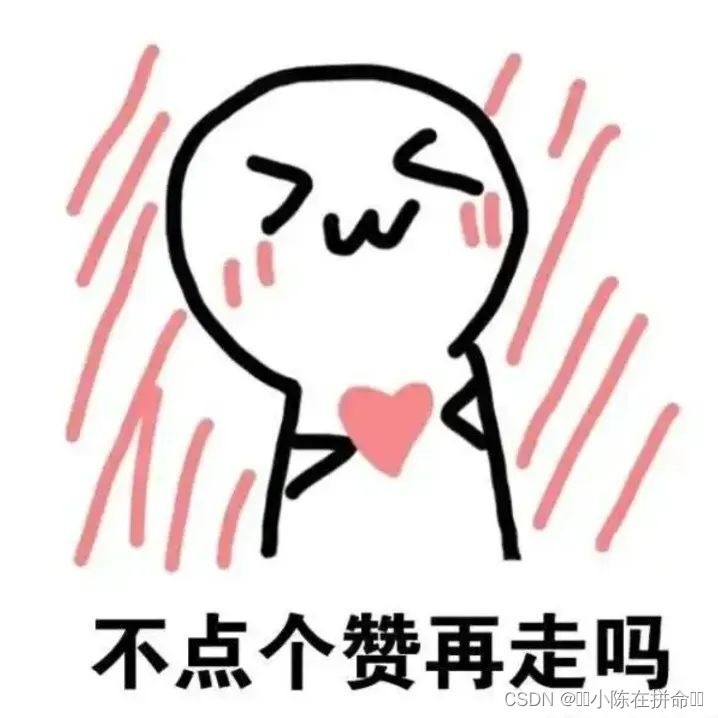
一、二叉树的层序遍历

该题的层序遍历和以往不同的是需要一层一层去遍历,每一次while循环都要知道在队列中节点的个数,然后用一个for循环将该层节点走完了再走下一层
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
if(root==nullptr) return ret;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int sz=q.size();//帮助我们控制一层一层出 因为上一层出完,下一层已经进去了
vector<int> path;//统计结果
for(int i=0;i<sz;++i)
{
TreeNode*t=q.front();
q.pop();
path.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
ret.push_back(path);;
}
return ret;
}
};二、N叉树的层序遍历
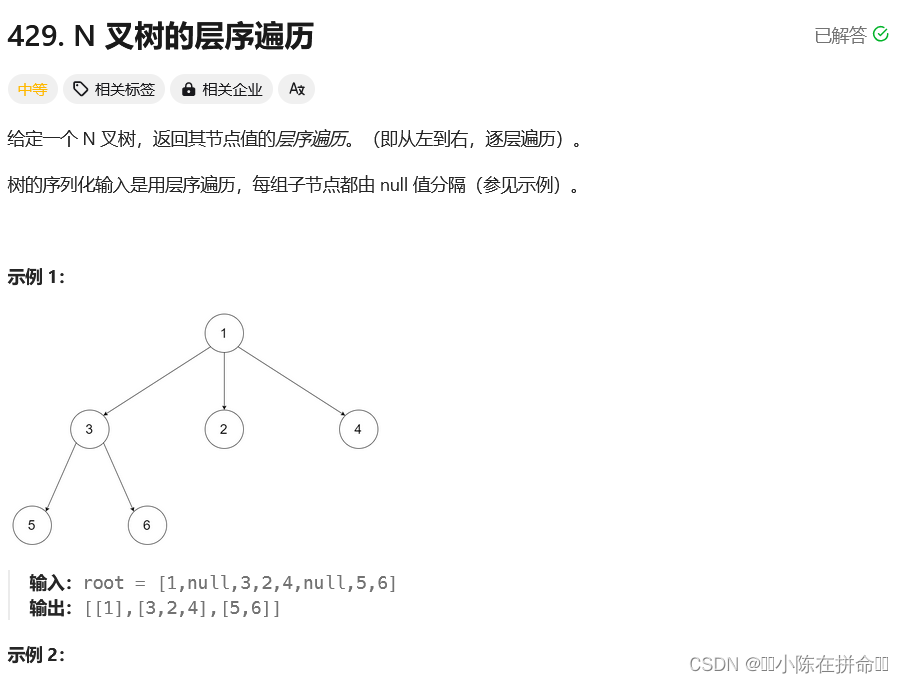
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(Node* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;//记录最终的返回结果
if(root==nullptr) return ret;
queue<Node*> q;//层序遍历所需要的队列
q.push(root);//先将根节点插入进去
while(!q.empty()) //因为统计的是每层,所以我们没进去一次就要去统计一层。
{
int sz=q.size();
//pop根节点的同时让他的孩子入队
//将左右孩子入队
