1、获取机器人模型
1、https://github.com/Xk-fly/clean-up-robot
2、代码修改
1>删除 m-explore(Multirobot Explore)功能包:
你可以把它理解为机器人的"好奇心模块"。它的作用是让机器人在不知道地图长啥样的时候,主动去探索那些"未知区域"(地图上的黑色部分),直到把图建完。
2、更新依赖
修改src/robot/package.xml文件
bash
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>robot</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>The robot package for simulation</description>
<maintainer email="thy@todo.todo">thy</maintainer>
<license>TODO</license>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<depend>rclcpp</depend>
<depend>rclpy</depend>
<depend>std_msgs</depend>
<depend>urdf</depend>
<depend>xacro</depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package>修改src/robot/CMakeLists.txt文件
bash
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(robot)
# 1. 寻找依赖库
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(rclpy REQUIRED)
find_package(std_msgs REQUIRED)
# 2. 安装资源文件 (这一步非常重要!)
# 只有把这些文件夹安装了,ros2 launch 才能找到你的模型和配置
install(DIRECTORY
config
launch
urdf
worlds
DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
# 3. 导出依赖并结束
ament_package()3、修改robot功能包:
1、机器人模型car.xacro:
<robot name="my_car_camera" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:include filename="head.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="car_base.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="car_camera.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="car_laser.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="car_move.xacro" />
</robot>2、机器人控制模型car_move.xacro:
<robot name="car_move" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<gazebo>
<plugin name="diff_drive" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so">
<ros>
</ros>
<update_rate>30</update_rate>
<left_joint>left_wheel2base_link</left_joint>
<right_joint>right_wheel2base_link</right_joint>
<wheel_separation>${base_link_radius * 2}</wheel_separation>
<wheel_diameter>${wheel_radius * 2}</wheel_diameter>
<max_wheel_torque>20</max_wheel_torque>
<max_wheel_acceleration>1.0</max_wheel_acceleration>
<command_topic>cmd_vel</command_topic>
<publish_odom>true</publish_odom>
<publish_odom_tf>true</publish_odom_tf>
<publish_wheel_tf>true</publish_wheel_tf>
<odometry_frame>odom</odometry_frame>
<robot_base_frame>base_footprint</robot_base_frame>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
</robot>3、机器人摄像头传感器-car_camera.xacro:
<robot name="car_camera" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:property name="camera_length" value="0.01" />
<xacro:property name="camera_width" value="0.025" />
<xacro:property name="camera_height" value="0.025" />
<xacro:property name="camera_x" value="0.08" />
<xacro:property name="camera_y" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="camera_z" value="${base_link_length / 2 + camera_height / 2}" />
<xacro:property name="camera_m" value="0.01" />
<link name="camera">
<visual>
<geometry>
<box size="${camera_length} ${camera_width} ${camera_height}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="black" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<box size="${camera_length} ${camera_width} ${camera_height}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<xacro:Box_inertial_matrix m="${camera_m}" l="${camera_length}" w="${camera_width}" h="${camera_height}" />
</link>
<joint name="camera2base_link" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="camera" />
<origin xyz="${camera_x} ${camera_y} ${camera_z}" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="camera">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="camera">
<sensor type="camera" name="camera_node">
<update_rate>30.0</update_rate>
<camera name="head">
<horizontal_fov>1.3962634</horizontal_fov>
<image>
<width>1280</width>
<height>720</height>
<format>R8G8B8</format>
</image>
<clip>
<near>0.02</near>
<far>300</far>
</clip>
<noise>
<type>gaussian</type>
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.007</stddev>
</noise>
</camera>
<plugin name="camera_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_camera.so">
<ros>
<remapping>~/image_raw:=/camera/image_raw</remapping>
<remapping>~/camera_info:=/camera/camera_info</remapping>
</ros>
<camera_name>camera</camera_name>
<frame_name>camera</frame_name>
<hack_baseline>0.07</hack_baseline>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
</robot>4、机器人雷达传感器--car_lase.xacro
<robot name="car_laser" xmlns:xacro="http://wiki.ros.org/xacro">
