目录
2.使用StatefulWidget和InheritedWidget局部刷新UI
3.ValueNotifier和ValueListenableBuilder

前言
在 Flutter 中,状态管理指的是如何管理和更新应用中的数据状态,并且根据状态的变化来更新 UI。有效的状态管理能够帮助开发者创建更高效、更可维护的应用。
setState是 Flutter 中最基本的状态管理方法,当状态发生变更的时候,会通知框架重新构建UI。当然我们知道当我们调用setState方法的时候,页面会重绘,当页面布局比较复杂的时候,有时候我们仅仅需要更新某个单独的UI,这个时候如果使用setState方法,则会有比较大的性能消耗去重绘当前页面UI.
那么Flutter中有哪些方法可以局部刷新UI呢,这篇博客列举了Flutter实现局部刷新的几种方式。
1.局部刷新的重要性
1.概念
局部刷新指的是只刷新界面的一部分,而不是整个页面。这样可以提高性能和用户体验。
2.重要性
- 避免不必要的重绘,提高性能
- 提供更流畅的用户体验
- 减少资源消耗
2.局部刷新实现的几种方式
1.通过setState局部刷新
setState是Flutter 中最常用的状态管理方法,用于通知框架状态发生变化,导致界面重建。
我们创建Flutter工程的时候,系统默认生成的计时器的例子,就是setState局部刷新的例子。
Dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class StatePartialRefreshPage extends StatefulWidget {
const StatePartialRefreshPage({super.key});
@override
State<StatePartialRefreshPage> createState() =>
_StatePartialRefreshPageState();
}
class _StatePartialRefreshPageState extends State<StatePartialRefreshPage> {
int _count = 0;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text(
"setState局部刷新",
style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold, fontSize: 14),
),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
Text(
'您点击了$_count次',
style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 12, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
const SizedBox(
height: 20,
),
FilledButton(
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
_count++;
});
},
child: const Icon(Icons.add)),
],
)),
);
}
}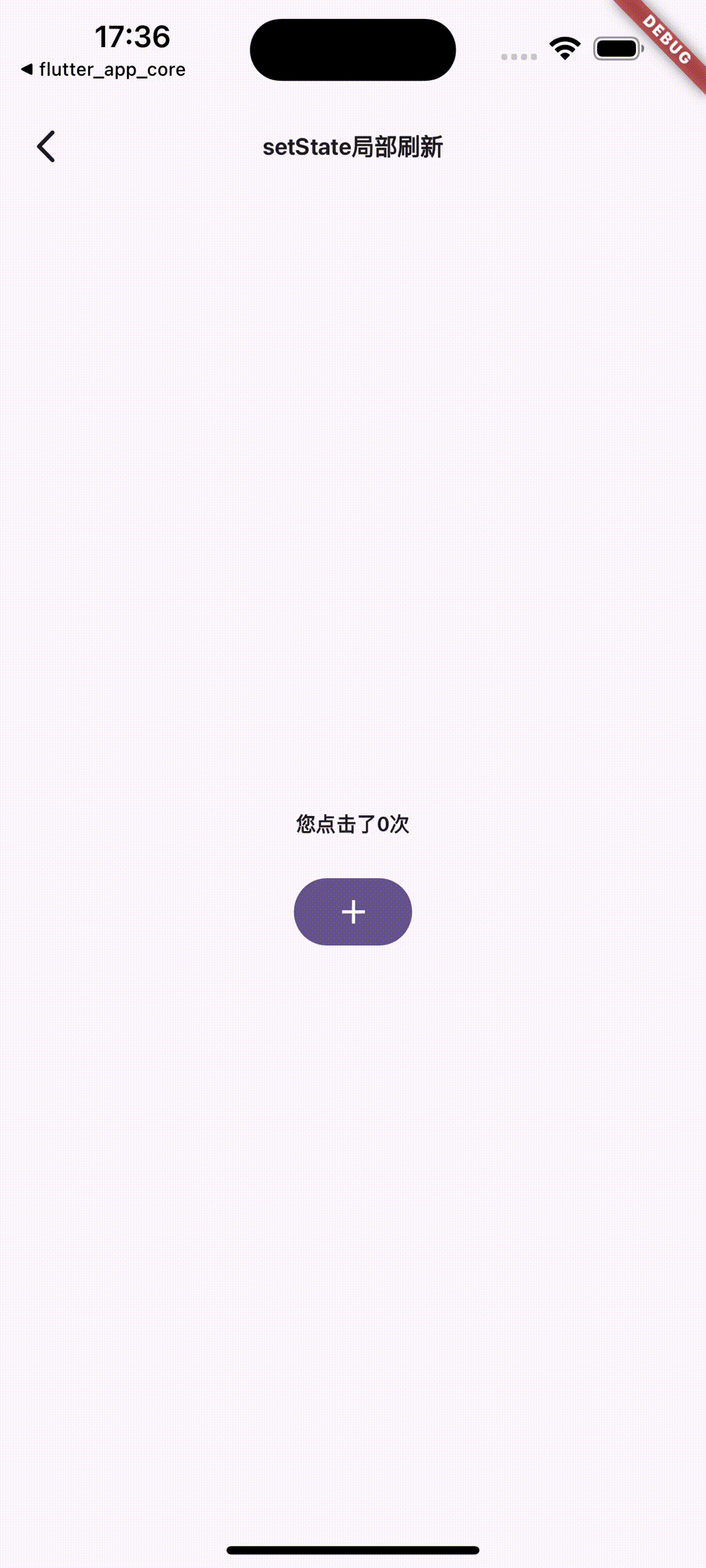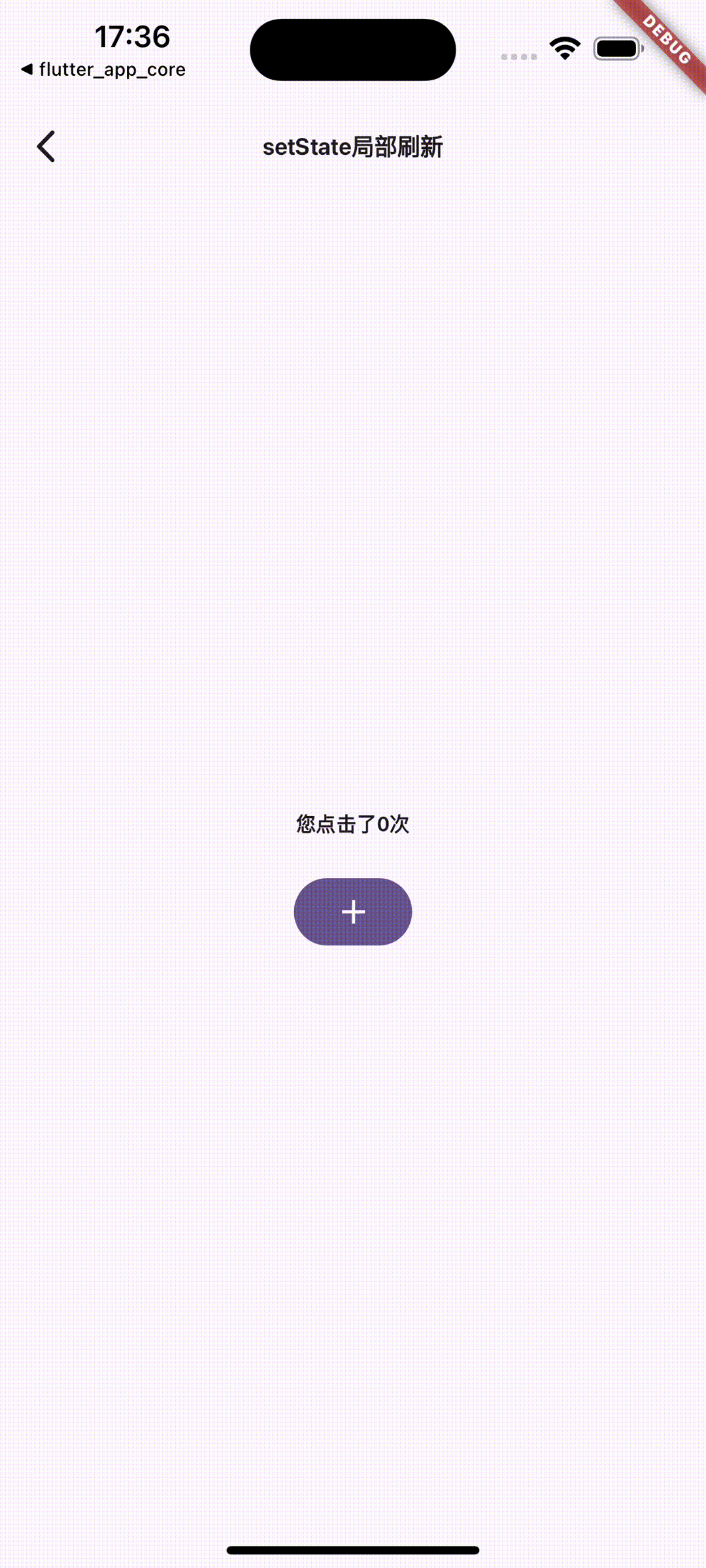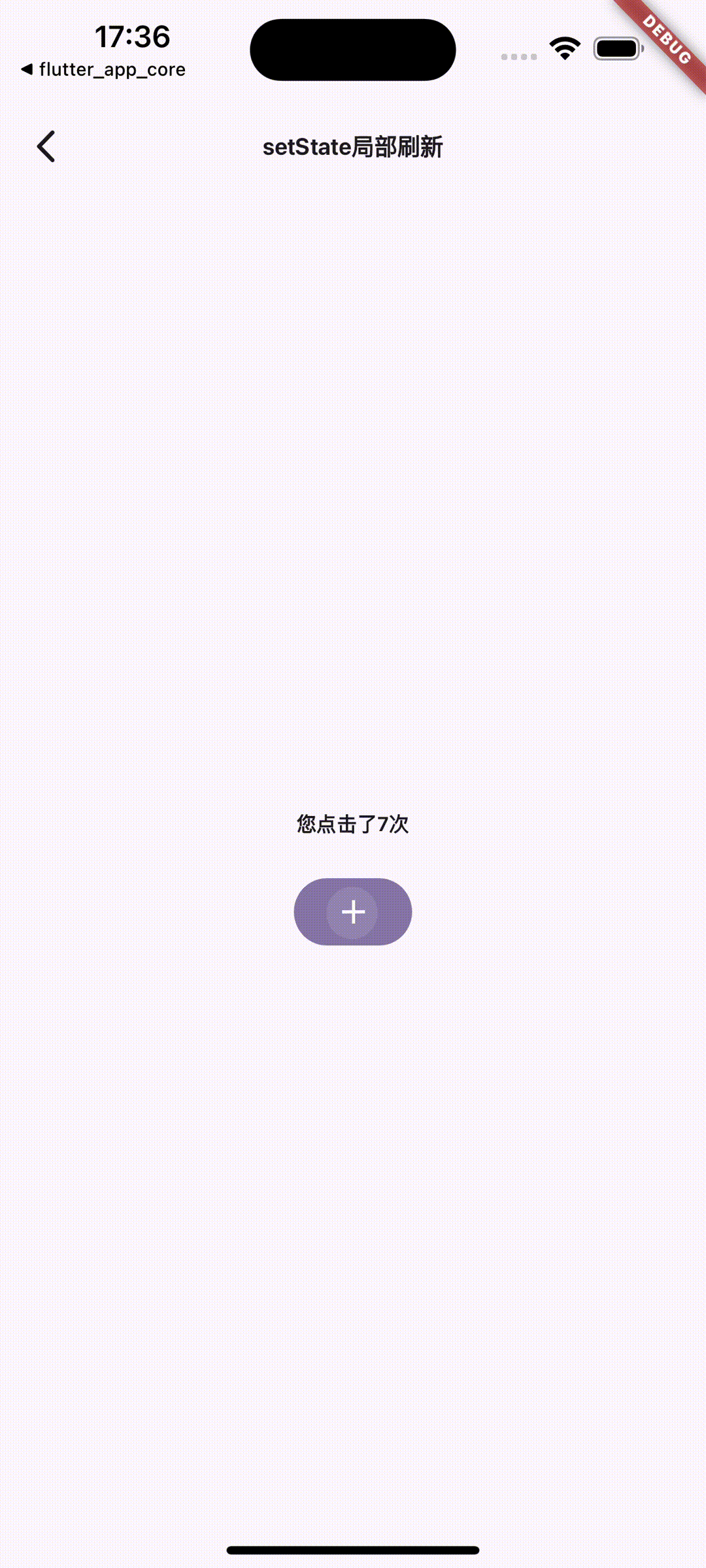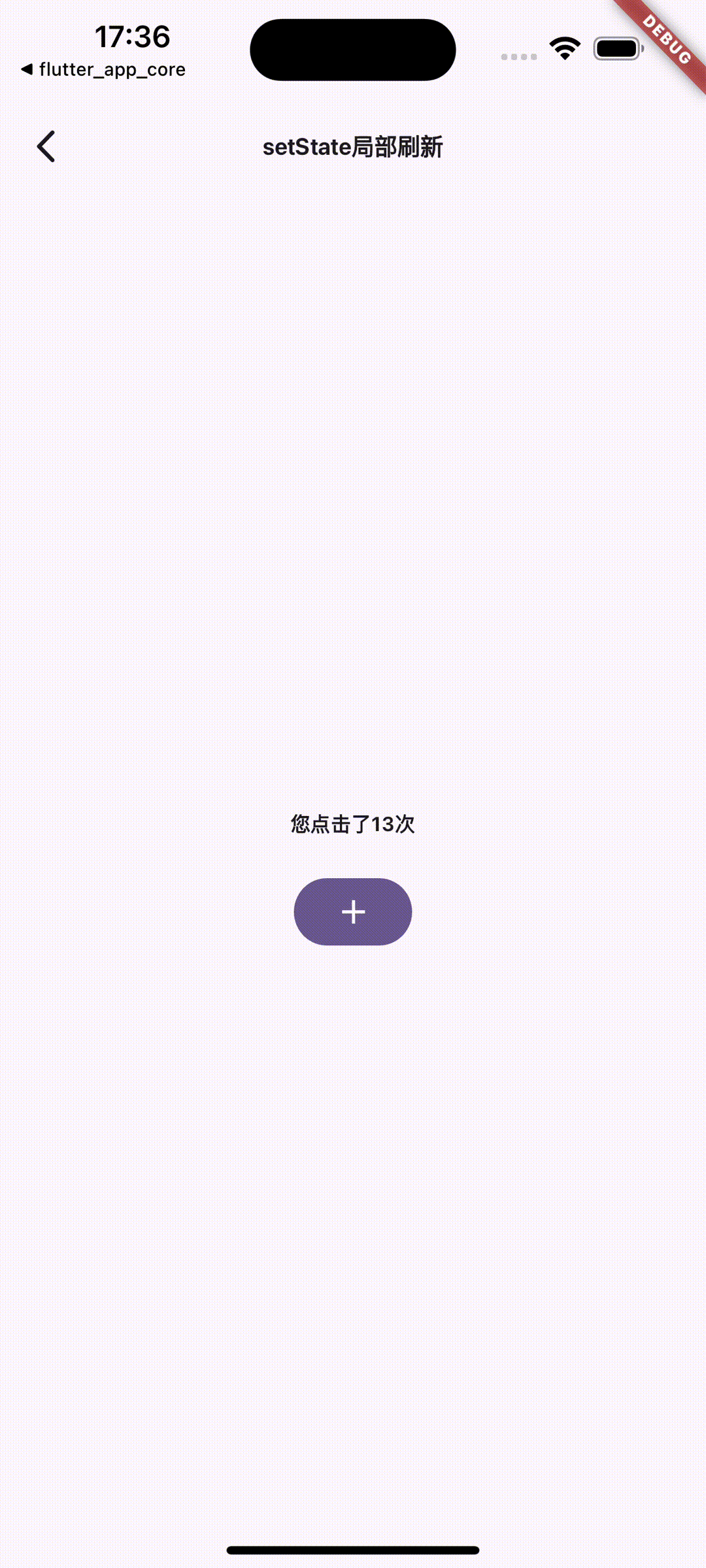
图1.setState局部刷新
当页面比较简单的时候,可以直接使用setState方法局部刷新UI。
使用场景:简单的状态变化,如按钮点击计数、开关状态等。
注意事项:
- 频繁调用 setState 可能导致性能问题
- 避免在 build 方法中调用 setState
2.使用StatefulWidget和InheritedWidget局部刷新UI
StatefulWidget 是具有状态的组件,InheritedWidget 用于在组件树中共享数据。
当我们需要共享数据的时候,可以考虑StatefulWidget和InheritedWidget局部刷新UI.
