
Conference:ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS)
CCF level:CCF A
Categories:network and information security
Year:2023
Num:25
1
Title:
Under the Dark: A Systematical Study of Stealthy Mining Pools (Ab)use in the Wild
黑暗之下:对野外隐秘矿池滥用的系统研究
Authors:****

Key words:
Cryptocurrency Mining; Cryptojacking; Malware; Botnet
加密货币挖矿;加密劫持;恶意软件;Botnet
Abstract:****
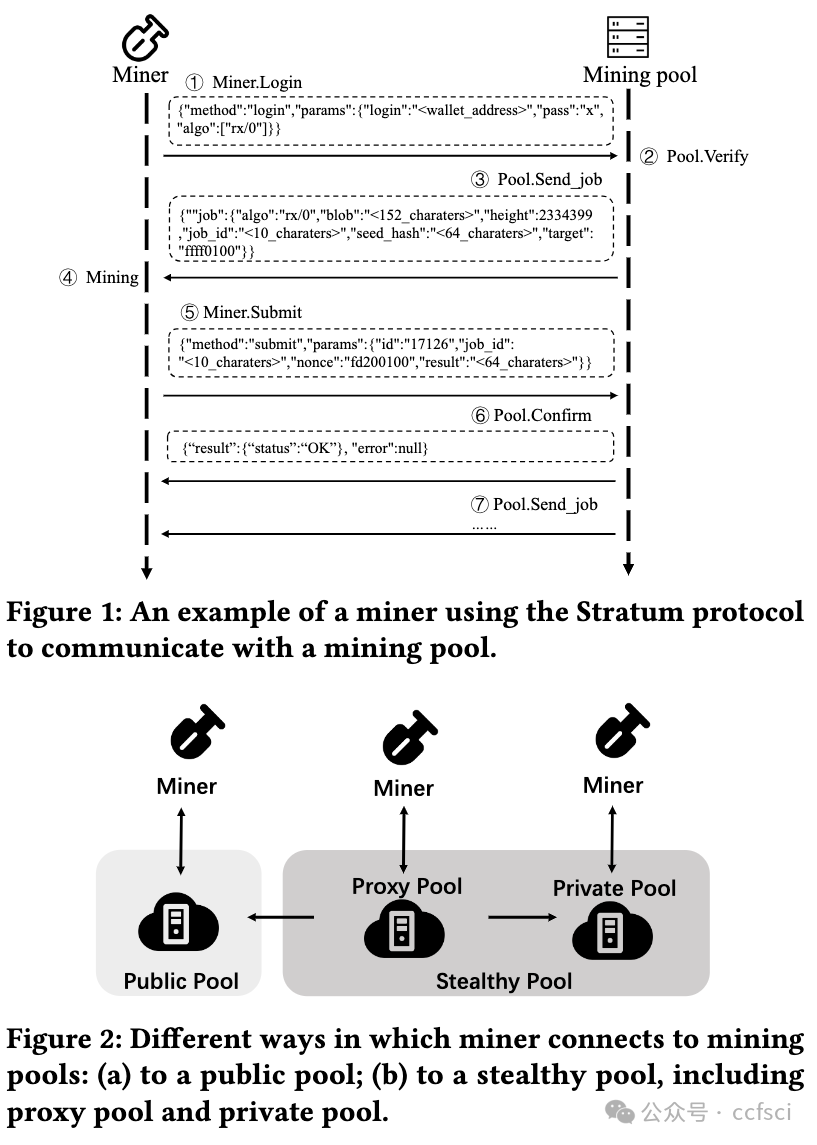
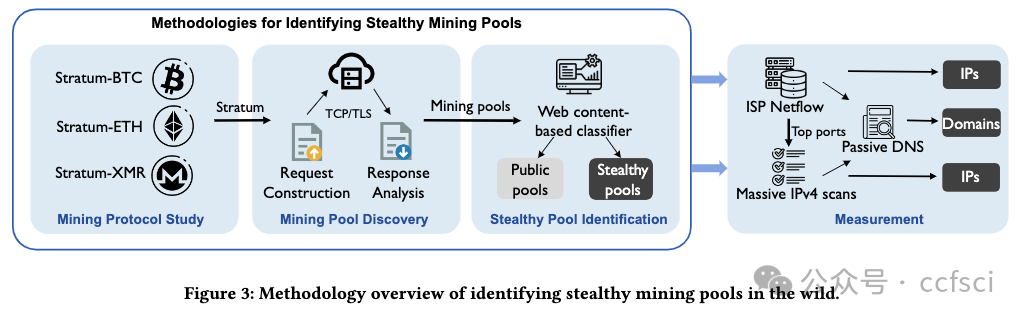
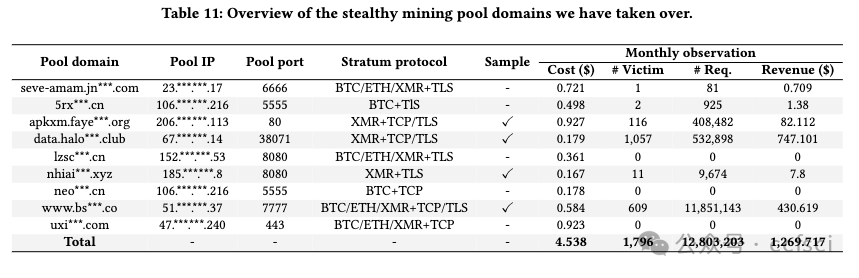
Cryptocurrency mining is a crucial operation in blockchains, and miners often join mining pools to increase their chances of earning rewards. However, the energy-intensive nature of PoW cryptocurrency mining has led to its ban in New York State of the United States, China, and India. As a result, mining pools, serving as a central hub for mining activities, have become prime targets for regulatory enforcement. Furthermore, cryptojacking malware refers to self-owned stealthy mining pools to evade detection techniques and conceal profit wallet addresses. However, no systematic research has been conducted to analyze it, largely due to a lack of full understanding of the protocol implementation, usage, and port distribution of the stealth mining pool. To the best of our knowledge, we carry out the first large-scale and longitudinal measurement research of stealthy mining pools to fill this gap. We report 7,629 stealthy mining pools among 59 countries. Further, we study the inner mechanisms of stealthy mining pools. By examining the 19,601 stealthy mining pool domains and IPs, our analysis reveals that stealthy mining pools carefully craft their domain semantics, protocol support, and lifespan to provide underground, user-friendly, and robust mining services. What's worse, we uncover a strong correlation between stealthy mining pools and malware, with 23.3% of them being labeled as malicious. Besides, we evaluate the tricks used to evade state-of-the-art mining detection, including migrating domain name resolution methods, leveraging the botnet, and enabling TLS encryption. Finally, we conduct a qualitative study to evaluate the profit gains of malicious cryptomining activities through the stealthy pool from an insider perspective. Our results show that criminals have the potential to earn more than 1 million USD per year, boasting an average ROI of 2,750%. We have informed the relevant ISPs about uncovered stealthy mining pools and have received their acknowledgments.