<xacro:property name="support_length" value="0.025" />
<xacro:property name="support_radius" value="0.01" />
<xacro:property name="support_x" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="support_y" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="support_z" value="${base_link_length / 2 + support_length / 2}" />
<xacro:property name="support_m" value="0.02" />
<link name="support">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${support_radius}" length="${support_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="red">
<color rgba="0.8 0.2 0.0 0.8" />
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${support_radius}" length="${support_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${support_m}" r="${support_radius}" h="${support_length}" />
</link>
<joint name="support2base_link" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link" />
<child link="support" />
<origin xyz="${support_x} ${support_y} ${support_z}" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="support">
<material>Gazebo/White</material>
</gazebo>
<xacro:property name="laser_length" value="0.05" />
<xacro:property name="laser_radius" value="0.03" />
<xacro:property name="laser_x" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="laser_y" value="0.0" />
<xacro:property name="laser_z" value="${support_length / 2 + laser_length / 2}" />
<xacro:property name="laser_m" value="0.1" />
<link name="laser">
<visual>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${laser_radius}" length="${laser_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
<material name="black" />
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<cylinder radius="${laser_radius}" length="${laser_length}" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0.0 0.0 0.0" rpy="0.0 0.0 0.0" />
</collision>
<xacro:cylinder_inertial_matrix m="${laser_m}" r="${laser_radius}" h="${laser_length}" />
</link>
<joint name="laser2support" type="fixed">
<parent link="support" />
<child link="laser" />
<origin xyz="${laser_x} ${laser_y} ${laser_z}" />
</joint>
<gazebo reference="laser">
<material>Gazebo/Black</material>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="laser">
<sensor type="ray" name="rplidar">
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
<visualize>true</visualize>
<update_rate>10</update_rate>
<ray>
<scan>
<horizontal>
<samples>360</samples>
<resolution>1</resolution>
<min_angle>-3.14159265</min_angle>
<max_angle>3.14159265</max_angle>
</horizontal>
</scan>
<range>
<min>0.1</min>
<max>10.0</max>
<resolution>0.01</resolution>
</range>
<noise>
<type>gaussian</type>
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.01</stddev>
</noise>
</ray>
<plugin name="gazebo_rplidar" filename="libgazebo_ros_ray_sensor.so">
<ros>
<remapping>~/out:=scan</remapping>
</ros>
<output_type>sensor_msgs/LaserScan</output_type>
<frame_name>laser</frame_name>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
</robot>5、对于head.xacro文件不做修改,他只是涉及到计算,符合ros1和ros2通用的方式,car_base.xacro也是如此,只是定义了小车的形状与颜色,并不涉及到底层驱动,不做修改。
6、创建启动文件(原先.launch文件只适用于ros1)
python
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch_ros.actions import Node
import xacro
def generate_launch_description():
# 1. 获取包路径
robot_name = 'robot' # 你的包名
pkg_path = get_package_share_directory(robot_name)
# 2. 准备 xacro 模型文件路径
xacro_file = os.path.join(pkg_path, 'urdf', 'car.xacro')
# 3. 解析 xacro 文件
# 在 ROS 2 中,我们需要在 launch 文件里显式运行 xacro
doc = xacro.process_file(xacro_file)
robot_description_config = doc.toxml()
# 4. 配置 Gazebo 启动文件
# 这一步代替了原来的 <include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
gazebo_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('gazebo_ros'), 'launch', 'gazebo.launch.py')]),
launch_arguments={'world': os.path.join(pkg_path, 'worlds', 'home.world')}.items(),
)
# 5. 定义 Robot State Publisher 节点
# 这个节点非常重要,它会把你的 URDF 模型发布给 Gazebo 和其他节点
node_robot_state_publisher = Node(
package='robot_state_publisher',
executable='robot_state_publisher',
output='screen',
parameters=[{'robot_description': robot_description_config}]
)
# 6. 定义 Spawn Entity 节点 (在 Gazebo 中生成机器人)
# 这一步代替了原来的 <node pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" ...>
spawn_entity = Node(
package='gazebo_ros',
executable='spawn_entity.py',
arguments=['-topic', 'robot_description',
'-entity', 'mycar'],
output='screen'
)
# 7. 返回 Launch 描述
return LaunchDescription([
gazebo_launch,
node_robot_state_publisher,
