目录
一、List的使用
补充
需要使用类域指向的:
1、内部类
2、类里面typedef的
构造函数
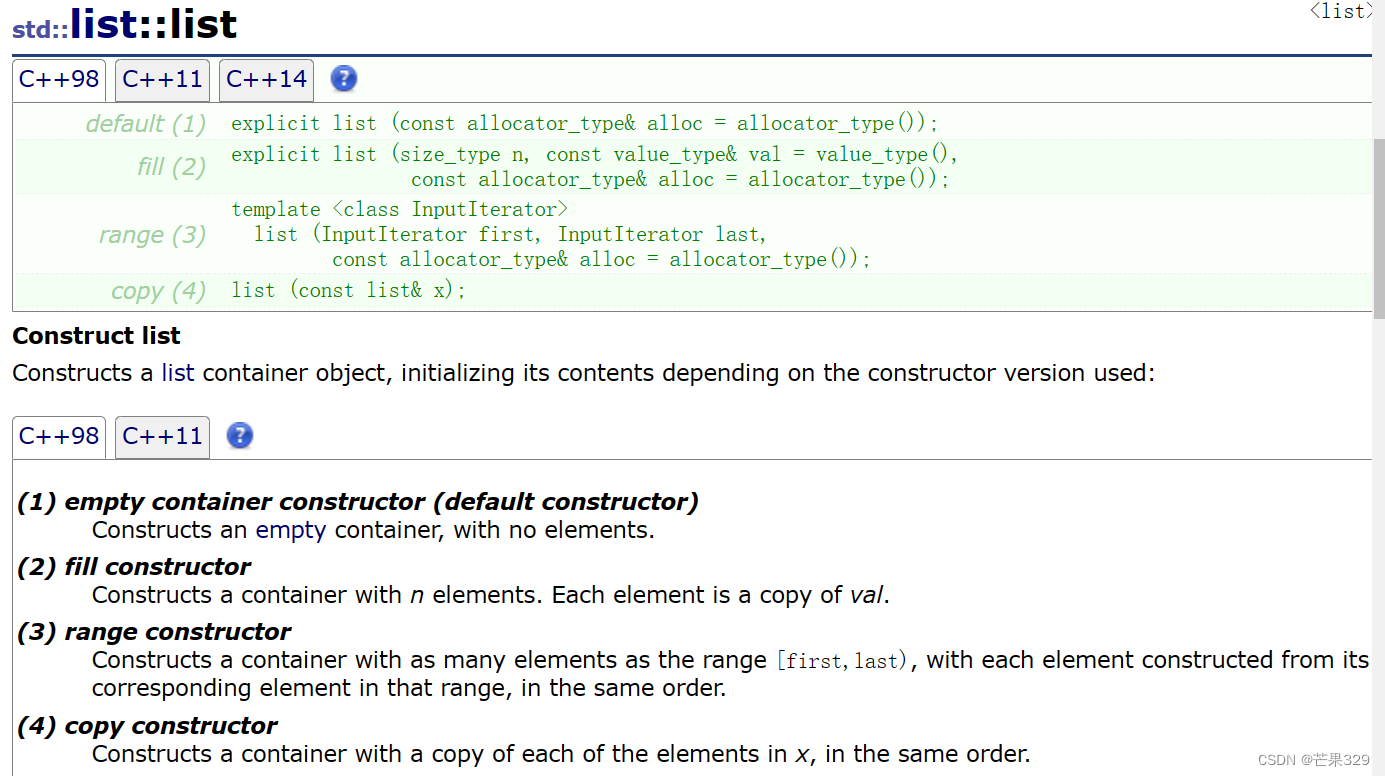
(1)构造一个空的list
(2)构造一个list,它里面的数据是n个val
(3)用迭代区间构造list
(4)用已有的一个list构造另一个list
List就是一个带头双向循环列表
List不支持[]
没有扩容什么的概念了
1、遍历
(1)迭代器
(2)范围for
但范围for的底层和迭代器没有区别
cpp
list<double> l2(5, 6.6);
for (auto e : l2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;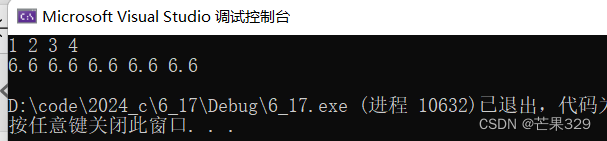
2、reverse
逆置
cpp
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(1);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(3);
l1.push_back(4);
list<int>::iterator it = l1.begin();
while (it != l1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
l1.reverse();
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;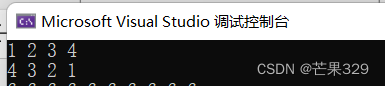
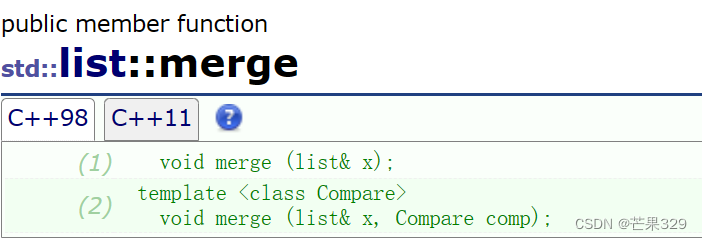
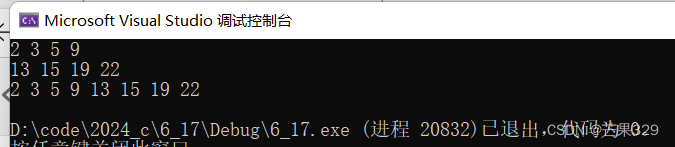
3、merge
归并:将两个有序的列表归并成一个有序的
使用merge的时候,可以先对列表进行sort排序
cpp
void test2()
{
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(3);
l1.push_back(5);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(9);
l1.sort();
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> l2;
l2.push_back(13);
l2.push_back(15);
l2.push_back(22);
l2.push_back(19);
l2.sort();
for (auto e : l2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
l1.merge(l2);
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
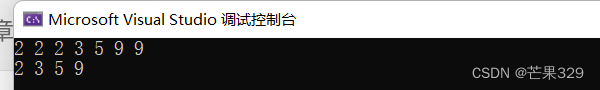
4、unique
去重:一般要求有序,无序必须相同的值是挨着的

cpp
void test3()
{
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(3);
l1.push_back(5);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(9);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(9);
l1.sort();
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
l1.unique();
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
5、sort
排序
list不能用算法库里面的sort,算法库里面的sort是快排(需要连续的空间,原地排序,不稳地排序,O(n2)),list自带的sort是归并(稳定排序,O(nlogn))
vector的排序用的是递归
实际中排序:拷贝到vector,进行排序,排完再assign到list里面

6、remove
相当于先find再删

cpp
void test4()
{
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(3);
l1.push_back(5);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(100);
l1.push_back(9);
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
l1.remove(100);
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
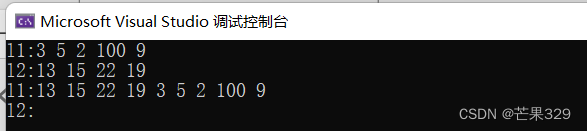
7、splice
把一个链表的值转移到另一个链表,是把一个链接里面的节点直接拿走

cpp
void test5()
{
list<int> l1;
l1.push_back(3);
l1.push_back(5);
l1.push_back(2);
l1.push_back(100);
l1.push_back(9);
cout << "l1:";
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