加密货币挖矿是区块链中的一项重要操作,矿工通常会加入矿池,以增加获得奖励的机会。然而,PoW 加密货币挖矿的高能耗特性已导致美国纽约州、中国和印度禁止其使用。因此,作为挖矿活动中心的矿池已成为监管执法的首要目标。此外,加密劫持恶意软件指的是自己拥有的隐形矿池,以躲避检测技术和隐藏获利钱包地址。然而,目前还没有系统的研究对其进行分析,这主要是由于缺乏对隐形矿池的协议实现、使用和端口分布的充分了解。据我们所知,我们首次对隐形矿池进行了大规模纵向测量研究,填补了这一空白。我们报告了 59 个国家的 7629 个隐形矿池。此外,我们还研究了隐形矿池的内在机制。通过研究 19,601 个隐形矿池域名和 IP,我们的分析揭示了隐形矿池精心设计其域名语义、协议支持和生命周期,以提供地下、用户友好和强大的挖矿服务。更糟糕的是,我们发现隐形矿池与恶意软件之间存在很强的相关性,其中 23.3% 的矿池被标记为恶意软件。此外,我们还评估了逃避最先进挖矿检测的伎俩,包括迁移域名解析方法、利用僵尸网络和启用 TLS 加密。最后,我们进行了一项定性研究,从内部人员的角度评估了通过隐身池进行恶意加密挖矿活动的利润收益。我们的研究结果表明,犯罪分子每年有可能获得超过 100 万美元的收益,平均投资回报率高达 2750%。我们已将发现的隐形矿池通知相关互联网服务提供商,并已收到他们的确认函。
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3616677
2
Title:
TxPhishScope: Towards Detecting and Understanding Transaction-based Phishing on Ethereum
TxPhishScope:检测和理解以太坊上基于交易的网络钓鱼
Authors:****

Key words:
Decentralized Finance, Ethereum, phishing detection
去中心化金融、以太坊、网络钓鱼检测
Abstract:****
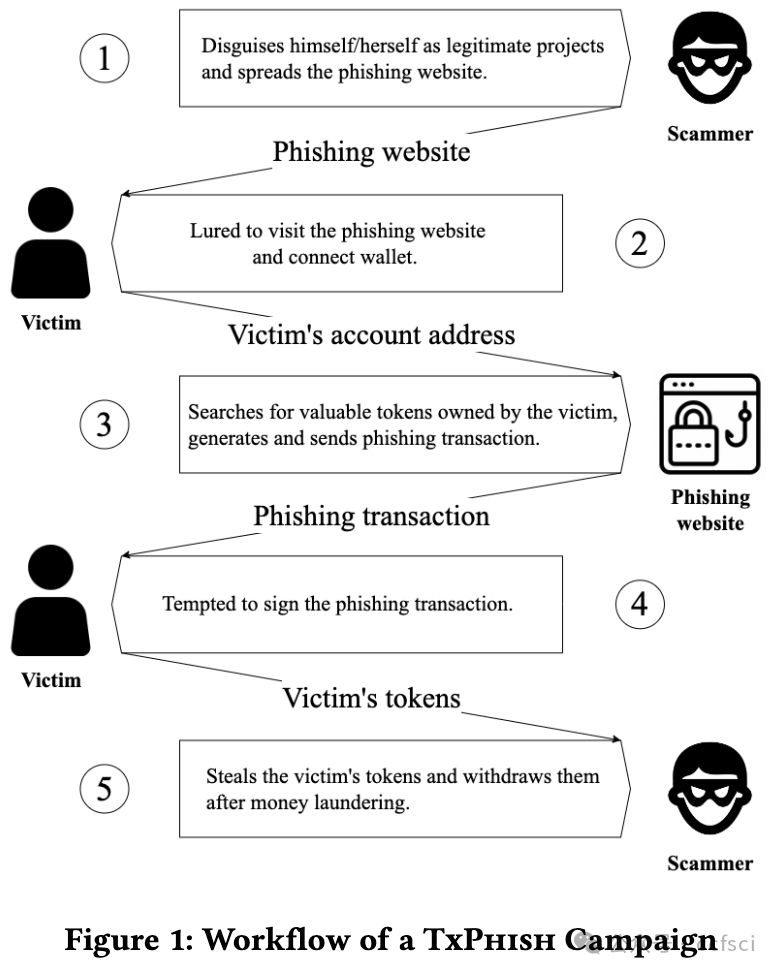
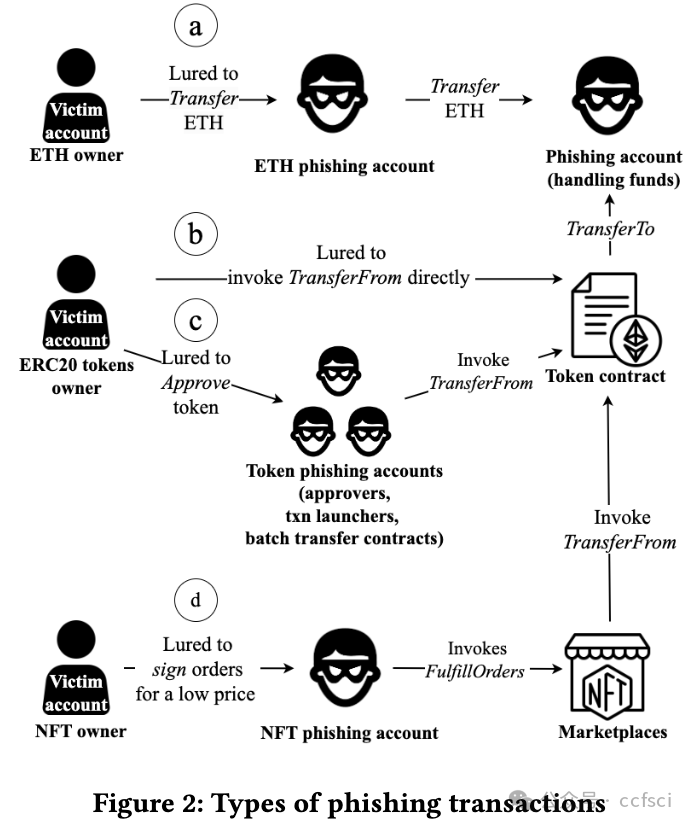
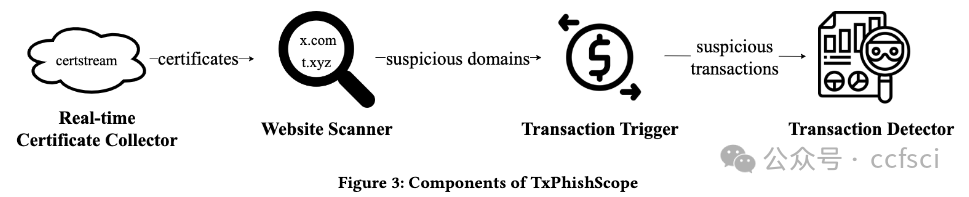
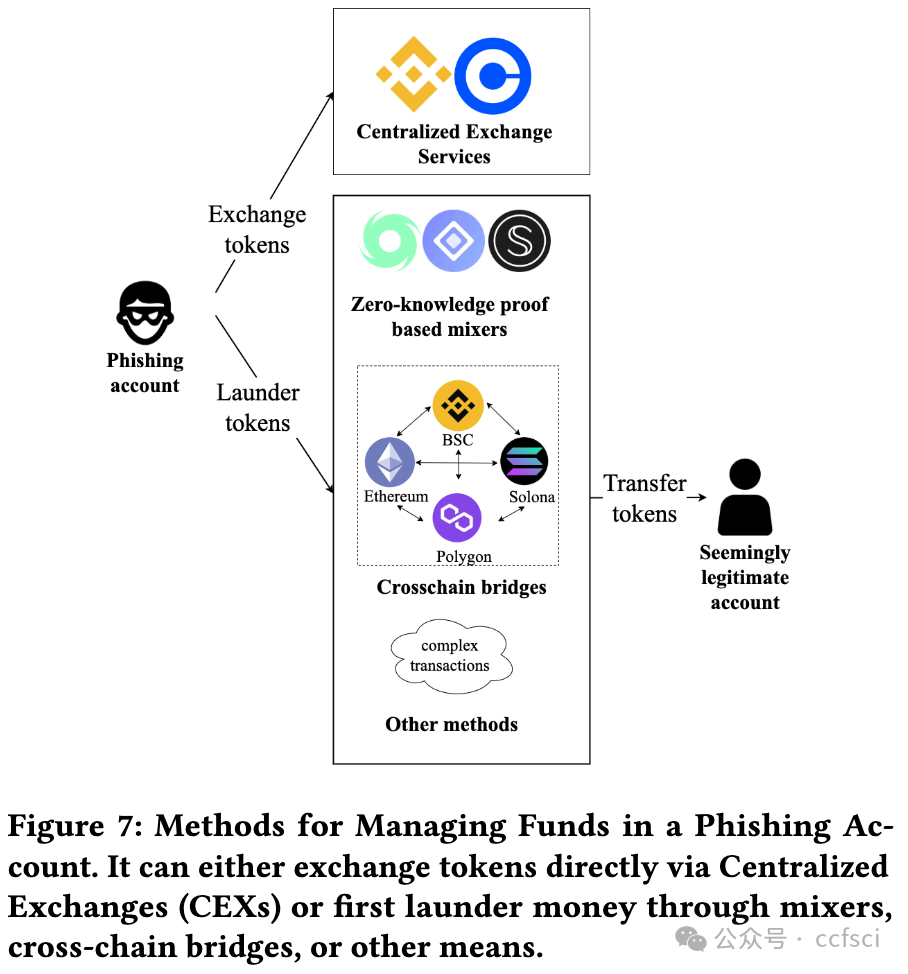
The prosperity of Ethereum attracts many users to send transactions and trade crypto assets. However, this has also given rise to a new form of transaction-based phishing scam, named TxPhish. Specifically, tempted by high profits, users are tricked into visiting fake websites and signing transactions that enable scammers to steal their crypto assets. The past year has witnessed 11 large-scale TxPhish incidents causing a total loss of more than 70 million. In this paper, we conduct the first empirical study of TxPhish on Ethereum, encompassing the process of a TxPhishTxPhish campaign and details of phishing transactions. To detect TxPhish websites and extract phishing accounts