spawn_entity
])7、编译与运行:
colcon build
ros2 launch robot robot.launch.py(先赋予权限)
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard(测试键盘控制)
4、修复manual_nav功能包
此功能包主要是为了进行手动建图,ros1中主要是用gmapping进行建图,ros2中一般用slam_toolbox功能包进行建图
1、清理旧残留:
rm -rf ~/clean_robot_ws/src/m-explore
这个m-explore是ros1常用的自主探索功能包,但是在ros2中不适用,在 ROS 2 Humble 里,我们稍后直接用命令 sudo apt install ros-humble-explore-lite 安装官方编译好的版本,比自己修源码稳得多。
2、安装ROS2官方建图功能包:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ros-humble-slam-toolbox ros-humble-navigation2 ros-humble-nav2-bringup -y
3、覆盖src/manual_nav/package.xml依赖文件:
XML
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>manual_nav</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>The manual_nav package for SLAM and Navigation</description>
<maintainer email="thy@todo.todo">thy</maintainer>
<license>TODO</license>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<depend>rclcpp</depend>
<depend>rclpy</depend>
<depend>robot</depend>
<depend>slam_toolbox</depend> <depend>nav2_map_server</depend> <depend>rviz2</depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package>4、覆盖src/manual_nav/CMakeLists.txt编译配置文件:
python
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(manual_nav)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
# 只要安装了对应的包,这里不需要显式 find_package 所有的 ros 包,
# 除非你要编译 C++ 节点。对于纯 launch 包,ament_cmake 足够了。
# 安装资源目录
install(DIRECTORY
config
launch
map
rviz
DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
ament_package()5、编写新的启动文件:
touch src/manual_nav/launch/slam.launch.py(记得给权限)
python
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
# 1. 基础配置
use_sim_time = LaunchConfiguration('use_sim_time', default='true')
manual_nav_dir = get_package_share_directory('manual_nav')
robot_dir = get_package_share_directory('robot')
# 2. 启动机器人底盘 (引用之前的 robot.launch.py)
robot_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join(robot_dir, 'launch', 'robot.launch.py')]),
launch_arguments={'use_sim_time': use_sim_time}.items(),
)
# 3. 启动 SLAM Toolbox (建图核心节点)
# 我们使用 async_slam_toolbox_node,这是最常用的异步建图模式
slam_node = Node(
package='slam_toolbox',
executable='async_slam_toolbox_node',
name='slam_toolbox',
output='screen',
parameters=[
{'use_sim_time': use_sim_time},
# 这里如果不指定配置文件,它会用默认参数,通常对于差速小车足够了
# 如果效果不好,我们后续再添加 mapper_params_online_async.yaml
],
)
# 4. 启动 RViz2
rviz_node = Node(
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
name='rviz2',
# # 加载你原本的 slam.rviz 配置
# arguments=['-d', os.path.join(manual_nav_dir, 'rviz', 'slam.rviz')],
parameters=[{'use_sim_time': use_sim_time}],
output='screen'
)
return LaunchDescription([
robot_launch,
slam_node,
rviz_node
])PS:这里有个小坑,启动文件里包括了RVIZ文件,但是目前的功能包里是没有rviz文件的,但是另外一个auto_nav文件里是由rviz文件的,而且rviz文件对于ros1和2版本差别不大,可以下拿过来用:
bash
# 1. 在 manual_nav 下创建 rviz 目录
mkdir -p ~/clean_robot_ws/src/manual_nav/rviz
# 2. 把 auto_nav 里的 slam.rviz 复制过来
cp ~/clean_robot_ws/src/auto_nav/rviz/slam.rviz ~/clean_robot_ws/src/manual_nav/rviz/6、编译与运行建图
cd ~/clean_robot_ws
colcon build --packages-select manual_nav
| 原 ROS 1 文件 | 功能 | 在 ROS 2 的现状 | 命运 |
|---|---|---|---|
slam.launch |
核心建图 (Gmapping + Rviz) | slam.launch.py (当前) |
✅ 已替换 。我们用 slam_toolbox 替代了 Gmapping,功能一样,性能更强。 |
save_map.launch |
保存地图 | 命令行工具 (CLI) | ❌ 淘汰 。ROS 2 推荐直接用 ros2 run nav2_map_server map_saver_cli ... 命令保存,不需要写个 launch 文件来占位置。 |
nav.launch |
自主导航总入口 | 还没做 | ⏳ 待办 。等图建好了,我们要写一个新的 nav.launch.py 来替代它。 |
amcl.launch |
机器人在地图里定位 | 还没做 | ⏳ 待办。这将包含在 Nav2 的配置里。 |
move.launch |
路径规划 (move_base) | 还没做 | ⏳ 待办 。这将升级为强大的 Nav2 (Navigation 2) 框架。 |
安装地图保存工具 (如果之前没装) sudo apt install ros-humble-nav2-map-server
启动运行:
ros2 launch manual_nav slam.launch.py会自动打开gazebo不用重复打开
启动运动控制节点:
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard
执行保存地图:
保存地图名为 my_home_map # 记得先 cd 到你想保存的目录,比如 src/manual_nav/map/ cd ~/clean_robot_ws/src/manual_nav/map/ ros2 run nav2_map_server map_saver_cli -f my_home_map
7、编写导航启动文件:
python
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
# 1. 获取各个包的路径
manual_nav_dir = get_package_share_directory('manual_nav')
robot_dir = get_package_share_directory('robot')
nav2_bringup_dir = get_package_share_directory('nav2_bringup')
# 2. 基础配置
use_sim_time = LaunchConfiguration('use_sim_time', default='true')
# ⚠️ 这里的地图名字一定要和你保存的一样!
map_yaml_file = os.path.join(manual_nav_dir, 'map', 'my_home_map.yaml')
# Nav2 的默认参数文件(如果是差速轮机器人,官方默认参数通常能跑,不需要自己手搓几十行参数,现在修改了amcl的初始位置节点)
params_file = os.path.join(manual_nav_dir, 'config', 'my_nav2_params.yaml')
