文章目录
打开目录
- 头文件:
#include <dirent.h>
- 函数原型:
DIR * opendir(const char *name);DIR * fdopendir(int fd);//使用文件描述符,要配合open函数使用
- 返回值:
- 成功时返回目录流指针,出错时返回NULL
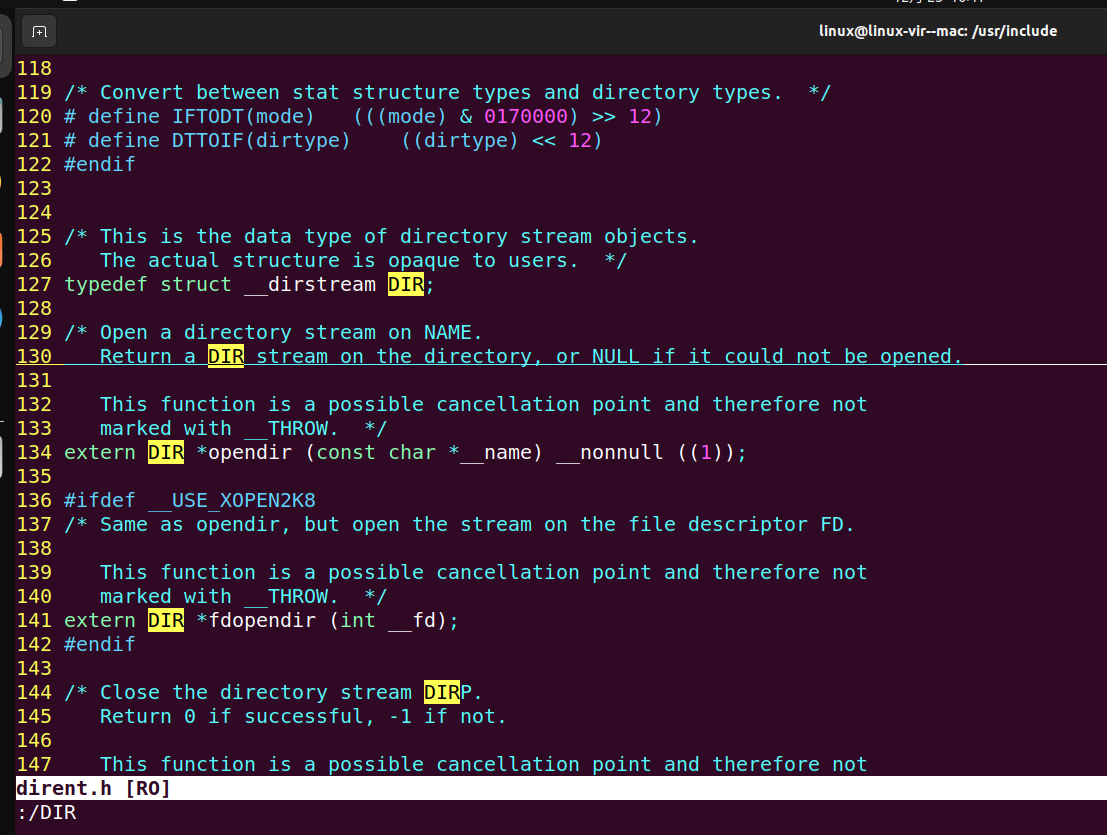
DIR是用来描述一个打开的目录文件的结构体类型,typedef重命名而来的类型名
vim /usr/include/dirent.h- 在C语言的标准库中,DIR 类型被用于表示一个目录流。它通常定义在 <dirent.h> 头文件中,并用于目录的遍历操作。DIR 类型可能是一个不完整类型(incomplete type),这意味着它的具体实现细节在<dirent.h> 头文件中并没有完全展开,而只是声明了它的存在,这样的设计允许库的实现者在不暴露内部数据结构的情况下提供接口
关闭目录
- 头文件:
#include <dirent.h>
- 函数原型:
int closedir(DIR * dirp);
- 返回值:
- 成功时返回0,出错时返回EOF
访问目录
- 头文件:
#include <dirent.h>
- 函数原型:
struct dirent * readdir(DIR * dirp);
- 参数
- 目录流指针
DIR * dirp
- 目录流指针
- 返回值:
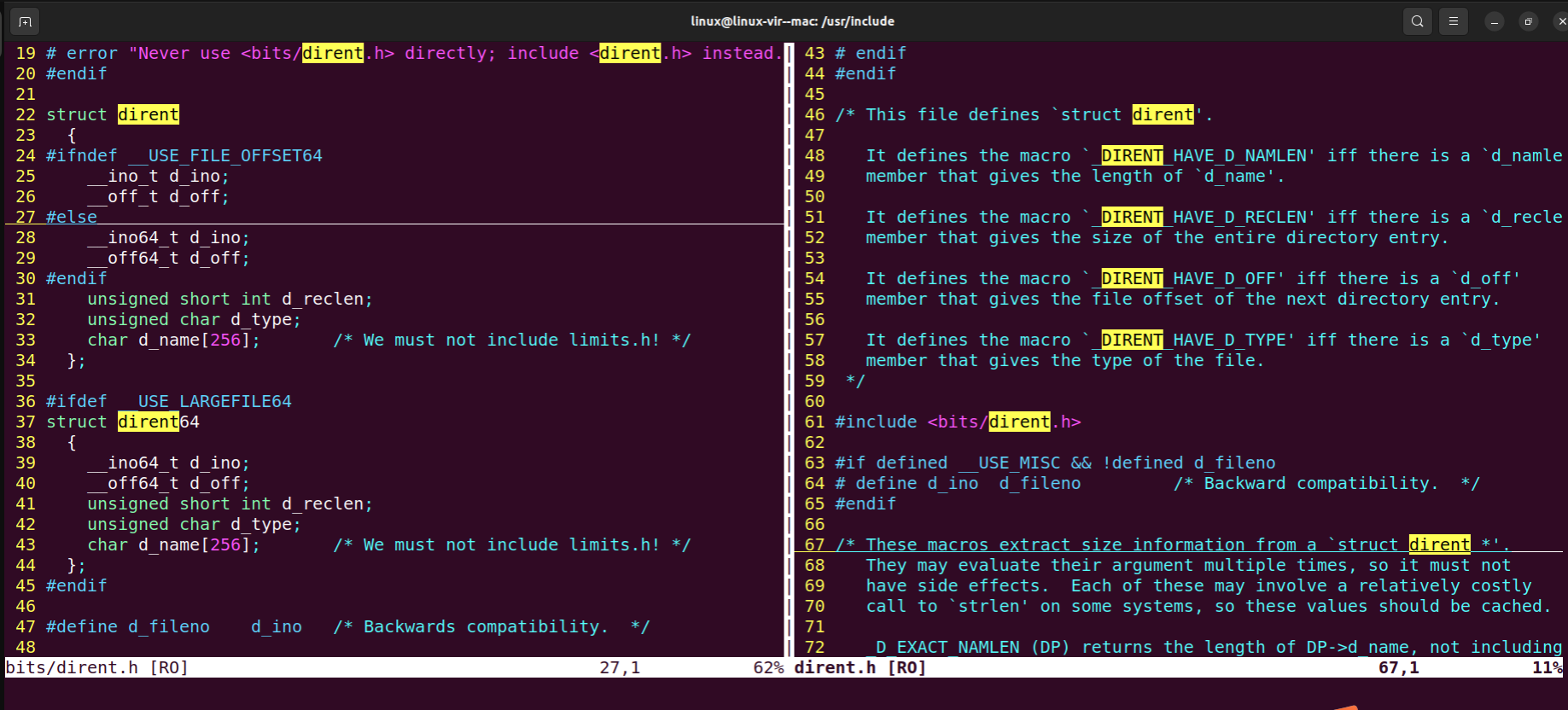
- struct dirent 描述目录流中一个目录项的结构体类型
- 成功时返回目录流dirp中一个目录项
- 出错或到末尾时返回NULL
struct dirent 和 DIR 是两个不同的结构体
例程:获取文件夹的内容
- 打印指定的目录下的文件的名称
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dirent.h>
int main(int argc, char * argv[]){
DIR *dirp;
struct dirent *dp;
if(argc < 2){
printf("Usage : %s <directory>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
if((dirp = opendir(argv[1])) == NULL){
perror("opendir");
return -1;
}
while((dp = readdir(dirp)) != NULL){
if(dp->d_type == DT_DIR){
printf("dirent file: %s\n", dp->d_name);
}else if(dp->d_type == DT_REG){
printf("regular file: %s\n", dp->d_name);
}else{
printf("%s\n", dp->d_name);
}
}
closedir(dirp);
return 0;
}