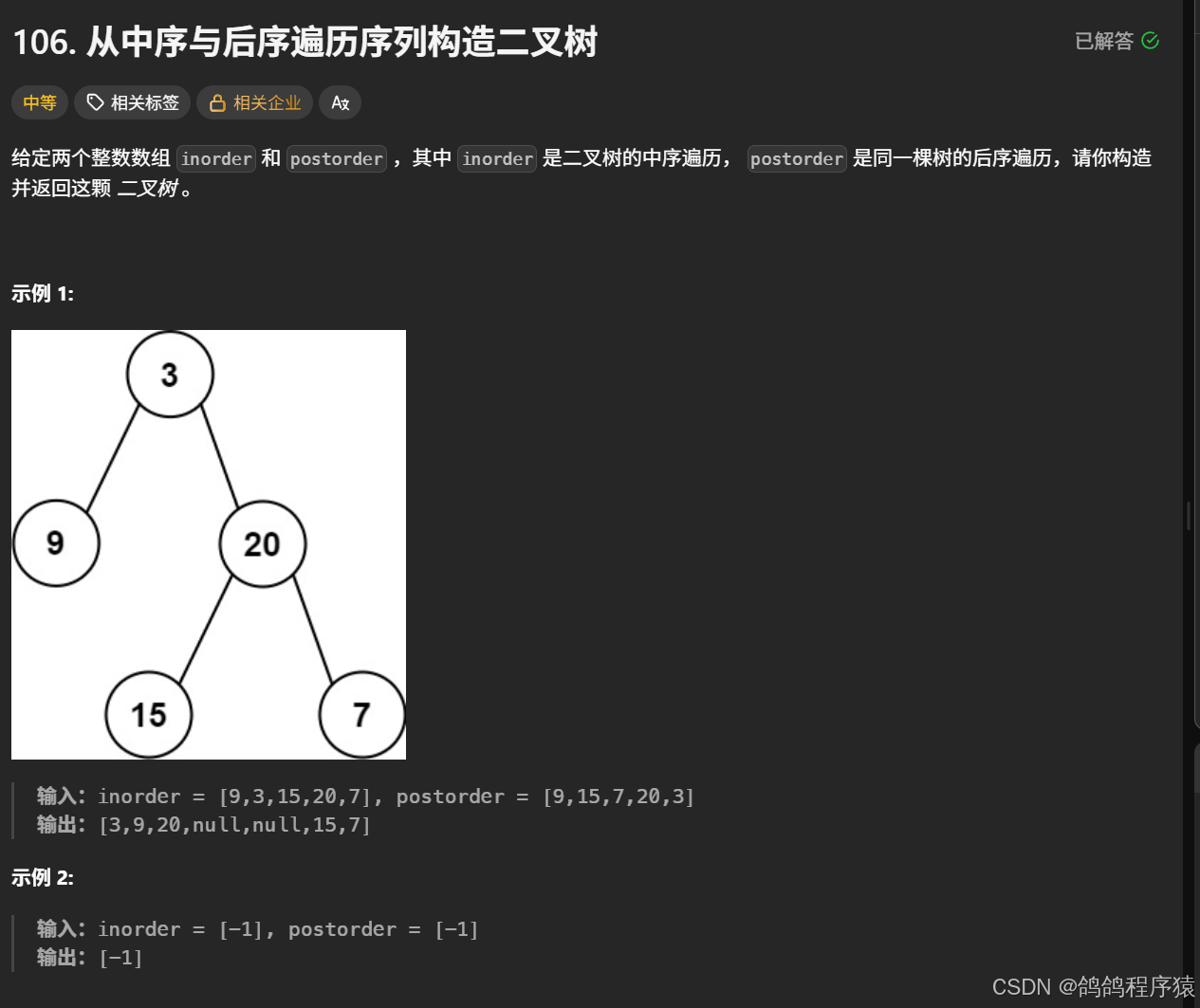
}二、从中序后续遍历构造二叉树
前面中序遍历,每一个节点前面的节点就是该节点的左子树节点,后面的节点就是该节点的右子树节点。
后序遍历,从后往前每个节点都是该子树的根节点。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int rootIndex;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
rootIndex = postorder.length-1;
return build(inorder, postorder, 0, inorder.length-1);
}
private TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int[] postorder, int begin, int end) {
if(begin > end) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[rootIndex]);
int index = findInorderIndex(inorder,begin,end,postorder[rootIndex]);
rootIndex--;
root.right = build(inorder,postorder,index+1,end);
root.left = build(inorder,postorder,begin,index-1);
return root;
}
private int findInorderIndex(int[] inorder, int begin, int end, int val) {
