1.YOLOv8图像分割支持的数据格式:
(1).用于训练YOLOv8分割模型的数据集标签格式如下:
1).每幅图像对应一个文本文件:数据集中的每幅图像都有一个与图像文件同名的对应文本文件,扩展名为".txt";
2).文本文件中每个目标(object)占一行:文本文件中的每一行对应图像中的一个目标实例;
3).每行目标信息:如下所示:之间用空格分隔
A.目标类别索引:整数,例如:0代表person,1代表car,等等;
B.目标边界坐标:mask区域周围的边界坐标,归一化为[0, 1];
bash
<class-index> <x1> <y1> <x2> <y2> ... <xn> <yn>注 :每行的长度不必相等;每个分隔label必须至少有3对xy点
(2).数据集YAML格式:Ultralytics框架使用YAML文件格式来定义用于训练分隔模型的数据集和模型配置,如下面测试数据集melon中melon_seg.yaml内容如下: 在网上下载了60多幅包含西瓜和冬瓜的图像组成melon数据集
bash
path: ../datasets/melon_seg # dataset root dir
train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path')
val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path')
test: # test images (optional)
# Classes
names:
0: watermelon
1: wintermelon2.使用半自动标注工具 EISeg 对数据集melon进行标注:
(1).从 PaddleSeg 中下载"通用场景的图像标注"高精度模型static_hrnet18_ocr64_cocolvis.zip;
(2).标注前先按照下面操作设置好:
1).选中JSON保存,取消COCO保存;
2).选中自动保存;
3).取消灰度保存.
3.编写Python脚本将EISeg生成的json文件转换成YOLOv8 segment支持的txt文件:
python
import os
import json
import argparse
import colorama
import random
import shutil
import cv2
# supported image formats
img_formats = (".bmp", ".jpeg", ".jpg", ".png", ".webp")
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="json(EISeg) to txt(YOLOv8)")
parser.add_argument("--dir", required=True, type=str, help="images directory, all json files are in the label directory, and generated txt files are also in the label directory")
parser.add_argument("--labels", required=True, type=str, help="txt file that hold indexes and labels, one label per line, for example: face 0")
parser.add_argument("--val_size", default=0.2, type=float, help="the proportion of the validation set to the overall dataset:[0., 0.5]")
parser.add_argument("--name", required=True, type=str, help="the name of the dataset")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def get_labels_index(name):
labels = {} # key,value
with open(name, "r") as file:
for line in file:
# print("line:", line)
key_value = []
for v in line.split(" "):
# print("v:", v)
key_value.append(v.replace("\n", "")) # remove line breaks(\n) at the end of the line
if len(key_value) != 2:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: each line should have only two values(key value):", len(key_value))
continue
labels[key_value[0]] = key_value[1]
with open(name, "r") as file:
line_num = len(file.readlines())
if line_num != len(labels):
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: there may be duplicate lables:", line_num, len(labels))
return labels
def get_json_files(dir):
jsons = []
for x in os.listdir(dir+"/label"):
if x.endswith(".json"):
jsons.append(x)
return jsons
def parse_json(name_json, name_image):
img = cv2.imread(name_image)
if img is None:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: unable to load image:", name_image)
raise
height, width = img.shape[:2]
with open(name_json, "r") as file:
data = json.load(file)