# 3. 启动机器人底盘 (Gazebo + Robot State Publisher)
robot_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join(robot_dir, 'launch', 'robot.launch.py')]),
launch_arguments={'use_sim_time': use_sim_time}.items(),
)
# 4. 启动 Nav2 (Bringup)
# 这一个文件会帮我们要启动 Map Server, AMCL (定位), Planner (规划), Controller (控制) 等所有节点
nav2_launch = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource([os.path.join(nav2_bringup_dir, 'launch', 'bringup_launch.py')]),
launch_arguments={
'map': map_yaml_file,
'use_sim_time': use_sim_time,
'params_file': params_file, # 使用默认参数
'autostart': 'true', # 自动进入活跃状态
}.items(),
)
# 5. 启动 RViz
# 这里我们先不加载特定的 .rviz 文件,因为导航需要的配置和建图不一样,我们进去手动配一次再保存
rviz_node = Node(
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
name='rviz2',
arguments=['-d', os.path.join(manual_nav_dir, 'rviz', 'plan_path.rviz')], # 暂时借用你刚才存的文件
parameters=[{'use_sim_time': use_sim_time}],
output='screen'
)
return LaunchDescription([
robot_launch,
nav2_launch,
rviz_node
])添加左侧对应的RVIZ插件,然后保存为.rviz文件,后面launch文件可以自行启动加载:
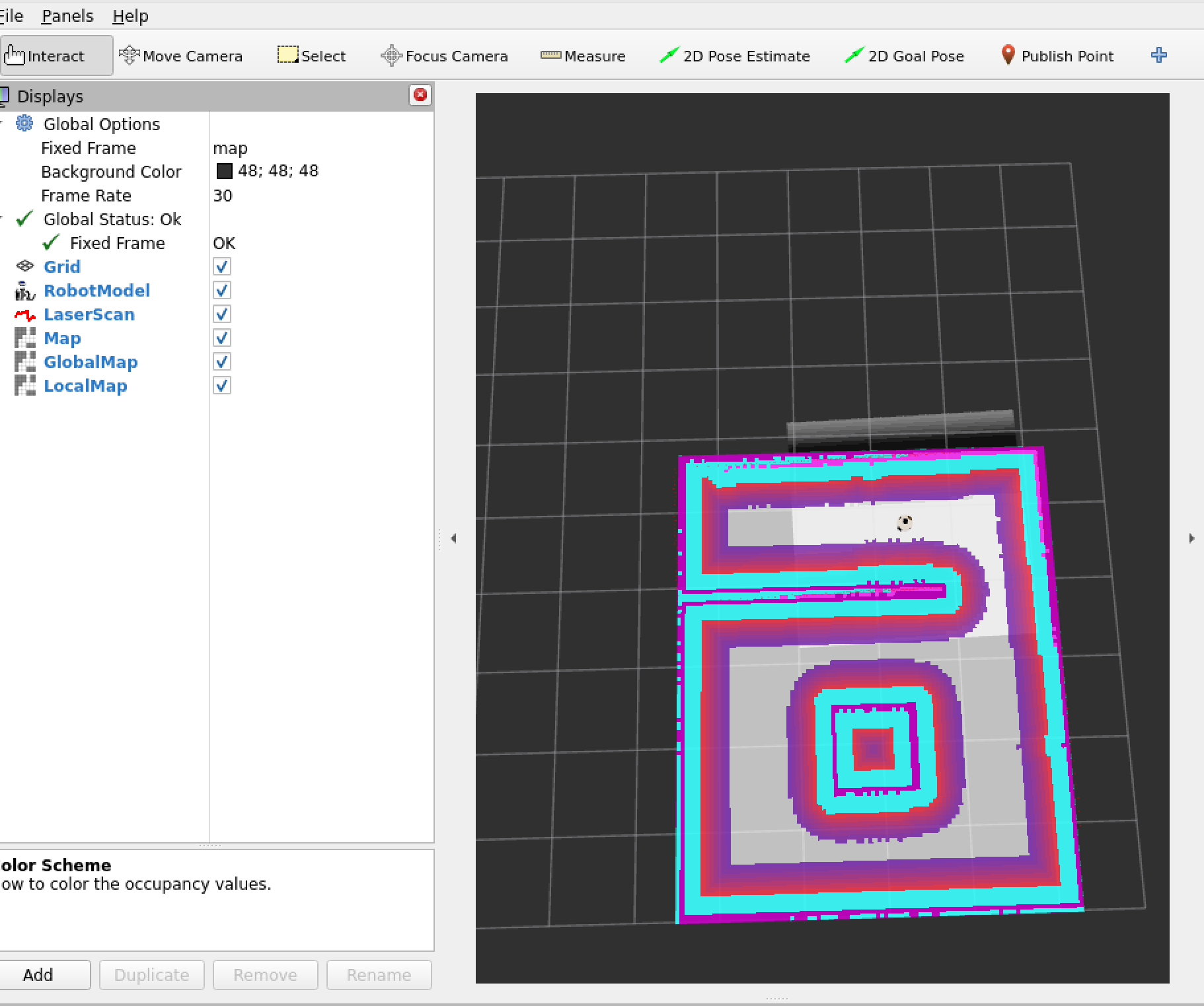
可以将左侧的插件另存为配置文件,修改nav.launch.py文件,加载新的配置文件,上述描述还有Path和Amcl粒子云没有添加,可以自行补充
5、修复auto_nav功能包
1、同样是先修改package.xml和CMakelist.txt文件,确保编译先通过。
CMakeList.txt
XML
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(auto_nav)
if(CMAKE_COMPILER_IS_GNUCXX OR CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER_ID MATCHES "Clang")
add_compile_options(-std=c++17 -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic)
endif()
# 1. 寻找依赖包
find_package(ament_cmake REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp REQUIRED)
find_package(rclcpp_action REQUIRED)
find_package(nav_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(geometry_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(nav2_msgs REQUIRED)
find_package(tf2 REQUIRED)
find_package(tf2_ros REQUIRED) # 关键依赖
find_package(tf2_geometry_msgs REQUIRED) # 关键依赖
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
include_directories(include)
# 2. 编译规划算法库
add_library(path_planning_lib src/path_planning.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(path_planning_lib
rclcpp
nav_msgs
geometry_msgs
tf2
tf2_ros
OpenCV
)
# 3. 编译规划节点 (大脑)
add_executable(path_planning_node src/path_planning_node.cpp)
target_link_libraries(path_planning_node path_planning_lib)
ament_target_dependencies(path_planning_node
rclcpp
nav_msgs
geometry_msgs
)
# 4. 编译执行节点 (手脚)
add_executable(path_executor src/path_executor.cpp)
ament_target_dependencies(path_executor
rclcpp
rclcpp_action
nav2_msgs
nav_msgs
geometry_msgs
tf2
tf2_ros # <--- 之前报错是因为漏了这一行!
tf2_geometry_msgs # <--- 加上这个更稳
)
# 5. 安装规则
install(TARGETS
path_planning_lib
path_planning_node
path_executor
DESTINATION lib/${PROJECT_NAME}
)
install(DIRECTORY include/ DESTINATION include/)
install(DIRECTORY launch config map rviz scripts DESTINATION share/${PROJECT_NAME})
ament_package()3、package.xml
XML
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<?xml-model href="http://download.ros.org/schema/package_format3.xsd" schematypens="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"?>
<package format="3">
<name>auto_nav</name>
<version>0.0.0</version>
<description>The auto_nav package for ROS 2</description>
<maintainer email="thy@todo.todo">thy</maintainer>
<license>TODO</license>
<buildtool_depend>ament_cmake</buildtool_depend>
<depend>rclcpp</depend>
<depend>rclcpp_action</depend> <depend>rclpy</depend>
<depend>std_msgs</depend>
<depend>geometry_msgs</depend>
<depend>nav_msgs</depend>
<depend>nav2_msgs</depend> <depend>nav2_costmap_2d</depend>
<depend>tf2</depend>
<depend>tf2_ros</depend>
<depend>tf2_geometry_msgs</depend>
<depend>cv_bridge</depend>
<depend>image_transport</depend>
<exec_depend>nav2_bringup</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>slam_toolbox</exec_depend>
<exec_depend>robot</exec_depend> <test_depend>ament_lint_auto</test_depend>
<test_depend>ament_lint_common</test_depend>
<export>
<build_type>ament_cmake</build_type>
</export>
</package>4、即便修改后也无法直接编译通过,仍需要修改src源码
-
path_planning.cpp(发的这个) :这是大脑。- 它里面藏着核心的**"全覆盖路径规划算法"**。它决定了机器人怎么走"弓"字形,怎么把房间每个角落都扫一遍。没有它,机器人就只能走直线,没法做清洁。
-
path_planning_node.cpp(没发的) :这是躯壳。- 它里面基本就是个
main函数,负责启动 ROS 节点,然后调用上面的"大脑"。在 ROS 2 里,这个"躯壳"的写法完全变了,所以旧的我不看也没事,我们直接重写一个新的。
- 它里面基本就是个
-
next_goal.cpp(没发的) :这是腿。- 它负责把"大脑"算出来的一长串路径,切成一个个小目标点发给
move_base。好消息是:在 ROS 2 的 Nav2 里,我们不需要这双旧腿了 ,Nav2 有更高级的FollowPath控制器,可以直接执行整条路径!
