📚博客主页:爱敲代码的小杨.
✨专栏:《Java SE语法》 | 《数据结构与算法》 | 《C生万物》 |《MySQL探索之旅》 |《Web世界探险家》
❤️感谢大家点赞👍🏻收藏⭐评论✍🏻,您的三连就是我持续更新的动力❤️
🙏小杨水平有限,欢迎各位大佬指点,相互学习进步!
小杨近些在学习人工智能方面的知识,发现了一个巨牛的人工智能学习网站,通俗易懂,风趣幽默,忍不住分享一下给大家。点击跳转到网站。

文章目录
- [1. 字体样式属性](#1. 字体样式属性)
-
- [1.1 字体样式(font-family)](#1.1 字体样式(font-family))
- [1.2 字体大小(font-size)](#1.2 字体大小(font-size))
- [1.3 字体粗细(font-weight)](#1.3 字体粗细(font-weight))
- [1.4 文字样式(font-style)](#1.4 文字样式(font-style))
- [1.5 字体复合属性](#1.5 字体复合属性)
- [1.6 总结](#1.6 总结)
- [2. 文本样式属性](#2. 文本样式属性)
-
- [2.1 文本颜色(color)](#2.1 文本颜色(color))
- [2.2 对齐文本(text-align)](#2.2 对齐文本(text-align))
- [2.3 装饰文本(text-decoration)](#2.3 装饰文本(text-decoration))
- [2.4 文本缩进(text-indent)](#2.4 文本缩进(text-indent))
- [2.5 行间距(line-height)](#2.5 行间距(line-height))
- [2.6 总结](#2.6 总结)
1. 字体样式属性
CSS Fonts(字体)属性用于定义字体系列,大小,粗细和文字样式(如斜体)。
1.1 字体样式(font-family)
font-family属性用于设置字体。网页中常用的字体有宋体,微软雅黑,黑体等
语法:
css
选择器 {
font-family: "字体样式";
}
/* 例子 : 将p标签的文字改成微软雅黑 */
p {
font-family: "黑体";
}
/* 可以同时设置多个字体,如果浏览器不支持第一个字体,则回尝试下一个,直到找到合适的字体 */
boday {
font-famliy: "微软雅黑","宋体","黑体";
}运行结果:
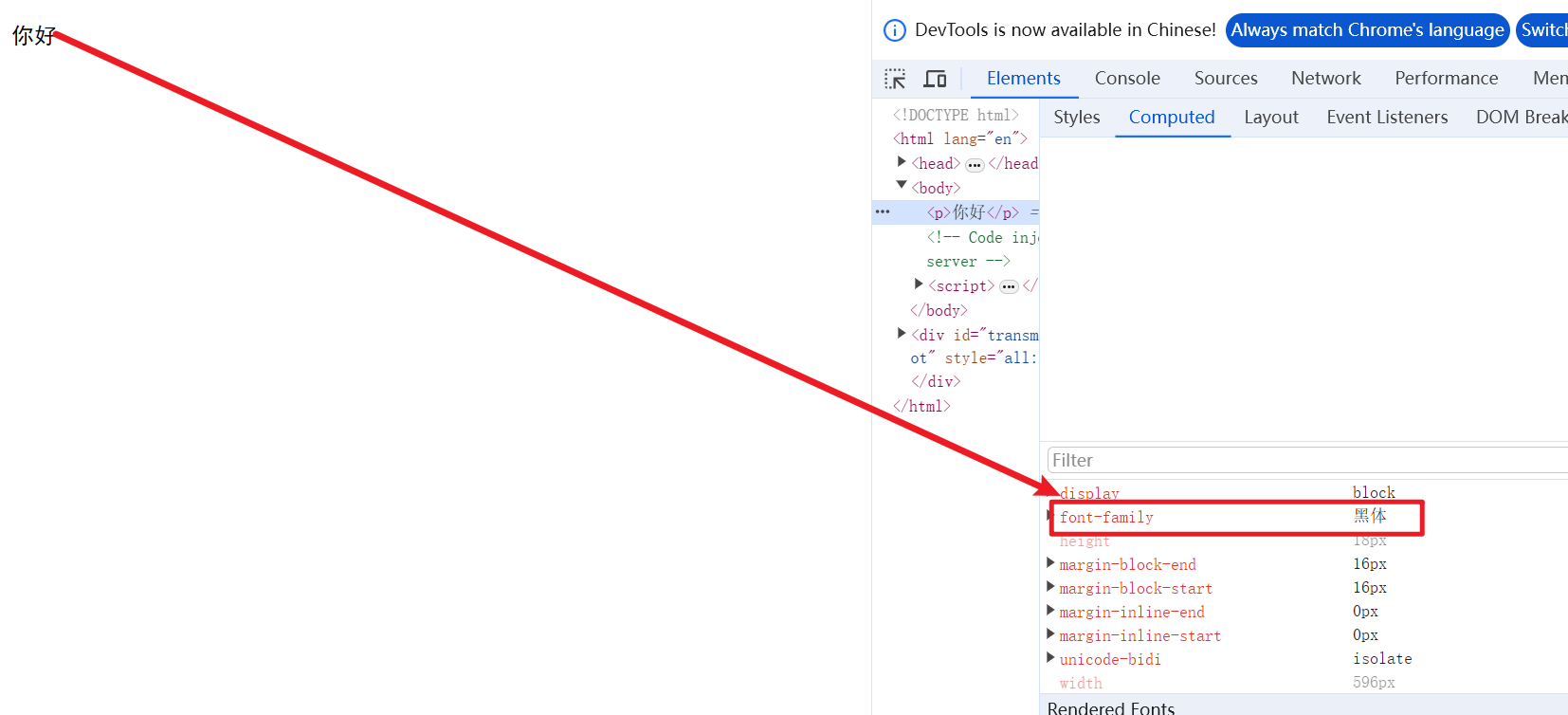
小结:
- 各种字体之间必须使用英文状态下的逗号分隔;
- 一般情况下,如果有空格隔开的多个单词组成的字体,加引号;
- 尽量使用系统默认自带字体,保证在任何用户的浏览器中都能正确显示。
1.2 字体大小(font-size)
font-size 属性用于设置字体大小。
语法:
css
标签名{
font-size: 数值px;
}
/* 例子:讲p标签的文字设置为20像素 */
p {
font-size: 20px;
}运行结果:
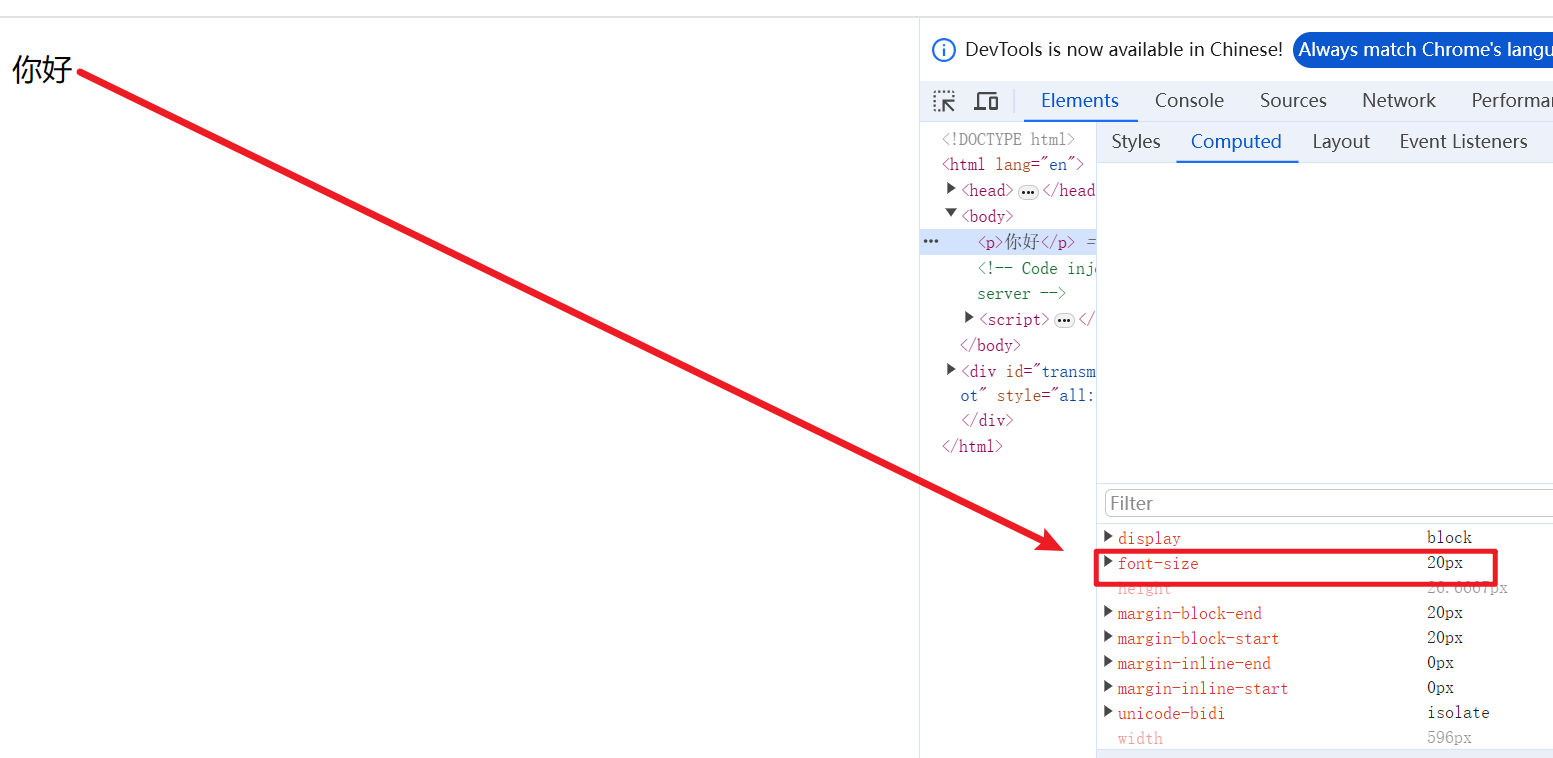