vector<int> path;//记录每层的结果
for(int i=0;i<sz;++i)
{
Node* t=q.front();
q.pop();
path.push_back(t->val);
//开始让后面的节点入队
for(Node* &child:t->children)
if(child!=nullptr)
q.push(child);
}
ret.push_back(path);
}
return ret;
}
};三、二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历

设置一个变量编辑层数,单层的不处理,双层的将path数组进行翻转
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<vector<int>> ret;//帮助我们记录要返回的数组
queue<TreeNode*> q;//层序遍历需要的队列
if(root==nullptr) return ret;
q.push(root);
int k=1;//标记位
while(!q.empty())
{
int sz=q.size();
vector<int> path;//记录要插入的结果
for(int i=0;i<sz;++i)
{
TreeNode*t=q.front();//删除前拿到队头节点
q.pop();
path.push_back(t->val);//将结果插入进去
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
if(k%2==0) reverse(path.begin(),path.end());
++k;
ret.push_back(path);
}
return ret;
}
};四、每个树行中找最大值
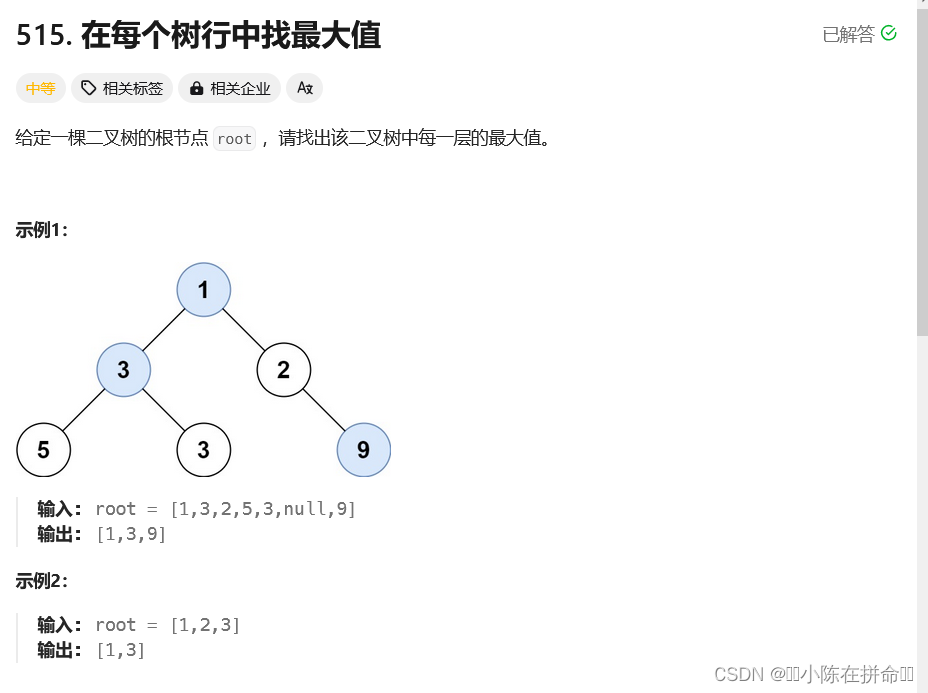
层序遍历的时候更新一下最大值即可!