list<int> l2;
l2.push_back(13);
l2.push_back(15);
l2.push_back(22);
l2.push_back(19);
cout << "l2:";
for (auto e : l2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
l1.splice(l1.begin(), l2);
cout << "l1:";
for (auto e : l1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "l2:";
for (auto e : l2)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
二、底层实现
1、带头双向循环列表
struct和class的区别(1)继承权限:struct默认为public,而class默认的为private。
(2)访问权限:struct默认的成员变量访问控制权限是public,而class默认的成员变量访问权限则为private。
(3)class可以用于定于template,struct不能。
列表节点的定义
cpp
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode(const T& x = T())
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{}
ListNode<T>* _prev;
ListNode<T>* _next;
T _data;
};列表的定义
cpp
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef __listiterator<T> iterator;
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = tmp;
tmp->_prev = tail;
_head->_prev = tmp;
tmp->_next = _head;
}
private:
Node* _head;
};2、迭代器
Node是自定义类型,但Node*是内置类型,是要改变的是Node*的指向,不能改变指针的运算符对
Node*类型进行运算符重载,但Node*是内置类型无法运算符重载,因此需要套一个类__listiterator
cpp
namespace zyh
{
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode(const T& x = T())
:_prev(nullptr)
,_next(nullptr)
,_data(x)
{}
ListNode<T>* _prev;
ListNode<T>* _next;
T _data;
};
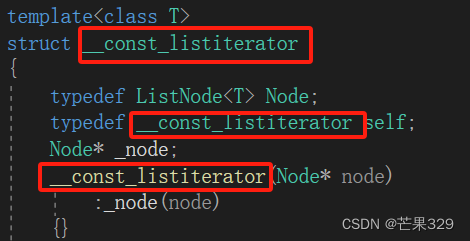
template<class T>
struct __listiterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef __listiterator self;
Node* _node;
__listiterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const self& x)
{
return _node != x._node;
}
T operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef __listiterator<T> iterator;
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = tmp;
tmp->_prev = tail;
_head->_prev = tmp;
tmp->_next = _head;
}
iterator begin()
{
//return iterator(_head->_next);
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
private:
Node* _head;
};
void list_test1()
{
list<int> lt1;
lt1.push_back(10);
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(2);
lt1.push_back(9);
lt1.push_back(3);
list<int>::iterator it = lt1.begin();
while (it != lt1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
3、迭代器的补充
这些都是在__listiterator类里面
(1)前置++:self& operator++()
cpp
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}(2)后置++:self& operator++(int)
cpp
self& operator++(int)
{
//Node* tmp = _node;
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
(3)前置- -:self& operator--()
cpp
