C++初学者指南第一步---11.字符串(基础)
文章目录
- C++初学者指南第一步---11.字符串(基础)
-
- [1. std::string](#1. std::string)
- [2. char = std::string的元素类型](#2. char = std::string的元素类型)
- [3. std::string字符串操作](#3. std::string字符串操作)
- [4. 字面量](#4. 字面量)
-
- [4.1 C风格字符串字面量](#4.1 C风格字符串字面量)
- [4.2 "std::string 字面量"s (C++14)](#4.2 "std::string 字面量"s (C++14))
- [4.3 字面量拼接](#4.3 字面量拼接)
- [4.4 原始字符串字面量](#4.4 原始字符串字面量)
- [5. 类似字符串的函数参数](#5. 类似字符串的函数参数)
- [6. std::getline 库函数](#6. std::getline 库函数)
1. std::string
- char类型的动态数组(类似于 vector)。
- 可以使用"+"或"+="连接。
- 使用下标[索引]方式进行单字符访问。
- 可修改的("可变的")与 Python 或 Java 中不同。
- 常规的:可深度复制,可深度比较。
cpp
#include <string>
std::string hw = "Hello";
std::string s = hw; // copy of hw
hw += " World!";
cout << hw << '\n'; // Hello World!
cout << hw[4] << '\n'; // o
cout << s << '\n'; // Hello2. char = std::string的元素类型
- 一个char可以容纳一个字符
- char是最小整数类型(通常为 1 字节)
- 字符必须用单引号括起来:'a', 'b', 'c', ...
cpp
char c1 = 'A';
char c2 = 65; // ASCII code of 'A'
cout << c1 << '\n'; // A
cout << c2 << '\n'; // A
cout << (c1 == c2) << '\n'; // 1
std::string s = "xyz";
s[1] = c1;
cout << s << '\n'; // xAz
s += c2;
cout << s << '\n'; // xAzA特殊字符(反斜杠 \ 用作转义字符)
| 特殊字符 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| \n | 换行符 | "Line1\nLine1\nLine3" |
| \t | tab制表符 | "Column1\tColumn1\tColumn3" |
| \' | 单引号 | "he said 'quote' to me" |
| \\ | 反斜杠 | "C:\\Users\me\\hello.cpp" |
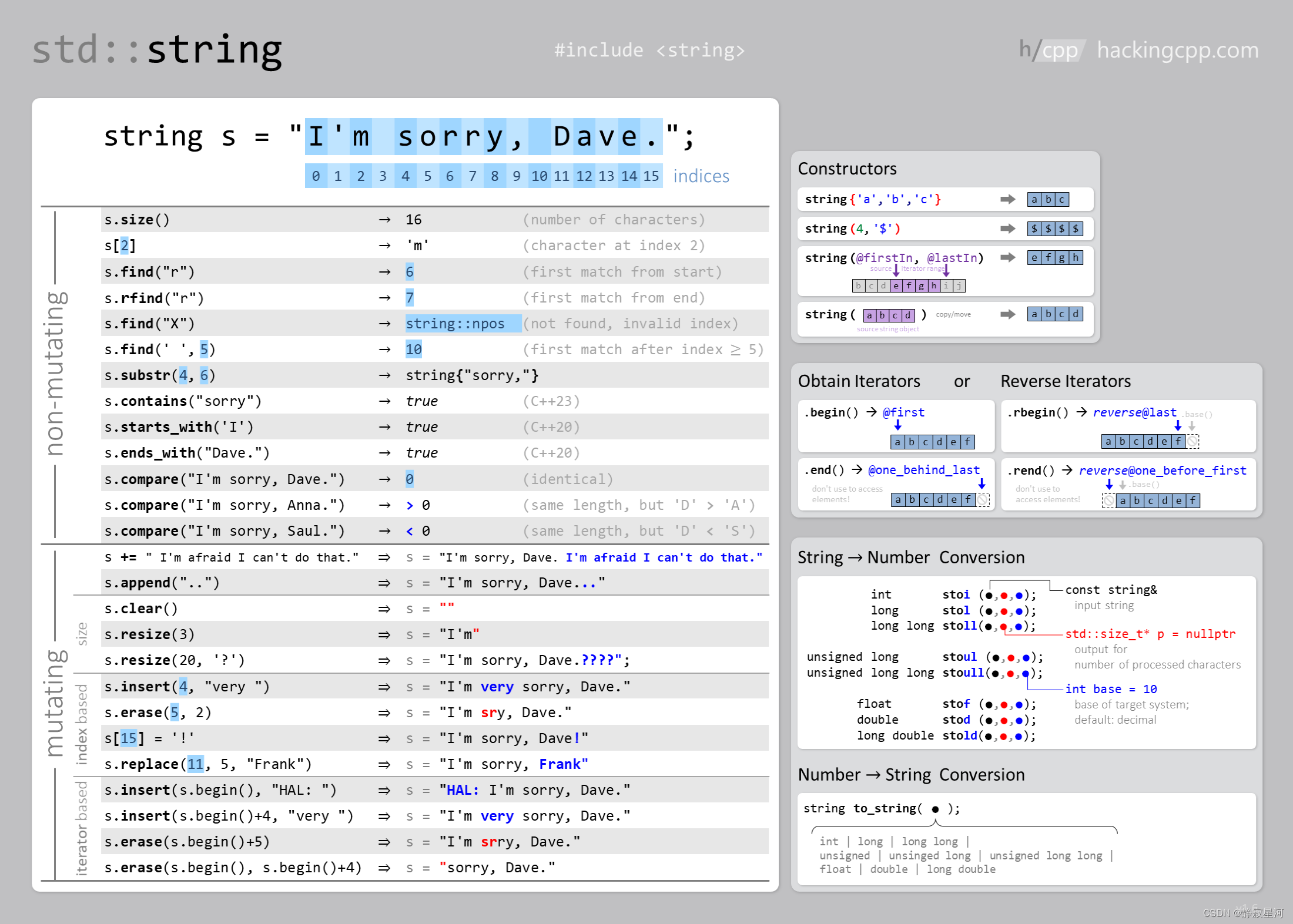
3. std::string字符串操作

std::string接口速查表
4. 字面量
'a' // 字符型字面量4.1 C风格字符串字面量
auto a = "seven of"; // a的类型是 char const[]
auto b = a; // b 指的是与 a 相同的对象
a += " nine"; // 编译错误:不能修改
auto c = "al" + "cove"; // 编译错误
std::string s = a; // a 被拷贝进 s