automatically, we present TxPhish, which dynamically visits the suspicious websites, triggers transactions, and simulates results. Between November 25, 2022, and July 31, 2023, we successfully detected and reported 26,333 TxPhish websites and 3,486 phishing accounts. Among all of documented TxPhish websites, 78.9% of them were first reported by us, making TxPhish the largest TxPhish website detection system. Moreover, we provided criminal evidence of four phishing accounts and their fund flow totaling 1.5 million to aid in the recovery of funds for the victims. In addition, we identified bugs in six Ethereum projects and received appreciation.
以太坊的繁荣吸引了许多用户发送交易和交易加密资产。然而,这也催生了一种新的交易型网络钓鱼骗局,名为 "TxPhish"。具体来说,在高额利润的诱惑下,用户被诱骗访问虚假网站并签署交易协议,从而使骗子窃取他们的加密资产。在过去的一年里,已经发生了 11 起大规模的 TxPhish 事件,造成的总损失超过 7000 万。在本文中,我们首次对以太坊上的 TxPhish 进行了实证研究,其中包括 TxPhishTxPhish 活动的过程和钓鱼交易的细节。为了自动检测 TxPhish 网站并提取钓鱼账户,我们提出了 TxPhish,它可以动态访问可疑网站、触发交易并模拟结果。从 2022 年 11 月 25 日到 2023 年 7 月 31 日,我们成功检测并报告了 26,333 个 TxPhish 网站和 3,486 个网络钓鱼账户。在所有记录在案的 TxPhish 网站中,78.9% 是由我们首次报告的,这使 TxPhish 成为最大的 TxPhish 网站检测系统。此外,我们还提供了四个网络钓鱼账户及其资金流的犯罪证据,总额达 150 万,帮助受害者追回了资金。此外,我们还发现了六个以太坊项目中的漏洞,并获得了赞赏。
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3623210
3
Title:
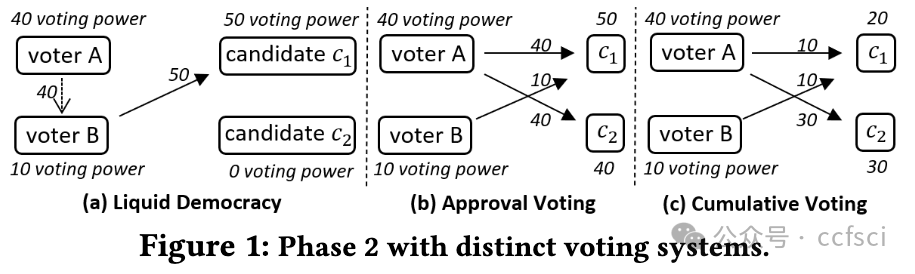
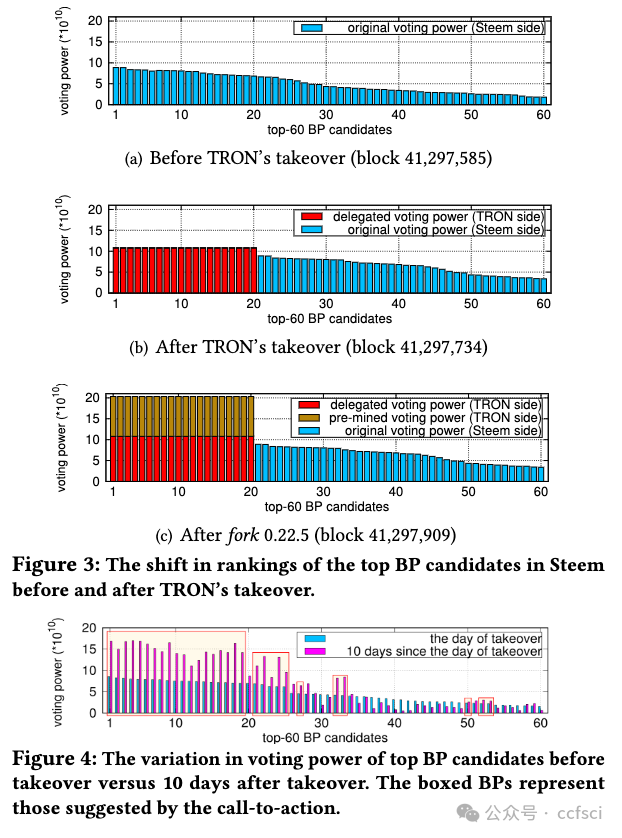
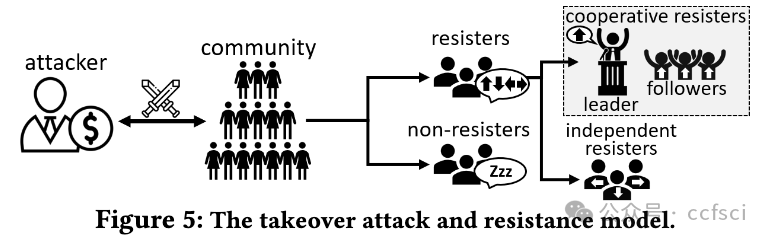
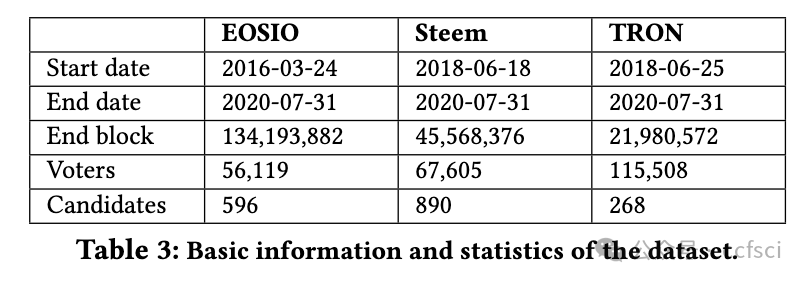
How Hard is Takeover in DPoS Blockchains? Understanding the Security of Coin-based Voting Governance
DPoS 区块链的接管有多难?了解基于代币的投票治理的安全性
Authors:****

Key words:
Blockchain; Decentralized Governance; Governance Security; Voting Governance; Delegated Proof of Stake; Web 3.0
区块链;去中心化治理;治理安全;投票治理;委托权益证明;Web 3.0
Abstract:****