小结:
- px(像素)大小是我们网页的最常用的单位
- 谷歌浏览器默认的文字大小为
16px - 不同浏览器可能默认显示的字号大小不一致,我们尽量给一个明确值大小,不要默认大小
- 可以给
body指定整个页面文字的大小
1.3 字体粗细(font-weight)
font-weight属性用于定义字体的粗细,其可用属性值如表:
| 值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| normal | 默认值。定义标准的字符 |
| bold | 定义粗体字符 |
| bolder | 定义更粗的字符 |
| lighter | 定义更细的字符 |
| 100~900(100的整数倍) | 定义由细到粗的字符。其中400等同于 normal,700等同于bold,值越大字体越粗 |
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.normal {
font-weight: normal;
}
.bold {
font-weight: bold;
}
.bolder {
font-weight: bolder;
}
.lighter {
font-weight: lighter;
}
.four-hundred {
font-weight: 400;
}
.seven-hundred {
font-weight: 700;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="normal">标准:你好</p>
<p class="bold">加粗:你好</p>
<p class="bolder">更粗:你好</p>
<p class="lighter">更细:你好</p>
<p class="four-hundred">400:你好</p>
<p class="seven-hundred">700:你好</p>
</body>
</html>运行结果:

1.4 文字样式(font-style)
CSS 使用 font-style属性设置文本的风格
语法:
css
选择器 {
font-style: 属性值;
}| 属性值 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| normal | 默认值,浏览器会显示标准的字体样式 |
| italic | 浏览器会显示斜体的字体样式 |
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.one {
font-style: normal;
}
.two {
font-style: italic;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="one">你好</p>
<p class="two">你好</p>
</body>
</html>运行结果:

注意:平时我们很少给文字加斜体,反而要给斜体标签(em,i)改为不倾斜字体
