List类
它本质是一个可变类的泛型数组------List帮助我们实现了很多方法,比如增删查改
增删查改
cs
//声明
List<int> list = new List<int>();
List<string> list2 = new List<string>();
List<string> list3 = new List<string>();
//⭕增 和ArrayList一样
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(3);
list2.Add("你好");
//范围增加
list3.Add("世界");//相当于新建一个List添加内容,然后将该内容添加到指定List中
list2.AddRange(list3);
//list2为 你好世界
//⭕插 参数1插入的位置 参数2插入的数据
list.Insert(0,99);
//⭕删
//1.移除指定元素
list.Remove(1);
//2.移除指定位置元素
list.RemoveAt(0);
//3.清空
list.Clear();
list.Add(1);
list.Add(2);
list.Add(3);
list.Add(2);
//⭕查
//1.得到元素指定位置
Console.WriteLine(list[0]);
//2.查看元素是否存在
if (list.Contains(2))
{
Console.WriteLine("list中元素2存在");
}
//3.正向查找
int index = list.IndexOf(2);
//返回 1
//4.反向查找
index = list.LastIndexOf(2);
//返回 3
//⭕改
list[0]=99;插入和遍历
cs
//⭕插 参数1插入的位置 参数2插入的数据
//相当于在线性表中第一个位置插入数据99
list.Insert(0,99);
//⭕遍历
//长度Count
//容量Capacity
for (int i = 0; i < list.Count; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(list[i]);
}
foreach (int item in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}Dictionary
与Hashtable比起来 键值对类型变为可以自己定义的泛型
可以将Dictionary理解为 拥有泛型的Hashtable
它也是基于键的哈希代码组织起来的 键/值对
键值对类型从Hashtable的object变为了可以自己制定的泛型
cs
//声明------这里键和值的数据类型 都可以发生变换
Dictionary<int, string> dictionary = new Dictionary<int, string>();增删查改
cs
//⭕增
dictionary.Add(1,"你好");
dictionary.Add(2,"世界");
dictionary.Add(3,"Hello");
//⭕删
//1.通过键去删除 键值对会一起被删除
dictionary.Remove(1);
//2.清空
dictionary.Clear();
//⭕查
//1.通过键查看值
Console.WriteLine(dictionary[2]);
//2.查看是否存在
if (dictionary.ContainsKey(2))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在键为2的键值对");
}
if (dictionary.ContainsValue("世界"))
{
Console.WriteLine("存在值为 \"世界\" 的键值对");
}
//⭕改
dictionary[3]="同学";遍历
cs
//⭕遍历
//1.遍历所有键
foreach (int item in dictionary.Keys)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
Console.WriteLine(dictionary[item]);
}
//2.遍历所有值
foreach (string item in dictionary.Values)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
//3.键值对一起遍历
foreach (KeyValuePair<int,string> item in dictionary)
{
Console.WriteLine(item.Key+item.Value);