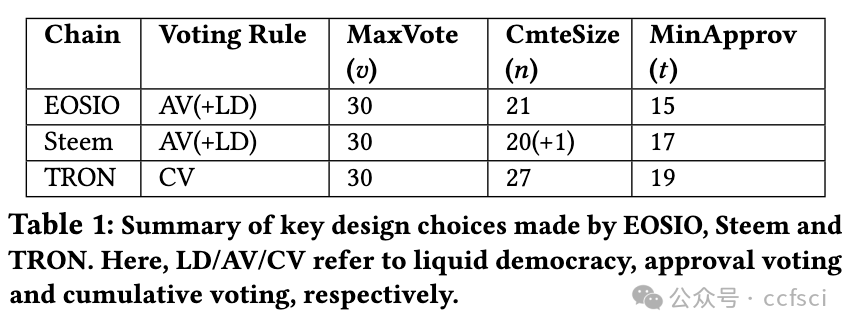
Delegated-Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) blockchains, such as EOSIO, Steem and TRON, are governed by a committee of block producers elected via a coin-based voting system. We recently witnessed the first de facto blockchain takeover that happened between Steem and TRON. Within one hour of this incident, TRON founder took over the entire Steem committee, forcing the original Steem community to leave the blockchain that they maintained for years. This is a historical event in the evolution of blockchains and Web 3.0. Despite its significant disruptive impact, little is known about how vulnerable DPoS blockchains are in general to takeovers and the ways in which we can improve their resistance to takeovers. In this paper, we demonstrate that the resistance of a DPoS blockchain to takeovers is governed by both the theoretical design and the actual use of its underlying coin-based voting governance system. When voters actively cooperate to resist potential takeovers, our theoretical analysis reveals that the current active resistance of DPoS blockchains is far below the theoretical upper bound. However in practice, voter preferences could be significantly different. This paper presents the first large-scale empirical study of the passive takeover resistance of EOSIO, Steem and TRON. Our study identifies the diversity in voter preferences and characterizes the impact of this diversity on takeover resistance. Through both theoretical and empirical analyses, our study provides novel insights into the security of coin-based voting governance and suggests potential ways to improve the takeover resistance of any blockchain that implements this governance model.