for(int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
if(val == inorder[i]) return i;
}
return -1;
}
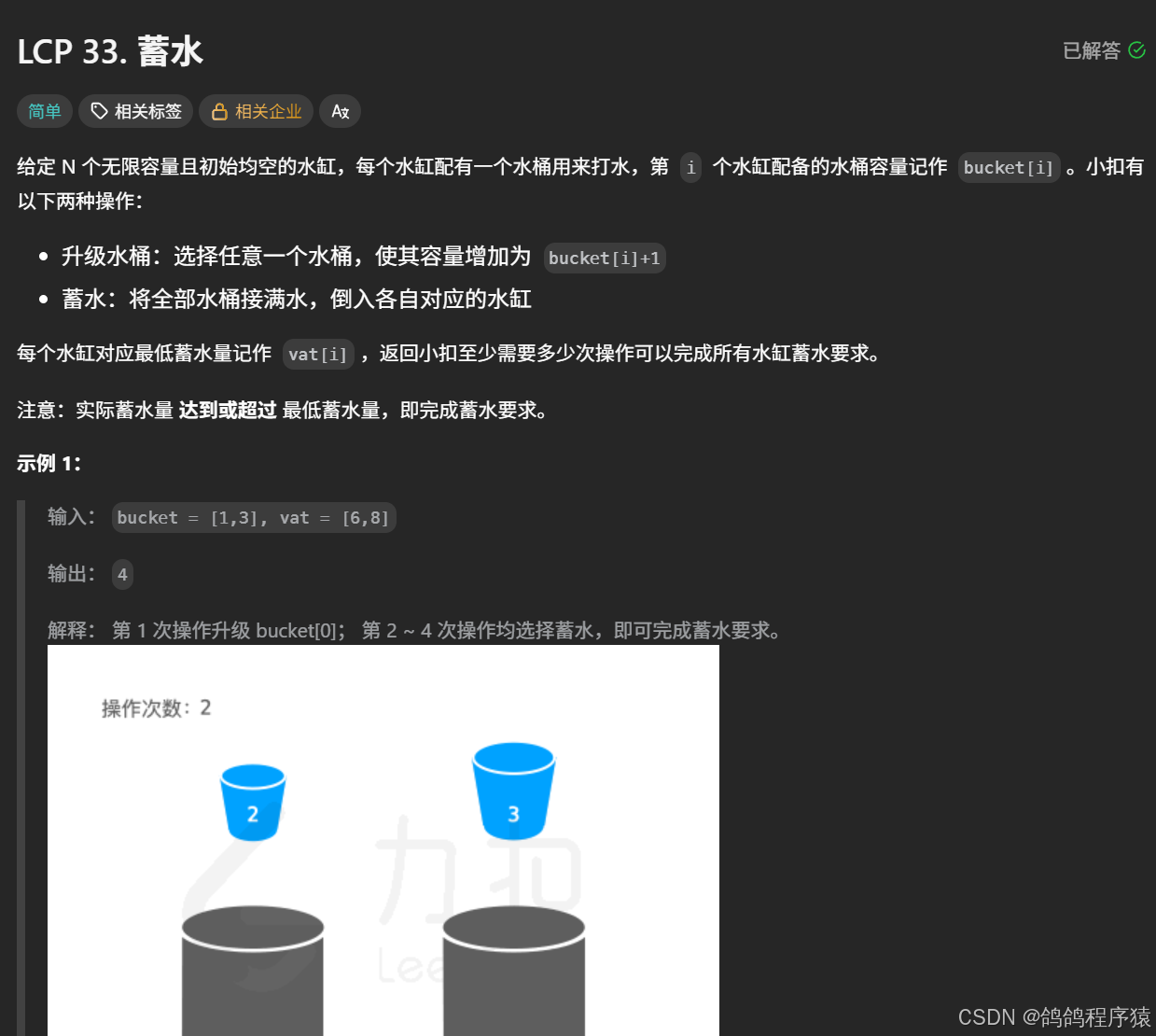
}三、蓄水
我们只需要先将水桶升级导致的所有结果枚举出来,再取最小结果即可。
先找到水桶最大容量,就是水桶最多升级的次数。对于第 j 个水桶需要的「升级水桶」操作次数为 i - bucket[ j ]
总的操作次数为 i + Math.max(0, (vat[j] + i - 1) / i - bucket[j])
时间复杂度:O(N*M)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int storeWater(int[] bucket, int[] vat) {
int len = bucket.length;
int maxVat = vat[0];
//找到最大蓄水
for(int i = 0; i < vat.length; i++) {
if(maxVat < vat[i]) maxVat = vat[i];
}
if (maxVat == 0) {
return 0;
}
int ret = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//枚举每个池子的最大蓄水次数
for(int i = 1; i <= maxVat && i < ret; i++) {
int t = 0;//表示升级水桶
//蓄水
for(int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
