- [Nest.js 介绍](#Nest.js 介绍)
-
- 核心功能
- [设计模式:IOC 控制反转 DI 依赖注入](#设计模式:IOC 控制反转 DI 依赖注入)
- 前置知识:装饰器
- 前置知识装饰器-实现一个GET请求
- Nestjs脚手架
-
- [Nestjs cli 常用命令](#Nestjs cli 常用命令)
- [RESTful 风格设计](#RESTful 风格设计)
- [Nestjs 控制器](#Nestjs 控制器)
- [Session 实例](#Session 实例)
- [Nestjs 提供者](#Nestjs 提供者)
- [Nestjs 模块](#Nestjs 模块)
- 中间件
Nest.js 介绍
- Nestjs 是一个用于构建高效可扩展的一个基于 Nodejs 服务端应用程序开发框架。完全支持 ts ,结合了 AOP 面向切面的编程方式
- 官方文档1. 英文文档 Nestjs中文文档简介2.中文文档
- 内置框架 Express(默认),nestjs维二内置框架 Fastify
1️⃣ 能够快速构建服务端应用程序,且学习成本非常低,容易上手
express 文档
2️⃣ Fastify,快速并且低开销的 web 框架,专为 Node.js 平台量身打造
高效的服务器意味着更低的基础设施成本、更好的负载响应能力和用户满意度。 在不牺牲安全验证和便捷开发的前提下,如何知道服务器正在处理尽可能多的请求,又如何有效地处理服务器资源?
Fastify 是一个 web 开发框架,其设计灵感来自 Hapi 和 Express,致力于以最少的开销和强大的插件结构提供最佳的开发体验。据我们所知,它是这个领域里速度最快的 web 框架之一。

核心功能
以下列出的是 Fastify 已经实现的主要功能及原理:
- 高性能: 据我们所知,Fastify 是这一领域中最快的 web 框架之一,另外,取决于代码的复杂性,Fastify 最多可以处理每秒 3 万次的请求。
- 可扩展: Fastify 通过其提供的钩子(hook)、插件和装饰器(decorator)提供完整的可扩展性。
- 基于 Schema: 即使这不是强制性的,我们仍建议使用 JSON Schema 来做路由(route)验证及输出内容的序列化,Fastify 在内部将 schema 编译为高效的函数并执行。
- 日志: 日志是非常重要且代价高昂的。我们选择了最好的日志记录程序来尽量消除这一成本,这就是 Pino!
- 对开发人员友好: 框架的使用很友好,帮助开发人员处理日常工作,并且不牺牲性能和安全性。
- 支持 TypeScript: 我们努力维护一个 TypeScript 类型声明文件,以便支持不断成长的 TypeScript 社区。
设计模式:IOC 控制反转 DI 依赖注入
⭐️控制反转(IOC)
控制反转是一种设计原则,目的是将对象的创建和依赖关系的管理从代码中分离出来,传统的编码方式是对象主动去获取它所需要的依赖,而控制反转则是由外部容器来管理对象的创建和依赖的注入。
⭐️依赖注入(DI)
实现控制反转的一种具体方式,通过依赖注入,组件所需的依赖对象由外部提供,而不是组件自己创建。依赖注入可以通过构造函数注入,属性注入或者方法注入实现。
js
// 未使用控制反转和依赖注入的代码
class A {
name: string
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name
}
}
class B {
age:number
entity:A
constructor (age:number) {
this.age = age;
this.entity = new A('小满')
}
}
const c = new B(18)
c.entity.name 使用了 IOC 容器
js
class A {
name: string
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name
}
}
class C {
name: string
constructor(name: string) {
this.name = name
}
}
//中间件用来收集依赖,用于解耦
class Container{
modeuls:any
constructor(){
this.modeuls = {}
}
provide(key:string,modeuls:any){
this.modeuls[key] = modeuls
}
get(key){
return this.modeuls[key]
}
}
const modelus = new Container()
modelus.provide('a',new A('koillin'))
class B{
a:any
c:any
constructor(container:Container){
this.a = container.get('a');
this.b = container.get('b')
}
}
new B(modelus)前置知识:装饰器
装饰器是一种特殊的类型声明(一个函数),他可以附加在类,方法,属性,参数上面
- 类装饰器:把构造函数传入到装饰器的第一个参数 target
js
function decotators(target:any){
target.prototype.name = 'koillin'
}
@decotators
class Koillin{
contructor(){}
}
const koi:any = new Koillin()
console.log(Koillin.name)//koillin- 属性装饰器:返回两个参数: 原型对象、属性的名称
js
const currency:PropertyDecorator = (target:any,key:string|symbol)=>{