完整代码如下:
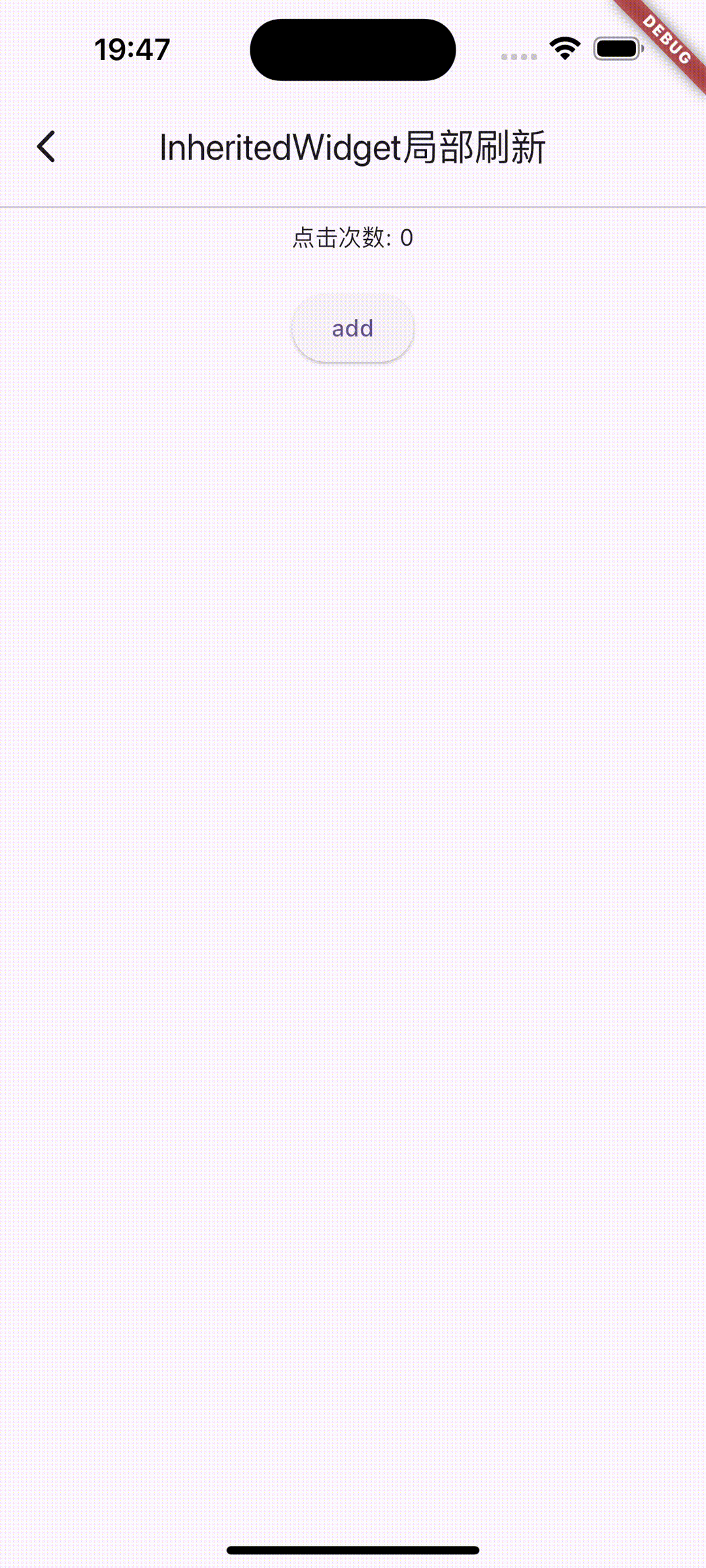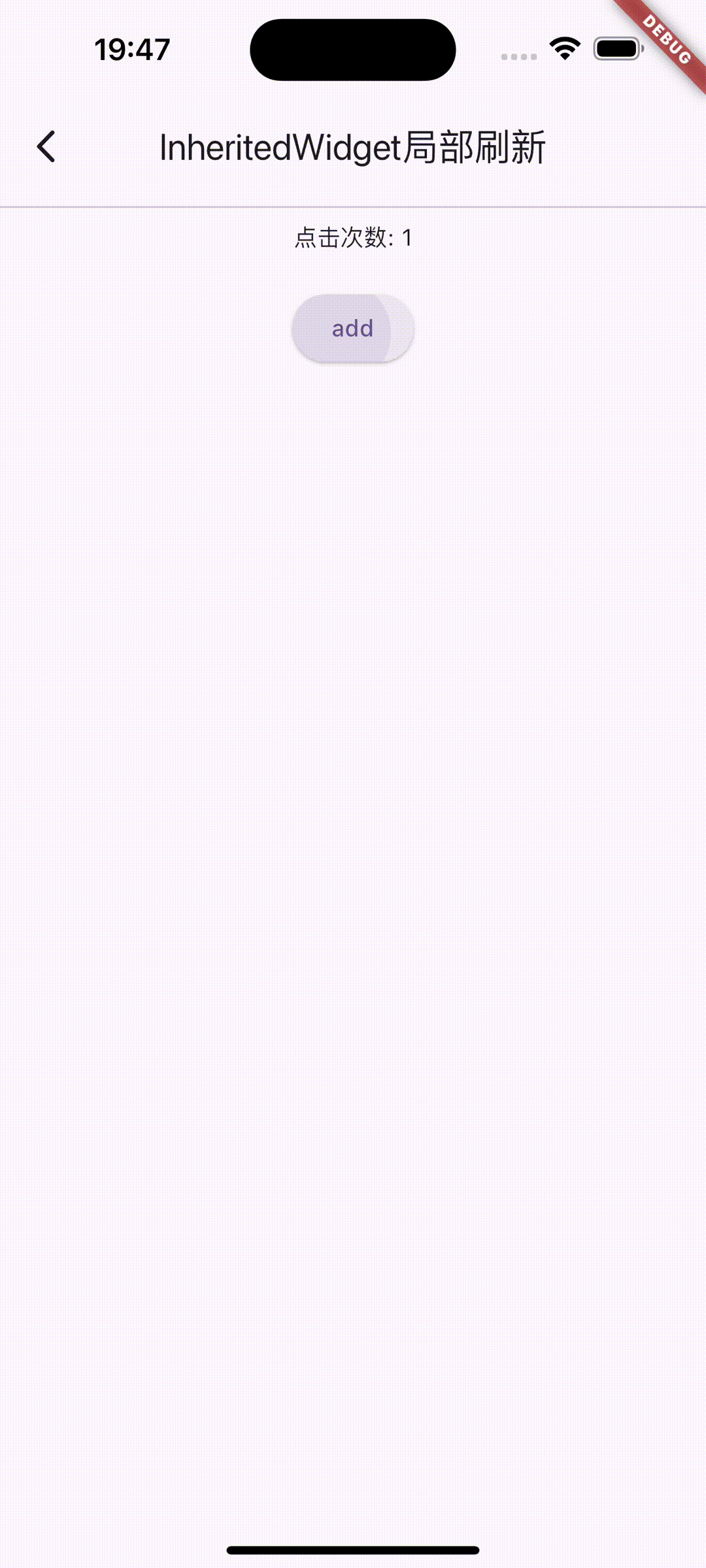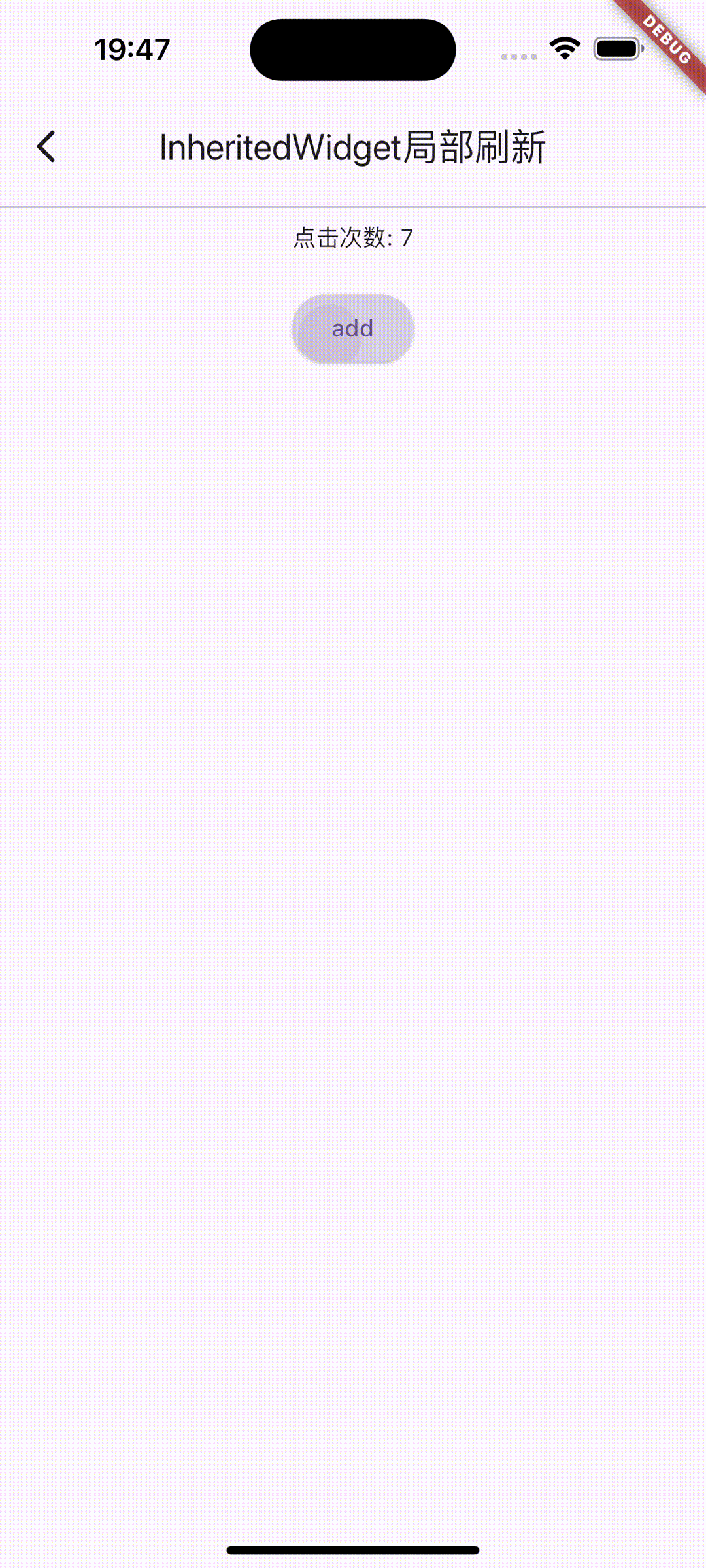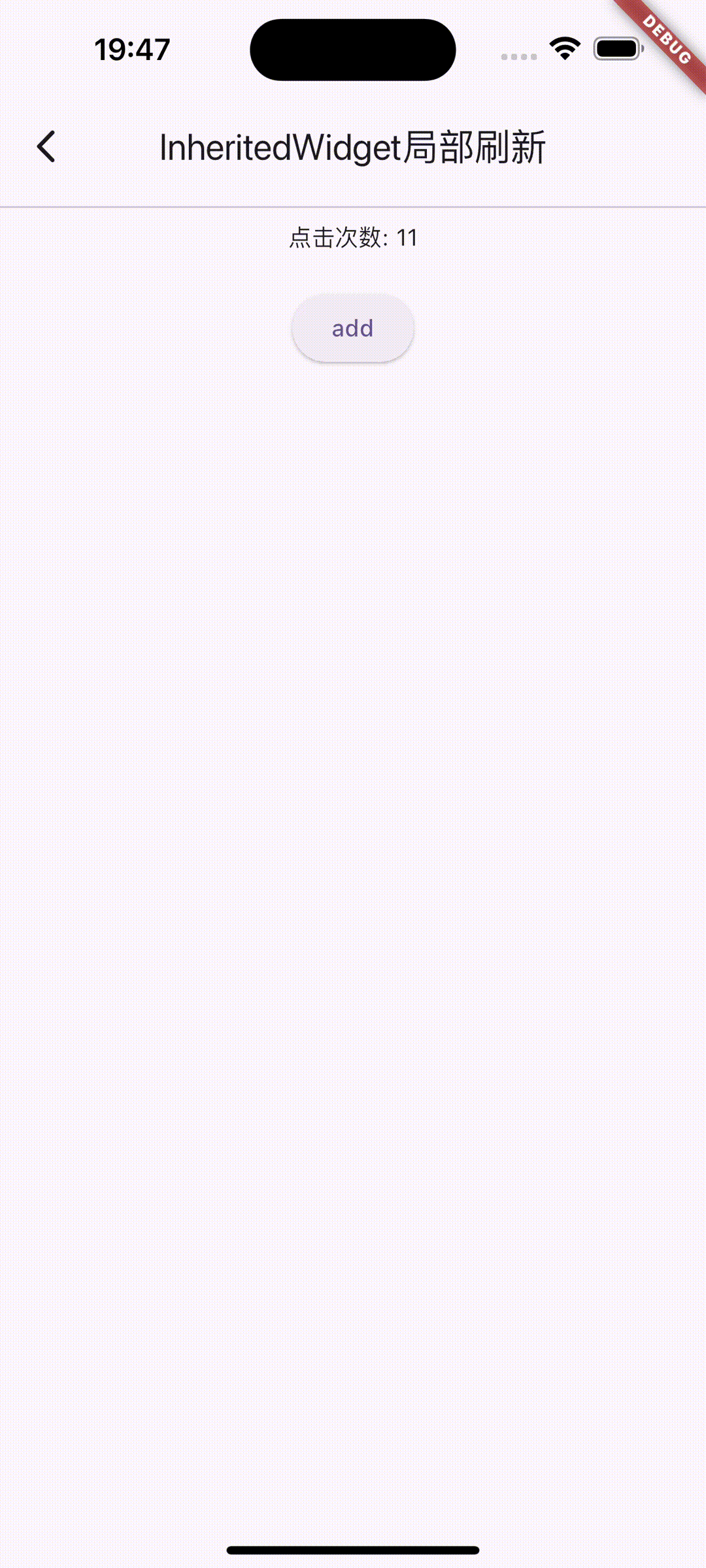
图2.共享数据的方式刷新UI
Dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class MyInheritedWidget extends InheritedWidget {
final int counter;
const MyInheritedWidget({
super.key,
required this.counter,
required super.child,
});
@override
bool updateShouldNotify(covariant InheritedWidget oldWidget) {
return true;
}
static MyInheritedWidget? of(BuildContext context) {
return context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<MyInheritedWidget>();
}
}
class InheritedWidgetPage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
const InheritedWidgetPage({super.key, required this.title});
@override
State<InheritedWidgetPage> createState() => _InheritedWidgetPageState();
}
class _InheritedWidgetPageState extends State<InheritedWidgetPage> {
int counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MyInheritedWidget(
counter: counter,
child: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(child: Column(
children: [
const Divider(),
const CounterDisplay(),
const SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
child: const Text('add'),
),
],
),),
),
);
}
}
class CounterDisplay extends StatelessWidget {
const CounterDisplay({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final inheritedWidget = MyInheritedWidget.of(context);
return Text('点击次数: ${inheritedWidget?.counter}');
}
}这种方式主要使用场景如下:组件树中共享状态时,如主题、语言设置等。
优点就是数据共享方便,代码简介
缺点就是使用复杂,性能可能收到影响
3.ValueNotifier和ValueListenableBuilder