objects=[]
for i in range(0, len(data)):
object = []
object.append(data[i]["name"])
object.append(data[i]["points"])
objects.append(object)
return width, height, objects
def write_to_txt(name_json, width, height, objects, labels):
name_txt = name_json[:-len(".json")] + ".txt"
# print("name txt:", name_txt)
with open(name_txt, "w") as file:
for obj in objects: # 0: name; 1: points
if len(obj[1]) < 3:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: must be at least 3 pairs:", len(obj[1]), name_json)
raise
if obj[0] not in labels:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: unsupported label:", obj[0], labels)
raise
string = ""
for pt in obj[1]:
string = string + " " + str(round(pt[0] / width, 6)) + " " + str(round(pt[1] / height, 6))
string = labels[obj[0]] + string + "\r"
file.write(string)
def json_to_txt(dir, jsons, labels):
for json in jsons:
name_json = dir + "/label/" + json
name_image = ""
for format in img_formats:
file = dir + "/" + json[:-len(".json")] + format
if os.path.isfile(file):
name_image = file
break
if not name_image:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: required image does not exist:", json[:-len(".json")])
raise
# print("name image:", name_image)
width, height, objects = parse_json(name_json, name_image)
# print(f"width: {width}; height: {height}; objects: {objects}")
write_to_txt(name_json, width, height, objects, labels)
def get_random_sequence(length, val_size):
numbers = list(range(0, length))
val_sequence = random.sample(numbers, int(length*val_size))
# print("val_sequence:", val_sequence)
train_sequence = [x for x in numbers if x not in val_sequence]
# print("train_sequence:", train_sequence)
return train_sequence, val_sequence
def get_files_number(dir):
count = 0
for file in os.listdir(dir):
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(dir, file)):
count += 1
return count
def split_train_val(dir, jsons, name, val_size):
if val_size > 0.5 or val_size < 0.01:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: the interval for val_size should be:[0.01, 0.5]:", val_size)
raise
dst_dir_images_train = "datasets/" + name + "/images/train"
dst_dir_images_val = "datasets/" + name + "/images/val"
dst_dir_labels_train = "datasets/" + name + "/labels/train"
dst_dir_labels_val = "datasets/" + name + "/labels/val"
try:
os.makedirs(dst_dir_images_train) #, exist_ok=True
os.makedirs(dst_dir_images_val)
os.makedirs(dst_dir_labels_train)
os.makedirs(dst_dir_labels_val)
except OSError as e:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: cannot create directory:", e.strerror)
raise
# print("jsons:", jsons)
train_sequence, val_sequence = get_random_sequence(len(jsons), val_size)
for index in train_sequence:
for format in img_formats:
file = dir + "/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + format
# print("file:", file)
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_images_train)