console.log(target,key)//{} name
}
class Koillin{
@currency
public name:string
constructor(){
this.name = ''
}
getName(){
return this.name
}
}- 参数装饰器:返回三个参数:
原型对象、方法的名称、参数的位置(从0开始)
bash
const currency = (target: any, key: string | symbol,index:number) => {
console.log(target, key,index) // {} getName 1
}
class Koillin{
public name: string
constructor() {
this.name = ''
}
getName(name:string, @currency age:number) {
return this.name
}
}- 方法装饰器:返回三个参数:原型对象、方法的名称、属性描述符(可写对应writable,可枚举对应enumerable,可配置对应configurable)
js
const currency: MethodDecorator = (target: any, key: string | symbol, descriptor:any) => {
// {} getName {
// value: [Function: getName], value 即是对应的方法 getName
// writable: true,//可写对应
// enumerable: false,//可枚举
// configurable: true//可配置
// }
console.log(target, key, descriptor)
}
class Koillin{
public name: string
constructor() {
this.name = ''
}
@currency
getName(name:string,age:number) {
return this.name
}
}前置知识装饰器-实现一个GET请求
安装依赖
npm install axios -S
定义控制器
bash
class Controller {
constructor() {
}
getList () {
}
}定义装饰器
使用装饰器工厂,应为装饰器默认会塞入一些参数,定义descriptor的类型 ,通过descriptor描述符里面的value,把axios的结果返回给当前使用装饰器的函数
bash
const Get = (url:string):MethodDecorator =>{
return (target,key,descriptor:PropertyDescriptor)=>{
const fnc = descriptor.value;
axios.get(url).then(res=>{
fnc(res,{status:200}
)
}).catch(e=>{
fnc(e,{status:500})
})
}
}完整代码
js
import axios from 'axios'
const Get = (url: string): MethodDecorator => {
return (target, key, descriptor: PropertyDescriptor) => {
const fnc = descriptor.value;
axios.get(url).then(res => {
fnc(res, {
status: 200,
})
}).catch(e => {
fnc(e, {
status: 500,
})
})
}
}
//定义控制器
class Controller {
constructor() {
}
@Get('https://api.apiopen.top/api/getHaoKanVideo?page=0&size=10')
getList (res: any, status: any) {
console.log(res.data.result.list, status)
}
}
Nestjs脚手架
1️⃣ 通过 cli 创建 Nestjs 项目
npm i -g @nestjs/cli
nest new [项目名称]
2️⃣ 使用npm run start:dev启动,具备热更新,简单访问地址http://localhost:3000/
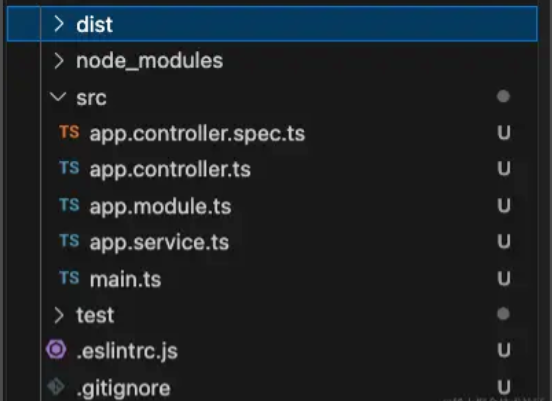
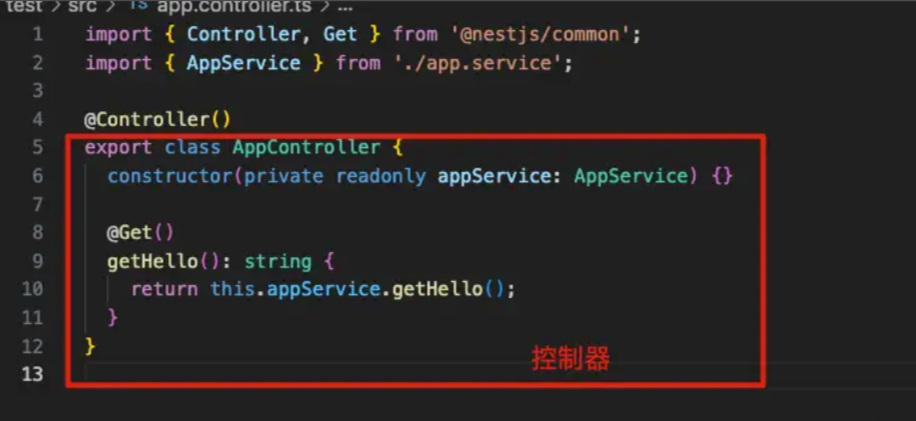
dist文件夹是运行时就会打包生成的.spec.ts是测试用文件.controller.ts是控制器,类似vue的 路由
⭐️private readonly appService: AppService这一行代码就是依赖注入不需要实例化,appService 内部会自己实例化.module.ts是模块文件,Nestjs使用模块打包特定功能,每个模块是高度封装的,只暴露必要的接口,它可以包含一些组件,如控制器、服务等.service.ts是现实业务逻辑文件,当然也可以放在控制器文件里面实现,但是拿出来是为了复用main.ts入口文件主文件 类似于vue 的main.ts
通过 NestFactory.create(AppModule) 创建一个app 就是类似于绑定一个根组件App.vue
app.listen(3000); 监听一个端口
bash
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();Nestjs cli 常用命令
nest --help 查看Nestjs所以命令
js
// 生成 controller.ts
nest g co user