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
em {
font-style: normal;
}
i {
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<em>em标签</em>
<i>i标签</i>
</body>
</html>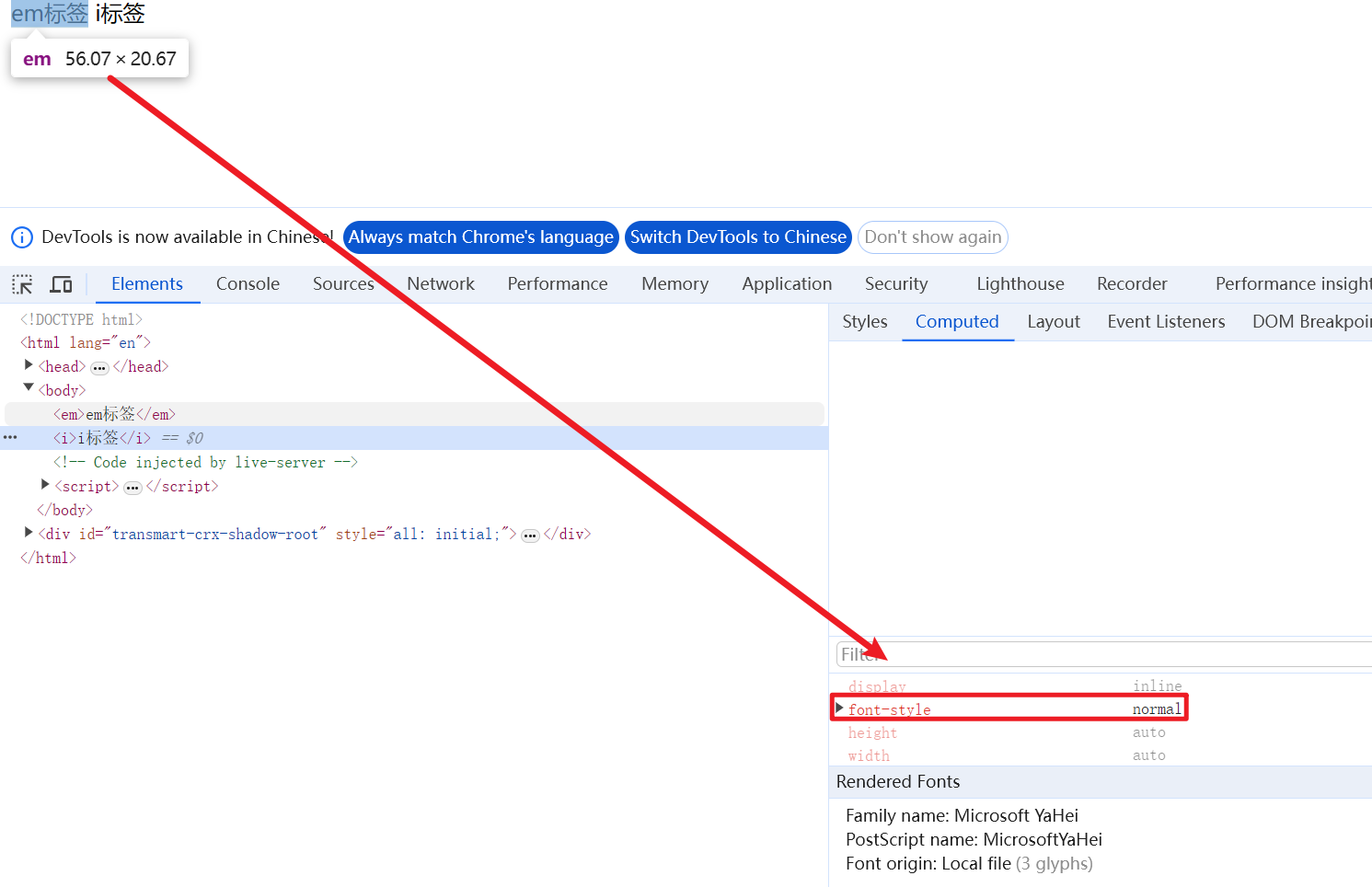
1.5 字体复合属性
字体属性可以把以上文字样式综合来写,这样可以更节约代码
语法格式:
css
选择器 {
font: font-style font-weight font-size/line-height font-family;
}代码:将网页所有文字设置为斜体,加粗,20px,黑体
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
body {
font: italic 700 20px "黑体";
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>你好</p>
<div>你好</div>
<span>你好</span>
</body>
</html>运行结果:

注意:
- 使用
font属性时,必须按上面语法格式中的顺序书写,不能更换顺序,并且各个属性间以空格隔开 - 不需要设置的属性可以省略(取默认值),但必须保留
font-size和font-family属性,否则font属性将不起作用
1.6 总结
| 属性 | 表示 | 注意点 |
|---|---|---|
| font-size | 字号 | 通常用的单位是 px 像素,一定要跟上单位 |
| font-famly | 字体 | 按照实际需求写字体 |
| font-weight | 字体粗细 | 加粗是700 或者 bold 不加粗是 normal 或者 400 数字不要跟单位 |
| font-style | 字体样式 | 倾斜是 italic 不倾斜是 noraml |
| font | 字体连写 | 连写的顺序,不能随意换位置;字号 和 字体 必须同时出现 |
2. 文本样式属性
CSS Text(文本)属性可定义文本的外观,其中包括颜色、对齐文本、修饰文本、文本缩进、行间距等。
2.1 文本颜色(color)
color 属性用于定义文本的颜色。
语法:
css
选择器 {
color: 颜色;
}| 表示方法 | 属性值 |
|---|---|
| 预定义的颜色值 | red,green,blue等等... |
| 十进制 | #FF0000,#FF6600 |
| RGB | rgb(255,0,0) 或 rgb(100%,0%,0%) |
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
color: red;
}
div {
color: #00FF00;
}
span {
