因为普通二叉树的增删查改这些基本操作没太大意义,AVL,B树,红黑树的应用较广,所以这里主要是体会递归的思想。
1.代码实现
链式二叉树的本质就是递归,分治,分而治之的思想,将问题分解拆解为规模相似的子问题,直到不能再拆。
c
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode {
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
//新建一个节点
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x) {
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL) {
perror("malloc fail");
return NULL;
}
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
//造一棵树用于人工测试
BTNode* CreateTree() {
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
//销毁
void Destory(BTNode** root) {
if (*root == NULL)
return;
Destory(&((*root)->left));
Destory(&((*root)->right));
free(*root);
*root = NULL;
}
void Destory2(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
Destory(root->left);
Destory(root->right);
free(root);
}上述代码对应的树如下图所示
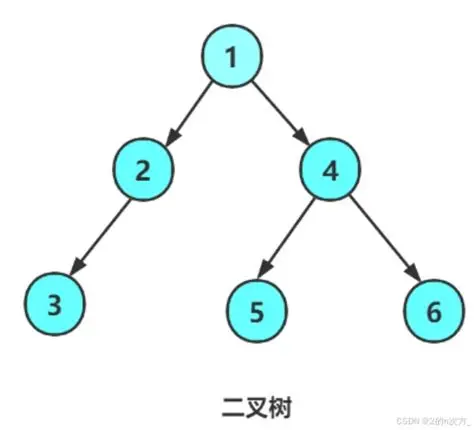
1.1 二叉树的遍历
链式二叉树的遍历
1.1.1 先序遍历
c
//前序
void PreOrder(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}1.1.2 中序遍历
c
//中序
void InOrder(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}1.1.3 后序遍历
c
//后序
void PostOrder(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
printf("NULL ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}1.2 求节点个数
求链式二叉树的节点个数
不能用局部变量,每次调用函数,建立函数栈帧都会初始化;
不能用局部静态变量,局部静态变量都不能改,只有第一次调用执行初始化,调用第二棵树怎么办;
不能用静态变量
静态变量也不行
1.2.1 使用全局变量
c
//方法一,使用全局变量,缺点:难以修改,而且会累加,除非每次使用函数前修改size=0;而且涉及到多线程中线程安全的问题
int size=0;
void TreeSize1(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
size++;
TreeSize1(root->left);
TreeSize1(root->right);
}下面代码的测试结果为:6,12.
c
int main() {
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
TreeSize1(root);
printf("%d\n", size);
TreeSize1(root);
printf("%d\n", size);
return 0;
}下面代码的测试结果为:6,6.
c
int main() {
BTNode* root = CreateTree();
TreeSize1(root);
printf("%d\n", size);
size = 0;
TreeSize1(root);
printf("%d\n", size);
return 0;
}1.2.2 变量引用
方法二:变量引用
c
void TreeSize2(BTNode* root, int* psize) {
if (root == NULL)
return;
(*psize)++;
TreeSize2(root->left,psize);
TreeSize2(root->right,psize);
}1.2.3 分治
c
//方法三:分治,分而治之
int TreeSize3(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
else
return TreeSize3(root->left) + TreeSize3(root->right) + 1;
}1.3 求树高
c
//计算树的高度
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
int leftheight = TreeHeight(root->left);
int rightheight = TreeHeight(root->right);
return leftheight > rightheight? leftheight + 1 : rightheight + 1;
}
//切记不要写成下面这种,时间复杂度是O(2^n);递归千万不要弄丢返回值,因为每个返回值都是千辛万苦递归来的
int TreeHeight2(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return TreeHeight2(root->left)> TreeHeight2(root->right)? TreeHeight2(root->left) + 1 : TreeHeight2(root->right) + 1;
}拿下面这幅图举例,计算出值为3的节点左右子树高度各是0,发现TreeHeight2(root->left)不大于TreeHeight2(root->right),返回TreeHeight2(root->right),需要重新调用TreeHeight2(root->right),得到返回结果是1,返回节点2, 2左子树高度是1,右子树高度是0,左子树高度大于右子树,返回TreeHeight2(root->left)+1,但没记录,需要重新计算,计算出值为3的节点左右子树高度各是0,发现TreeHeight2(root->left)不大于TreeHeight2(root->right),返回TreeHeight2(root->right),需要重新调用TreeHeight2(root->right),得到返回结果是1这个过程需要重复一遍,接着返回结点1,结点1左子树高度是2,接着5右子树高度会计算两遍, 6右子树的高度会计算四遍,因为6的高度要计算两遍,得到4的返回值是2,接着4的高度要再计算一遍.

1.4 找特定值节点
找到值为X的结点并返回其指针
c
BTNode* FindX(BTNode* root, BTDataType x) {
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->data == x)
return root;
BTNode* left = FindX(root->left, x);
if (left != NULL)
return left;
BTNode* right = FindX(root->right, x);
if (right != NULL)
return right;
return NULL;
}1.5 层序遍历
层序遍历,借助队列
层序变量是一种BFS,严格来说,先序是DFS,但如果不考虑何时访问节点值,中序和后序也算DFS.