// 生成 module.ts
nest g mo user
// 生成 service.ts
nest g s user
// 直接生成一个 CURD
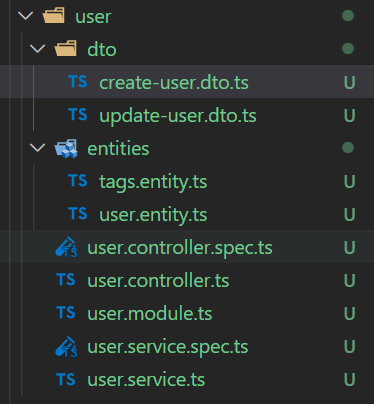
nest g res user 生成的文件结构如下
dto文件是用来定义数据传输对象的,用于验证请求体中的数据或者控制返回的数据格式,例如:
js
export class CreateUserDto {
name: string;
desc: string;
}entities文件是后续连接数据库后用来表示数据库中的表的结构,例如:
js
import { Entity, Column,PrimaryGeneratedColumn, CreateDateColumn, Generated, ManyToOne } from 'typeorm';
import { User } from './user.entity';
@Entity()
export class Tags {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column()
tags:string;
@ManyToOne(()=>User,(user)=>user.tags)
user:User;
}
RESTful 风格设计
RESTful 是一种软件架构风格、设计风格,也是一种开发规范,其核心是面向资源(Resource)进行设计
HTTP 方法(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)作为通用接口方法,被用来对资源进行操作,可以表示对资源的增删改查。
例如一个用户资源的 CRUD 操作的 RESTful 设计可能是:
- 创建用户:POST /users
- 获取用户:GET /users/{id}
- 更新用户:PUT /users/{id}
- 删除用户:DELETE /users/{id}
可以用一个接口完成对资源的crud,只是通过不同的请求方式来区分,生成user.controller.ts文件就是这样实现的。
传统接口
http://localhost:8080/api/get_list?id=1
http://localhost:8080/api/delete_list?id=1
http://localhost:8080/api/update_list?id=1
RESTful接口
http://localhost:8080/api/get_list/1 查询 删除 更新
通过不同请求方式来区分
查询GET
提交POST
更新PUT、PATCH
删除 DELETE
js
import { Controller, Get, Post, Body, Patch, Param, Delete, Query } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from './dto/update-user.dto';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
constructor(private readonly userService: UserService) {}
@Post('/add/tags')
addTags (@Body() params:{tags:string[],userId:number}) {
return this.userService.addTags(params)
}
@Post()
create(@Body() createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
return this.userService.create(createUserDto);
}
@Get()
findAll(@Query() query:{keyWord:string,page:number,pageSize:number}) {
return this.userService.findAll(query);
}
@Patch(':id')
update(@Param('id') id: string, @Body() updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto) {
return this.userService.update(+id, updateUserDto);
}
@Delete(':id')
remove(@Param('id') id: string) {
return this.userService.remove(+id);
}
}main.ts
js
// 跨域
app.use(cors());
// 全局拦截器
app.useGlobalInterceptors(new Response())
// 全局异常处理
app.useGlobalFilters(new HttpFilter())
// 路由前缀
app.setGlobalPrefix('api')
// 验证数据
app.useGlobalPipes(new ValidationPipe())
// 路由守卫
app.useGlobalGuards(new RoleGuard())
// 版本
app.enableVersioning({type:VersioningType.URI})
// 中间件
app.use(MiddleWareAll)
// session
app.use(session({secret:"koillin",rolling:true,name:"koillin.sid",cookie:{maxAge:null}}))
// 静态资源
app.useStaticAssets(join(__dirname, 'image'))然后在user.controller 配置版本