- 它负责把"大脑"算出来的一长串路径,切成一个个小目标点发给
结论 :只要有了大脑(算法逻辑),剩下的躯壳和腿,我们用 ROS 2 的新技术直接重造,甚至比原来的更好、更稳。
5、路径规划代码
path_plan.cpp
cpp
#include "auto_nav/path_planning.h"
// 构造函数
PathPlanning::PathPlanning(rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr node) : node_(node)
{
m_planPub = node_->create_publisher<nav_msgs::msg::Path>("/plan_path", 1);
// 获取参数
node_->declare_parameter("size_of_cell", 3);
m_cellSize = node_->get_parameter("size_of_cell").as_int();
// TF 初始化
tf_buffer_ = std::make_shared<tf2_ros::Buffer>(node_->get_clock());
tf_listener_ = std::make_shared<tf2_ros::TransformListener>(*tf_buffer_);
}
// 接收地图并初始化
void PathPlanning::setMap(const nav_msgs::msg::OccupancyGrid::SharedPtr map_msg)
{
if (m_initialized) return; // 只初始化一次
current_map_ = *map_msg;
int width = map_msg->info.width;
int height = map_msg->info.height;
m_srcMap = Mat(height, width, CV_8U);
for (int r = 0; r < height; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < width; c++) {
int8_t data = map_msg->data[r * width + c];
unsigned char val = 0;
if (data == -1) val = 255; // 未知
else if (data >= 90) val = 254; // 障碍
else val = 0; // 空闲
m_srcMap.at<uchar>(height - r - 1, c) = val;
}
}
initMat();
if (!m_srcMap.empty()) {
m_initialized = true;
RCLCPP_INFO(node_->get_logger(), "算法初始化完成,地图尺寸: %dx%d", width, height);
getPathInCV();
}
}
void PathPlanning::initMat()
{
m_cellMat = Mat(m_srcMap.rows / m_cellSize, m_srcMap.cols / m_cellSize, m_srcMap.type());
m_freeSpaceVec.clear();
bool isFree = true;
for (int r = 0; r < m_cellMat.rows; r++) {
for (int c = 0; c < m_cellMat.cols; c++) {
isFree = true;
for (int i = 0; i < m_cellSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m_cellSize; j++) {
if (m_srcMap.at<uchar>(r * m_cellSize + i, c * m_cellSize + j) != 0) {
isFree = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (isFree) {
CellIndex ci;
ci.row = r; ci.col = c; ci.theta = 0;
m_freeSpaceVec.push_back(ci);
m_cellMat.at<uchar>(r, c) = 0;
} else {
m_cellMat.at<uchar>(r, c) = 254;
}
}
}
m_neuralMat = Mat(m_cellMat.rows, m_cellMat.cols, CV_32F);
for (int i = 0; i < m_neuralMat.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m_neuralMat.cols; j++) {
if (m_cellMat.at<uchar>(i, j) == 254)
m_neuralMat.at<float>(i, j) = -100000.0;
else
m_neuralMat.at<float>(i, j) = 50.0;
}
}
}
// 核心规划逻辑
void PathPlanning::getPathInCV()
{
CellIndex initPoint, nextPoint, currentPoint;
initPoint.theta = 0;
// 获取机器人位置 (带重试机制)
geometry_msgs::msg::TransformStamped transform;
bool got_tf = false;
// 尝试 10 次,每次等 0.2 秒 (总共等 2 秒)
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
transform = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform("map", "base_link", tf2::TimePointZero);
got_tf = true;
break; // 成功拿到,跳出循环
} catch (tf2::TransformException &ex) {
if (i == 0) {
RCLCPP_WARN(node_->get_logger(), "正在等待坐标变换 (TF) ...");
}
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(200));
}
}
if (got_tf) {
// 成功获取:转换坐标
double wx = transform.transform.translation.x;
double wy = transform.transform.translation.y;
double origin_x = current_map_.info.origin.position.x;
double origin_y = current_map_.info.origin.position.y;
double res = current_map_.info.resolution;
unsigned int mx = (int)((wx - origin_x) / res);
unsigned int my = (int)((wy - origin_y) / res);
initPoint.row = m_cellMat.rows - my / m_cellSize - 1;
initPoint.col = mx / m_cellSize;
RCLCPP_INFO(node_->get_logger(), "成功锁定机器人位置!从 (%.2f, %.2f) 开始规划", wx, wy);
} else {
// 彻底失败:使用默认起点
RCLCPP_ERROR(node_->get_logger(), "TF 获取超时!将使用默认空地作为起点。");
if(!m_freeSpaceVec.empty()) {
initPoint = m_freeSpaceVec[0];
} else {
initPoint.row = 0; initPoint.col = 0;
}
}
// 坐标转换 World -> Map -> Grid
double wx = transform.transform.translation.x;
double wy = transform.transform.translation.y;
// --- 修复点:变量只定义一次 ---
double origin_x = current_map_.info.origin.position.x;
double origin_y = current_map_.info.origin.position.y;
double res = current_map_.info.resolution;
unsigned int mx = (int)((wx - origin_x) / res);
unsigned int my = (int)((wy - origin_y) / res);
initPoint.row = m_cellMat.rows - my / m_cellSize - 1;
initPoint.col = mx / m_cellSize;
if(initPoint.row < 0) initPoint.row = 0;
if(initPoint.col < 0) initPoint.col = 0;
currentPoint = initPoint;
m_pathVec.clear();
m_pathVec.push_back(initPoint);
float initTheta = initPoint.theta;
const float c_0 = 50;
float e = 0.0, v = 0.0, deltaTheta = 0.0, lastTheta = initTheta;
vector<float> thetaVec = {0, 45, 90, 135, 180, 225, 270, 315};