ValueNotifier 是一个简单的状态管理工具,ValueListenableBuilder 用于监听 ValueNotifier 的变化。
使用方法也非常简单:
1.实例化ValueNotifier
2.要监听的Widget对象是用ValueListenableBuilder包裹起来
3.事件触发数据的变更方法
这种方式和前几种方式比较非常的简单易容,性能也很高
缺点:只能处理简单的状态变化
完整的代码如下:
Dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class ValueNotifierPage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
const ValueNotifierPage({super.key, required this.title});
@override
State<ValueNotifierPage> createState() => _ValueNotifierPageState();
}
class _ValueNotifierPageState extends State<ValueNotifierPage> {
final ValueNotifier<int> _counter = ValueNotifier<int>(0);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: ValueListenableBuilder<int>(
valueListenable: _counter,
builder: (context, value, child) {
return Text(
'您点击了$value次',
style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 12, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
);
},
)
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
onPressed: () {
_counter.value ++;
},
)
);
}
}4.StreamBuilder
Stream是一种用于传递异步事件的对象,可以通过StreamController发送事件。在需要刷新UI的地方,可以发送一个事件到Stream,然后使用StreamBuilder监听该Stream,当收到新的事件时,StreamBuilder会自动重新构建UI。这种方式适用于需要监听多个异步事件的情况。
当我们需要处理异步数据流,如网络请求、实时数据等的时候,可以考虑使用StreamBuilder。例如在下面的例子中,我们写了一个模拟网络请求的异步方法,当网络请求没返回正确结果的时候,我们可以加载进度条。
这种方式的优点就是可以对异步请求进行更加精准的控制,例如网络请求的状态等。却迪奥就是复杂度比较高,可能需要更多的代码。
完整的代码如下:
Dart
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class StreamBuilderRefreshUIPage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
const StreamBuilderRefreshUIPage({super.key, required this.title});
@override
State<StreamBuilderRefreshUIPage> createState() =>
_StreamBuilderRefreshUIPageState();