Controller 变成一个对象 通过version 配置版本
js
import { Controller, Get, Post, Body, Patch, Param, Delete, Version } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from './dto/update-user.dto';
@Controller({
path:"user",
version:'1'
})
export class UserController {
constructor(private readonly userService: UserService) {}
@Post()
create(@Body() createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
return this.userService.create(createUserDto);
}
@Get()
// @Version('1')
findAll() {
return this.userService.findAll();
}
@Get(':id')
findOne(@Param('id') id: string) {
return this.userService.findOne(+id);
}
@Patch(':id')
update(@Param('id') id: string, @Body() updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto) {
return this.userService.update(+id, updateUserDto);
}
Nestjs 控制器
在编程中,控制器是一种设计模式,通常在实现模型-视图-控制器(MVC)架构时使用
在Nestjs框架中,控制器只要负责接受特定路由的请求。根据请求就行处理,然后返回响应,主要表现时@Controller修饰的类
控制器中常见的参数装饰器
| 装饰器 | 能力 |
|---|---|
| @Request() | req |
| @Response() | res |
| @Next | next |
| @Session | req.session |
| @Param(key?:string) | req.params/req.params[key] |
| @Body(key?:string) | req.body / req.body[key] |
| @Query(key?:string) | req.query / req,query[key] |
| @Headers(name?:string) | req.headers / req.headers[name] |
| HttpCode | 控制接口返回的状态码 |
js
import { Controller, Get, Post, Body, Patch, Param, Delete, Query } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { CreateUserDto } from './dto/create-user.dto';
import { UpdateUserDto } from './dto/update-user.dto';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
constructor(private readonly userService: UserService) {}
@Post('/add/tags')
addTags (@Body() params:{tags:string[],userId:number}) {
return this.userService.addTags(params)
}
@Post()
create(@Body() createUserDto: CreateUserDto) {
return this.userService.create(createUserDto);
}
@Get()
findAll(@Query() query:{keyWord:string,page:number,pageSize:number}) {
return this.userService.findAll(query);
}
@Patch(':id')
update(@Param('id') id: string, @Body() updateUserDto: UpdateUserDto) {
return this.userService.update(+id, updateUserDto);
}
@Delete(':id')
remove(@Param('id') id: string) {
return this.userService.remove(+id);
}
}Session 实例
session 是服务器 为每个用户的浏览器创建的一个会话对象 这个session 会记录到 浏览器的 cookie 用来区分用户,使用的是nestjs 默认框架express 他也支持express 的插件所以我们就可以安装express的session
npm i express-session --save
需要智能提示可以装一个声明依赖
npm i @types/express-session -D
然后在main.ts 引入 通过app.use 注册session
js
import * as session from 'express-session'
app.use(session())参数配置详解
| secret | 生成服务端session签名 可以理解为加密 |
|---|---|