for (int loop = 0; loop < 9000; loop++)
{
int maxIndex = 0;
float max_v = -300;
if(currentPoint.row >= 0 && currentPoint.row < m_neuralMat.rows &&
currentPoint.col >= 0 && currentPoint.col < m_neuralMat.cols) {
m_neuralMat.at<float>(currentPoint.row, currentPoint.col) = -250.0;
}
lastTheta = currentPoint.theta;
for (int id = 0; id < 8; id++)
{
deltaTheta = std::max(thetaVec[id], lastTheta) - std::min(thetaVec[id], lastTheta);
if (deltaTheta > 180) deltaTheta = 360 - deltaTheta;
e = 1 - abs(deltaTheta) / 180;
auto isValid = [&](int r, int c) {
return r >= 0 && r < m_neuralMat.rows && c >= 0 && c < m_neuralMat.cols;
};
v = -100000;
int nr = currentPoint.row, nc = currentPoint.col;
switch (id) {
case 0: nc++; break;
case 1: nr--; nc++; break;
case 2: nr--; break;
case 3: nr--; nc--; break;
case 4: nc--; break;
case 5: nr++; nc--; break;
case 6: nr++; break;
case 7: nr++; nc++; break;
}
if (isValid(nr, nc)) {
v = m_neuralMat.at<float>(nr, nc) + c_0 * e;
if (id % 2 != 0) v -= 200;
}
if (v > max_v) {
max_v = v;
maxIndex = id;
}
}
if (max_v <= 0) {
float dist = 0.0, minDist = 1e9;
int minIndex = -1;
for (size_t ii = 0; ii < m_freeSpaceVec.size(); ii++) {
CellIndex& p = m_freeSpaceVec[ii];
if (m_neuralMat.at<float>(p.row, p.col) > 0) {
if (boundingJudge(p.row, p.col)) {
dist = sqrt(pow(currentPoint.row - p.row, 2) + pow(currentPoint.col - p.col, 2));
if (dist < minDist) {
minDist = dist;
minIndex = ii;
}
}
}
}
if (minIndex != -1) {
nextPoint = m_freeSpaceVec[minIndex];
currentPoint = nextPoint;
m_pathVec.push_back(nextPoint);
continue;
} else {
break;
}
}
switch (maxIndex) {
case 0: nextPoint.col++; break;
case 1: nextPoint.row--; nextPoint.col++; break;
case 2: nextPoint.row--; break;
case 3: nextPoint.row--; nextPoint.col--; break;
case 4: nextPoint.col--; break;
case 5: nextPoint.row++; nextPoint.col--; break;
case 6: nextPoint.row++; break;
case 7: nextPoint.row++; nextPoint.col++; break;
}
nextPoint.theta = thetaVec[maxIndex];
currentPoint = nextPoint;
m_pathVec.push_back(nextPoint);
}
m_pathVecInROS.clear();
geometry_msgs::msg::PoseStamped ps;
ps.header.frame_id = "map";
ps.header.stamp = node_->get_clock()->now();
// --- 修复点:直接使用上面已经定义的变量,不再重复定义 ---
int sizey = m_cellMat.rows;
// origin_x, origin_y, res 已经在函数开头定义过了,直接用
for (auto &pt : m_pathVec) {
double wx = (pt.col * m_cellSize + m_cellSize / 2.0) * res + origin_x;
double wy = ((sizey - pt.row - 1) * m_cellSize + m_cellSize / 2.0) * res + origin_y;
ps.pose.position.x = wx;
ps.pose.position.y = wy;
ps.pose.position.z = 0;
// --- 修复点:移除了未使用的 yaw 变量 ---
ps.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
m_pathVecInROS.push_back(ps);
}
}
bool PathPlanning::boundingJudge(int a, int b)
{
for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++) {
for (int m = -1; m <= 1; m++) {
if (i == 0 && m == 0) continue;
int r = a + i, c = b + m;
if (r >= 0 && r < m_neuralMat.rows && c >= 0 && c < m_neuralMat.cols) {
if (m_neuralMat.at<float>(r, c) == -250.0) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void PathPlanning::publishCoveragePath()
{
if (!m_initialized) return;
nav_msgs::msg::Path gui_path;
gui_path.header.frame_id = "map";
gui_path.header.stamp = node_->get_clock()->now();
gui_path.poses = m_pathVecInROS;
m_planPub->publish(gui_path);
}6、路径发布节点
path_planing_node.cpp
cpp
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "nav_msgs/msg/occupancy_grid.hpp"
#include "auto_nav/path_planning.h"
class PathPlanningNode : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
PathPlanningNode() : Node("path_planning_node")
{
// 构造函数保持为空,或者只做简单的参数声明
// 绝对不要在这里调用 shared_from_this()
}
// 新增一个初始化函数
void init()
{
// 此时节点已经构造完成,可以安全地把 shared_ptr 传给大脑了
planner_ = std::make_shared<PathPlanning>(shared_from_this());
// 订阅地图
sub_map_ = this->create_subscription<nav_msgs::msg::OccupancyGrid>(
"/global_costmap/costmap", 10,
std::bind(&PathPlanningNode::map_callback, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// 定时发布路径
timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
std::chrono::seconds(1),
std::bind(&PathPlanningNode::timer_callback, this));
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "C++ 规划节点已启动!等待地图...");
}
private:
void map_callback(const nav_msgs::msg::OccupancyGrid::SharedPtr msg)
{
if (planner_) planner_->setMap(msg);
}
void timer_callback()
{
if (planner_) planner_->publishCoveragePath();
}
std::shared_ptr<PathPlanning> planner_;