t += Math.max(0, (vat[j] + i - 1) / i - bucket[j]);
}
ret = Math.min(ret, t + i);
}
return ret;
}
}四、随机链表的复制
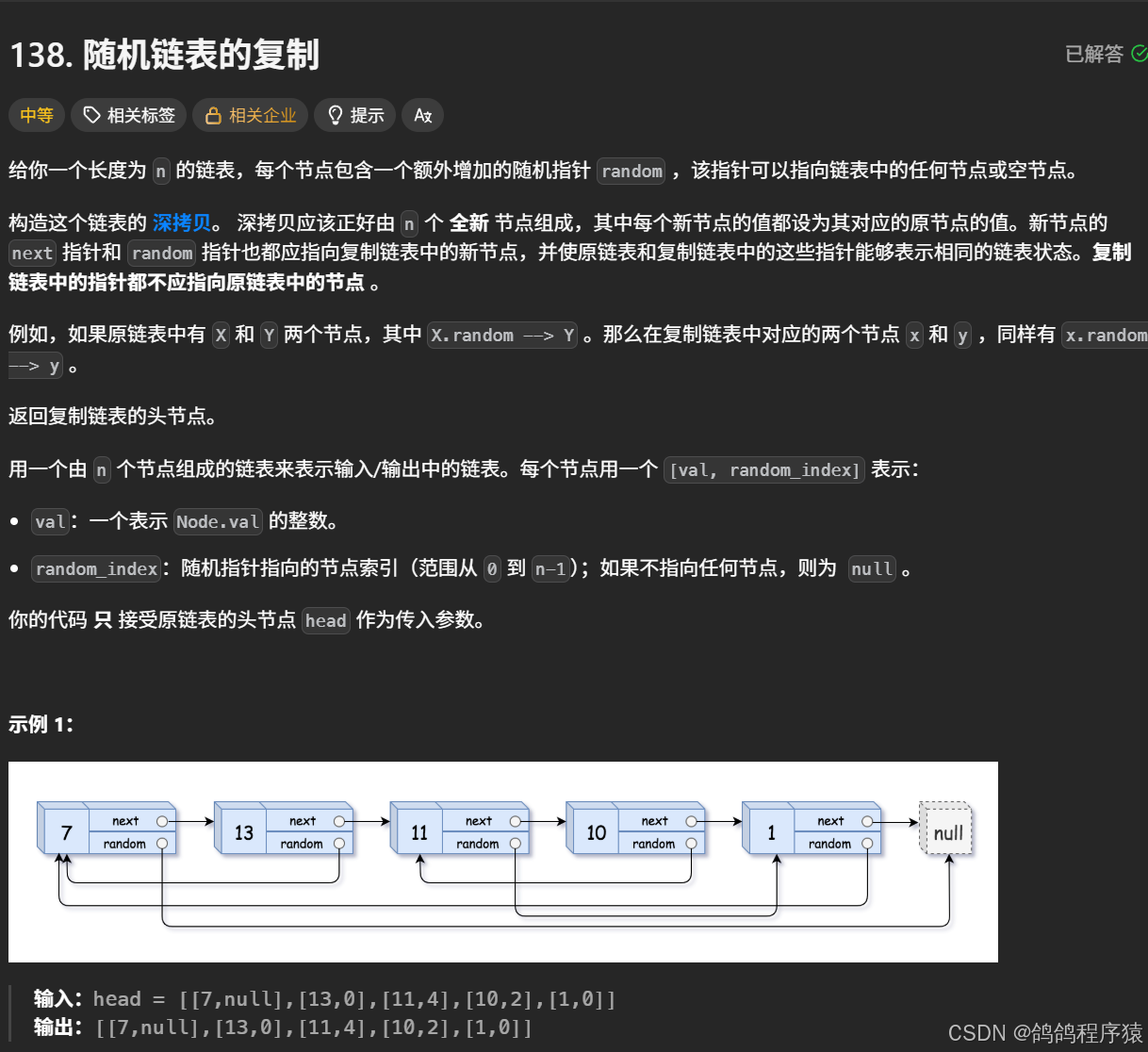
思路就是hash表 + 递归,hash表中就存储新老节点之间的对应,我们递归遍历head链表中的节点,当前节点在hash表中没有的时候,就拷贝,拷贝的新节点的next和random就递归调用函数即可完成拷贝。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Node, Node> hash = new HashMap<>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) {
return null;
}
if(!hash.containsKey(head) ) {
Node newHead = new Node(head.val);
hash.put(head, newHead);
newHead.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
newHead.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
}
return hash.get(head);
}
}五、二叉树的右视图
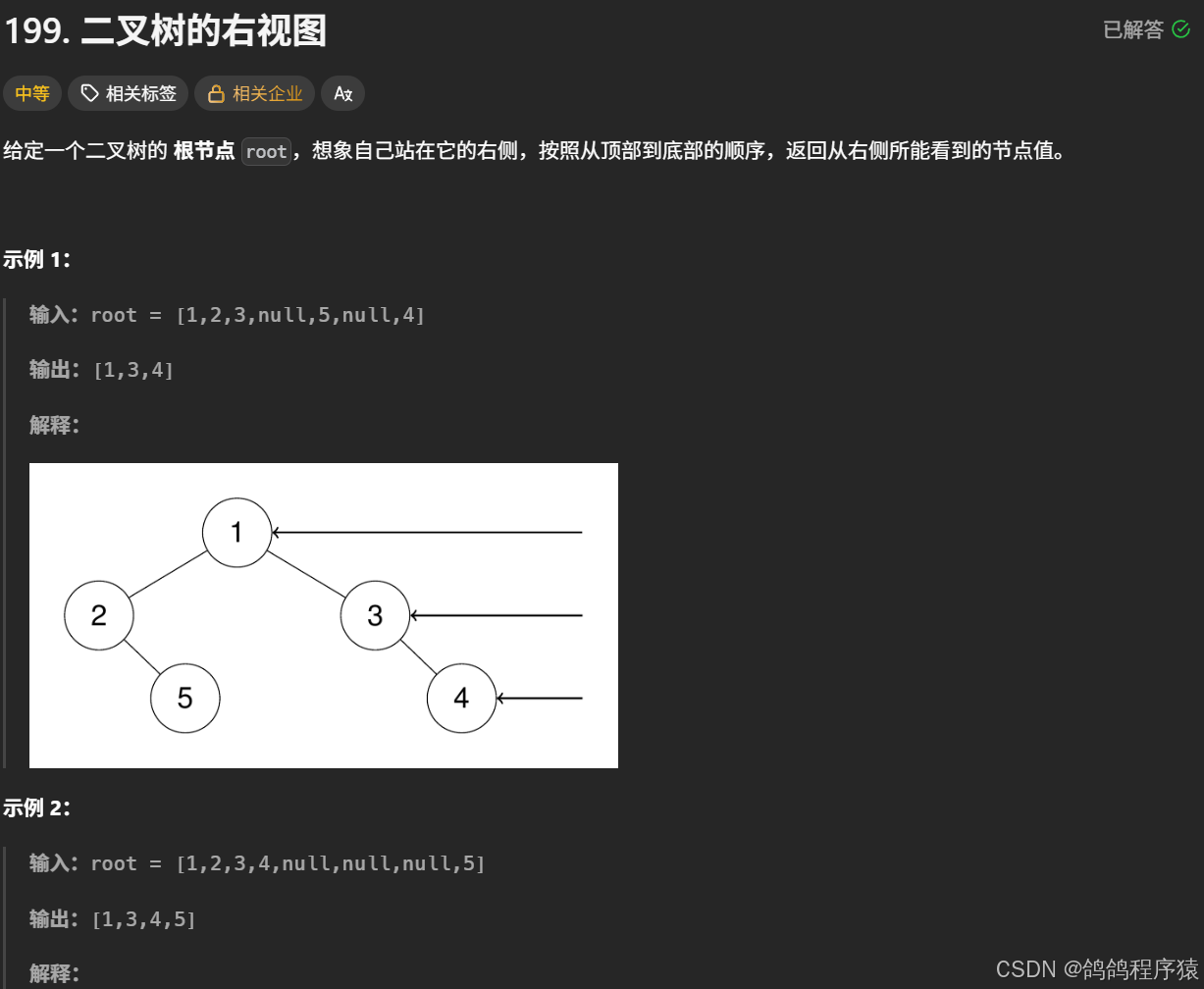
只需要拿每一层的最后一个节点即可,我们借助队列层序遍历二叉树即可。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(root == null) {