}
class _StreamBuilderRefreshUIPageState extends State<StreamBuilderRefreshUIPage> {
late Future<String> _data;
Future<String> fetchData() async {
// 模拟网络请求延迟
await Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 2));
// 返回模拟数据
return 'Hello, Flutter!';
}
@override
void initState() {
// TODO: implement initState
super.initState();
_data = fetchData();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: FutureBuilder<String>(
future: _data,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.connectionState == ConnectionState.waiting) {
return const CircularProgressIndicator();
} else if (snapshot.hasError) {
return Text('Error: ${snapshot.error}');
} else {
return Text('Data: ${snapshot.data}');
}
},
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: fetchData,
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}5.Provider
Provider 是 Flutter 推荐的状态管理解决方案,Consumer 用于读取和监听状态。
我们还以定时器为例。
1.首先我们导入Provider.
provider: ^6.1.2
2.自定义ChangeNotifier类。
ChangeNotifier 是 Flutter SDK 中的一个简单的类。它用于向监听器发送通知。换言之,如果被定义为 ChangeNotifier,你可以订阅它的状态变化。(这和大家所熟悉的观察者模式相类似)。
在我们要实现的代码中,有两个变量_counter1和_counter2.代码定义如下:
Dart
class CounterModel extends ChangeNotifier {
int _counter1 = 0;
int _counter2 = 0;
void addCounter1(){
debugPrint('counter:$_counter1');
_counter1 += 1;
notifyListeners();
}
void addCounter2(){
debugPrint('counter:$_counter2');
_counter2 += 1;
notifyListeners();
}
}3.使用Customer把我们要刷新的Widget包裹起来
Dart
Consumer<CounterModel>(
builder: (context, counterModel, child) {
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
Text('计数器1个数: ${counterModel._counter1}'),
