一、ff_ctz函数的作用
ff_ctz定义在FFmpeg源码目录的libavutil/intmath.h 下:
cpp
#ifndef ff_ctz
#define ff_ctz ff_ctz_c
/**
* Trailing zero bit count.
*
* @param v input value. If v is 0, the result is undefined.
* @return the number of trailing 0-bits
*/
/* We use the De-Bruijn method outlined in:
* http://supertech.csail.mit.edu/papers/debruijn.pdf. */
static av_always_inline av_const int ff_ctz_c(int v)
{
//...
}
#endif可以看到ff_ctz函数等价于ff_ctz_c函数。其作用是:如果形参v的值为0,返回0。否则将形参v转成二进制,返回其最后一个"1"后面"0"的个数。
形参v:输入型参数。需要被计算的值。
返回值:将形参v转成二进制,返回的最后一个"1"后面"0"的个数。
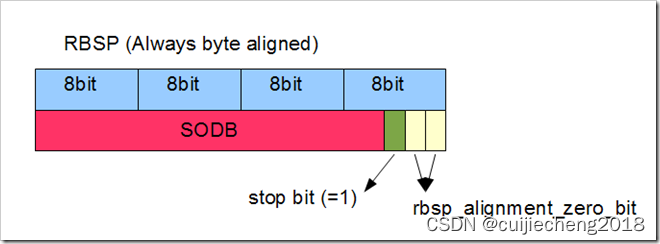
ff_ctz函数一般用在统计H.264 RBSP最后补齐了多少个0位。也就是stop bit后面rbsp_alignment_zero_bit的个数。详情可以参考:《音视频入门基础:H.264专题(3)------EBSP, RBSP和SODB》
二、ff_ctz函数的内部实现
cpp
#ifndef ff_ctz
#define ff_ctz ff_ctz_c
/**
* Trailing zero bit count.
*
* @param v input value. If v is 0, the result is undefined.
* @return the number of trailing 0-bits
*/
/* We use the De-Bruijn method outlined in:
* http://supertech.csail.mit.edu/papers/debruijn.pdf. */
static av_always_inline av_const int ff_ctz_c(int v)
{
static const uint8_t debruijn_ctz32[32] = {
0, 1, 28, 2, 29, 14, 24, 3, 30, 22, 20, 15, 25, 17, 4, 8,
31, 27, 13, 23, 21, 19, 16, 7, 26, 12, 18, 6, 11, 5, 10, 9
};
return debruijn_ctz32[(uint32_t)((v & -v) * 0x077CB531U) >> 27];
}
#endif三、编写测试例子,测试ff_ctz函数
main.c :
cpp
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#ifdef __GNUC__
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(x,y) (__GNUC__ > (x) || __GNUC__ == (x) && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= (y))
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_MOST(x,y) (__GNUC__ < (x) || __GNUC__ == (x) && __GNUC_MINOR__ <= (y))
#else
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(x,y) 0
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_MOST(x,y) 0
#endif
#ifndef av_always_inline
#if AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(3,1)
# define av_always_inline __attribute__((always_inline)) inline
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
# define av_always_inline __forceinline
#else
# define av_always_inline inline
#endif
#endif
#if AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(2,6) || defined(__clang__)
# define av_const __attribute__((const))
#else
# define av_const
#endif
#ifndef ff_ctz
#define ff_ctz ff_ctz_c
/**
* Trailing zero bit count.
*
* @param v input value. If v is 0, the result is undefined.
* @return the number of trailing 0-bits
*/
/* We use the De-Bruijn method outlined in:
* http://supertech.csail.mit.edu/papers/debruijn.pdf. */
static av_always_inline av_const int ff_ctz_c(int v)
{
static const uint8_t debruijn_ctz32[32] = {
0, 1, 28, 2, 29, 14, 24, 3, 30, 22, 20, 15, 25, 17, 4, 8,
31, 27, 13, 23, 21, 19, 16, 7, 26, 12, 18, 6, 11, 5, 10, 9
};
return debruijn_ctz32[(uint32_t)((v & -v) * 0x077CB531U) >> 27];
}
#endif
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", ff_ctz(0));
printf("%d\n", ff_ctz(80));
printf("%d\n", ff_ctz(100));
printf("%d\n", ff_ctz(128));
printf("%d\n", ff_ctz(255));
return 0;
}Linux平台下使用gcc编译(我用的是CentOS 7.5,通过10.2.1版本的gcc编译)。输出为:
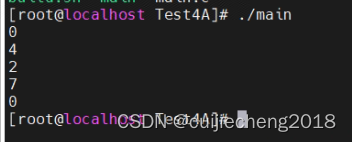
ff_ctz函数形参v的值为0时,返回0,所以ff_ctz(0)值为0。
80转成二进制为01010000。最后的1后面有4位0。所以ff_ctz(80)值为4。
100转成二进制为01100100。最后的1后面有2位0。所以ff_ctz(100)值为2。
128转成二进制为10000000。最后的1后面有7位0。所以ff_ctz(128)值为7。
255转成二进制为11111111。最后的1后面有0位0。所以ff_ctz(255)值为0。