EOSIO、Steem 和 TRON 等委托证明(DPoS)区块链由一个通过基于代币的投票系统选出的区块生产者委员会管理。我们最近目睹了 Steem 和 TRON 之间发生的第一次事实上的区块链接管。在事件发生后一小时内,TRON 创始人接管了整个 Steem 委员会,迫使原 Steem 社区离开了他们维护多年的区块链。这是区块链和 Web 3.0 演进过程中的一个历史性事件。尽管这一事件产生了重大的破坏性影响,但人们对 DPoS 区块链在一般情况下有多容易被接管,以及我们可以通过哪些方式提高其抵御接管的能力知之甚少。在本文中,我们证明了 DPoS 区块链抵御接管的能力受其底层基于代币的投票治理系统的理论设计和实际使用的制约。当投票者积极合作抵制潜在收购时,我们的理论分析表明,目前 DPoS 区块链的主动抵制能力远低于理论上限。然而,在实践中,选民的偏好可能会有很大不同。本文首次对 EOSIO、Steem 和 TRON 的被动抵制收购能力进行了大规模实证研究。我们的研究确定了voter偏好的多样性,并描述了这种多样性对收购阻力的影响。通过理论和实证分析,我们的研究为基于代币的投票治理的安全性提供了新的见解,并提出了潜在的方法来提高任何实施这种治理模式的区块链的抗接管能力。

Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3623171
4
Title:
Demystifying DeFi MEV Activities in Flashbots Bundle
解密 Flashbots Bundle 中的 DeFi MEV 活动
Authors:****

Key words:
DeFi, Smart contract, Miner Extractable Value, Flashbots Bundle
DeFi、智能合约、矿工可提取价值、Flashbots Bundle
Abstract:****
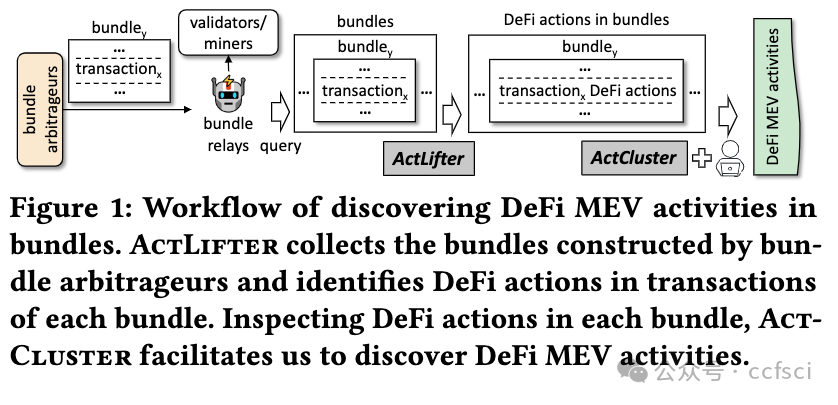
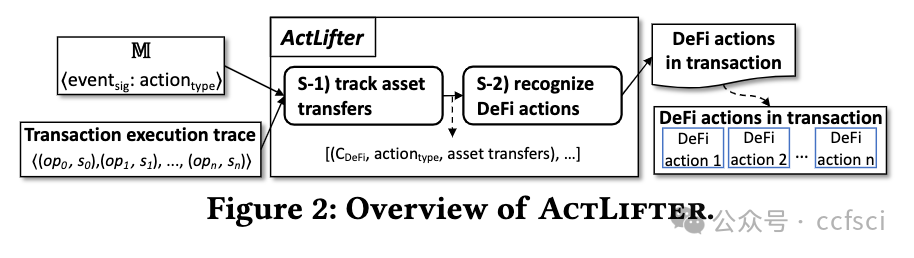
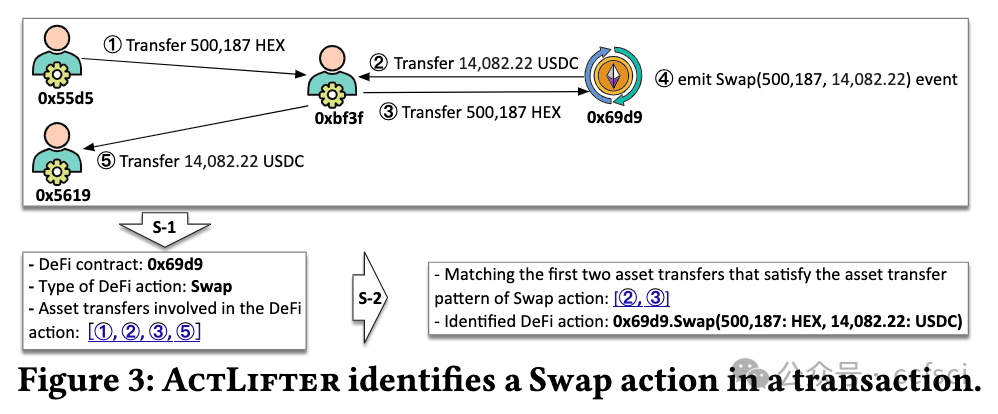
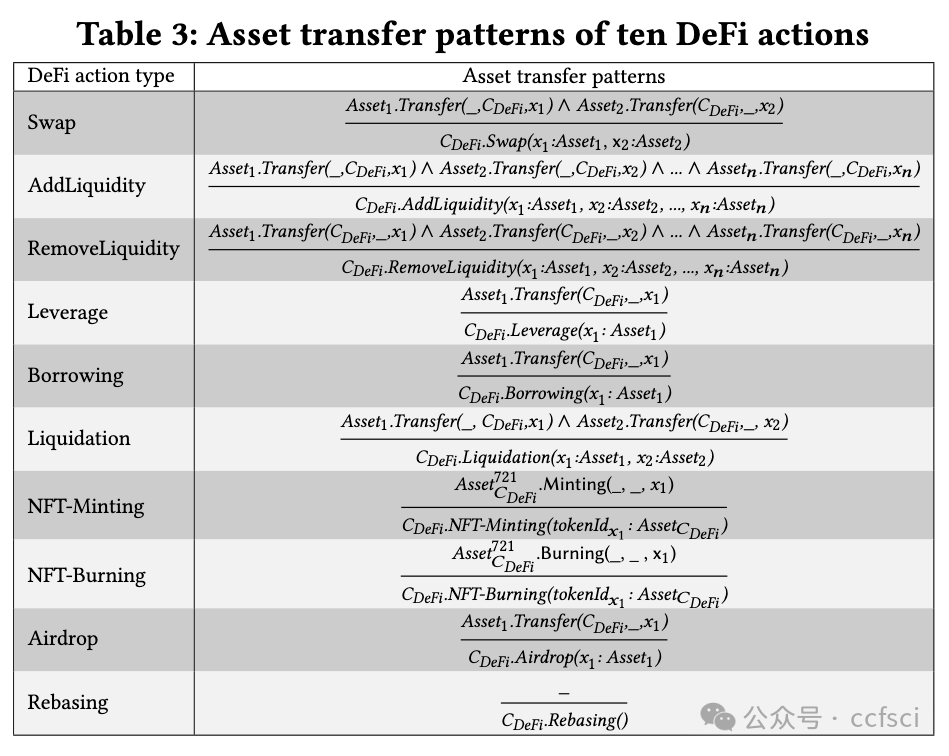
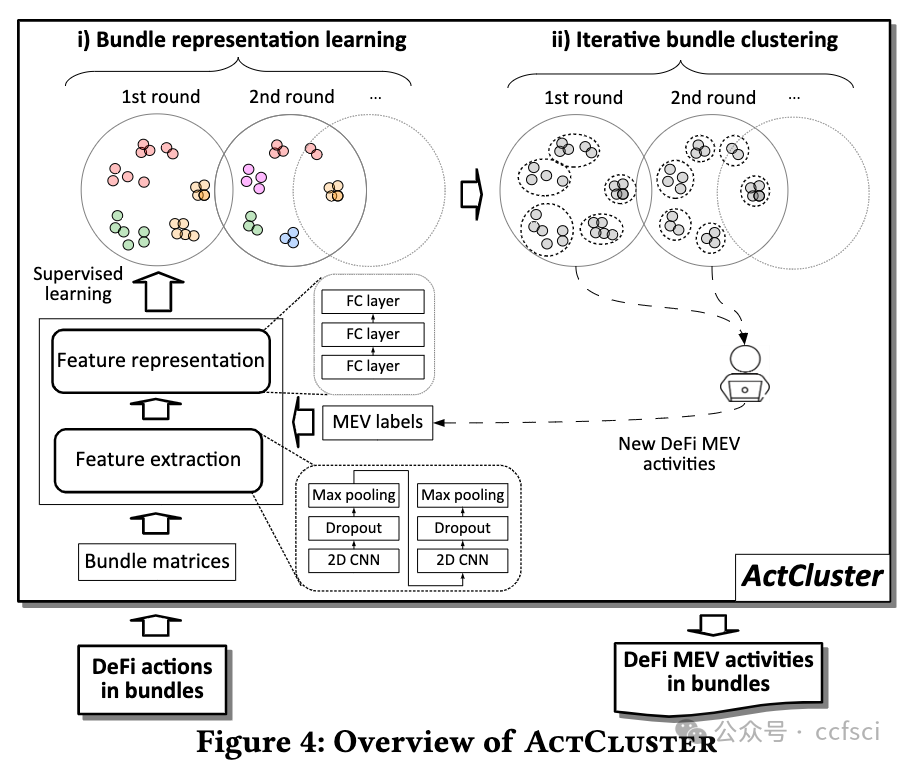
Decentralized Finance, mushrooming in permissionless blockchains, has attracted a recent surge in popularity. Due to the transparency of permissionless blockchains, opportunistic traders can compete to earn revenue by extracting Miner Extractable Value (MEV), which undermines both the consensus security and efficiency of blockchain systems. The Flashbots bundle mechanism further aggravates the MEV competition because it empowers opportunistic traders with the capability of designing more sophisticated MEV extraction. In this paper, we conduct the first systematic study on DeFi MEV activities in Flashbots bundle by developing ActLifter, a novel automated tool for accurately identifying DeFi actions in transactions of each bundle, and ActCluster, a new approach that leverages iterative clustering to facilitate us to discover known/unknown DeFi MEV activities. Extensive experimental results show that ActLifter can achieve nearly 100% precision and recall in DeFi action identification, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art techniques. Moreover, with the help of ActCluster, we obtain many new observations and discover 17 new kinds of DeFi MEV activities, which occur in 53.12% of bundles but have not been reported in existing studies.