BFS不等价于二叉树的层序遍历,因为BFS, DFS不仅用于二叉树的遍历,还有二维数组(迷宫问题)、多维数组、图,DFS一般递归实现,非递归也可。
c
void LevelOrder(BTNode* root) {
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root == NULL)
return;
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) {
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
/*if(front!=NULL)*/ //这个地方其实是不用判断的,因为root不为空,则队头不为空;接着,只有当左右子树不为空,才会入队.
printf("%d ", front->data);
if (front->left != NULL)
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
if(front->right!=NULL)
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}1.6 判断是否为完全二叉树
借助队列
c
bool TreeComplete(BTNode* root) {
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) {
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL) {
while (!QueueEmpty(&q)) {
front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front != NULL) {
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
}
else {
QueuePush(&q, front->left);
QueuePush(&q, front->right);
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);//本项目队列实现的是不带头结点的队列,进程走到这,队列已经为空啦,不销毁也可以,但如果是带哨兵位的队列,就要销毁;所以在这里还是销毁,软件工程上成为耦合,我的程序和队列到底如何实现的无关,怎么都是对的.
return true;
}1.7 求第K层的节点个数
c
//计算第K层的节点个数(根节点为第一层)
int KLevel(BTNode* root, int k) {
assert(k > 0);
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
else
return KLevel(root->left,k-1) + KLevel(root->right,k-1);
}1.8 求叶子结点个数
c
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root) {
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
return 1;
else
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->left) + BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->right);
}2. OJ题
2.1 相同的树
100. 相同的树//接口型
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL)
return false;
//p!=NULL q!=NULL
if(p->val!=q->val)//这个地方不能用p!=q,因为此时p->val可能等于q->val
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}2.2 二叉树的最大深度
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
int left=maxDepth(root->left);
int right=maxDepth(root->right);
return left>right?left+1:right+1;
}2.3 二叉树的前序遍历
二叉树的先序序列存储到数组中,返回数组的起始地址;注意在先序遍历的时候传的是i的指针,不然在递归子程序中修改的变量,其栈帧销毁后,不改变源程序变量的值,修改形参不改变实参。
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root){
return root==NULL?0:TreeSize(root->left)+TreeSize(root->right)+1;
}
void PreOrder(struct TreeNode* root,int *a, int* pi){
if(root==NULL)
return;
a[*pi]=root->val;
(*pi)++;
PreOrder(root->left, a,pi);
PreOrder(root->right, a,pi);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize) {
*returnSize=TreeSize(root);
int* a=(int*)malloc(*returnSize*sizeof(int));
int i=0;
PreOrder(root,a,&i);
return a;
}2.4 翻转二叉树
将二叉树进行镜像翻转
226. 翻转二叉树
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return NULL;
struct TreeNode* tmp=root->left;
root->left=root->right;
root->right=tmp;
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}2.5 另一棵树的子树
树A是否为树B的子树,将树A与树B的每一个子树进行判断是否为同一棵树
572. 另一棵树的子树
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL||q==NULL)
return false;
if(p->val==q->val)
{
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
return false;
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot) {
if(root==NULL)
return false;
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot))
return true;
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot)||isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);//这个地方用isSub不是isSame,因为后者范围窄了
}2.6 单值二叉树
整个二叉树的值是否为同一个值
965. 单值二叉树
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return true;
if(root->left!=NULL&&root->left->val!=root->val)
return false;
if(root->right!=NULL&&root->right->val!=root->val)
return false;
return isUnivalTree(root->left)&&isUnivalTree(root->right);
}2.7 二叉树遍历
将输入的先序序列转化成中序序列输出
TSINGK110 二叉树遍历//IO型
c
#include <stdio.h>
struct TreeNode{
char val;
struct TreeNode* left;
struct TreeNode* right;
};
struct TreeNode* CreateTree(char* a,int* pi){
if(a[*pi]=='#'){
(*pi)++;
return NULL;
}
struct TreeNode* root=(struct TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode));
root->val=a[(*pi)++];
root->left=CreateTree(a, pi);
root->right=CreateTree(a, pi);
return root;
}
void InOrder(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root==NULL)
return;
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c ",root->val);
InOrder(root->right);
}
int main() {
char a[100];
scanf("%s",a);
int i=0;
struct TreeNode* root=CreateTree(a, &i);
InOrder(root);
return 0;
}2.8 对称二叉树
c
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return NULL;
struct TreeNode* tmp=root->left;
root->left=root->right;
root->right=tmp;
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
if(p==NULL && q==NULL)
return true;
if(p==NULL || q==NULL)
return false;
//p!=NULL q!=NULL
if(p->val!=q->val)//这个地方不能用p!=q,因为此时p->val可能等于q->val
return false;
return isSameTree(p->left,q->left)&&isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root) {
if(root==NULL)
return true;
struct TreeNode* right=invertTree(root->right);
return isSameTree(root->left,right);
}