ElevatedButton(onPressed: (){
counterModel.addCounter1();
}, child: const Icon(Icons.add),),
],
);
},
),4.完整代码如下:
Dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:provider/provider.dart';
class ProviderRefreshPage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
const ProviderRefreshPage({super.key, required this.title});
@override
State<ProviderRefreshPage> createState() => _ProviderRefreshPageState();
}
class CounterModel extends ChangeNotifier {
int _counter1 = 0;
int _counter2 = 0;
void addCounter1(){
debugPrint('counter:$_counter1');
_counter1 += 1;
notifyListeners();
}
void addCounter2(){
debugPrint('counter:$_counter2');
_counter2 += 1;
notifyListeners();
}
}
class _ProviderRefreshPageState extends State<ProviderRefreshPage> {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
const SizedBox(height: 10,), // 添加一些间距
const Divider(),
const Text('计数器实例',style: TextStyle(fontSize: 12,fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),),
Consumer<CounterModel>(
builder: (context, counterModel, child) {
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
Text('计数器1个数: ${counterModel._counter1}'),
ElevatedButton(onPressed: (){
counterModel.addCounter1();
}, child: const Icon(Icons.add),),
],
);
},
),
Consumer<CounterModel>(
builder: (context, counterModel, child) {
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
Text('计数器1个数: ${counterModel._counter2}'),
ElevatedButton(onPressed: (){
counterModel.addCounter2();
}, child: const Icon(Icons.add),),
],
);
},
),
const Divider(height: 20,),
],
),
),
);
}
}6.GetX
我们还可以使用GetX实现UI的局部刷新。
首先安装GetX:
get: ^4.6.6
然后我们把变量封装在GetxController中.