| name | 生成客户端cookie的名字 默认connect.sld |
| cookie | 设置返回到前端key的属性,默认值为{path:"/",httpOnly:true,secure:false.maxAge:null} |
| rolling | 在每次请求时强行设置cookie,这将重置cookie过期时间 |
ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { VersioningType } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import * as session from 'express-session'
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.enableVersioning({
type: VersioningType.URI
})
app.use(session({ secret: "koillin", name: "xm.session", rolling: true, cookie: { maxAge: null } }))
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();Nestjs 提供者
Provider 只是一个用
@Injectable()装饰器注释的类
service.ts
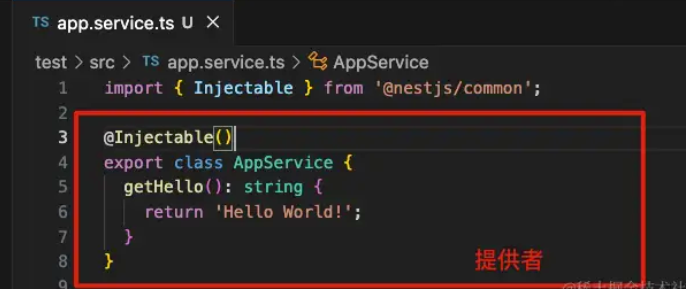
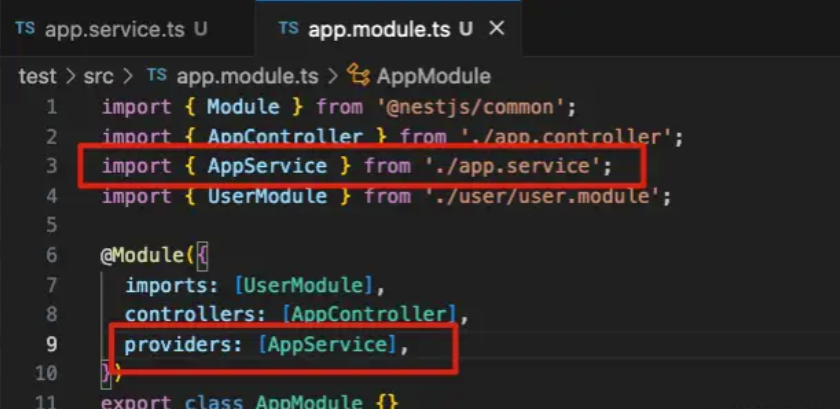
⭐️基本用法:在模块 .module.ts 文件中引入 service,在 providers 注入
⭐️在 .controller.ts 文件就可以使用注入好的 service
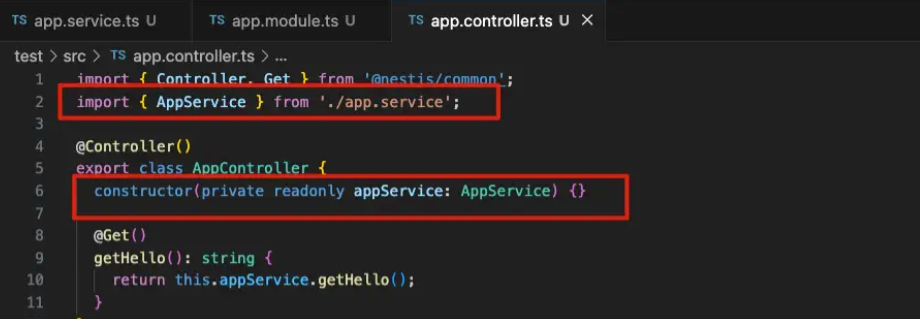
第二种写法
⭐️ 在.modules.ts写法
ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { UserController } from './user.controller';
@Module({
controllers: [UserController],
providers: [{
provide: "Koillin", // 自定义名称
useClass: UserService
}]
})
export class UserModule { }⭐️ 在 .controller.ts 文件就可以使用注入 自定义名称后,需要用对应的 Inject 取用,不然找不到
ts
import { Controller, Inject } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
constructor(@Inject('Koillin') private readonly userService: UserService) {}
}自定义注入值
⭐️ 在.modules.ts写法
ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { UserController } from './user.controller';
@Module({
controllers: [UserController],
providers: [{
provide: "Xiaoman",
useClass: UserService
}, {
provide: "JD",
useValue: ['TB', 'PDD', 'JD']
}]
})
export class UserModule { }⭐️ 在 .controller.ts 文件就可以使用注入 自定义值
ts
import { Controller, Inject } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
constructor(
@Inject('Xiaoman') private readonly userService: UserService,
@Inject('JD') private shopList: string[]
) {}
}工厂模式
如果服务之间有相互的依赖或者逻辑处理,可以使用 useFactory
⭐️ 在.modules.ts
ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { UserService2 } from './user.service2';
import { UserService3 } from './user.service3';
import { UserController } from './user.controller';
@Module({
constrollers:[UserController],
providers:[{
provide:"Koillin",
useClass:UserService
},{
provide:"JD",
useValue: ['TB', 'PDD', 'JD']
}, UserService2,{
provide:"Test",
inject:[UserService2],
useFactory(UserService2:UserService2) {
return new UserService3(UserService2)
}
}
]
})⭐️ 在 .controller.ts 文件
ts
import { Controller, Inject } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
@Controller('user')