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}(3)后置- -:self& operator--(int)
cpp
self& operator--(int)
{
Node* tmp = _node;
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}迭代器这个类里面没有析构函数
默认的析构函数对类里面的成员是不做处理的
这个类里面没有写析构函数,是因为这个类只是listnode的节点给它访问,他不能把人家删除吧
4、insert
不存在迭代器失效的问题
cpp
void insert(const iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(x);
Node* forward = (pos._node)->_prev;
forward->_next = tmp;
tmp->_prev = forward;
tmp->_next = pos._node;
(pos._node)->_prev = tmp;
}5、push_front
不存在迭代器失效问题
cpp
iterator push_front(const T& x)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(x);
tmp->_next = begin();
tmp->_prev = end();
end()._node->_next = tmp;
begin()._node->_prev = tmp;
return tmp;
}6、erase
pos迭代器失效问题
cpp
iterator erase(iterator& pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* next = pos._node->_next;
delete pos._node;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
return next;
}7、析构和clear
析构:列表的所以节点要释放,哨兵位的头节点也要释放
clear:只释放列表的所以节点,哨兵位的头节点不释放
clear
cpp
bool empty()
{
if (_head->_next == _head->_prev)
return true;
else
return false;
}
void clear()
{
if (empty())
return;
Node* cur = _head->_next;
while (cur != _head)
{
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
}问题:写的过于复杂,可以复用erase
cpp
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}注意:
it = erase(it)这里一定要再赋值给it,因为erase之后的it就是失效了
析构
cpp
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}8、拷贝构造
没有加const迭代器
cpp
//list(const list<T>& x)
list(list<T>& x)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
iterator it = x.begin();
while (it != x.end())
{
push_back(*it);
++it;
}
}9、赋值=
cpp
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}10、const迭代器
传参的时候会有const的对象
const迭代器不是自身不能修改,是指向的内容不能被修改
const迭代器不是const对象,自己可以修改
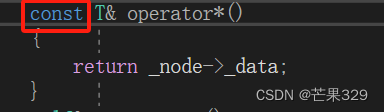
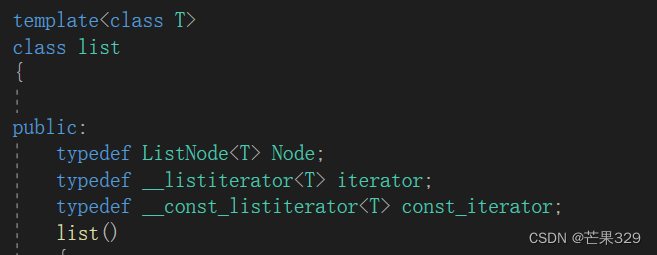
const迭代器 - 第一版
与普通迭代不同的地方
__const_listiterator类里面
cpp
template<class T>
struct __const_listiterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef __const_listiterator self;
Node* _node;
__const_listiterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self& operator++(int)
{
//Node* tmp = _node;
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& x)
{
return _node != x._node;
}
const T& operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self& operator--(int)
{
Node* tmp = _node;
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
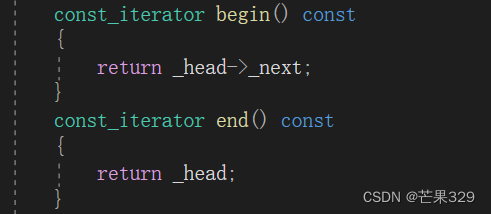
};list类里面
cpp
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef __listiterator<T> iterator;