s += " nine"; // 正确(s 是 std::string)4.2 "std::string 字面量"s (C++14)
#include <string>
using namespace std::string_literals;
auto s1 = "seven of"s; // s1的类型是 std::string
auto s2 = s1; // s2 是 s1的拷贝
s1 += " nine"; //
cout << s1 << '\n'; // seven of nine
cout << s2 << '\n'; // seven of
auto s3 = "uni"s + "matrix"s; //
cout << s3 << '\n'; // unimatrix4.3 字面量拼接
只有被空白字符分隔的字符串字面量会被连接起来:
"first" "second" ⇒ "first second"
std::string s =
"This is one literal"
"split into several"
"source code lines!";4.4 原始字符串字面量
优势:可以使用特殊字符而无需转义
R"(raw "C"-string c:\users\joe)" char const[] C++11
R"(raw "std"-string c:\users\moe)"s std::string C++14
语法: R"DELIMITER(characters...)DELIMITER"DELIMITER(定界符,用于表明字符串的开始和结束)可以是0到16个字符的序列,但不能包含空格、(、)和\。
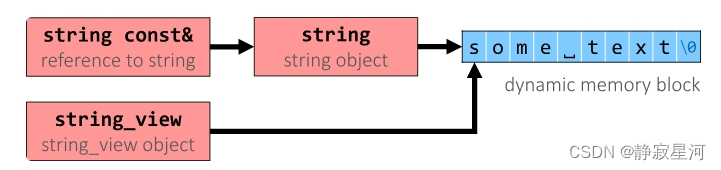
5. 类似字符串的函数参数
注意:std::string_view被用于只读参数(C++17)
-
轻量级(= 复制成本低,可以按值传递)
-
非所有者(= 不负责分配或释放内存)
-
只读视图(= 不允许修改目标字符串)
-
字符串类似对象(std::string / "literal" / ...)
-
主要用例:只读的函数参数
#include <string>
#include <string_view>
int edit_distance (std::string_view s1, std::string_view s2) { ... }
std::string input = "abx";
int dist = edit_distance("abc", input); -
在将字符串字面量传递给函数时,避免使用开销很大的临时字符串
-
通过避免一层间接访问,可以加快访问速度:
| 如果你... | 使用的参数类型 |
|---|---|
| 在函数里总是需要一个输入字符串的拷贝。 | std::string "按值传递" |
| 想要只读访问: 不需要(总是)复制 使用C++17或C++20 | #include <string_view> std::string_view |
| 想要只读访问: 不需要(总是)复制 使用C++98或C++11 | std::string const& "用常量引用传递参数" |
| 想要函数修改字符串 应该尽量避免这样的输出参数 | std::string & 传递std::string的(非常量)引用 |
6. std::getline 库函数
-
一次读取整行/整块文本
-
目标字符串可以重复使用(节省内存)
std::string s;
getline(std::cin, s); // 读取整行
getline(std::cin, s, '\t'); // 读取直到遇到tab结束
getline(std::cin, s, 'a'); // 读取直到遇到'a'结束
如果文章对您有用,请随手点个赞,谢谢!^_^