export class UserController {
constructor(
@Inject('Xiaoman') private readonly userService: UserService,
@Inject('JD') private shopList: string[],
@Inject('Test') private readonly Test: any,
) {}
}异步模式
ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { UserService2 } from './user.service2';
import { UserService3 } from './user.service3';
import { UserController } from './user.controller';
@Module({
controllers: [UserController],
providers: [{
provide: "Xiaoman",
useClass: UserService
}, {
provide: "JD",
useValue: ['TB', 'PDD', 'JD']
},
UserService2,
{
provide: "Test",
inject: [UserService2],
useFactory(UserService2: UserService2) {
return new UserService3(UserService2)
}
},
{
provide: "sync",
async useFactory() {
return await new Promise((r) => {
setTimeout(() => {
r('sync')
}, 3000)
})
}
}
]
})
export class UserModule { }Nestjs 模块
当使用 nest g res user创建一个新的CURD模块时,nestjs 会自动帮我们引入.module.ts模块
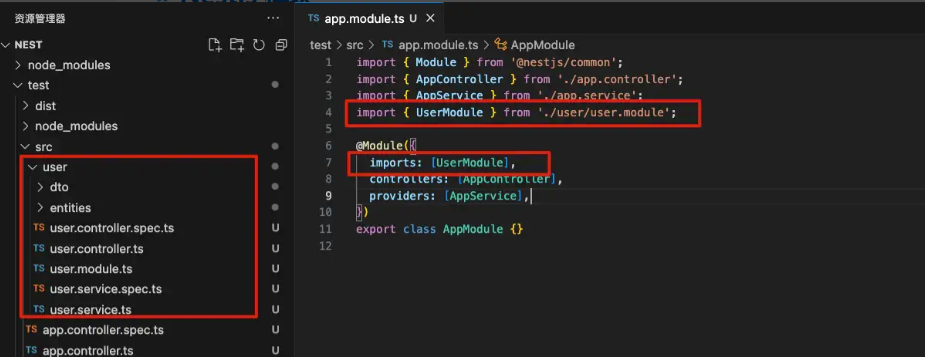
共享模块
例如 user 的 Service 想暴露给其他模块使用就可以使用 exports 导出该服务
ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { UserController } from './user.controller';
@Module({
controllers: [UserController],
providers: [UserService],
exports: [UserService],
})
export class UserModule {}由于其他.moudles.ts 已经引入过该模块,就可以直接使用了
ts
import { Controller, Get } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { UserService } from './user/user.service';
@Controller()
export class AppController {
constructor(
private readonly appService: AppService,
private readonly userService: UserService,
) {}
@Get()
getHello(): string {
return this.userService.findAll(); // 自动生成的模块里有这个方法
}
}全局模块
给 user 模块添加 @Global() 他便注册为全局模块
ts
import { Global, Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { UserController } from './user.controller';
@Global()
@Module({
controllers: [UserController],
providers: [UserService],
})
export class UserModule {}动态模块
为了给模块传递参数 可以给该模块添加一个静态方法用来接受参数
创建一个 config.module.ts
ts
import { Module, DynamicModule, Global } from '@nestjs/common'
interface Options {
path: string
}
@Global()
@Module({
})
export class ConfigModule {
static forRoot(options: Options): DynamicModule {
return {
module: ConfigModule,
providers: [
{
provide: "Config",
useValue: { baseApi: "/api" + options.path }
}
],
exports: [
{
provide: "Config",
useValue: { baseApi: "/api" + options.path }
}
]
}
}
} 在 app.module.ts 文件引入
ts
import { Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { AppController } from './app.controller';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
import { UserModule } from './user/user.module';