typedef __const_listiterator<T> const_iterator;
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
}
//list(const list<T>& x)
list(list<T>& x)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
iterator it = x.begin();
while (it != x.end())
{
push_back(*it);
++it;
}
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = tmp;
tmp->_prev = tail;
_head->_prev = tmp;
tmp->_next = _head;
}
iterator begin()
{
//return iterator(_head->_next);
return _head->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _head;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _head->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _head;
}
iterator insert(const iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* tmp = new Node(x);
Node* forward = (pos._node)->_prev;
forward->_next = tmp;
tmp->_prev = forward;
tmp->_next = pos._node;
(pos._node)->_prev = tmp;
return tmp;
}
//iterator push_front(const T& x)
//{
// Node* tmp = new Node(x);
// tmp->_next = begin();
// tmp->_prev = end();
// end()._node->_next = tmp;
// begin()._node->_prev = tmp;
// return tmp;
//}
iterator push_front(const T& x)
{
return insert(begin(), x);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;
Node* next = pos._node->_next;
delete pos._node;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
return next;
}
iterator pop_back()
{
return erase(--end());
}
iterator pop_front()
{
return erase(begin());
}
bool empty()
{
if (_head->_next == _head->_prev)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//void clear()
//{
// if (empty())
// return;
// Node* cur = _head->_next;
// while (cur != _head)
// {
// Node* prev = cur->_prev;
// Node* next = cur->_next;
// prev->_next = next;
// next->_prev = prev;
// delete cur;
// cur = next;
// }
//}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
private:
Node* _head;
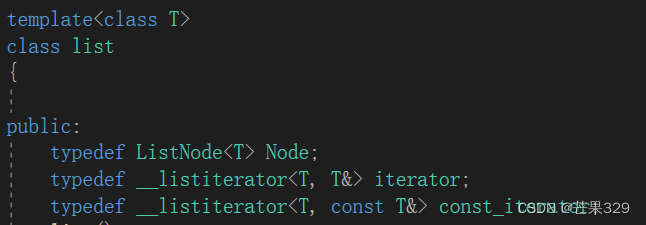
};问题:迭代器的类和const迭代器的类两个类有点冗余
const迭代器 - 第二版
cpp
template<class T, class Ref>
struct __listiterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef __listiterator self;
Node* _node;
__listiterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self& operator++(int)
{
//Node* tmp = _node;
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& x)
{
return _node != x._node;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self& operator--(int)
{
Node* tmp = _node;
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
};
在const迭代器中实现->的运算符重载
当ListNode里面的data是个结构体时,使用->进行访问