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestValues(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ret;
if(root==nullptr) return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
size_t n=q.size();//统计当前层
int temp=INT_MIN;
for(size_t i=0;i<n;++i)
{
TreeNode*t=q.front();
q.pop();
temp=max(temp,t->val);//更新最大值
//将孩子进队列
if(t->left) q.push(t->left);
if(t->right) q.push(t->right);
}
ret.emplace_back(temp);
}
return ret;
}
};五、二叉树的最大宽度(非常经典)
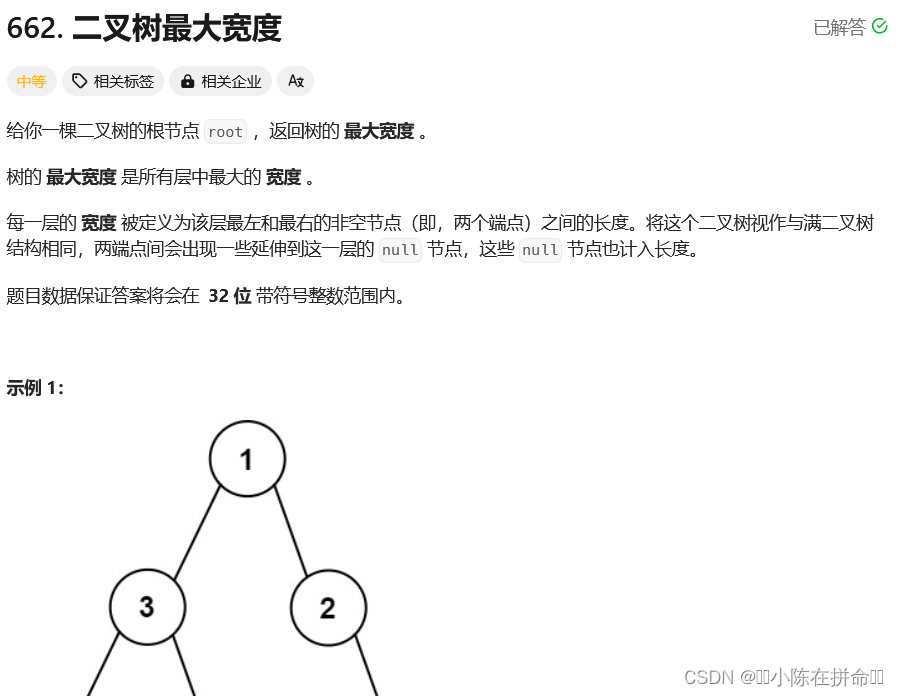
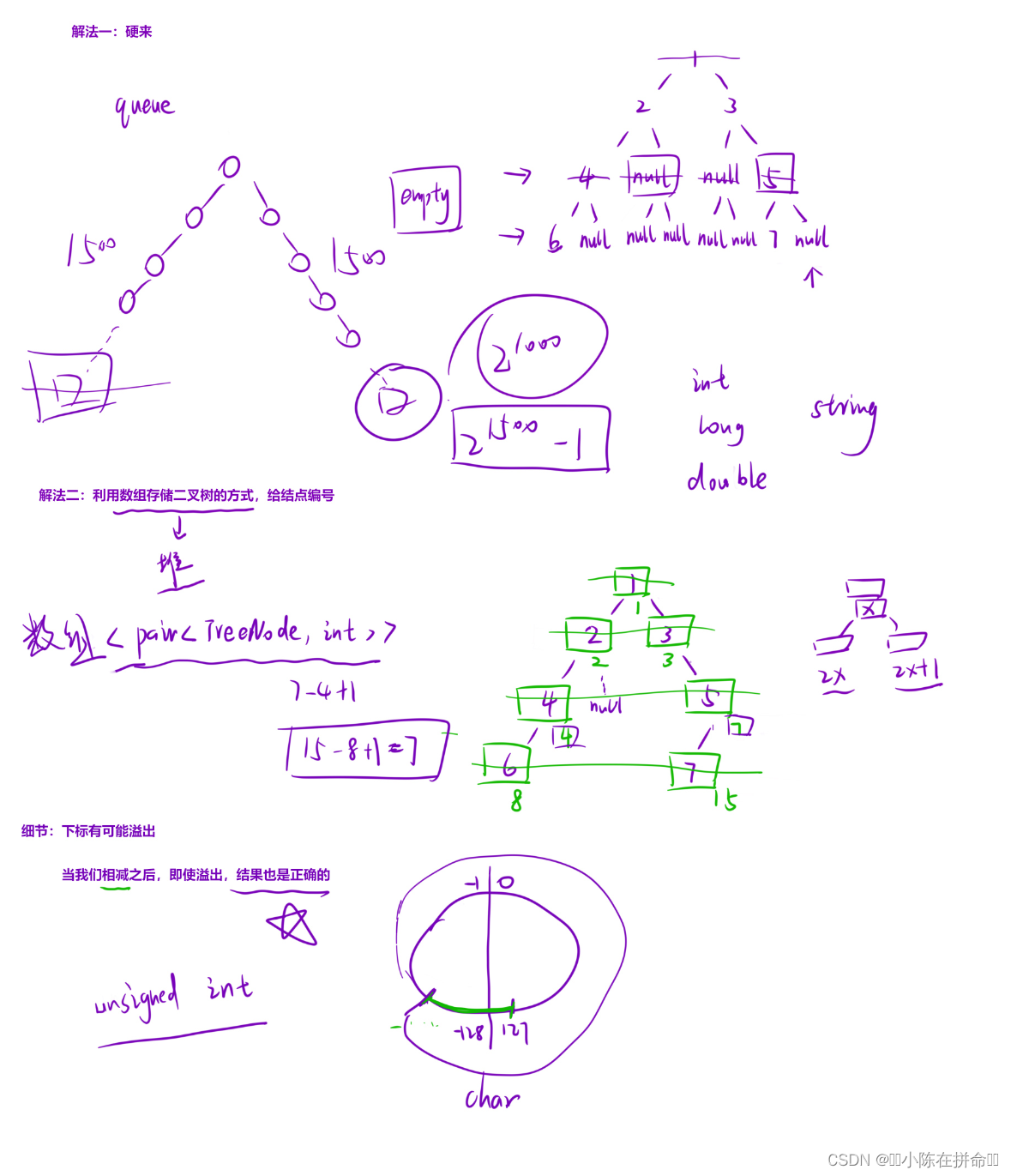
细节1:下标可能溢出
关键是这里借助**无符号整型**在溢出的时候自动根据32位,或者64位取模。
细节2:利用数组的存储方式给节点编号+移动赋值(右值引用提高效率)
用vector模拟queue 把孩子和其对应的下标存在数组中,每一层处理完再进行移动赋值。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
typedef pair<TreeNode*,unsigned int> PTU;
int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
//用队列 直接连空节点也丢 超时
//用数组模拟
vector<PTU> q;//用数组来模拟队列
q.emplace_back(root,1);
unsigned int ret=1; //减掉之后不会影响结果
while(!q.empty())
{
//先更新一下长度
auto&[x1,y1]=q[0];
auto&[x2,y2]=q.back();
ret=max(ret,y2-y1+1);
//用一个新的数组入队
vector<PTU> temp;//用数组来模拟队列
//让下一层进队列
for(auto&[x,y]:q)
{
if(x->left) temp.emplace_back(x->left,y*2); //插入pair类型可以体现出emplace_back
//和push_back的区别 push_back({x->left,y*2})
if(x->right) temp.emplace_back(x->right,y*2+1);
}
//更新一个新的数组
q=move(temp); //移动赋值 窃取资源 效率更高
}
return ret;
}
};