rclcpp::Subscription<nav_msgs::msg::OccupancyGrid>::SharedPtr sub_map_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
// 1. 先创建节点 (此时 shared_ptr 正在管理它)
auto node = std::make_shared<PathPlanningNode>();
// 2. 再手动初始化 (此时 shared_from_this() 是安全的)
node->init();
rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}7、轨迹控制节点:
path_execute.cpp
cpp
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "rclcpp_action/rclcpp_action.hpp"
#include "nav_msgs/msg/path.hpp"
#include "nav2_msgs/action/navigate_to_pose.hpp"
#include <tf2_ros/buffer.h>
#include <tf2_ros/transform_listener.h>
#include <tf2_geometry_msgs/tf2_geometry_msgs.hpp>
#include <tf2/LinearMath/Quaternion.h>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class PathExecutor : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
using NavigateToPose = nav2_msgs::action::NavigateToPose;
PathExecutor() : Node("path_executor")
{
tf_buffer_ = std::make_shared<tf2_ros::Buffer>(this->get_clock());
tf_listener_ = std::make_shared<tf2_ros::TransformListener>(*tf_buffer_);
sub_path_ = this->create_subscription<nav_msgs::msg::Path>(
"/plan_path", 10, std::bind(&PathExecutor::path_cb, this, std::placeholders::_1));
action_client_ = rclcpp_action::create_client<NavigateToPose>(
this, "navigate_to_pose");
timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
std::chrono::milliseconds(100),
std::bind(&PathExecutor::control_loop, this));
// 参数配置
this->declare_parameter("tolerance_goal", 0.6); // 到达判定距离
this->declare_parameter("max_lookahead", 15); // 最大前瞻步数 (直路最远看多远)
normeNextGoal_ = this->get_parameter("tolerance_goal").as_double();
max_lookahead_ = this->get_parameter("max_lookahead").as_int();
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "C++ 执行官 (智能前瞻版 v7.0) 就位!");
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "策略:直路加速(max=%d),弯道精准(自动锁定弯心)", max_lookahead_);
}
private:
void path_cb(const nav_msgs::msg::Path::SharedPtr msg)
{
if (path_.empty() || msg->poses.size() != path_.size()) {
path_.clear();
for (auto &p : msg->poses) {
Goal g;
g.x = p.pose.position.x;
g.y = p.pose.position.y;
path_.push_back(g);
}
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "装载新路径,共 %ld 个点", path_.size());
count_ = 0;
goal_reached_ = false;
last_stuck_time_ = this->now();
}
}
// 🧠 核心算法:智能计算动态前瞻点
int get_smart_lookahead_index(int current_idx) {
int target_idx = current_idx;
if (current_idx + 1 >= (int)path_.size()) return current_idx;
// 1. 计算当前起步的朝向
float dx_ref = path_[current_idx+1].x - path_[current_idx].x;
float dy_ref = path_[current_idx+1].y - path_[current_idx].y;
float angle_ref = atan2(dy_ref, dx_ref);
// 2. 往后探索,直到遇到拐弯
for (int i = 1; i <= max_lookahead_; i++) {
int check_idx = current_idx + i;
if (check_idx >= (int)path_.size()) {
target_idx = check_idx - 1; // 到头了
break;
}
// 计算这一段的朝向
float dx = path_[check_idx].x - path_[check_idx-1].x;
float dy = path_[check_idx].y - path_[check_idx-1].y;
float angle_curr = atan2(dy, dx);
// 计算角度差 (处理 -PI 到 PI 的跳变)
float angle_diff = fabs(atan2(sin(angle_curr - angle_ref), cos(angle_curr - angle_ref)));
// ⚠️ 发现拐弯!(角度变化超过 30度)
if (angle_diff > 0.5) {
// 立即停止前瞻,锁定在拐弯前的最后一个直路点
// 这样小车就会直直地开到墙角,绝对不会切内线撞墙
target_idx = check_idx - 1;
// RCLCPP_DEBUG(this->get_logger(), "检测到弯道,前瞻锁定在点 %d", target_idx);
return target_idx;
}
// 如果是直路,就继续往远了看
target_idx = check_idx;
}
return target_idx;
}
bool get_robot_pose(float &x, float &y)
{
try {
geometry_msgs::msg::TransformStamped t;
t = tf_buffer_->lookupTransform("map", "base_link", tf2::TimePointZero);
x = t.transform.translation.x;
y = t.transform.translation.y;
return true;
} catch (const tf2::TransformException &ex) {
return false;
}
}
void control_loop()
{
if (path_.empty()) return;
if ((size_t)count_ >= path_.size()) return;
float current_x = 0, current_y = 0;
if (!get_robot_pose(current_x, current_y)) return;
float dist = sqrt(pow(current_x - path_[count_].x, 2) + pow(current_y - path_[count_].y, 2));
// 调试日志
static auto last_print = this->now();
if ((this->now() - last_print).seconds() > 2.0) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "进度 %d/%ld | 距离: %.2f m", count_, path_.size(), dist);
last_print = this->now();
}
// 超时判定
bool is_close = dist <= normeNextGoal_;
bool is_stuck = (this->now() - last_stuck_time_).seconds() > 8.0; // 稍微放宽到8秒,给拐弯多点时间
if (is_close || is_stuck) {
if (is_stuck && !is_close) {
RCLCPP_WARN(this->get_logger(), "⚠️ 点 %d 卡顿超时,尝试切换...", count_);
}
count_++;
goal_reached_ = false;
