1.消息总线在微服务中的应用
BUS- 消息总线-将消息变更发送给所有的服务节点。
在微服务架构的系统中,通常我们会使用消息代理来构建一个Topic,让所有
服务节点监听这个主题,当生产者向topic中发送变更时,这个主题产生的消息会被
所有实例消费,这就是消息总线的工作模式。也是我们熟悉的发布-订阅模型。
其实广义的消息总线不单指这种"发布-订阅"模型!也可以代指分布式服务间进行通信,
消息分发的单播模式,甚至有的公司既不使用HTTP也不用RPC来构建微服务。完全靠消息
总线来做服务调用。比如,银行老系统采用总线型架构,在不同服务结点之间做消息分发
SpringCloud中的Bus职责范围就相对小了很多,因为还有一个Stream组件代理了大部分的消息中间件通信服务,因此BUS在实际应用中大多是为了应对"消息广播"的场景。比如和config异同搭配使用推送配置信息。
总线式架构的完整流程 :
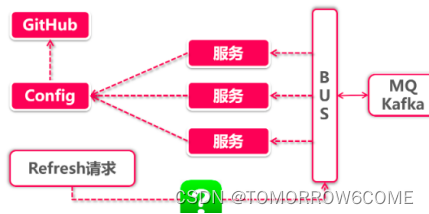
我们要关注一下白底红框那三个和BUS有关系的步骤 :
MQ/KAFKA :BUS是一个调用封装,它的背后还是需要依赖消息中间件来完成底层的消息
分发,实际项目中最常用的两个中间件分别是RabbitMQ和kafka。
BUS :作为对接上游应用和下游中间件系统的中间层,当接到刷新请求的时候,通知底层中间件向所有服务结点推送消息。
Refresh :类比config-center中可以通过actuator的Refresh请求刷新配置,那么对于总线式架构的ReFresh请求来说,有两个需要解决的问题:
谁来发起变更,服务结点还是由ConfigServer发起变更请求?
何时发起变更-时手工发起变更?还是每次Github改动完成后自动推送?
2.BUS简介
BUS实现:
加入我们所有的节点都订阅了topic(消息组件这个属性刷新这个topic)当你的属性发生变动的时候,只要发送一个广播消息,所有的节点都会消费消息,并且触发刷新动作。
BUS的标签:
BUS只是对消息进行了简单的封装,底层是依赖Stream(专业用来与消息中间件进行通信的组件)来广播消息。
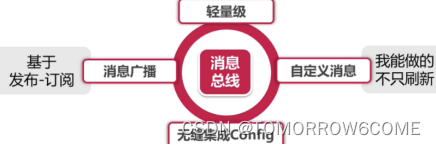
BUS的两个场景:
配置变更通知;自定义消息广播;
3.BUS体系结构解析
BUS的三个角色:
消息的发布者,是一个中间件;
事件监听者,监听事件动态,各个监听消息的服务节点;
事件主体,配置变更就是事件
事件的架构:
在BUS配置刷新的事件类是RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent。在 BUS的规范下,所有事件都包含三个维度的信息:
**source:**这是一个必填信息,它可以是一个自定义并且能够被序列化反序列化的pojo对象,它包含了一个事件想要传达的信息;
Original Service 消息来源方,通常是事件发布方的机器ID,或者AppId等;
Destination Service 目标机器,Bus会根据Destination Service指定的过滤条件(比如服务名,端口等),只让指定的监听者响应事件;
消息发布者
我们所有的"事件"都是通过Bus来发布的,Bus默认提供了两个Endpoint作为消息发布者:
bus-env :在本地发布EnvironmentChangeRemoteApplicationEvent事件,表示一个远程环境变更事件。进一步查看这个事件的内容,我们发现其中包含了一个Map<String, String>属性,事件监听者接收到这个事件之后,会将事件中的Map添加到Spring环境变量中(由Spring Cloud的EnvironmentManager负责具体处理),从而达到修改环境变量的目的
bus-refresh :发布RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent事件,表示一个远程配置刷新事件,这个事件会触发@RefreshScope注解所修饰的Java类中属性的刷新(@RefreshScope修饰的类可以在运行期更改属性)
以上两个ENDpoint就是BUS通过、actuator服务对外提供出来的
消息监听者:
BUS中默认创建了两个消息监听器,分别对应上面两个消息发布的Endpoints。

在spring-cloud-context这个依赖中定义了大量的事件。
4.Bus的接入方式RabbitMQ & Kafka
Spring的组件一向是以一种插件式的方式提供功能,将组件自身和我们项目中的业务代码隔离,使得我们更换组件的成本可以降到最低。Spring Cloud Bus也不例外,它的底层消息组件非常容易替换,替换过程不需要对业务代码引入任何变更。Bus就像一道隔离了底层消息组件和业务应用的中间层,比如我们从RabbitMQ切换为Kafka的时候,只需要做两件事就好了:
在项目pom中替换依赖组件;
更改配置文件里的连接信息。
RabbitMQ和Kafka两种消息组件如何接入Bus :
接入RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是实现了AMQP(Advanced Message Queue Protocal)的开源消息代理软件,也是平时项目中应用最广泛的消息分发组件之一。
接入RabbitMQ的方式很简单,我们只要在项目中引入以下依赖:
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp
点进去发现,它还依赖于spring-cloud-starter-stream-rabbit。
也就是说stream组件是被真正用来发送广播消息到RabbitMQ,
BUS只是帮我们封装了整个消息的发布和监听动作!