color: rgb(0, 0, 255);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>你好</p>
<div>你好</div>
<span>你好</span>
</body>
</html>运行结果:

2.2 对齐文本(text-align)
text-align 属性用于设置元素内文本内容的水平对齐方式
语法:
css
选择器 {
text-align: 对齐方式;
}| 属性值 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| left | 左对齐(默认值) |
| right | 右对齐 |
| center | 居中对齐 |
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.left {
text-align: left;
}
.right {
text-align: right;
}
.center {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1 class="left">左对齐</h1>
<h1 class="right">右对齐</h1>
<h1 class="center">居中对齐</h1>
</body>
</html>运行结果:

2.3 装饰文本(text-decoration)
text-decoration 属性规定添加到文本的修饰。可以给文本添加下划线、删除线、上划线等
语法:
css
选择器 {
text-decoration: 属性值;
}| 属性值 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| none | 默认。没有装饰线 |
| underline | 下划线 |
| overline | 上划线 |
| line-through | 删除线 |
代码
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.none {
text-decoration: none;
}
.underline {
text-decoration: underline;
}
.overline {
text-decoration: overline;
}
.line-through {
text-decoration: line-through;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="none">默认</p>
<p class="underline">下划线</p>
<p class="overline">上划线</p>
<p class="line-through">删除线</p>
<a href="#">去掉a标签默认的下划线</a>
</body>
</html>运行结果:

2.4 文本缩进(text-indent)
text-indent 属性用来指定文本的第一行的缩进,通常是将段落的首行缩进。
语法:
css
选择器 {
text-indent: px;
