1、算法

2、算法分类

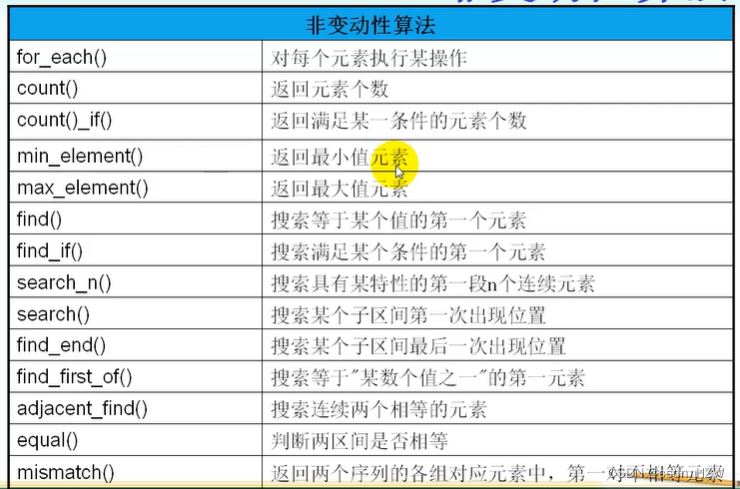
3、非变动性算法
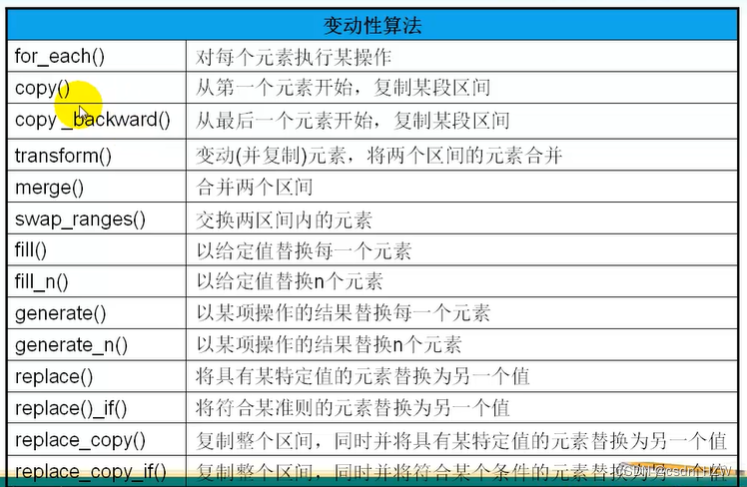
4、变动性算法
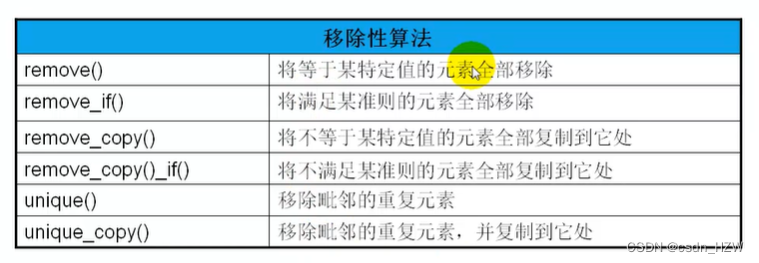
5、移除性算法
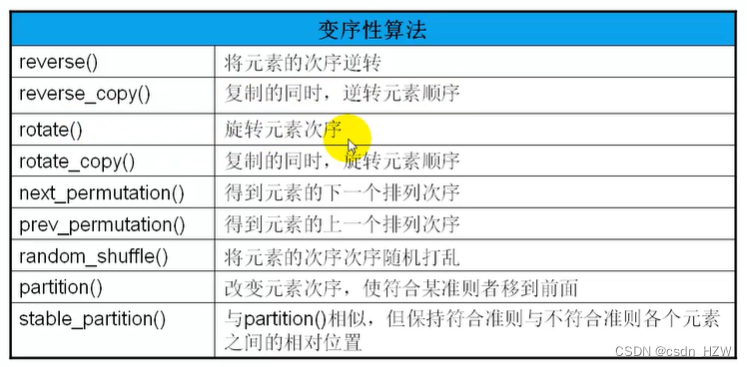
6、变序性算法
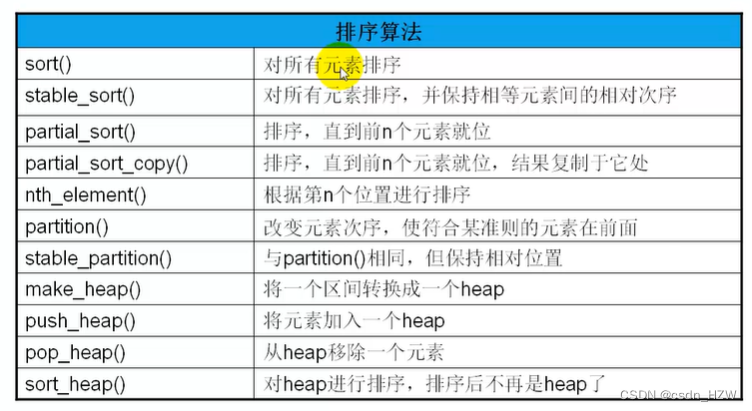
7、排序算法
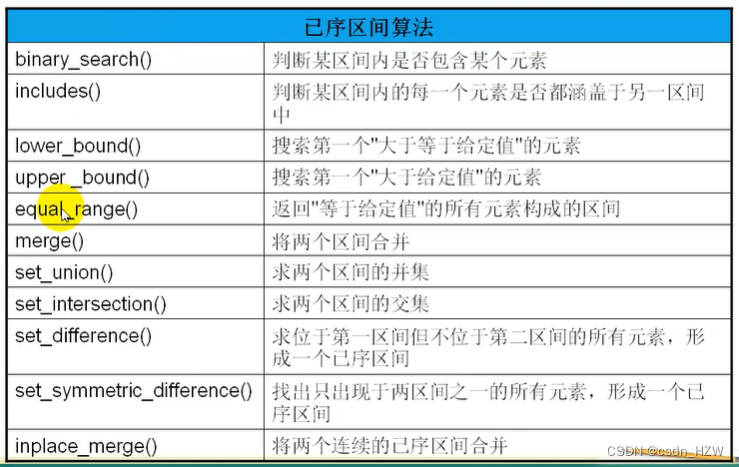
8、已序区间算法
9、数值算法

10、算法尾词

11、非变动性算法示例

在使用的时候,会拷贝一份出来,所以不会对原数据有影响。主要是要点进去看内部源码的实现。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void print_element(int n)
{
cout << n << ' ';
}
bool bigger_than_4(int n)
{
return n > 4;
}
int main() {
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
vector<int> v(a, a+5);
vector<int>::const_iterator it;
for(it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
// 这个其实就是用for循环遍历,然后把每次遍历的元素当作参数传给print_element去执行
// 所以print_element中参数的类型要和v的类型一致
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print_element);
cout << endl;
it = min_element(v.begin(), v.end());
if (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
it = max_element(v.begin(), v.end());
if (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
it = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 4);
if (it != v.end())
{
cout << it - v.begin() << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "not found" << endl;
}
it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), bigger_than_4);
if (it != v.end())
{
cout << it - v.begin() << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "not found" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
// 输出
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
1
5
3
4