数据库初始化
在安装完数据库后,需要进行初始化数据库操作,对应PostgreSQL数据库中就是需要进行initdb后,才能对数据库进行启动。initdb的过程,其实就是创建数据库实例的过程,生成模板数据库和相应的目录、文件信息,系统表也是在这个阶段生成的。我们想一下,数据库运行都需要什么? 数据库是用来存取数据的,需要有存放数据的目录,执行过程中需要存放WAL日志,需要pg_wal目录存放日志,需要配置文件,最重要的是数据库怎么把一些文件抽象为表,表在数据库中存储形式就是文件,那么怎么对文件进行"解码"呢?那就是系统表,通过系统表,我们知道表中有多少列,每个列是什么类型,有什么约束等等。可以说,系统表是至关重要的。而initdb最重要的事情之一,就是生成系统表。
我们先看一下initdb后,
c++
postgres@slpc:~/pgsql$ ./bin/initdb -D pgdata/
The files belonging to this database system will be owned by user "postgres".
This user must also own the server process.
The database cluster will be initialized with locales
COLLATE: en_US.UTF-8
CTYPE: en_US.UTF-8
MESSAGES: en_US.UTF-8
MONETARY: zh_CN.UTF-8
NUMERIC: zh_CN.UTF-8
TIME: zh_CN.UTF-8
The default database encoding has accordingly been set to "UTF8".
The default text search configuration will be set to "english".
Data page checksums are disabled.
fixing permissions on existing directory pgdata ... ok
creating subdirectories ... ok
selecting dynamic shared memory implementation ... posix
selecting default max_connections ... 100
selecting default shared_buffers ... 128MB
selecting default time zone ... Asia/Shanghai
creating configuration files ... ok
running bootstrap script ... ok
performing post-bootstrap initialization ... ok
syncing data to disk ... ok
initdb: warning: enabling "trust" authentication for local connections
You can change this by editing pg_hba.conf or using the option -A, or
--auth-local and --auth-host, the next time you run initdb.
Success. You can now start the database server using:
./bin/pg_ctl -D pgdata/ -l logfile start
postgres@slpc:~/pgsql$ cd pgdata/ && ls
base pg_logical pg_stat pg_wal
global pg_multixact pg_stat_tmp pg_xact
pg_commit_ts pg_notify pg_subtrans postgresql.auto.conf
pg_dynshmem pg_replslot pg_tblspc postgresql.conf
pg_hba.conf pg_serial pg_twophase
pg_ident.conf pg_snapshots PG_VERSION源码分析
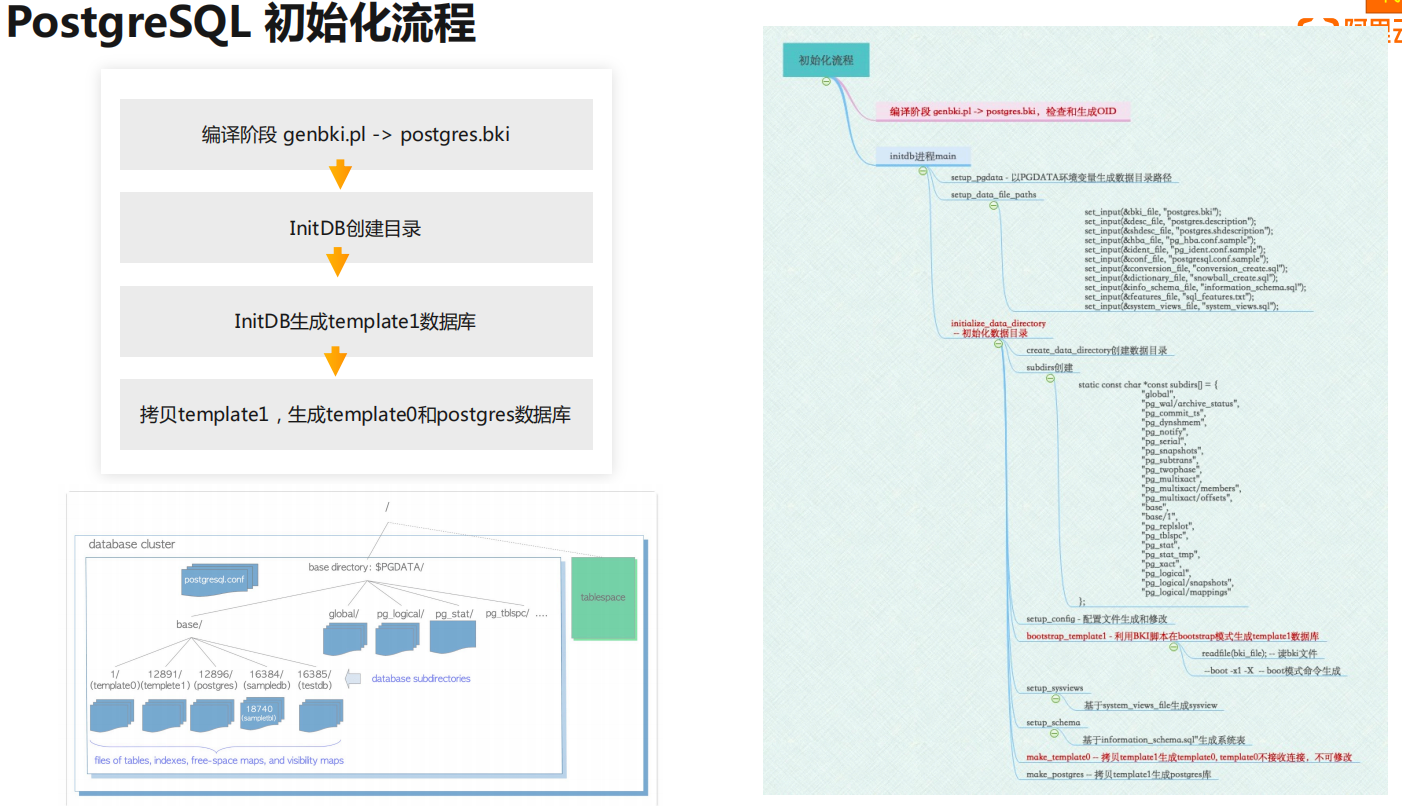
PostgreSQL初始化流程:
- 编译阶段,由genbki.pl脚本读取系统表定义文件(
src/backend/catalog/pg_*.h),生成postgres.bki文件
perl
# genbki.pl
# Perl script that generates postgres.bki and symbol definition
# headers from specially formatted header files and data files.
# postgres.bki is used to initialize the postgres template database.- initdb创建目录
- initdb生成template1数据库
- 由template1生成template0和postgres数据库
其核心的说明可以参考其代码注释:
c++
/* initdb --- initialize a PostgreSQL installation
*
* initdb creates (initializes) a PostgreSQL database cluster (site,
* instance, installation, whatever). A database cluster is a
* collection of PostgreSQL databases all managed by the same server.
*
* To create the database cluster, we create the directory that contains
* all its data, create the files that hold the global tables, create
* a few other control files for it, and create three databases: the
* template databases "template0" and "template1", and a default user
* database "postgres".
*
* The template databases are ordinary PostgreSQL databases. template0
* is never supposed to change after initdb, whereas template1 can be
* changed to add site-local standard data. Either one can be copied
* to produce a new database.
*
* For largely-historical reasons, the template1 database is the one built
* by the basic bootstrap process. After it is complete, template0 and
* the default database, postgres, are made just by copying template1.
*
* To create template1, we run the postgres (backend) program in bootstrap
* mode and feed it data from the postgres.bki library file. After this
* initial bootstrap phase, some additional stuff is created by normal
* SQL commands fed to a standalone backend. Some of those commands are
* just embedded into this program (yeah, it's ugly), but larger chunks
* are taken from script files.现在我们分析一下initdb的源码,核心代码在src/bin/initdb/initdb.c中, 源码的解析可以参考《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》第2章。
c++
main(int argc, char *argv[])
--> atexit(cleanup_directories_atexit); // 如果执行失败,清除已创建的目录文件
--> setup_pgdata(); // 获取PGDATA目录,或从-D 中获取
--> setup_data_file_paths();
--> initialize_data_directory();
--> create_data_directory(); // 创建PGDATA目录
--> create_xlog_or_symlink(); // 创建pg_wal目录
--> mkdir(path, pg_dir_create_mode) //创建其他的目录,base,global, pg_xact等等
--> write_version_file(NULL); // 创建PG_VERSION文件,写入主版本号, 数据库启动时会检查应用程序与实例版本好是否兼容
--> set_null_conf(); // 创建配置文件postgresql.conf
--> test_config_settings();
--> setup_config(); // 写配置文件,postgresql.conf pg_hba.conf postgresql.auto.conf
--> bootstrap_template1(); // run the BKI script in bootstrap mode to create template1,数据存储在base/1中
--> snprintf(cmd, sizeof(cmd), "\"%s\" --boot -x1 -X %u %s %s %s %s", backend_exec, wal_segment_size_mb * (1024 * 1024), data_checksums ? "-k" : "", boot_options, extra_options, debug ? "-d 5" : "");
--> PG_CMD_OPEN;
for (line = bki_lines; *line != NULL; line++)
{
PG_CMD_PUTS(*line);
free(*line);
}
--> PG_CMD_CLOSE;
--> write_version_file("base/1");
--> setup_auth(cmdfd);
--> setup_run_file(cmdfd, system_constraints_file);
--> setup_run_file(cmdfd, system_functions_file);
--> setup_depend(cmdfd);
--> setup_run_file(cmdfd, system_views_file);
--> load_plpgsql(cmdfd); // load PL/pgSQL server-side language
--> vacuum_db(cmdfd);
--> make_template0(cmdfd);
--> make_postgres(cmdfd);创建数据库其实并不是initdb独立去完成的,只是initdb向Postgres进程发送命令,由postgres进程通过--boot进入特殊的bootstrap模式运行执行。bootstrap_template1,这个比较重要,主要是启动postgres进程,执行postgres.bki中特殊的语句,创建系统表。这里说明一下,PG_CMD_OPEN,PG_CMD_PUTS,PG_CMD_CLOSE是什么意思:
c++
#define PG_CMD_OPEN \
do { \
cmdfd = popen_check(cmd, "w"); \
if (cmdfd == NULL) \
exit(1); /* message already printed by popen_check */ \
} while (0)
/* Open a subcommand with suitable error messaging */
static FILE * popen_check(const char *command, const char *mode)
{
FILE *cmdfd;
fflush(stdout);
fflush(stderr);
errno = 0;
cmdfd = popen(command, mode);
if (cmdfd == NULL)
pg_log_error("could not execute command \"%s\": %m", command);
return cmdfd;
}实质是调用popen函数去执行指定的命令。
最后,借用阿里云的分享文档,已加深大家对此的理解。详细文档见PostgreSQL体系结构。
参考文档:
《PostgreSQL数据库内核分析》 第2章
《openGauss数据库源码解析》 第3章