}通过设置该属性,所有元素的第一行都可以缩进一个给定的长度,甚至该长度可以是负值。
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
text-indent: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
这是一篇高质量的好文,深度理解和清晰的表达方式使复杂的技术概念变得容易理解,值得收藏点赞。博主用心很有耐心,更有对知识的热忱和热爱,写了这么实用有效的分享,期盼博主能够光顾我的博客,给予宝贵的指导!优质好文,博主的文章细节很到位,兼顾实用性和可操作性,感谢博主的分享,期待博主持续带来更多好文
</p>
</body>
</html>运行结果:

css
选择器 {
text-indent: em;
}em 是一个相对单位,就是当前元素(font-size) 1 个文字的大小, 如果当前元素没有设置大小,则会按照父元素的 1 个文字大小。
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
p {
text-indent: 2em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
这是一篇高质量的好文,深度理解和清晰的表达方式使复杂的技术概念变得容易理解,值得收藏点赞。博主用心很有耐心,更有对知识的热忱和热爱,写了这么实用有效的分享,期盼博主能够光顾我的博客,给予宝贵的指导!优质好文,博主的文章细节很到位,兼顾实用性和可操作性,感谢博主的分享,期待博主持续带来更多好文
</p>
</body>
</html>
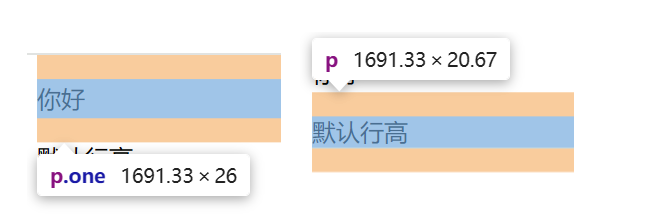
2.5 行间距(line-height)
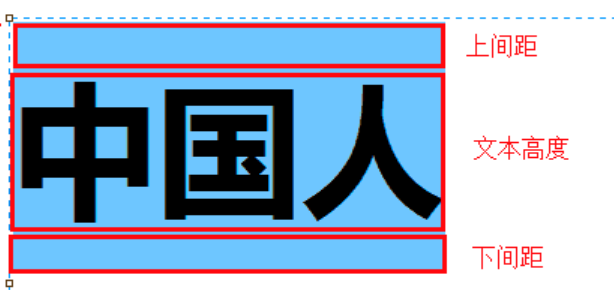
line-height 属性用于设置行间的距离(行高)。可以控制文字行与行之间的距离.
语法:
css
选择器 {
line-height: px;
}
代码:
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.one {
line-height: 26px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="one">你好</p>
<p>默认行高</p>
</body>
</html>运行结果:
2.6 总结
| 属性 | 表示 | 注意点 |
|---|---|---|
| color | 文本颜色 | 通常用 十进制 |
| text-align | 文本对齐 | 设定文字水平的对齐方式 |
| text-indent | 文本缩进 | 用于段落首行缩进2个字的距离:text-indent: 2em |
| text-decoration | 文本修饰 | 添加下划线 underline 取消下划线 none |
| line-height | 行高 | 控制行与行之间的距离 |