Dart
class CounterManagerController extends GetxController {
final counter1 = 0.obs;
final counter2 = 0.obs;
void incrementCount1() {
counter1.value++;
}
void incrementCount2() {
counter2.value++;
}
}再使用Obx把需要显示逻辑的Widget包裹起来。
Obx(()=> Text('计数器1个数: ${controller.counter2.value}'))
完整的代码如下:
Dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:get/get.dart';
class CounterManagerController extends GetxController {
final counter1 = 0.obs;
final counter2 = 0.obs;
void incrementCount1() {
counter1.value++;
}
void incrementCount2() {
counter2.value++;
}
}
class GetXRefreshUIPage extends StatelessWidget {
final String title;
const GetXRefreshUIPage({super.key, required this.title});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final CounterManagerController controller = Get.put(CounterManagerController());
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
const SizedBox(
height: 10,
), // 添加一些间距
const Divider(),
const Text(
'计数器实例',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 12, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
Obx(()=> Text('计数器1个数: ${controller.counter1.value}')),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
controller.incrementCount1();
},
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
],
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
Obx(()=> Text('计数器1个数: ${controller.counter2.value}')),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
controller.incrementCount2();
},
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
],
),
const Divider(
height: 20,
),
],
),
),
);
}
}当然GetX中实现局部刷新的方式还有其它几种写法,大家可以看一下它的文档。这里只是提供了其中的一种实现思路。
7.通过GlobalKey局部刷新
上述三种实现方式都是通过框架实现的,如果你不想导入这个框架,我们可以使用GlobalKey来实现UI的局部刷新功能。
在整个应用程序中是唯一的Key GlobalKey可以唯一标识元素,GlobalKey提供了对这些元素相关联的访问,比如BuildContext。对于StatefulWidgets,GlobalKey也提供对State的访问。
在我们的计时器的demo中,如果我们通过GlobalKey的方式局部刷新UI,首先我们把要局部刷新的Widget提出来,单独封装成一个组件。
完整代码如下,我们封装要局部刷新的Widget,并且提供一个刷新内部数据的接口,onPressed.
Dart
class CounterText extends StatefulWidget {
const CounterText(Key key) : super(key: key);
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return CounterTextState();
}
}
class CounterTextState extends State<CounterText> {
String _text="0";
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Text(_text,style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 20),),
);
}
void onPressed(int count) {
setState(() {
_text = count.toString();
});
}
}然后在我们的主界面实例化GlobaKey:
Dart
int _count = 0;
int _count2 = 0;
GlobalKey<CounterTextState> textKey = GlobalKey();
GlobalKey<CounterTextState> textKey2 = GlobalKey(); 在需要刷新UI的事件中,通过GlobalKey调用上一步提供的接口,刷新即可。
完整代码如下:
Dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
class GlobalKeyRefreshPage extends StatefulWidget {
final String title;
const GlobalKeyRefreshPage({super.key, required this.title});
@override
State<GlobalKeyRefreshPage> createState() => _GlobalKeyRefreshPageState();
}
class _GlobalKeyRefreshPageState extends State<GlobalKeyRefreshPage> {
int _count = 0;
int _count2 = 0;
//包裹你定义的需要更新的weight
GlobalKey<CounterTextState> textKey = GlobalKey();
GlobalKey<CounterTextState> textKey2 = GlobalKey();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
const SizedBox(
height: 10,
), // 添加一些间距
const Divider(),
const Text(
'计数器实例',
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 12, fontWeight: FontWeight.bold),
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
CounterText(textKey),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
_count++;
textKey.currentState?.onPressed(_count);
},
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
],
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: [
CounterText(textKey2),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
_count2++;
textKey2.currentState?.onPressed(_count2);
},
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
],
),
const Divider(
height: 20,
),
],
),
),
);
}
}
class CounterText extends StatefulWidget {
const CounterText(Key key) : super(key: key);
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return CounterTextState();
}
}
class CounterTextState extends State<CounterText> {
String _text="0";
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Center(
child: Text(_text,style: const TextStyle(fontSize: 20),),
);
}
void onPressed(int count) {
setState(() {
_text = count.toString();
});
}
}