import { ListModule } from './list/list.module';
import { ConfigModule } from './config/config.module';
@Module({
imports: [UserModule, ListModule, ConfigModule.forRoot({
path: '/koillin'
})],
controllers: [AppController],
providers: [AppService],
})
export class AppModule {}中间件
中间件是在路由处理程序之前调用的函数,中间件函数可以访问请求和响应对象
中间件函数可以执行以下任务:
- 执行任何代码。
- 对请求和响应对象进行更改。
- 结束请求-响应周期。
- 调用堆栈中的下一个中间件函数。
- 如果当前的中间件函数没有结束请求-响应周期, 它必须调用
next()将控制传递给下一个中间件函数。否则, 请求将被挂起。
第三方中间件
cors 处理跨域
npm install cors
npm install @types/cors -D
main.ts
ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
import * as cors from 'cors'
const whiteList = ['/list']
function middleWareAll (req,res,next) {
console.log(req.originalUrl,'我收全局的')
if(whiteList.includes(req.originalUrl)){
next()
}else{
res.send({code:200})
}
}
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.use(cors())
app.use(middleWareAll)
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap(); 创建一个依赖注入中间件
middleware
ts
import {Injectable,NestMiddleware} from '@nestjs/common'
@Injectable()
export class Logger implements NestMiddleware {
use(req: any, res: any, next: () => void) {
// 打印请求信息
console.log('request...')
// 执行下一个中间件或路由处理函数
next()
}
} 其他模块.module.ts导入
ts
import { MiddlewareConsumer, Module, RequestMethod } from '@nestjs/common';
import { UserService } from './user.service';
import { UserController } from './user.controller';
import { Logger } from 'src/mddleware';
import { User } from './entities/user.entity';
import { TypeOrmModule } from '@nestjs/typeorm';
import { Tags } from './entities/tags.entity';
@Module({
imports:[TypeOrmModule.forFeature([User,Tags])],
controllers: [UserController],
providers: [UserService],
exports:[UserService]
})
export class UserModule {
/**
* 配置中间件
*
* @param consumer 中间件消费者
*/
configure(consumer:MiddlewareConsumer){
// 为 'user' 路由应用 Logger 中间件
consumer.apply(Logger).forRoutes('user')
//也可以指定拦截的方法,比如拦截GET POST 等 forRoutes 使用对象配置
// 为满足 {path: 'user', method: RequestMethod.GET} 条件的路由应用 Logger 中间件
consumer.apply(Logger).forRoutes({path: 'user',method:RequestMethod.GET})
// 为 UserController 控制器对应的路由应用 Logger 中间件
consumer.apply(Logger).forRoutes(UserController)
}
}全局中间件
全局中间件只能使用函数模式,案例可以做白名单拦截之类的
ts
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
const whiteList = ['/list']
function middleWareAll (req,res,next) {
console.log(req.originalUrl,'我收全局的')
if(whiteList.includes(req.originalUrl)){
next()
}else{
res.send('小黑子露出鸡脚')
}
}
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
app.use(middleWareAll)
await app.listen(3000);
}
bootstrap();