在无许可区块链中如雨后春笋般出现的去中心化金融最近大受欢迎。由于无许可区块链的透明性,机会主义交易者可以竞相通过提取矿工可提取价值(MEV)来赚取收入,这破坏了区块链系统的共识安全性和效率。Flashbots 捆绑机制进一步加剧了 MEV 竞争,因为它赋予了机会主义交易者设计更复杂的 MEV 提取的能力。在本文中,我们通过开发 ActLifter(一种新型自动工具,用于准确识别每个捆绑交易中的 DeFi 行为)和 ActCluster(一种新方法,利用迭代聚类促进我们发现已知/未知的 DeFi MEV 活动),首次对 Flashbots 捆绑交易中的 DeFi MEV 活动进行了系统研究。广泛的实验结果表明,ActLifter 在 DeFi 行动识别方面可以达到近 100% 的精确度和召回率,明显优于最先进的技术。此外,在 ActCluster 的帮助下,我们获得了许多新的观察结果,并发现了 17 种新的 DeFi MEV 活动,这些活动出现在 53.12% 的捆绑中,但在现有研究中却未见报道。

Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3616590
5
Title:
Uncle Maker: (Time)Stamping Out The Competition in Ethereum
Uncle Maker:(及时)消灭以太坊中的竞争对手
Authors:****

Key words:
cryptocurrency, blockchain, proof of work, consensus, security
加密货币、区块链、工作证明、共识、安全性
Abstract:****
We present and analyze an attack on Ethereum 1's consensus mechanism, which allows miners to obtain higher mining rewards compared to their honest peers. This attack is novel in that it relies on manipulating block timestamps and the difficulty-adjustment algorithm (DAA) to give the miner an advantage whenever block races ensue. We call our attack Uncle Maker, as it induces a higher rate of uncle blocks. We describe several variants of the attack. Among these, one that is risk-free for miners. Our attack differs from past attacks such as Selfish Mining, that have been shown to be profitable but were never observed in practice: We analyze data from Ethereum's blockchain and show that some of Ethereum's miners have been actively running a variant of this attack for several years without being detected, making this the first evidence of miner manipulation of a major consensus mechanism. We present our evidence, as well as estimates of the profits gained by attackers, at the expense of honest miners. Since several blockchains are still running Ethereum 1's protocol, we suggest concrete fixes and implement them as a patch for geth.