项目所需要的具体的配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
接入Kafka;
要使用kafka来实现消息代理,只需要把上一步中引入spring-cloud-starter-bus-amqp
依赖替换成spring-cloud-starter-bus-kafka依赖
org.springframework.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-bus-kafka
如果大家的Kafka和ZooKeeper都运行在本地,并且采用了默认配置,那么不需要做任何额外的配置,就可以直接使用。但是在生产环境中往往Kafka和ZooKeeper会部署在不同的环境,所以就需要做一些额外配置:
spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.brokers Kafka服务节点(默认localhost)
spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.defaultBrokerPort Kafka端口(默认9092)
spring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.zkNodes ZooKeeper服务节点(默认localhost)
zspring.cloud.stream.kafka.binder.defaultZkPort ZooKeeper端口(默认2181)
5.部分关键源码:
内置事件的架构RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent
刷新事件的发送端-RefreshBusEndpoint
开端:RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent
java
public class RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent extends RemoteApplicationEvent {
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent() {
// for serializers
}
public RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent(Object source, String originService,
String destinationService) {
super(source, originService, destinationService);
}查看find usage:有两个大类:RefreshBusEndpoint以及RefreshListener类。
一个是起点RefreshBusEndpoint,一个是终点RefreshListener。
关注起点:RefreshBusEndpoint
java
@Endpoint(id = "bus-refresh") // TODO: document new id
public class RefreshBusEndpoint extends AbstractBusEndpoint {
public RefreshBusEndpoint(ApplicationEventPublisher context, String id) {
super(context, id);
}
@WriteOperation
public void busRefreshWithDestination(@Selector String destination) { // TODO:
// document
// destination
publish(new RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent(this, getInstanceId(), destination));
}
@WriteOperation
public void busRefresh() {
publish(new RefreshRemoteApplicationEvent(this, getInstanceId(), null));
}
}关注到主类的super方法,就是到了RemoteApplicationEvent类
java
protected RemoteApplicationEvent(Object source, String originService,
String destinationService) {
super(source);
this.originService = originService;
if (destinationService == null) {
destinationService = "**";
}
// If the destinationService is not already a wildcard, match everything that
// follows
// if there at most two path elements, and last element is not a global wildcard
// already
if (!"**".equals(destinationService)) {
if (StringUtils.countOccurrencesOf(destinationService, ":") <= 1
&& !StringUtils.endsWithIgnoreCase(destinationService, ":**")) {
// All instances of the destination unless specifically requested
destinationService = destinationService + ":**";
}
}
this.destinationService = destinationService;
this.id = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}本人进行测试的接口是:
测试的接口是:localhost:60002/actuator/bus-refresh
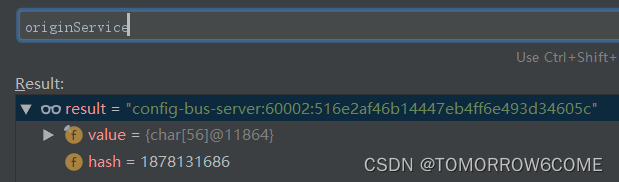
研究了发现对于RemoteApplicationEvent就是确定destination!
在RefreshBusEndpoint中,将contex存放在ApplicationEventPublisher里。
这就是ApplicationEventPublisher,用来发布上下文消息的!
接下来到了AbstractApplicationContext中
java
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");
// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary
ApplicationEvent applicationEvent;
if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {
applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;
}
else {
applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);
if (eventType == null) {
eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();
}
}
// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized
if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {
this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);
}
else {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
// Publish event via parent context as well...
if (this.parent != null) {
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}
}整个过程是事件驱动,编程解耦!
6.如何实现自动推送?Git WebHook
问题:由谁来发起状态的变更请求?
如何通过GitHub的Webhook机制实现自动推送!
Webhook?Git的一种机制,可以用于自动化的构建。
当每次提交代码到Git以后,会触发Webhook执行一段程序,来完成预定义的操作。比如说让钩子通知CI/CD系统从Github拉取最新代码开始执行构建过程或者执行其他操作!
Webhook三步走:
设置encrypt.key;
将上一步中的key添加到Github仓库设置中;
设置Webhook url;
设置encrypt.key,类似属性加解密方式,只需要在application.yml中设置一个key就好!
encrypt:
key: yourKey
自动推送需要注意的问题
无法测试:改动只要一提交就被推送到所有机器,假如不小心修改错了属性,那所有服务器就要团灭了
定点推送:尽管Bus支持在URL中添加目标范围,定向推送到指定机器,但毕竟URL在Webhook里面是写死的,不方便我们根据实际情况做定点推送