break
file = dir + "/label/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + ".txt"
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_labels_train)
for index in val_sequence:
for format in img_formats:
file = dir + "/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + format
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_images_val)
break
file = dir + "/label/" + jsons[index][:-len(".json")] + ".txt"
if os.path.isfile(file):
shutil.copy(file, dst_dir_labels_val)
num_images_train = get_files_number(dst_dir_images_train)
num_images_val = get_files_number(dst_dir_images_val)
num_labels_train = get_files_number(dst_dir_labels_train)
num_labels_val = get_files_number(dst_dir_labels_val)
if num_images_train + num_images_val != len(jsons) or num_labels_train + num_labels_val != len(jsons):
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: the number of files is inconsistent:", num_images_train, num_images_val, num_labels_train, num_labels_val, len(jsons))
raise
def generate_yaml_file(labels, name):
path = os.path.join("datasets", name, name+".yaml")
# print("path:", path)
with open(path, "w") as file:
file.write("path: ../datasets/%s # dataset root dir\n" % name)
file.write("train: images/train # train images (relative to 'path')\n")
file.write("val: images/val # val images (relative to 'path')\n")
file.write("test: # test images (optional)\n\n")
file.write("# Classes\n")
file.write("names:\n")
for key, value in labels.items():
# print(f"key: {key}; value: {value}")
file.write(" %d: %s\n" % (int(value), key))
if __name__ == "__main__":
colorama.init()
args = parse_args()
# 1. parse JSON file and write it to a TXT file
labels = get_labels_index(args.labels)
# print("labels:", labels)
jsons = get_json_files(args.dir)
# print(f"jsons: {jsons}; number: {len(jsons)}")
json_to_txt(args.dir, jsons, labels)
# 2. split the dataset
split_train_val(args.dir, jsons, args.name, args.val_size)
# 3. generate a YAML file
generate_yaml_file(labels, args.name)
print(colorama.Fore.GREEN + "====== execution completed ======")以上脚本包含3个功能:
1).将json文件转换成txt文件;
2).将数据集随机拆分成训练集和测试集;
3).产生需要的yaml文件
4.编写Python脚本进行train:
python
import argparse
import colorama
from ultralytics import YOLO
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="YOLOv8 train")
parser.add_argument("--yaml", required=True, type=str, help="yaml file")
parser.add_argument("--epochs", required=True, type=int, help="number of training")
parser.add_argument("--task", required=True, type=str, choices=["detect", "segment"], help="specify what kind of task")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def train(task, yaml, epochs):
if task == "detect":
model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # load a pretrained model
elif task == "segment":
model = YOLO("yolov8n-seg.pt") # load a pretrained model