我们提出并分析了对以太坊 1 共识机制的一种攻击,该机制允许矿工获得比诚实同行更高的挖矿奖励。这种攻击的新颖之处在于,它依靠操纵区块时间戳和难度调整算法(DAA),使矿工在区块竞赛中获得优势。我们称这种攻击为 "叔叔制造者"(Uncle Maker),因为它会诱发更高的 "叔块 "率。我们描述了该攻击的几种变体。其中,有一种对矿工来说是无风险的。我们的攻击与过去的攻击不同,比如自私挖矿(Selfish Mining),这种攻击被证明是有利可图的,但从未在实践中观察到:我们分析了来自以太坊区块链的数据,结果表明以太坊的一些矿工几年来一直在积极运行这种攻击的变种,却从未被发现,这是矿工操纵主要共识机制的首个证据。我们提供了证据,并估算了攻击者以牺牲诚实矿工为代价所获得的利润。由于多个区块链仍在运行以太坊 1 的协议,我们提出了具体的修复建议,并作为 geth 的补丁加以实施。
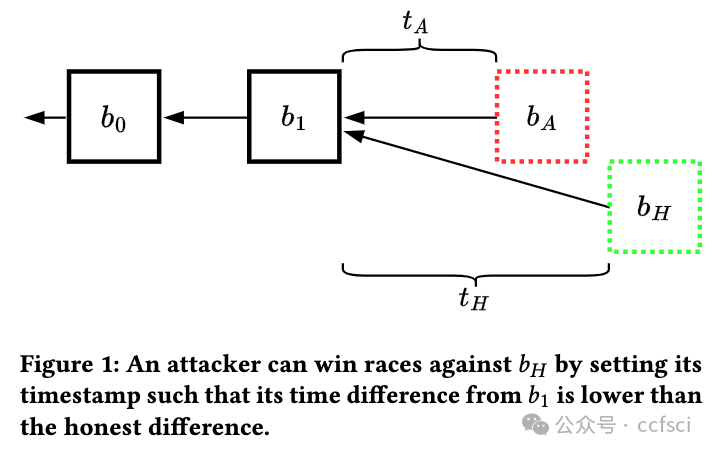
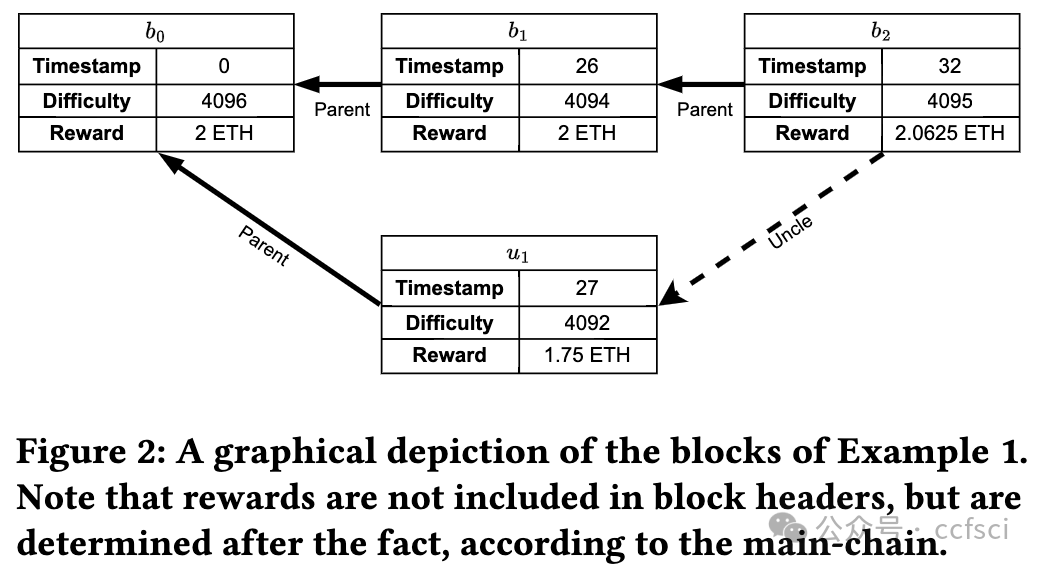
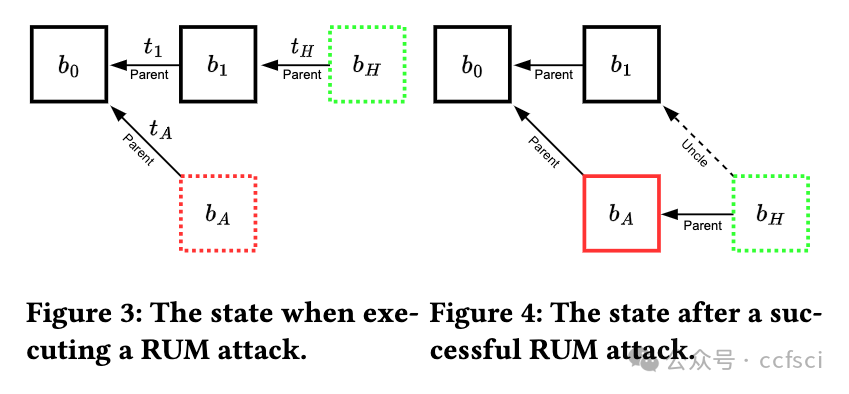
注:RUM为riskless uncle maker
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3616674
6
Title:
Themis: Fast, Strong Order-Fairness in Byzantine Consensus
Themis:拜占庭共识中的快速、强排序公平
Authors:****

Key words:
Order-Fair Consensus; Transaction Ordering; Blockchains
公平秩序共识;交易排序;区块链
Abstract:****
We introduce Themis, a scheme for introducing fair ordering of transactions into (permissioned) Byzantine consensus protocols with at most ƒ faulty nodes among n ≥ 4ƒ + 1. Themis enforces the strongest notion of fair ordering proposed to date. It also achieves standard liveness, rather than the weaker notion of previous work with the same fair ordering property. We show experimentally that Themis can be integrated into state-of-the-art consensus protocols with minimal modification or performance overhead. Additionally, we introduce a suite of experiments of general interest for evaluating the practical strength of various notions of fair ordering and the resilience of fair-ordering protocols to adversarial manipulation. We use this suite of experiments to show that the notion of fair ordering enforced by Themis is stronger in practice than those of competing systems. We believe Themis offers strong practical protection against many types of transaction-ordering attacks-such as front-running and back-running-that are currently impacting commonly used smart contract systems.
