GitCheatSheet_issue#2366_102019-V5
https://training.github.com/downloads/github-git-cheat-sheet.pdf
Git is the open source distributed version control system.
This cheat sheet summarizes commonly used Git command line instructions for quick reference.
Git for All Platforms
Git distributions for Linux and POSIX systems are available on the official Git SCM web site.
Configure tooling
Configure user information for all local repositories
$ git config --global user.name "[name]"
Sets the name you want attached to your commit transactions
$ git config --global user.email "[email address]"
Sets the email you want attached to your commit transactions
$ git config --global color.ui auto
Enables helpful colorization of command line output
Branches
Branches are an important part of working with Git. Any commits you make will be made on the branch you're currently "checked out" to. Use git status to see which branch that is.
$ git branch [branch-name]
Creates a new branch
$ git checkout [branch-name]
Switches to the specified branch and updates the working directory
$ git merge [branch]
Combines the specified branch's history into the current branch. This is usually done in pull requests, but is an important Git operation.
$ git branch -d [branch-name]
Deletes the specified branch
Create repositories
When starting out with a new repository, you only need to do it once; either locally, then push to GitHub, or by cloning an existing repository.
$ git init
Turn an existing directory into a git repository
$ git clone [url]
Clone (download) a repository that already exists on GitHub, including all of the files, branches, and commit
The .gitignore file
Sometimes it may be a good idea to exclude files from being tracked with Git. This is typically done in a special file named .gitignore . You can find helpful templates for .gitignore files at github.com/github/gitignore .
Synchronize changes
Synchronize your local repository with the remote repository on GitHub.com
$ git fetch
Downloads all history from the remote tracking branches
$ git merge
Combines remote tracking branch into current local branch
$ git push
Uploads all local branch commits to GitHub
$ git pull
Updates your current local working branch with all new commits from the corresponding remote branch on GitHub.
git pull is a combination of git fetch and git merge
Make changes
Browse and inspect the evolution of project files
$ git log
Lists version history for the current branch
$ git log --follow [file]
Lists version history for a file, including renames
$ git diff [first-branch]...[second-branch]
Shows content differences between two branches
$ git show [commit]
Outputs metadata and content changes of the specified commit
$ git add [file]
Snapshots the file in preparation for versioning
$ git commit -m "[descriptive message]"
Records file snapshots permanently in version history
Redo commits
Erase mistakes and craft replacement history
$ git reset [commit]
Undoes all commits after [commit], preserving changes locally
$ git reset --hard [commit]
Discards all history and changes back to the specified commit
GitHub Flow

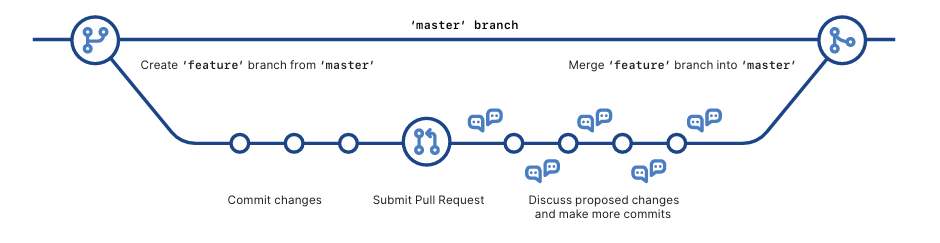
Glossary
git: an open source, distributed version-control system
GitHub: a platform for hosting and collaborating on Git repositories
commit: a Git object, a snapshot of your entire repository compressed into a SHA
branch: a lightweight movable pointer to a commit
clone: a local version of a repository, including all commits and branches
remote: a common repository on GitHub that all team member use to exchange their changes
fork: a copy of a repository on GitHub owned by a different user
pull request: a place to compare and discuss the differences introduced on a branch with reviews, comments, integrated
tests, and more
HEAD: representing your current working directory, the HEAD pointer can be moved to different branches, tags, or commits
when using git checkout
GitHub Training