else:
print(colorama.Fore.RED + "Error: unsupported task:", task)
raise
results = model.train(data=yaml, epochs=epochs, imgsz=640) # train the model
metrics = model.val() # It'll automatically evaluate the data you trained, no arguments needed, dataset and settings remembered
model.export(format="onnx") #, dynamic=True) # export the model, cannot specify dynamic=True, opencv does not support
# model.export(format="onnx", opset=12, simplify=True, dynamic=False, imgsz=640)
model.export(format="torchscript") # libtorch
if __name__ == "__main__":
colorama.init()
args = parse_args()
train(args.task, args.yaml, args.epochs)
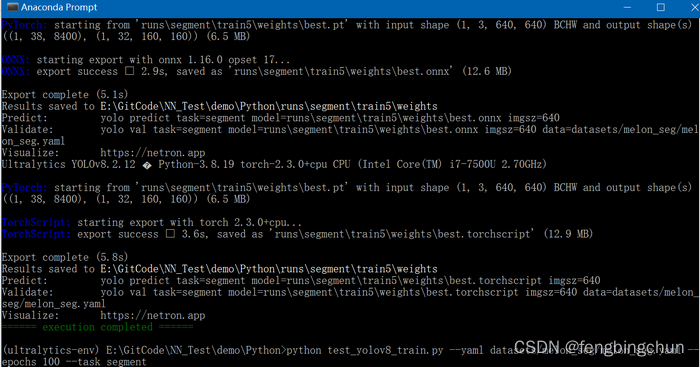
print(colorama.Fore.GREEN + "====== execution completed ======")执行结果如下图所示:会生成best.pt、best.onnx、best.torchscript
5.生成的best.onnx使用Netron进行可视化,结果如下图所示:
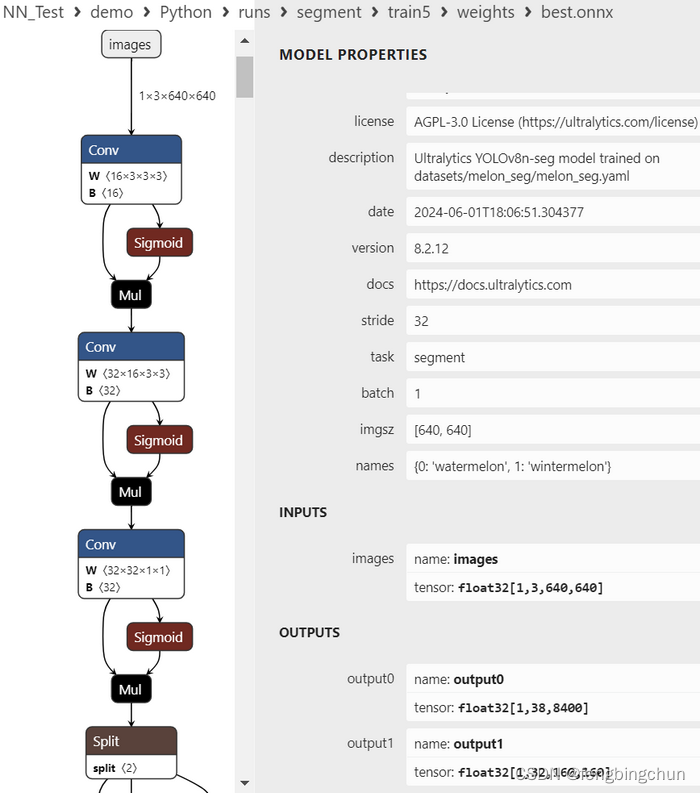
说明:
1).输入:images: float32[1,3,640,640] :与YOLOv8 detect一致,大小为3通道640*640
2).输出:包括2层,output0和output1
A.output0: float32[1,38,8400] :
a.8400:模型预测的所有box的数量,与YOLOv8 detect一致;
b.38: 每个框给出38个值:4:xc, yc, width, height;2:class, confidences;32:mask weights
B.output1: float32[1,32,160,160] :最终mask大小是160*160;output1中的masks实际上只是原型masks,并不代表最终masks。为了得到某个box的最终mask,你可以将每个mask与其对应的mask weight相乘,然后将所有这些乘积相加。此外,你可以在box上应用NMS,以获得具有特定置信度阈值的box子集
6.编写Python脚本实现predict:
python
import colorama
import argparse
from ultralytics import YOLO
import os
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="YOLOv8 predict")
parser.add_argument("--model", required=True, type=str, help="model file")
parser.add_argument("--dir_images", required=True, type=str, help="directory of test images")
parser.add_argument("--dir_result", required=True, type=str, help="directory where the image results are saved")
args = parser.parse_args()
return args
def get_images(dir):
# supported image formats
img_formats = (".bmp", ".jpeg", ".jpg", ".png", ".webp")
images = []
for file in os.listdir(dir):
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(dir, file)):
# print(file)
_, extension = os.path.splitext(file)
for format in img_formats:
if format == extension.lower():
images.append(file)
break
return images
def predict(model, dir_images, dir_result):
model = YOLO(model) # load an model
model.info() # display model information
images = get_images(dir_images)
# print("images:", images)
os.makedirs(dir_result) #, exist_ok=True)
for image in images:
results = model.predict(dir_images+"/"+image)
for result in results:
# print(result)
result.save(dir_result+"/"+image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
colorama.init()
args = parse_args()
predict(args.model, args.dir_images, args.dir_result)
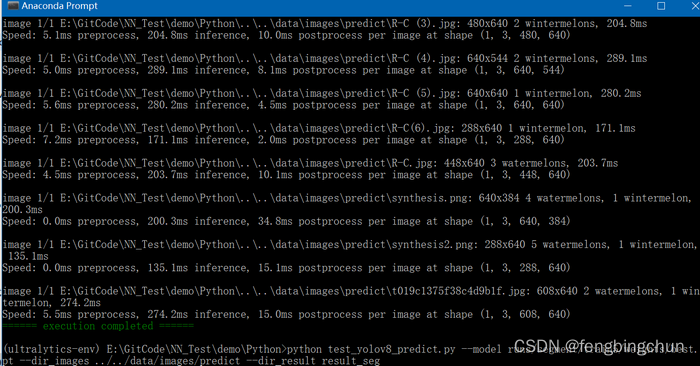
print(colorama.Fore.GREEN + "====== execution completed ======")执行结果如下图所示:
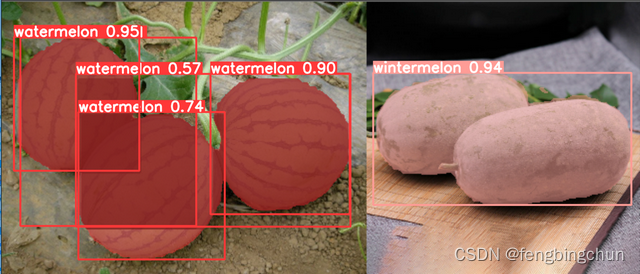
其中一幅图像的分割结果如下图所示:以下是epochs设置为100时生成的best.pt的结果