我们引入了 Themis,这是一种将交易公平排序引入(许可的)拜占庭共识协议的方案,在 n ≥ 4ƒ + 1 中最多有 ƒ 个故障节点。Themis 执行了迄今为止提出的最强的公平排序概念。它还实现了标准活性,而不是以前具有相同公平排序属性的工作中较弱的概念。我们通过实验表明,Themis 可以以最小的修改或性能开销集成到最先进的共识协议中。此外,我们引入了一套普遍感兴趣的实验,用于评估各种公平排序概念的实际强度以及公平排序协议对对抗性操纵的弹性。我们使用这套实验来表明,Themis 执行的公平排序概念在实践中比竞争系统更强大。我们相信 Themis 提供了强大的实际保护,可以抵御许多类型的交易排序攻击 - 例如抢先交易和反向交易 - 这些攻击目前正在影响常用的智能合约系统。
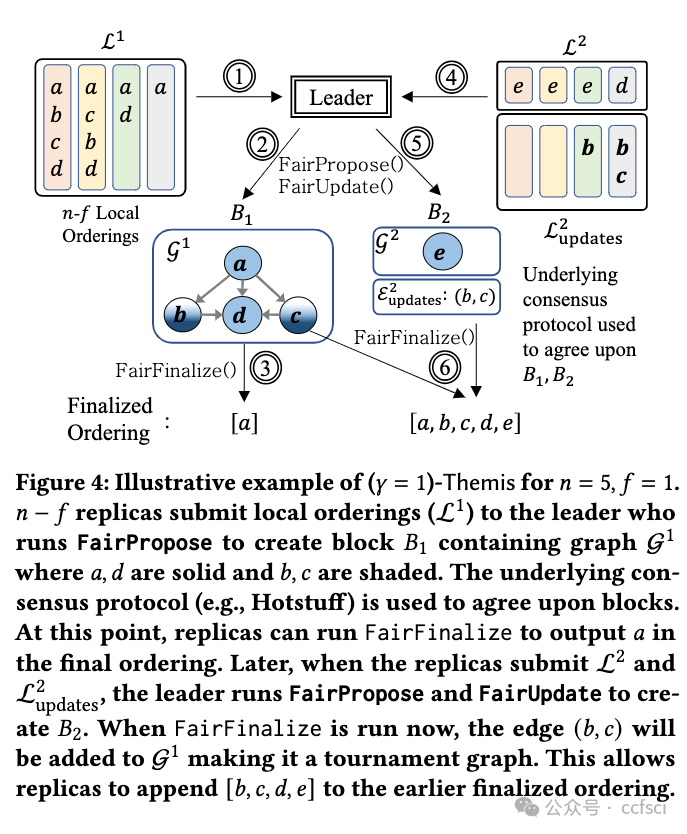
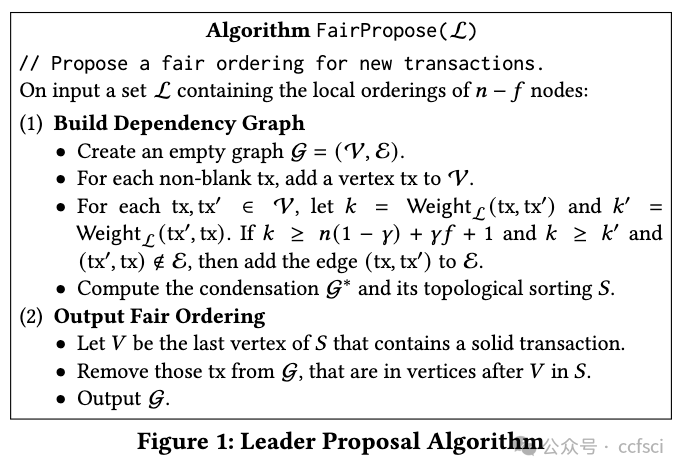
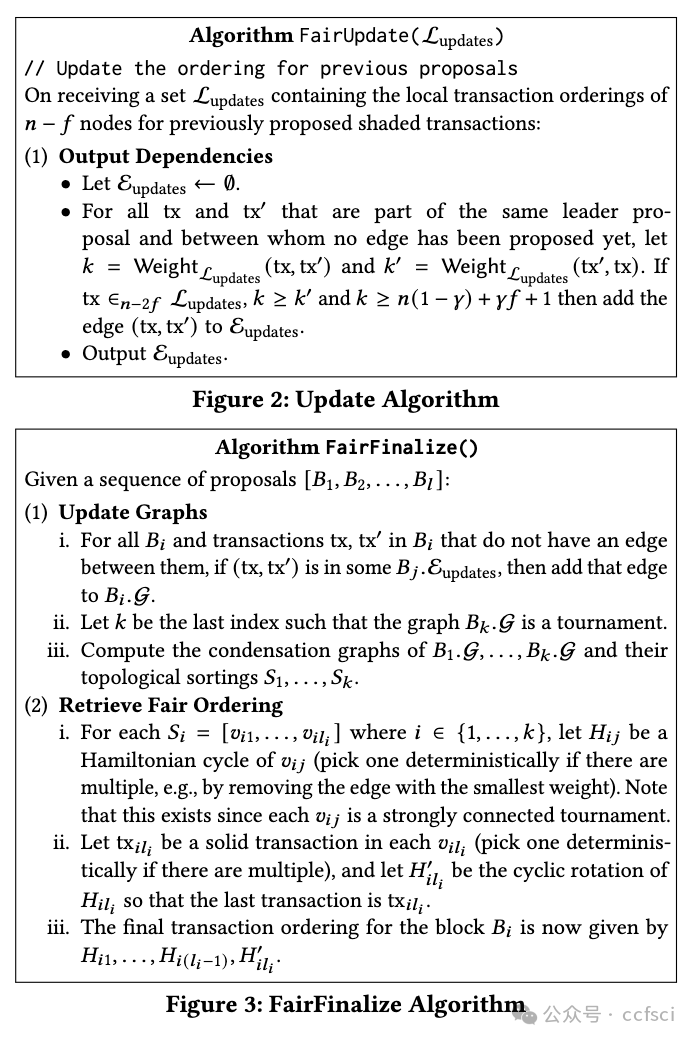
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3616658
7
Title:
Towards Practical Sleepy BFT
迈向实用的 Sleepy BFT
Authors:****

Key words:
BFT Protocols; Blockchain; Dynamic Participation; Sleepy Model
BFT 协议;区块链;动态参与;Sleepy模型
Abstract:****
Bitcoin's longest-chain protocol pioneered consensus under dynamic participation, also known as sleepy consensus, where nodes do not need to be permanently active. However, existing solutions for sleepy consensus still face two major issues, which we address in this work. First, existing sleepy consensus protocols have high latency (either asymptotically or concretely). We tackle this problem and achieve 4Δ latency (Δ is the bound on network delay) in the best case, which is comparable to classic BFT protocols without dynamic participation support. Second, existing protocols have to assume that the set of corrupt participants remains fixed throughout the lifetime of the protocol due to a problem we call costless simulation. We resolve this problem and support growing participation of corrupt nodes. Our new protocol also offers several other important advantages, including support for arbitrary fluctuation of honest participation as well as an efficient recovery mechanism for new active nodes.
比特币最长链协议开创了动态参与下的共识,也被称为 "睡眠共识",在这种共识下,节点不需要一直处于活跃状态。然而,现有的休眠共识解决方案仍然面临两大问题,我们将在本文中解决这些问题。首先,现有的睡眠共识协议具有较高的延迟(无论是渐进延迟还是具体延迟)。我们解决了这个问题,并在最佳情况下实现了 4Δ 延迟(Δ 是网络延迟的约束),这与没有动态参与支持的经典 BFT 协议相当。其次,由于我们称之为无成本模拟的问题,现有协议必须假设腐败参与者的集合在整个协议期间保持固定。我们解决了这一问题,支持越来越多的腐败节点参与。我们的新协议还具有其他一些重要优势,包括支持诚实参与的任意波动,以及针对新活跃节点的高效恢复机制。

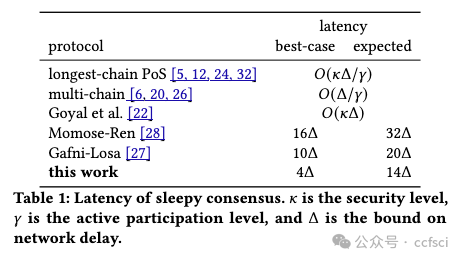
Pdf link:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3576915.3623073
篇幅有限,下篇文章将继续分享剩余论文

关注ccfsci,持续接收区块链最新论文
洞察区块链技术发展趋势
Follow us to keep receiving the latest blockchain papers
Insight into Blockchain Technology Trends