return ret;
}
queue.offer(root);
//层序遍历
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if(cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if(cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
if(i == size) {
ret.add(cur.val);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
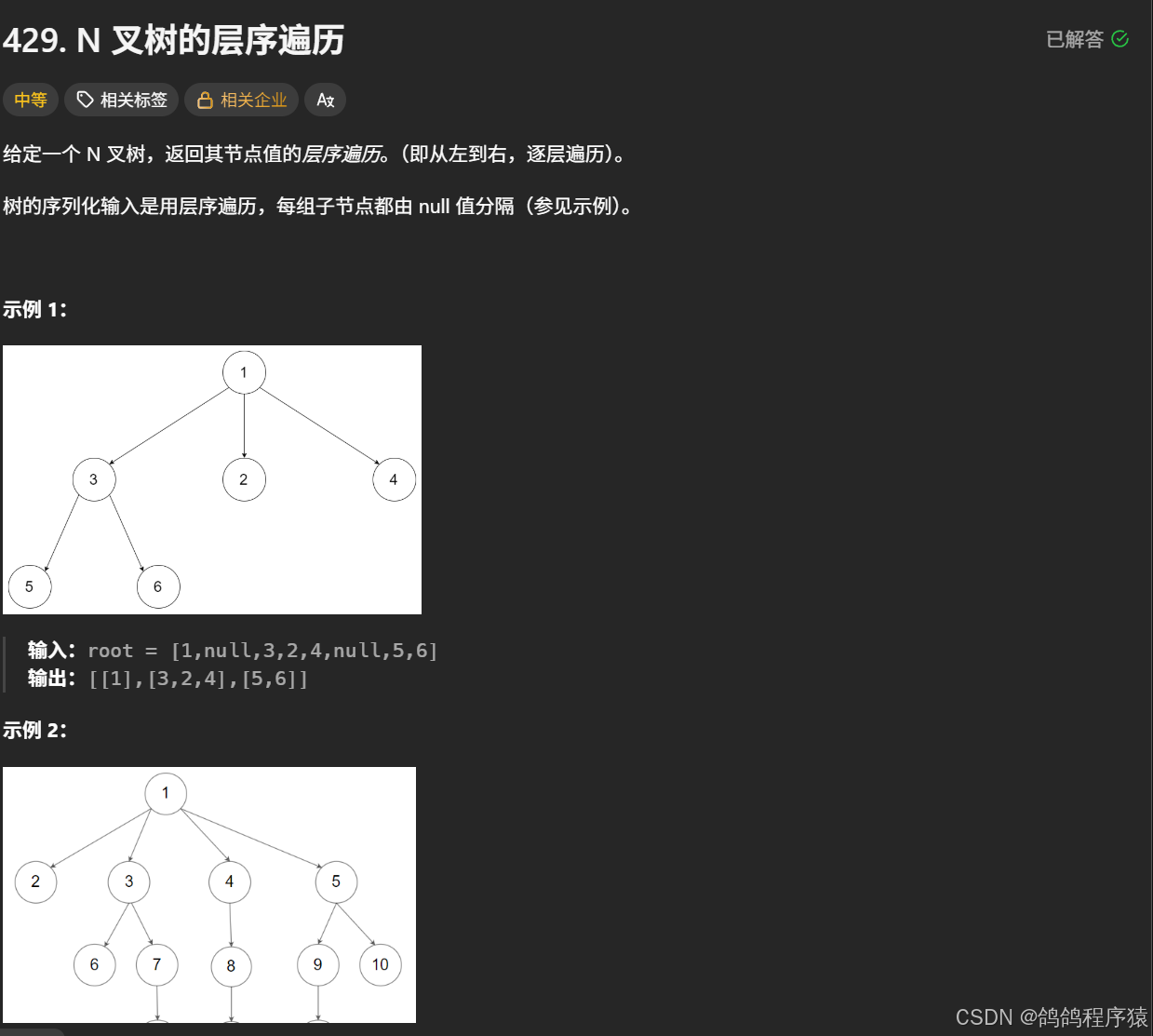
}六、N叉树的层序遍历
借助一个队列,每次出队列就只出当前有的元素,不出在出队列的同时进的元素。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
java
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(Node root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) {
return ret;
}
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
Node cur = queue.poll();
List<Node> childrens = cur.children;
for(Node children : childrens ) {
if(children != null) {