}顺序存储和链式存储
线性表和顺序存储
线性表是一种数据结构,是由n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有序序列。
比如数组、ArrayList、Stack、Queue、链表等等
顺序存储
数组、Stack、Queue、List、ArrayList ------ 顺序存储
但是 数组、Stack、Queue的 组织规则不同而已
用一维地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表的各个数据元素
顺序存储![]() https://blog.csdn.net/2303_80204192/article/details/133823668#t2
https://blog.csdn.net/2303_80204192/article/details/133823668#t2
链式存储
链式存储![]() https://blog.csdn.net/2303_80204192/article/details/133823668#t7
https://blog.csdn.net/2303_80204192/article/details/133823668#t7
节点的代码
cs
节点的代码
class LinkedNode<T>
{
public T value;
//这个存储下一个元素是谁
public LinkedNode<T> nextNode;
public LinkedNode(T value)
{
this.value = value;
}
}
--主函数--
LinkedNode<int> node =new LinkedNode<int>(1);//声明一个int为1的结点整个链表的管理方案------添加节点
cs
整个链表的管理方案
class LinkedList <T>
{
public LinkedNode<T> head;
public LinkedNode<T> last;
public void Add(T value)
{
//创建新结点,必然是new一个
LinkedNode<T> node = new LinkedNode<T>(value);
//当 head == null 时,说明链表为空(没有任何节点)
//此时新创建的节点 node 就是第一个也是唯一一个节点。
因此:head = node; → 链表的头指向这个新节点;
last = node; → 链表的尾也指向这个新节点。
if (head == null)
{
head = node;
last = node;
}
//如果链表不为空,则将该节点加到链表的尾部
//并使该节点为尾节点
else
{
last.nextNode = node;
last = node;
}
}
}
LinkedList<int> linkedList = new LinkedList<int>();
linkedList.Add(111);
linkedList.Add(222);
linkedList.Add(333);整个链表的管理方案------删除节点
链表删除中间元素![]() https://blog.csdn.net/2303_80204192/article/details/133823668#t9
https://blog.csdn.net/2303_80204192/article/details/133823668#t9
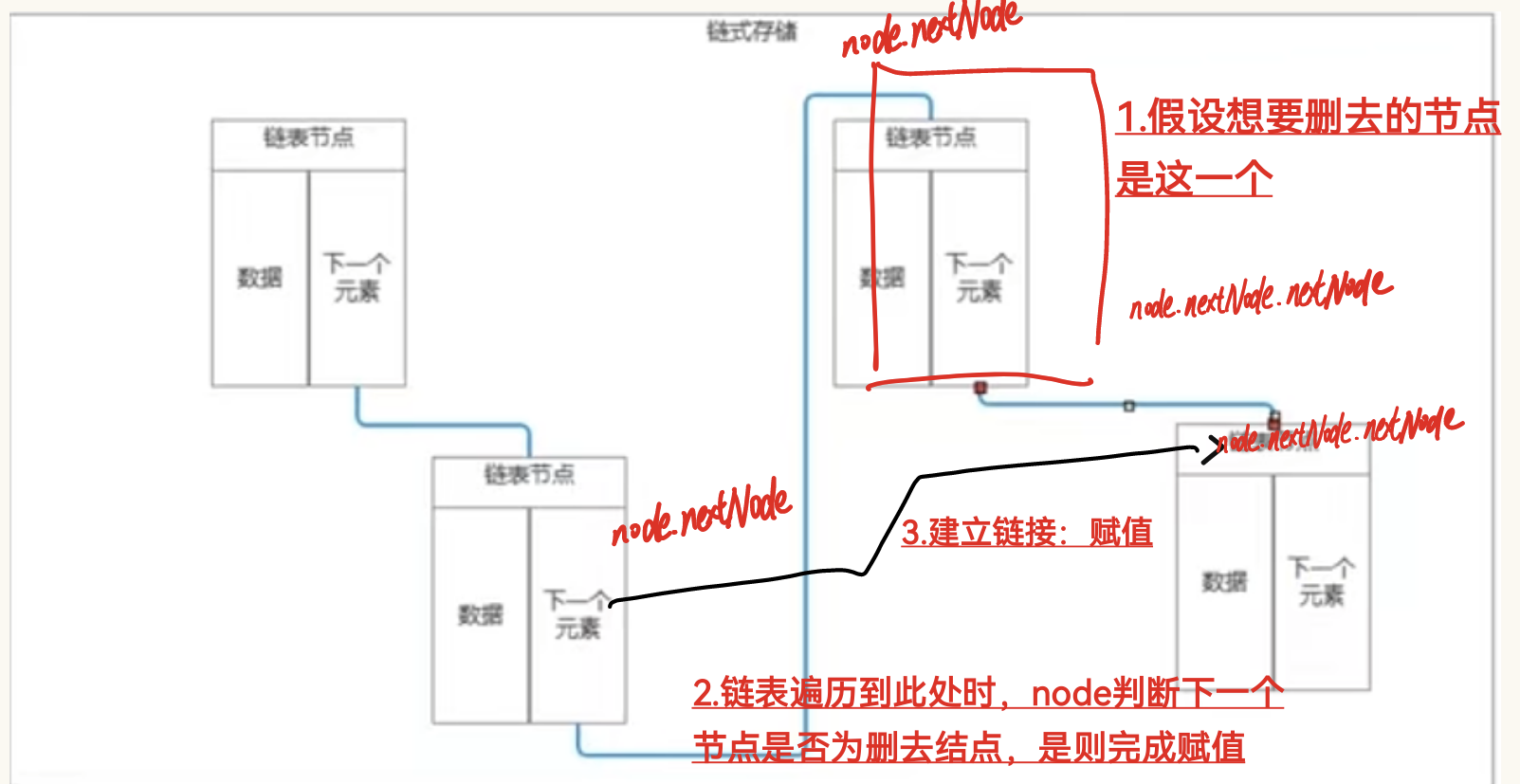
cs
public void Remove(T value)
{
//如果头节点是空则返回
if (head == null)
{
return;
}
//如果头节点的元素与要移除的元素一致
//使头节等于头节点的下一个节点
if (head.value.Equals(value))
{
head = head.nextNode;
//如果头节点被移除后为空
//证明只有一个节点 那尾节点也要为空
if (head == null)
{
last = null;
}
return;
}
//如果中间节点的元素与要移除的元素一致
LinkedNode<T> node = head; //声明一个临时变量用于遍历,从头节点开始遍历
while (node.nextNode!=null)//一直遍历结点
{
if(node.nextNode.value.Equals(value))//找到需要移除的结点
{
//让当前找到的这个元素的上一个节点
//指向自己的下一个节点
node.nextNode = node.nextNode.nextNode;
break;
}
//依靠将当前指针 node 从当前节点移动到下一个节点,即"进入下一个结点"。