last_stuck_time_ = this->now();
if ((size_t)count_ >= path_.size()) {
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "🎉 全屋清扫任务完成!");
return;
}
}
if (!goal_reached_) {
// 🧠 调用智能前瞻函数
int smart_target_idx = get_smart_lookahead_index(count_);
send_goal_to_nav2(path_[smart_target_idx]);
goal_reached_ = true;
}
}
struct Goal { float x, y; };
void send_goal_to_nav2(Goal g)
{
if (!action_client_->wait_for_action_server(std::chrono::seconds(1))) return;
auto goal_msg = NavigateToPose::Goal();
goal_msg.pose.header.frame_id = "map";
goal_msg.pose.header.stamp = this->now();
goal_msg.pose.pose.position.x = g.x;
goal_msg.pose.pose.position.y = g.y;
// 计算朝向 (简单指向目标)
// 在弯道处,这会让机器人车头对准拐角,非常合理
double angle = 0.0;
float dx = g.x - path_[count_].x; // 注意:朝向是相对于当前位置的
float dy = g.y - path_[count_].y;
if (sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy) > 0.01) {
angle = atan2(dy, dx);
} else if (count_ + 1 < (int)path_.size()) {
angle = atan2(path_[count_+1].y - path_[count_].y, path_[count_+1].x - path_[count_].x);
}
tf2::Quaternion q;
q.setRPY(0, 0, angle);
goal_msg.pose.pose.orientation.x = q.x();
goal_msg.pose.pose.orientation.y = q.y();
goal_msg.pose.pose.orientation.z = q.z();
goal_msg.pose.pose.orientation.w = q.w();
auto send_goal_options = rclcpp_action::Client<NavigateToPose>::SendGoalOptions();
action_client_->async_send_goal(goal_msg, send_goal_options);
}
rclcpp::Subscription<nav_msgs::msg::Path>::SharedPtr sub_path_;
rclcpp_action::Client<NavigateToPose>::SharedPtr action_client_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
std::shared_ptr<tf2_ros::Buffer> tf_buffer_;
std::shared_ptr<tf2_ros::TransformListener> tf_listener_;
vector<Goal> path_;
float normeNextGoal_ = 0.6;
int max_lookahead_ = 15;
int count_ = 0;
bool goal_reached_ = false;
rclcpp::Time last_stuck_time_;
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared<PathExecutor>());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}8、path_planning.cpp代码深度分析
bash
经过对 path_planning.cpp 的四百行代码分析,我发现它使用的是一种经典的**"生物激励神经网络 (Bio-inspired Neural Network)"**覆盖算法。
它的工作原理(用人话讲):
地图栅格化:它把房间地图切成一个个小格子(initMat 函数)。
能量场机制:
障碍物/墙壁:被标记为 -100000 分(极度讨厌,绝对不去)。
未扫过的空地:被标记为 +50 分(有吸引力)。
扫过的区域:被标记为 -250 分(有点讨厌,尽量不走回头路)。
贪婪寻路 (getPathInCV 函数):
机器人每次都会看周围 8 个格子,挑分数最高(最吸引它)的那个格子走。
如果周围全是走过的路(死胡同),它会启动"搜寻模式" (boundingJudge),跳到离它最近的没扫过的地方继续扫。
循环:它循环 9000 次(loop<9000),生成一条长长的路径。6、自主建图算法复现
1、源码编译explore lite自主建图算法:
bash
# 1. 安装 SLAM 工具箱 (替代 Gmapping)
sudo apt install ros-humble-slam-toolbox
# 2. 安装自主探索算法 (Explore Lite 的 ROS 2 版)
cd ~/robot_cleac_ws/src
# 下载 m-explore-ros2 源码 (这是 explore_lite 的 ROS 2 版本仓库)
git clone https://github.com/robo-friends/m-explore-ros2.git
cd ~/robot_cleac_ws/
# 安装源码所需的依赖库 (这一步是个好习惯)
rosdepc install --from-paths src --ignore-src -y
# 只编译这个新包,节省时间
colcon build --packages-select explore_lite
# 刷新环境 (非常重要!否则系统还是找不到它)
source install/setup.bash2、安装官方模型:
bash
# 安装 TurtleBot3 的仿真包、导航包和描述文件
sudo apt install ros-humble-turtlebot3-gazebo ros-humble-turtlebot3-bringup ros-humble-turtlebot3-description
# 这一步很重要!设置默认模型名称 (否则 Gazebo 可能会加载出空壳或者报错)
echo "export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=burger" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc3、创建全自动脚本
explore_auto.sh记得赋予权限
bash
#!/bin/bash
# 文件名: explore_auto.sh
# 1. 清理旧进程
./clean_kill.sh
source install/setup.bash
export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=burger
echo "🚀 [1/4] 启动 Gazebo 仿真环境..."
# 启动仿真
ros2 launch turtlebot3_gazebo turtlebot3_world.launch.py > /dev/null 2>&1 &
SIM_PID=$!
sleep 5
echo "🗺️ [2/4] 启动 SLAM Toolbox (在线建图)..."
# 🔴 关键修改:加上 use_sim_time:=True
ros2 launch slam_toolbox online_async_launch.py use_sim_time:=True > /dev/null 2>&1 &
sleep 5
echo "🧭 [3/4] 启动 Nav2 导航栈..."
# 这里原本就有 use_sim_time,保持不变
ros2 launch nav2_bringup navigation_launch.py use_sim_time:=True > /dev/null 2>&1 &
sleep 8
echo "🕵️ [4/4] 启动 Explore Lite (自主探索)..."
# 🔴 关键修改:加上 -p use_sim_time:=true
ros2 run explore_lite explore \
--ros-args \
-p use_sim_time:=true \
-p robot_base_frame:=base_link \
-p costmap_topic:=/map \
-p visualize:=true \
-p planner_frequency:=0.33 \
-p progress_timeout:=30.0 \
-p potential_scale:=3.0 \
-p orientation_scale:=0.0 \
-p gain_scale:=1.0 \
-p transform_tolerance:=0.3 \
-p min_frontier_size:=0.75 &
echo "✨ 系统全开!打开 RViz 查看效果..."
# 启动 RViz
ros2 launch nav2_bringup rviz_launch.py > /dev/null 2>&1 &
wait $SIM_PID4、保存地图
bash
ros2 run nav2_map_server map_saver_cli -f my_map