queue.offer(children);
}
}
tmp.add(cur.val);
}
ret.add(tmp);
}
return ret;
}
}七、验证回文串II

只需要双指针前后便利字符串,当遇到不相同的字符,就减去一个字符看剩下还是不是回文字符串即可。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public boolean validPalindrome(String s) {
int prev = 0;
int last = s.length()-1;
boolean ret = true;
while(prev < last) {
if(s.charAt(prev) == s.charAt(last)) {
prev++;
last--;
} else {
//验证取出一个还是不是回文字符串
ret = validPalindrome(s, prev+1, last) || validPalindrome(s, prev, last-1);
return ret;
}
}
return ret;
}
private boolean validPalindrome(String s, int prev, int last) {
while(prev < last) {
if(s.charAt(prev) == s.charAt(last)) {
prev++;
last--;
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}八、x的平方根
使用二分查找即可。
时间复杂度:O(logN)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int mySqrt(int x) {
if(x == 0) return x;
int left = 1;
int right = x;
while(left < right) {
long mid = left + (right - left + 1) / 2 ;
if((long)mid * mid <= x) left = mid;
else right = mid - 1;
}
return left;
}
}九、最长回文串
我们使用一个数组来记录每个字母在字符串中出现的次数,行使hash表的用途。
使用一个标记,记录没有构成回文串的字符数,为返回结果时要不要加上一个独立的字母放中间做判断。
便利字符串,再遍历数组即可。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int longestPalindrome(String s) {
int len = s.length();
int[] hash = new int[128];
int ret = 0;
//剩下没有构成回文串的字符数
int lose = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
hash[s.charAt(i)-'A']++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 128; i++) {
if(hash[i] != 0) {
if(hash[i] % 2 == 0) {
ret += hash[i];
} else {
ret = ret + hash[i] - 1;
lose++;
}
}
}
return lose == 0? ret : ret + 1;
}
}