//所以放在if外面的后面,找到对应节点后,退出Remove方法不再遍历
node = node.nextNode;
}
}
- 每次循环,我们先检查
node.nextNode。
- 如果
node.nextNode是要删的 → 删除它(node.nextNode = node.nextNode.nextNode),然后break,不再继续遍历。- 如果 不是 要删的 → 我们才需要向前移动 :
node = node.nextNode,去检查下一个节点。
链表遍历输出
cs
LinkedNode<int> node = linkedList.head;
while (node != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(node.value);
node = node.nextNode;
}顺序存储和链式存储的优缺点
从增删查改的角度去思考
增:链式存储 计算上 优于顺序存储(中间插入时链式不用像顺序一样去移动位置)
删:链式存储 计算上 优于顺序存储(中间删除时链式不用像顺序一样去移动位置)
查:顺序存储 使用上 优于链式存储(数组可以直接通过下标得到元素,链式需要遍历)
改:顺序存储 使用上 优于链式存储(数组可以直接通过下标得到元素,链式需要遍历)
LinkedList类
LinkedList是一个C#为我们封装好的类
它的本质是一个可变类型的泛型双向链表
链表对象 需要掌握两个类------一个是链表本身 一个是链表节点类LinkedListNode
增删查改
cs
//⭕增
//1.在链表尾部添加元素
linkedList.AddLast(111);
linkedList.AddLast(222);
//2.在链表头部添加元素
linkedList.AddFirst(999);
//3.在某一个节点之后添加一个节点
//在值为111的节点后加一个值为112的节点
linkedList.AddAfter(linkedList.Find(111), 112);
//4.在某一个节点之前添加一个节点
linkedList.AddBefore(linkedList.Last, 221);
//⭕删
//1.移除头节点
linkedList.RemoveFirst();
//2.移除尾节点
linkedList.RemoveLast();
//3.移除指定节点
linkedList.Remove(222);
//4.清空
linkedList.Clear();
//⭕查
//1.头节点
LinkedListNode<int> frist = linkedList.First;
//2.尾节点
LinkedListNode<int> last = linkedList.Last;
//3.找到指定值的节点(无法通过下标获取指定元素)
LinkedListNode<int> node = linkedList.Find(222);
//4.判断是否存在
if (linkedList.Contains(111))
{
Console.WriteLine("链表中存在111");
}
//⭕改
//先得再改(通过查找到对应节点)
linkedList.First.Value = 100;
(linkedList.Find(222)).Value = 200;
//linkedList中元素为: 100 200 333 444遍历
cs
LinkedListNode<int> nowNode = linkedList.First;
while (nowNode!=null)
{
Console.WriteLine(nowNode.Value);
nowNode = nowNode.Next;
}
//打印结果为: 999 111 112 221 222
//2.从尾到头
nowNode = linkedList.Last;
while (nowNode != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(nowNode.Value);
nowNode = nowNode.Previous;
}
//打印结果为:222 221 112 111 999
//3.foreach遍历
foreach (int item in linkedList)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
//打印结果为: 999 111 112 221 222泛型栈和泛型队列
声明后 使用方式与 栈和队列一模一样
cs
Stack <int> stake = new Stack<int>();
Queue <object> queue = new Queue<object>();